Journal Description
Animals
Animals
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal devoted entirely to animals, including zoology and veterinary sciences, published semimonthly online by MDPI. The World Association of Zoos and Aquariums (WAZA), European College of Animal Welfare and Behavioural Medicine (ECAWBM), and Federation of European Laboratory Animal Science Associations (FELASA) are affiliated with Animals and their members receive a discount on the article processing charges.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within Scopus, SCIE (Web of Science), PubMed, PMC, Embase, PubAg, AGRIS, Animal Science Database, CAB Abstracts, and other databases.
- Journal Rank: JCR - Q1 (Veterinary Sciences) / CiteScore - Q1 (General Veterinary)
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 19.1 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 2.6 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the first half of 2023).
- Recognition of Reviewers: reviewers who provide timely, thorough peer-review reports receive vouchers entitling them to a discount on the APC of their next publication in any MDPI journal, in appreciation of the work done.
- Companion journals for Animals include: Birds, Ruminants and Zoonotic Diseases.
Impact Factor:
3.0 (2022);
5-Year Impact Factor:
3.2 (2022)
Latest Articles
The Fecundity Characteristics and Spawning Strategy of Uroteuthis edulis in the East China Sea
Animals 2023, 13(17), 2786; https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13172786 (registering DOI) - 01 Sep 2023
Abstract
The fecundity characteristics and spawning strategy of Uroteuthis edulis in the East China Sea were investigated by observing the potential fecundity (PF), relative fecundity by dorsal mantle length (PFML) and relative fecundity by body weight (PFBW
[...] Read more.
The fecundity characteristics and spawning strategy of Uroteuthis edulis in the East China Sea were investigated by observing the potential fecundity (PF), relative fecundity by dorsal mantle length (PFML) and relative fecundity by body weight (PFBW). The relationship between fecundity and a single biological indicator was measured, and generalized additive models (GAMs) were fit by adding environmental variables to help better understand this comprehensive relationship. The long diameter and short diameter of the ovarian oocytes ranged from 0.72 mm to 4.74 mm and from 0.46 mm to 3.67 mm, respectively. The long and short diameters of oviducal eggs ranged from 0.61 mm to 5.12 mm and from 0.39 mm to 3.81 mm, respectively. The egg diameter had a unimodal distribution. The PF, PFML and PFBW ranged from 540 to 13,743 cells, 5 to 86 cells/mm and 6 to 53 cells/g, respectively. Three fecundity indicators were unimodally distributed, and the PFBW was more stable than the PFML (δ2PFBW < δ2PFML). The fecundity and single biological indicators were fitted, and it was found that the PF and PFML were positively correlated with dorsal mantle length (ML) and body weight (BW). The generalized additive model (GAM) fitting showed that when considering the interaction between dorsal mantle length and sea surface height (M13), the deviation explanation rate of the PF and PFML was the highest. Studies have shown that the ovary oocytes of U. edulis mature in batches, and then the eggs are laid in batches. The dorsal mantle length (ML), water temperature at 25 m depth (T25) and sea surface height (SSH) are important indicators to measure the fecundity of U. edulis. These findings allow for a deeper understanding of the U. edulis population dynamics for the future management of this economically and ecologically important species.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Aquatic Animals)
►
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Towards an Evidence-Based Classification System for Para Dressage: Associations between Impairment and Performance Measures
by
, , , , , , , and
Animals 2023, 13(17), 2785; https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13172785 (registering DOI) - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
This study follows a previously defined framework to investigate the impact of impairment on performance in Para dressage athletes. Twenty-one elite Para dressage athletes (grades I to V) and eleven non-disabled dressage athletes (competing at Prix St. Georges or Grand Prix) participated. Data
[...] Read more.
This study follows a previously defined framework to investigate the impact of impairment on performance in Para dressage athletes. Twenty-one elite Para dressage athletes (grades I to V) and eleven non-disabled dressage athletes (competing at Prix St. Georges or Grand Prix) participated. Data were collected in two phases: performing a two minute custom dressage test on a riding simulator while kinematic data were synchronously collected using inertial measurement units (2000 Hz) and optical motion capture (100 Hz), and clinically assessed using a battery of impairment assessment tools administered by qualified therapists. Impairment and performance measures were compared between Para and non-disabled athletes. Significant differences between athlete groups were found for all impairment measures and two performance measures: simulator trunk harmonics (p = 0.027) and athlete trunk dynamic symmetry (p < 0.001). Impairment assessments of sitting function and muscle tone could predict 19 to 35% of the impact of impairment on performance in Para athletes but not in non-disabled athletes. These findings provide the basis for a robust, scientific evidence base, which can be used to aid in the refinement of the current classification system for Para dressage, to ensure that it is in line with the International Paralympic Committee’s mandate for evidence-based systems of classification.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue New Challenges in Horse–Rider Interaction)
Open AccessArticle
Luteotropic and Luteolytic Factors Modulate the Expression of Nuclear Receptor Coregulators in Bovine Luteal Cells Independently of Histone Acetyltransferase and Histone Deacetylase Activities
by
, , , and
Animals 2023, 13(17), 2784; https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13172784 (registering DOI) - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
The aims of this study were to examine the effect of luteotropic and luteolytic factors on the mRNA and protein expression of the coactivators HAT: histone acetyltransferase p300 (P300), cyclic adenosine monophosphate response element-binding protein (CREB), and steroid receptor coactivator-1 (SRC-1) and the
[...] Read more.
The aims of this study were to examine the effect of luteotropic and luteolytic factors on the mRNA and protein expression of the coactivators HAT: histone acetyltransferase p300 (P300), cyclic adenosine monophosphate response element-binding protein (CREB), and steroid receptor coactivator-1 (SRC-1) and the corepressor: nuclear receptor corepressor-2 (NCOR-2) in bovine luteal cells on days 6–10 and 16–20. HAT and HDAC activities were also measured. The obtained results showed that luteotropic and luteolytic factors influence changes in the mRNA and protein levels of the coregulators of PGRs. However, they did not affect the activity of related HAT and HDAC, respectively. Therefore, it is possible that these factors, through changes in the expression of nuclear receptor coactivators and corepressors, may affect the functioning of the nuclear receptors, including PGRs, in the bovine CL.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Molecular Regulations of Female Livestock Reproduction)
►▼
Show Figures
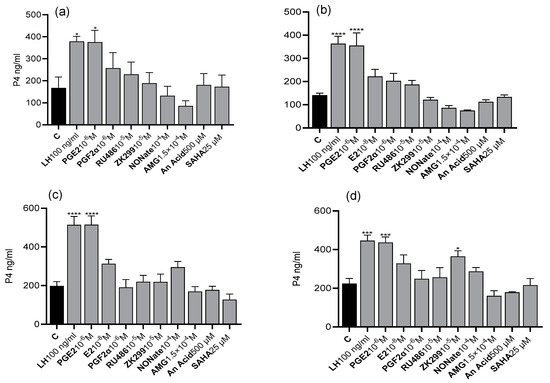
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Responses to Reduced Feeding Frequency in Captive-Born Cheetahs (Acinonyx jubatus): Implications for Behavioural and Physiological Stress and Gastrointestinal Health
Animals 2023, 13(17), 2783; https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13172783 (registering DOI) - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
Unnatural diet composition and frequent feeding regimes may play an aetiological role in the multiple diseases prevalent in captive cheetahs. This study investigated the responses of captive-born (hand-reared) cheetahs (n = 6) to a reduced feeding frequency schedule distinguished by offering larger
[...] Read more.
Unnatural diet composition and frequent feeding regimes may play an aetiological role in the multiple diseases prevalent in captive cheetahs. This study investigated the responses of captive-born (hand-reared) cheetahs (n = 6) to a reduced feeding frequency schedule distinguished by offering larger quantities of food less frequently. The study cheetahs were fed four once-daily meals per week during the 3-week treatment period, followed by a 3-week control period in which they were fed two daily rations six days a week. Total weekly food intake was maintained throughout the study. Variations in behaviour, faecal consistency score (FCS), and faecal glucocorticoid metabolite concentration were measured. Less frequent feeding resulted in higher FCS (p < 0.01) and locomotory behaviour (p < 0.05) among the studied cheetahs. Faecal glucocorticoid metabolite concentration demonstrated an initial acute stress response to the change in feeding frequency (p < 0.05) and subsequent adaptation. The results of the FCS analysis suggest that the more natural feeding pattern could have benefited the studied cheetahs’ gastrointestinal health without a significant behavioural or physiological stress response overall to the change in feeding frequency.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Zoo Animals: How Actual Zoological Institutions Assess, Ensure, and Promote Their Animals’ Welfare?)
►▼
Show Figures
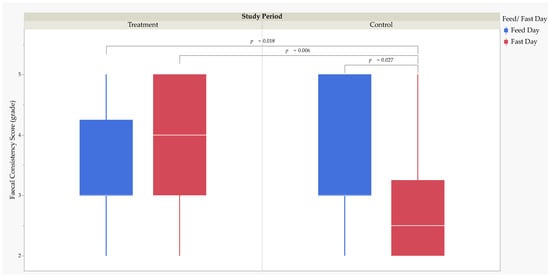
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Inferring on Speleomantes Foraging Behavior from Gut Contents Examination
by
and
Animals 2023, 13(17), 2782; https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13172782 - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
We here provide the first comprehensive analysis and discussion on prey consumed by the European cave salamanders of the genus Speleomantes. Our study stems from the need to shed light on the still unknown foraging behavior adopted by Speleomantes cave salamanders. Starting
[...] Read more.
We here provide the first comprehensive analysis and discussion on prey consumed by the European cave salamanders of the genus Speleomantes. Our study stems from the need to shed light on the still unknown foraging behavior adopted by Speleomantes cave salamanders. Starting from the published datasets on gut contents from all Speleomantes species (including hybrids), we here discuss additional information (i.e., species ecology, lower taxonomic level), which were systematically omitted from those data sets. We analyzed a data set consisting of 17,630 records from 49 categories of consumed prey recognized from gut contents of 2060 adults and juveniles Speleomantes. Flying prey accounted for more than 58% of the prey items, while elongated crawling prey accounted for no more than 16% of the diet within a single population. Among the total recognized prey items, only three can be surely ascribed to the group of strictly-cave species (i.e., troglobites), meaning that European cave salamanders mostly forage in surface environment, and therefore represent one of the major drivers of allochthonous organic matter in subterranean environments. Some of the consumed prey seemed to be aquatic, allowing us to hypothesize whether Speleomantes are able to catch prey from a shallow body water. Furthermore, European cave salamanders possess the ability to prey upon taxa characterized by particular anti-predator defenses, while morphological constraints seem to be the most important limit to prey consumption. For each specific case, we provide insights and propose hypotheses concerning the foraging behavior that need to be tested to properly understand the foraging behavior of this cryptic salamanders.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Predator-Prey Interactions in Amphibians and Reptiles)
Open AccessArticle
Grape Seed Proanthocyanidins Improve the Quality of Fresh and Cryopreserved Semen in Bulls
Animals 2023, 13(17), 2781; https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13172781 - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
Oxidative stress leads to a decrease in semen quality during semen cryopreservation and fresh semen production. Grape seed proanthocyanidins (GSPs) are endowed with well-recognized antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anti-cancer, and anti-aging activities. Therefore, the objective of this experiment was to explore the effects of GSPs
[...] Read more.
Oxidative stress leads to a decrease in semen quality during semen cryopreservation and fresh semen production. Grape seed proanthocyanidins (GSPs) are endowed with well-recognized antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anti-cancer, and anti-aging activities. Therefore, the objective of this experiment was to explore the effects of GSPs on the quality of fresh and cryopreserved semen to provide a basis for GSPs as a new dietary additive and semen diluent additive for males’ reproduction. Fresh semen from three healthy bulls aged 3 to 5 years old were gathered and mixed with semen diluents dissolved with 0 µg/mL, 30 µg/mL, 40 µg/mL, 50 µg/mL, and 60 µg/mL GSPs respectively. The motility, physiological structures (acrosome integrity, membrane integrity, mitochondrial activity), and antioxidant capacity of frozen–thawed sperm were measured after storage in liquid nitrogen for 7 days (d). Bulls were fed with 20 mg/kg body weight (BW) GSPs in their diet for 60 days; the weight of the bull is about 600 kg. Then, the reproductive performance and antioxidant indexes of bulls were measured before and after feeding. The results demonstrated that GSPs supplementation significantly increased sperm motility, physiological structures, GSH-Px, and CAT enzyme activities and significantly decreased MDA content in sperm during semen cryopreservation. The optimal concentration of GSPs was 40 µg/mL (p < 0.05). After 20 mg/kg (body weight) GSP supplementation, sperm motility was significantly heightened (p < 0.05), the sperm deformity rate was significantly reduced (p < 0.05), and antioxidant enzyme activities (such as SOD, CAT, and GSH-Px) were significantly enhanced (p < 0.05), and the production of MDA was significantly suppressed (p < 0.05) in serum compared with that before feeding. In conclusion, these results reveal that a certain concentration of GSPs has a good protective effect on sperm damage caused by semen cryopreservation and the reproductive performance reduction caused by stress in bulls, which may be attributed to the antioxidant function of GSPs. In summary, GSPs are a useful cryoprotective adjuvant and dietary additive for bull sperm quality.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Frozen Semen in Ruminants)
►▼
Show Figures
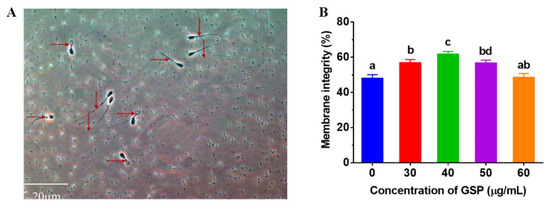
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Relationship between CT-Derived Bone Mineral Density and UTE-MR-Derived Porosity Index in Equine Third Metacarpal and Metatarsal Bones
by
, , , , , and
Animals 2023, 13(17), 2780; https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13172780 - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
Fatigue-related subchondral bone injuries of the third metacarpal/metatarsal (McIII/MtIII) bones are common causes of wastage, and they are welfare concerns in racehorses. A better understanding of bone health and strength would improve animal welfare and be of benefit for the racing industry. The
[...] Read more.
Fatigue-related subchondral bone injuries of the third metacarpal/metatarsal (McIII/MtIII) bones are common causes of wastage, and they are welfare concerns in racehorses. A better understanding of bone health and strength would improve animal welfare and be of benefit for the racing industry. The porosity index (PI) is an indirect measure of osseous pore size and number in bones, and it is therefore an interesting indicator of bone strength. MRIs of compact bones using traditional methods, even with short echo times, fail to generate enough signals to assess bone architecture as water protons are tightly bound. Ultra-short echo time (UTE) sequences aim to increase the amount of signals detected in equine McIII/MtIII condyles. Cadaver specimens were imaged using a novel dual-echo UTE MRI technique, and PI was calculated and validated against quantitative CT-derived bone mineral density (BMD) measures. BMD and PI are inversely correlated in equine distal Mc/MtIII bones, with a weak mean r value of −0.29. There is a statistically significant difference in r values between the forelimbs and hindlimbs. Further work is needed to assess how correlation patterns behave in different areas of bones and to evaluate PIs in horses with and without clinically relevant stress injuries.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Diagnostic Imaging in Equine Lameness Diagnosis—Where Are We in 2023?)
►▼
Show Figures
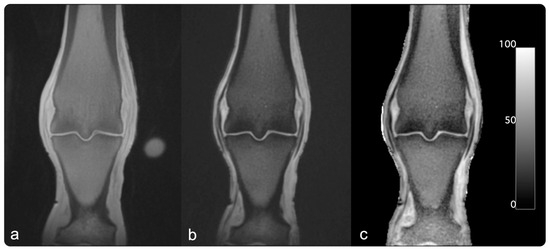
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
First Isolation and Identification of Aeromonas veronii in a Captive Giant Panda (Ailuropoda melanoleuca)
by
, , , , , , , , and
Animals 2023, 13(17), 2779; https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13172779 - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
The objective of this study was to understand biological characteristics of one bacteria strain named as VPG which was isolated from multiple organs of a dead captive giant panda cub. Here, we use biochemical tests, 16S rRNA and gyrB genes for bacterial identification,
[...] Read more.
The objective of this study was to understand biological characteristics of one bacteria strain named as VPG which was isolated from multiple organs of a dead captive giant panda cub. Here, we use biochemical tests, 16S rRNA and gyrB genes for bacterial identification, the disk diffusion method for antibiotic resistance phenotype, smart chip real-time PCR for the antibiotic resistance genotype, multiplex PCR for determination of virulence genes, and the acute toxicity test in mice for testing the pathogenicity of isolates. The isolate was identified as A. veronii strain based on the biochemical properties and genetic analysis. We found that the strain carried 31 antibiotic resistance genes, revealed antimicrobial resistance phenotypically to several antibiotics including penicillin, ampicillin, oxacillin, amoxicillin, imipenem, and vancomycin, and carried virulence genes including aer, act, lip, exu, ser, luxs, and tapA. The main pathological changes in giant panda were congestion, necrotic lesions and a large number of bacteria in multiple organs. In addition, the LD50 in Kunming mice infected with strain VGP was 5.14 × 107 CFU/mL by intraperitoneal injection. Infection with strain VGP led to considerable histological lesions such as hemorrhage of internal organs, necrosis of lymphocytes and neurons in Kunming mice. Taken together, these results suggest that infection with strain VGP would be an important causes of death in this giant panda cub.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Mammals)
►▼
Show Figures
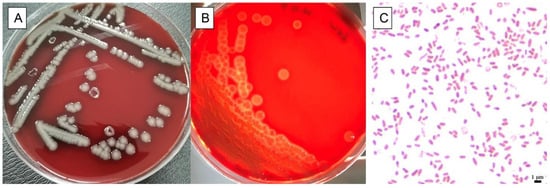
Figure 1
Open AccessCase Report
Effect of Rehabilitation in a Dog with Delayed Recovery following TPLO: A Case Report
Animals 2023, 13(17), 2778; https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13172778 - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
A 7-year-old neutered Maltese dog weighing 5.1 kg was presented, with a tibial plateau-leveling osteotomy (TPLO) on the right hindlimb 42 days prior. The patient’s right hind limb showed lameness, intermittent limping, and atrophy, and the patient had not experienced rehabilitation since TPLO
[...] Read more.
A 7-year-old neutered Maltese dog weighing 5.1 kg was presented, with a tibial plateau-leveling osteotomy (TPLO) on the right hindlimb 42 days prior. The patient’s right hind limb showed lameness, intermittent limping, and atrophy, and the patient had not experienced rehabilitation since TPLO surgery. The patient showed a pain reaction at the end of the stifle extension, and an increased body temperature was identified on the medial side of the right hindlimb when compared with the left hindlimb using a digital thermal imaging device. In addition, a type of lameness, only partial weight bearing in the right hindlimb, was also identified during the gait analysis. The pain was relieved by applying a cold pack and transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation, and the patient’s weak muscles were strengthened through treadmill exercises. In this study, physical therapy and rehabilitation exercises controlled pain and induced rapid recovery, indicating that rehabilitative intervention is required after TPLO surgery.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Veterinary Clinical Studies)
►▼
Show Figures
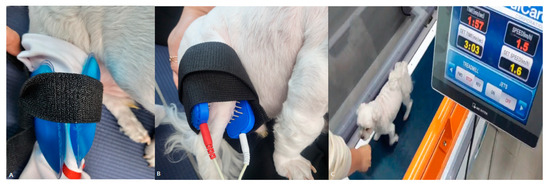
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Occurrence and Genotypic Identification of Blastocystis spp., Enterocytozoon bieneusi, and Giardia duodenalis in Leizhou Black Goats in Zhanjiang City, Guangdong Province, China
by
, , , , , , , and
Animals 2023, 13(17), 2777; https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13172777 - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
Blastocystis spp., Enterocytozoon bieneusi, and Giardia duodenalis are three common zoonotic intestinal parasites that cause severe diarrhea and enteric diseases. Leizhou black goats are characterized by a high reproductive rate, fast growth, and good meat quality, making them one of the pre-eminent
[...] Read more.
Blastocystis spp., Enterocytozoon bieneusi, and Giardia duodenalis are three common zoonotic intestinal parasites that cause severe diarrhea and enteric diseases. Leizhou black goats are characterized by a high reproductive rate, fast growth, and good meat quality, making them one of the pre-eminent goat breeds in China. Goats are reportedly common reservoirs of these three intestinal pathogens, but no information on their prevalence or genotypic distributions in black goats in Guangdong Province, China, is available. A total of 226 fecal samples were collected from goats in Zhanjiang city and genomic DNA was extracted from them. The presence of the three pathogens was detected using nested PCR targeting the sequences encoding SSU rRNA (Blastocystis spp.), the internal transcribed spacer of rRNA (ITS; E. bieneusi), as well as beta-giardin, glutamate dehydrogenase, and triosephosphate isomerase (G. duodenalis). All PCR products were sequenced to determine the species and genotypes of the organisms. The total prevalence rates of Blastocystis spp., E. bieneusi, and G. duodenalis were 33.63% (76/226), 17.70% (40/226), and 24.78% (56/226), respectively. Four subtypes of Blastocystis spp. were detected: ST5 (n = 6), ST10 (n = 50), ST14 (n = 14), and ST21 (n = 6). Among them, ST10 was the dominant genotype, accounting for 65.79% of strains, followed by the genotypes ST14 (18.42%), zoonotic ST5 (7.89%), and ST21 (7.89%). Four genotypes of E. bieneusi were detected: CHG3 (n = 32), CM21 (n = 4), CHG1 (n = 2), and ET-L2 (n = 2). Among these, CHG3 was the dominant genotype. Assemblage E (n = 54) and concurrent assemblages A and E (n = 2) were identified in the G. duodenalis-positive goats using multilocus genotyping. Blastocystis spp., E. bieneusi, and G. duodenalis infections were common in Leizhou black goats, all of which have zoonotic genotypes, indicating the potential risk of zoonotic transmission. Our results provide basic data for the prevention and control of these three intestinal pathogens. Further studies are required to better understand their genetic characteristics and zoonotic potential in Guangdong Province.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Parasite Epidemiology and Molecules Identification in Wild and Domestic Animals)
►▼
Show Figures
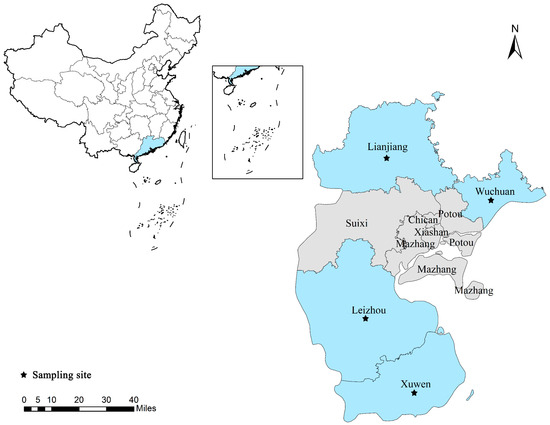
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Genomic Characterization and Initial Insight into Mastitis-Associated SNP Profiles of Local Latvian Bos taurus Breeds
by
, , , , , , , and
Animals 2023, 13(17), 2776; https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13172776 - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
Latvia has two local Bos taurus breeds—Latvian Brown (LBG) and Latvian Blue (LZG)—characterized by a good adaptation to the local climate, longevity, and high fat and protein contents in milk. Since these are desired traits in the dairy industry, this study investigated the
[...] Read more.
Latvia has two local Bos taurus breeds—Latvian Brown (LBG) and Latvian Blue (LZG)—characterized by a good adaptation to the local climate, longevity, and high fat and protein contents in milk. Since these are desired traits in the dairy industry, this study investigated the genetic background of the LBG and LZG breeds and identified the genetic factors associated with mastitis. Blood and semen samples were acquired, and whole genome sequencing was then performed to acquire a genomic sequence with at least 35× or 10× coverage. The heterozygosity, nucleotide diversity, and LD analysis indicated that LBG and LZG cows have similar levels of genetic diversity compared to those of other breeds. An analysis of the population structure revealed that each breed clustered together, but the overall differentiation between the breeds was small. The highest genetic variance was observed in the LZG breed compared with the LBG breed. Our results show that SNP rs721295390 is associated with mastitis in the LBG breed, and SNPs rs383806754, chr29:43998719CG>C, and rs462030680 are associated with mastitis in the LZG breed. This study shows that local Latvian LBG and LZG breeds have a pronounced genetic differentiation, with each one suggesting its own mastitis-associated SNP profile.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Collection Advances in Cattle Breeding, Genetics and Genomics)
►▼
Show Figures
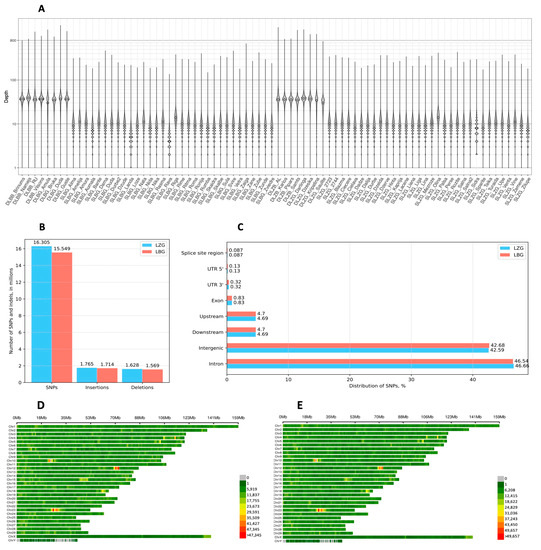
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Key Factors behind the Dynamic Stability of Pairs of Egyptian Vultures in Continental Spain
by
, , , and
Animals 2023, 13(17), 2775; https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13172775 - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
Conservation science aims to identify the factors influencing the distribution of threatened species, thereby permitting the implementation of effective management strategies. This is key for long-lived species that require long-term monitoring such as the worldwide endangered Egyptian vulture (Neophron percnopterus). We
[...] Read more.
Conservation science aims to identify the factors influencing the distribution of threatened species, thereby permitting the implementation of effective management strategies. This is key for long-lived species that require long-term monitoring such as the worldwide endangered Egyptian vulture (Neophron percnopterus). We studied temporal and spatial variations in the distribution of breeding pairs and examined the intrinsic and anthropic factors that may be influencing the abundance of breeding territories in continental Spain. Based on the census data of breeding pairs from 2000, 2008, and 2018, we used Rank Occupancy–Abundance Profiles to assess the temporal stability of the population and identified the spatial heterogeneity through a Local Index of Spatial Autocorrelation analysis. The GLMs showed that the abundance distribution was mainly influenced by the abundance of griffon vultures (Gyps fulvus) and cattle at a regional scale. Nonparametric comparisons showed that the presence of wind farms had a significant negative effect on local breeding pairs abundance, but that supplementary feeding stations and food resource-related variables had a positive impact. In light of these findings, we recommend a hierarchical approach in future conservation programs involving actions promoting regional-scale food resource availability and highlight the need to address the negative impact of wind farms at local levels.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Vulture Ecology and Conservation)
►▼
Show Figures
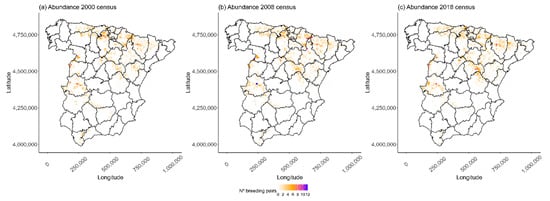
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Heat Tolerance of Siberian Husky Dogs Living in Brazil: A Case Study on the Perceptions and Attitudes of Their Owners
by
, , , , , , , , , and
Animals 2023, 13(17), 2774; https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13172774 - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
The management of the thermal environment to which dogs are exposed should be included in strategies to improve their welfare. An online questionnaire was administered to 624 owners of Siberian Husky dogs residing in Brazil, with the objective of assessing their perceptions regarding
[...] Read more.
The management of the thermal environment to which dogs are exposed should be included in strategies to improve their welfare. An online questionnaire was administered to 624 owners of Siberian Husky dogs residing in Brazil, with the objective of assessing their perceptions regarding their dogs’ capacity to adapt to heat, and its association with the owners’ routine care. Owners who believed that dogs are low-heat-tolerant animals were more likely to report heat response behaviors from their dogs. Overall, owners reported walk with their dogs during early morning, late afternoon and nighttime. They also reported solar radiation as the primary criteria for determining the time to walk with their dogs. However, owners who reported walking with their dogs at noon mentioned time availability as their primary criteria. In conclusion, owners perceive Siberian Husky dogs living in Brazil as being poorly adapted to heat, and this perception appeared to influence their positive attitudes towards protecting their dogs from heat stress by choosing to walk them during times with less solar exposure. However, the lack of time for owners to walk with their dogs during cooler periods can still be a risk factor in exposing the animals to extreme hot conditions.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Animal Welfare)
►▼
Show Figures
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Relationship between Microflora Changes and Mammary Lipid Metabolism in Dairy Cows with Mastitis
Animals 2023, 13(17), 2773; https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13172773 - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
Dairy mastitis is an inflammatory reaction caused by mechanical injury and stress within the mammary gland, during which microbial changes and abnormal lipid metabolism occur. However, the underlying mechanism is still unclear. The present study used a combination of 16S rDNA sequencing technology
[...] Read more.
Dairy mastitis is an inflammatory reaction caused by mechanical injury and stress within the mammary gland, during which microbial changes and abnormal lipid metabolism occur. However, the underlying mechanism is still unclear. The present study used a combination of 16S rDNA sequencing technology and lipidomics techniques to reveal the effects of mastitis on lactic microbiota and metabolites in the milk of dairy cows. Twenty multiparous Holstein dairy cows (2–3 parities) with an average body weight of 580 ± 30 kg were selected for this study. The dairy cows were allocated to control group (<5 × 104 cells /mL)) and mastitis group (>5 × 106 cells /mL) based on the somatic cell count. The results showed that mastitis caused a decrease trend in milk production (p = 0.058). The results of the 16 s sequencing indicated a significant decrease (p < 0.05) in the number of Proteobacteria, Tenericutes colonized in mastitis milk, and the number of Firmicutes, Bacteroidetes and Actinobacteria communities increased significantly (p < 0.05). The lipidomics results revealed that the changes in lipid content in mastitis milk were correlated with arachidonic acid metabolism, α -linolenic acid metabolism and glycerol phospholipid metabolism. The results showed that mastitis may cause abnormal lipid metabolism in milk by regulating the diversity of milk microflora, and ultimately affect the milk quality.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Molecular and Cellular Changes in Animal Metabolism, Health and Welfare)
►▼
Show Figures
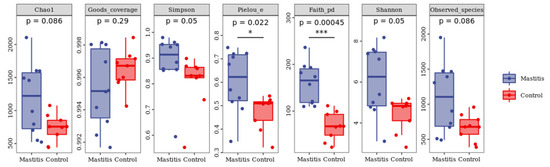
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Application of Machine Learning Algorithms to Describe the Characteristics of Dairy Sheep Lactation Curves
by
, , , , , , and
Animals 2023, 13(17), 2772; https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13172772 - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
In recent years, machine learning (ML) algorithms have emerged as powerful tools for predicting and modeling complex data. Therefore, the aim of this study was to evaluate the prediction ability of different ML algorithms and a traditional empirical model to estimate the parameters
[...] Read more.
In recent years, machine learning (ML) algorithms have emerged as powerful tools for predicting and modeling complex data. Therefore, the aim of this study was to evaluate the prediction ability of different ML algorithms and a traditional empirical model to estimate the parameters of lactation curves. A total of 1186 monthly records from 156 sheep lactations were used. The model development process involved training and testing models using ML algorithms. In addition to these algorithms, lactation curves were also fitted using the Wood model. The goodness of fit was assessed using correlation coefficient (r), mean absolute error (MAE), root mean square error (RMSE), relative absolute error (RAE), and relative root mean square error (RRSE). SMOreg was the algorithm with the best estimates of the characteristics of the sheep lactation curve, with higher values of r compared to the Wood model (0.96 vs. 0.68) for the total milk yield. The results of the current study showed that ML algorithms are able to adequately predict the characteristics of the lactation curve, using a relatively small number of input data. Some ML algorithms provide an interpretable architecture, which is useful for decision-making at the farm level to maximize the use of available information.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Lactation Physiology and Milk Quality of Small Ruminants)
►▼
Show Figures
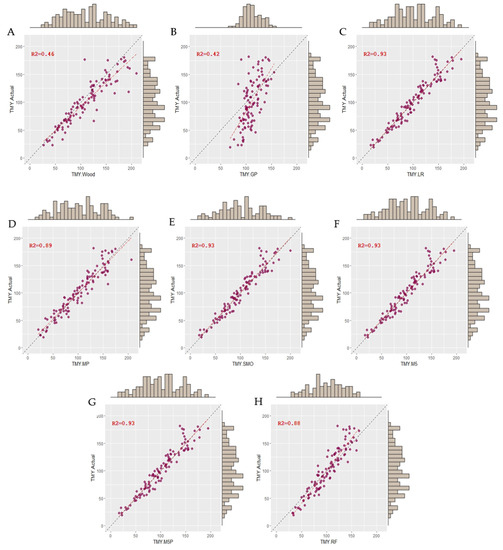
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Effect of Slow-Release Urea Partial Replacement of Soybean Meal on Lactation Performance, Heat Shock Signal Molecules, and Rumen Fermentation in Heat-Stressed Mid-Lactation Dairy Cows
by
, , , , , , , and
Animals 2023, 13(17), 2771; https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13172771 - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
This study aimed to assess the effects of partially substituting soybean meal in the diet with slow-release urea (SRU) on the lactation performance, heat shock signal molecules, and environmental sustainability of heat-stressed lactating cows in the middle stage of lactation. In this study,
[...] Read more.
This study aimed to assess the effects of partially substituting soybean meal in the diet with slow-release urea (SRU) on the lactation performance, heat shock signal molecules, and environmental sustainability of heat-stressed lactating cows in the middle stage of lactation. In this study, 30 healthy Holstein lactating dairy cattle with a similar milk yield of 22.8 ± 3.3 kg, days in milk of 191.14 ± 27.24 days, and 2.2 ± 1.5 parity were selected and randomly allocated into two groups. The constituents of the two treatments were (1) basic diet plus 500 g soybean meal (SM) for the SM group and (2) basic diet plus 100 g slow-release urea and 400 g corn silage for the SRU group. The average temperature humidity index (THI) during the experiment was 84.47, with an average THI of >78 from day 1 to day 28, indicating the cow experienced moderate heat stress conditions. Compared with the SM group, the SRU group showed decreasing body temperature and respiratory rate trends at 20:00 (p < 0.1). The substitution of SM with SRU resulted in an increasing trend in milk yield, with a significant increase of 7.36% compared to the SM group (p < 0.1). Compared to the SM group, AST, ALT, and γ-GT content levels were significantly increased (p < 0.05). Notably, the levels of HSP-70 and HSP-90α were significantly reduced (p < 0.05). The SRU group showed significantly increased acetate and isovalerate concentrations compared with the SM group (p < 0.05). The prediction results indicate that the SRU group exhibits a significant decrease in methane (CH4) emissions when producing 1 L of milk compared to the SM group (p < 0.05). In summary, dietary supplementation with SRU tended to increase the milk yield and rumen fermentation and reduce plasma heat shock molecules in mid-lactation, heat-stressed dairy cows. In the hot summer, using SRU instead of some soybean meal in the diet alleviates the heat stress of dairy cows and reduces the production of CH4.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue The Use of Phytogenic Feed Additives to Enhance Productivity and Health in Animals)
►▼
Show Figures
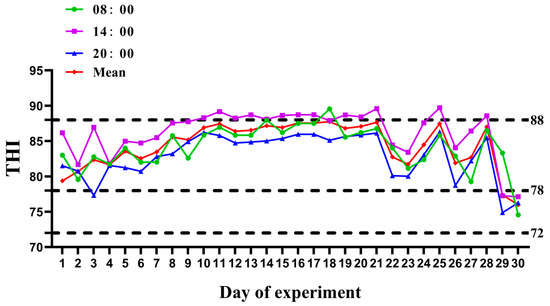
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Association between Phenotypes of Antimicrobial Resistance, ESBL Resistance Genes, and Virulence Genes of Salmonella Isolated from Chickens in Sichuan, China
by
, , , , , , , , , , and
Animals 2023, 13(17), 2770; https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13172770 - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
The aim of this study was to explore the association between antimicrobial resistance, ESBL genes, and virulence genes of Salmonella isolates. From 2019 to 2021, a total of 117 Salmonella isolates were obtained from symptomatic chickens in Sichuan Province, China. The strains were
[...] Read more.
The aim of this study was to explore the association between antimicrobial resistance, ESBL genes, and virulence genes of Salmonella isolates. From 2019 to 2021, a total of 117 Salmonella isolates were obtained from symptomatic chickens in Sichuan Province, China. The strains were tested for antimicrobial resistance and the presence of ESBL according to the Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI) instructions. The presence of ESBL genes and genes for virulence was determined using Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR). In addition, Multilocus Sequence Typing (MLST) was applied to confirm the molecular genotyping. Moreover, the mechanism of ESBL and virulence gene transfer and the relationships between the resistance phenotype, ESBL genes, and virulence genes were explored. The isolates exhibited different frequencies of resistance to antibiotics (resistance rates ranged from 21.37% to 97.44%), whereas 68.38% and 41.03% of isolates were multi-drug resistance (MDR) and ESBL-producers, respectively. In the PCR analysis, blaCTX-M was the most prevalent ESBL genotype (73.42%, 58/79), and blaCTX-M-55 showed the most significant effect on the resistance to cephalosporins as tested by logistic regression analysis. Isolates showed a high carriage rate of invA, avrA, sopB, sopE, ssaQ, spvR, spvB, spvC, stn, and bcfC (ranged from 51.28% to 100%). MLST analysis revealed that the 117 isolates were divided into 11 types, mainly ST92, ST11, and ST3717. Of 48 ESBL-producers, 21 transconjugants were successfully obtained by conjugation. Furthermore, ESBL and spv virulence genes were obtained simultaneously in 15 transconjugants. These results highlighted that Salmonella isolates were common carriers of ESBLs and multiple virulence genes. Horizontal transfer played a key role in disseminating antimicrobial resistance and pathogenesis. Therefore, it is necessary to continuously monitor the use of antimicrobials and the prevalence of AMR and virulence in Salmonella from food animals and to improve the antibiotic stewardship for salmonellosis.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Poultry)
►▼
Show Figures
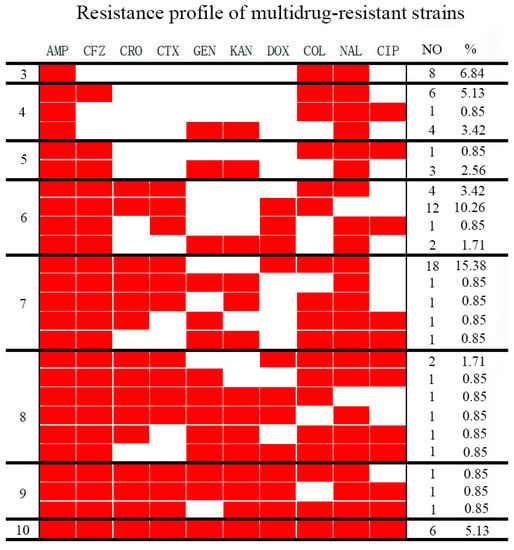
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Stress Factors and Their Effects on Productivity in Sheep
by
and
Animals 2023, 13(17), 2769; https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13172769 - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
Products obtained from sheep have an economically important place in the world. Their adaptability to different climatic conditions, their ease of care and feeding, their high utilization of poor pasture areas with low yield and quality, the ease of flock management, their high
[...] Read more.
Products obtained from sheep have an economically important place in the world. Their adaptability to different climatic conditions, their ease of care and feeding, their high utilization of poor pasture areas with low yield and quality, the ease of flock management, their high twinning rate, and their short intergenerational period are some of the advantages of sheep production. Sheep production has the ability to adapt better to environmental stress factors, as can be understood from the presence of sheep in different geographical regions at a global level. However, the changes in environmental conditions and production cause some negative results in animals. All these negative results expose animals to various stress factors (heat, cold, transport, treatment, nutritional, shearing, weaning, etc.). All stress factors that directly and indirectly affect sheep production ultimately lead to compromised performance, decreased productivity, increased mortality, and adverse effects on the immune system. In order to cope with the current stress parameters in animals and to achieve optimum production, a holistic approach is needed according to the environmental conditions and available resources. It is important to consider the factors involved in these responses in order to manage these processes correctly and to develop adequate strategies and improve sheep welfare. This review aimed to reveal the importance of some stress factors in sheep and their effects on sheep productivity.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Small Ruminants)
►▼
Show Figures
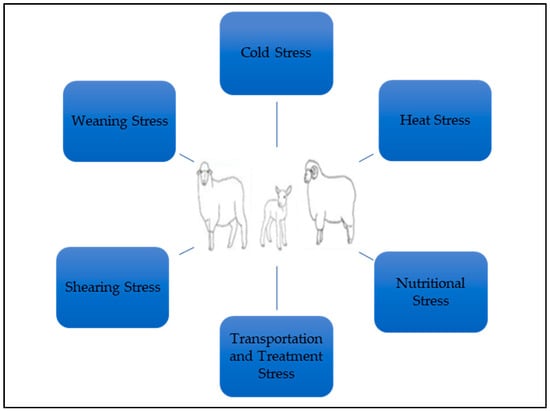
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Effect of Different Vitrification Techniques on Viability and Apoptotic Index of Domestic Cat Testicular Tissue Cells
by
, , , , , and
Animals 2023, 13(17), 2768; https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13172768 - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
Vitrification is essential for successful tissue cryopreservation and biobanking in wild cats. This study aimed to compare different methods of vitrification (Ovarian Tissue Cryosystem—OTC, Straws—STW, and Solid Surface vitrification—SSV) for testicular fragment vitrification in tom cats. Testicular fragments were recovered from five adult
[...] Read more.
Vitrification is essential for successful tissue cryopreservation and biobanking in wild cats. This study aimed to compare different methods of vitrification (Ovarian Tissue Cryosystem—OTC, Straws—STW, and Solid Surface vitrification—SSV) for testicular fragment vitrification in tom cats. Testicular fragments were recovered from five adult tom cats and subjected to equilibrium vitrification using different cryovials and methods under the same conditions of vitrification solutions and cryoprotectants. The efficiencies of the methods were evaluated using histological analysis of spermatogonia and Sertoli cell nuclei, seminiferous tubular basement membrane detachment, and the gonadal epithelium shrinkage score scale. Cell viability was assessed using Hoechst PI and Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase nick end labeling (TUNEL) assay. The results showed that OTC is an effective vitrification method for maintaining the distinction between spermatogonia and Sertoli cells. OTC was similar to the control for basal membrane detachment parameters (p = 0.05). Epithelial shrinkage was low in the SSV group, which showed the highest percentage of viable cells among the vitrified groups (p = 0.0023). The OTC and SSV vitrification methods were statistically similar in terms of the percentage of TUNEL-positive cells (p = 0.05). Therefore, OTC and SSV provide favorable conditions for maintaining viable cat testicular tissue cells after vitrification.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Effective Option regarding Wildlife Resources Protection: Assisted Reproductive Technology)
►▼
Show Figures
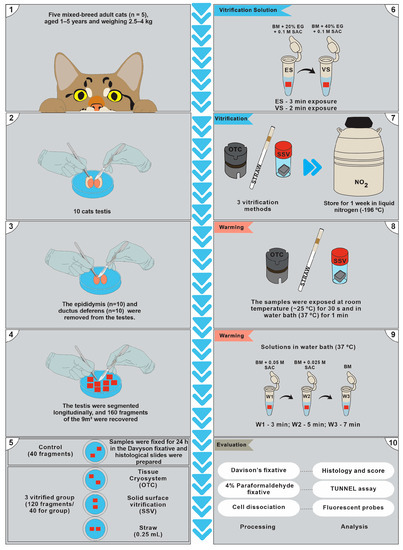
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Transport of Pigs of Two Market Weights at Two Space Allowances: Effects on Behaviour, Blood Parameters, and Meat Quality under Summer and Winter Conditions
by
, , , , , , , and
Animals 2023, 13(17), 2767; https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13172767 - 30 Aug 2023
Abstract
This study was carried out through two separate experiments aiming at evaluating the effects of two space allowances (0.54 and 0.62 m2/pig in summer and 0.44 m2/pig and 0.50 m2/pig in winter) on the behavioural and physiological
[...] Read more.
This study was carried out through two separate experiments aiming at evaluating the effects of two space allowances (0.54 and 0.62 m2/pig in summer and 0.44 m2/pig and 0.50 m2/pig in winter) on the behavioural and physiological response, and meat quality of pigs of two slaughter weights (120 kg and 140 kg). In summer, higher blood haematocrit levels were found at slaughter in heavier pigs transported at a smaller space allowance (p = 0.04). During lairage, pigs transported at a smaller space allowance started fighting later (p = 0.04). Fighting behaviour was greater in heavier pigs (p ≤ 0.05), whilst their drinking activity was lower (p < 0.05). This resulted in greater exsanguination blood CK levels (p < 0.01) and drier hams (p = 0.05) in heavier pigs. In winter, only lower space allowance influenced some meat quality traits (p < 0.05), but these effects were minor. The effects of space allowance during summer transports on within-truck ambient conditions, post-transport pigs’ welfare, and meat quality are similar. Mixing heavier pigs may result in greater aggressiveness and more fatigue-related meat quality variation during summer. Overall, winter transport results may have been biased by the short journey and within-truck load distribution.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Live Animal Transportation: A Risk for Animal and Human Health and Welfare)
►▼
Show Figures
Figure 1

Journal Menu
► ▼ Journal Menu-
- Animals Home
- Aims & Scope
- Editorial Board
- Reviewer Board
- Topical Advisory Panel
- Instructions for Authors
- Special Issues
- Topics
- Sections & Collections
- Article Processing Charge
- Indexing & Archiving
- Editor’s Choice Articles
- Most Cited & Viewed
- Journal Statistics
- Journal History
- Journal Awards
- Society Collaborations
- Conferences
- Editorial Office
Journal Browser
► ▼ Journal BrowserHighly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Animals, Behavioral Sciences, Diversity, Insects, Life
Arthropod Biodiversity: Ecological and Functional Aspects
Topic Editors: Paolo Solari, Giorgia Sollai, Roberto Massimo Crnjar, Anita Giglio, Piero G. GiulianiniDeadline: 30 September 2023
Topic in
Diversity, Geosciences, Life, Quaternary, Animals, Fishes, Minerals, Heritage
Unanswered Questions in Palaeontology
Topic Editors: Eric Buffetaut, Julien ClaudeDeadline: 15 November 2023
Topic in
Animals, Dairy, Foods
New Insights into the Milk 2.0
Topic Editors: Hasitha Priyashantha, Janak VidanarachchiDeadline: 30 November 2023
Topic in
Animals, Aquaculture Journal, Fishes, Life, Poultry
Feeding Strategies to Improve Sustainability and Welfare in Fish and Poultry Production
Topic Editors: Sihem Dabbou, Giulia Secci, Hung Quang TranDeadline: 20 December 2023

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
Animals
Gut Health in Small Ruminants
Guest Editors: Juan Alberto Corbera, Sergio MartínDeadline: 2 September 2023
Special Issue in
Animals
Dietary Proteins and Amino Acids: Postnatal Growth and Long-Term Health
Guest Editor: Adel PezeshkiDeadline: 15 September 2023
Special Issue in
Animals
New Tools for Monitoring Genetic Diversity in Animals
Guest Editors: Giovanni Forcina, Qian Tang, María Pilar Cabezas RodríguezDeadline: 30 September 2023
Special Issue in
Animals
Innovations in Aquaculture Sustainability and Endangered Aquatic Species Conservation: Advances in Reproduction, New Aquafeed Formulations, Sustainable Farming Systems, Emerging Contaminants, and Waste Treatment and Revalorization
Guest Editors: Matteo Zarantoniello, Ike OlivottoDeadline: 15 October 2023
Topical Collections
Topical Collection in
Animals
Recent Advances in Fish Nutrition: Insights on the Nutritional Implications of Modern Formulations
Collection Editors: Artur Rombenso, Bruno Araújo, Erchao Li
Topical Collection in
Animals
Gut Microbiota and Growth and Health of Monogastric Farm Animals
Collection Editor: Paolo Bosi
Topical Collection in
Animals
Current Advances in Poultry Research
Collection Editors: John Michael Gonzalez, Casey M. Owens
Topical Collection in
Animals
Nanotechnology in Animal Science
Collection Editors: Antonio Gonzalez-Bulnes, Nesrein M. Hashem




.jpg)






.jpg)






