-
 Variations in Gold Nanoparticle Size on DNA Damage: A Monte Carlo Study Based on a Multiple-Particle Model Using Electron Beams
Variations in Gold Nanoparticle Size on DNA Damage: A Monte Carlo Study Based on a Multiple-Particle Model Using Electron Beams -
 Laser-Induced Graphene for Multifunctional and Intelligent Wearable Systems
Laser-Induced Graphene for Multifunctional and Intelligent Wearable Systems -
 Transformative Technology for FLASH Radiation Therapy
Transformative Technology for FLASH Radiation Therapy -
 Petrographic and Chemical Characterization of the Frescoes by Saturnino Gatti (Central Italy, 15th Century)
Petrographic and Chemical Characterization of the Frescoes by Saturnino Gatti (Central Italy, 15th Century) -
 Effect of Cohesive Properties on Low-Velocity Impact Simulations of Woven Composite Shells
Effect of Cohesive Properties on Low-Velocity Impact Simulations of Woven Composite Shells
Journal Description
Applied Sciences
Applied Sciences
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal on all aspects of applied natural sciences published semimonthly online by MDPI.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within Scopus, SCIE (Web of Science), Inspec, CAPlus / SciFinder, and other databases.
- Journal Rank: JCR - Q2 (Engineering, Multidisciplinary) / CiteScore - Q1 (General Engineering)
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 15.8 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 2.6 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the first half of 2023).
- Recognition of Reviewers: reviewers who provide timely, thorough peer-review reports receive vouchers entitling them to a discount on the APC of their next publication in any MDPI journal, in appreciation of the work done.
- Testimonials: See what our authors say about Applied Sciences.
- Companion journals for Applied Sciences include: Applied Nano, AppliedChem, Applied Biosciences, Virtual Worlds, Spectroscopy Journal and JETA.
Impact Factor:
2.7 (2022);
5-Year Impact Factor:
2.9 (2022)
Latest Articles
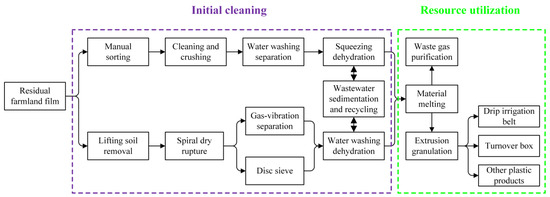
Analysis of Feed Inlet and Optimal Feeding Amount of Waste Ground Film Impurity Removal Equipment
Appl. Sci. 2023, 13(17), 9905; https://doi.org/10.3390/app13179905 (registering DOI) - 01 Sep 2023
Abstract
A tumbler screen-type residual film–impurity mixture wind separator is the key equipment for the secondary utilization of farmland residual film. During its operation, the proportion of impurities in the separated waste mulch film intermittently increases, resulting in poor working stability of the device,
[...] Read more.
A tumbler screen-type residual film–impurity mixture wind separator is the key equipment for the secondary utilization of farmland residual film. During its operation, the proportion of impurities in the separated waste mulch film intermittently increases, resulting in poor working stability of the device, which may hamper long-term operation. To address the above issues, the material inside the separation unit was continuously monitored, and the main factor affecting separator performance was determined to be the challenges in the effective depolymerization of some residual film-impurity mixtures. The principles of agglomeration and depolymerization of the residual film-impurity mixtures were analyzed using computational fluid dynamics (CFD) and discrete element method (DEM) flow-solid coupling simulation methods. The key factor affecting the disaggregation of the mixture was the collision force between the residual film–impurity mixture and the trommel screen. The collision force was maximum when the residual film–impurity mixture first collided with the trommel screen when it was fed into the separation device. Furthermore, simulations were carried out for different inlet structure forms; the evaluation index was the maximum collision force of the residual film–impurity mixture agglomerate on the trommel screen. The best disaggregation effect was obtained with a square feed inlet and at a feeding rate of 202 kg/h. A prototype was built using these specifications for verification. The average value of the ratio of impurities in the residual film was 6.966%, the coefficient of variation was 7.38%, and the dispersion of statistical results was small. The ratio of impurities in the residual film was kept constant during the continuous operation of the wind separator. Thus, in this study, we analyzed the agglomerate disaggregation process and provided theoretical insights for determining the optimal structures of the inlets of various cleaning devices and the feeding volumes.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Advances in Waste Treatment and Resource Utilization)
►
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
The Influence of the Hardness of the Tested Material and the Surface Preparation Method on the Results of Ultrasonic Testing
Appl. Sci. 2023, 13(17), 9904; https://doi.org/10.3390/app13179904 (registering DOI) - 01 Sep 2023
Abstract
Non-destructive ultrasonic testing can be used to assess the properties and condition of real machine elements during their operation, with limited (one-sided) access to these elements. A methodological question then arises concerning the influence of the material properties of such elements and the
[...] Read more.
Non-destructive ultrasonic testing can be used to assess the properties and condition of real machine elements during their operation, with limited (one-sided) access to these elements. A methodological question then arises concerning the influence of the material properties of such elements and the condition of their surfaces on the result of ultrasonic testing. This paper attempts to estimate the influence of material hardness and surface roughness on the result of such testing study area testing machine or plant components of unknown exact thickness. Ultrasonic testing was carried out on specially prepared steel samples. These samples had varying surface roughness (Ra from 0.34 to 250.73 µm) of the reflection surface of the longitudinal ultrasonic wave (the so-called reflectors) and hardness (32 and 57 HRC). The ultrasonic measures were the attenuation of the wave, estimated by the decibel drop in the gain of its pulses, and the propagation velocity of the longitudinal ultrasonic wave. Ultrasonic transducers (probes) of varying frequencies (from 2 to 20 MHz), excited by a laboratory and industrial defectoscope were used as the source of such a wave. The results of our research provide a basis for the recommendation of two considered ultrasonic quantities for assessing the material properties of the tested element. This is of particular importance when testing machines or plant components of unknown exact thickness and unknown roughness of inaccessible surfaces, which are the reflectors of the longitudinal ultrasonic wave used for testing. It has been demonstrated that by using the ultrasonic echo technique, it is possible to evaluate the roughness and hardness of the tested elements.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Advance of Structural Health Monitoring in Civil Engineering)
►▼
Show Figures
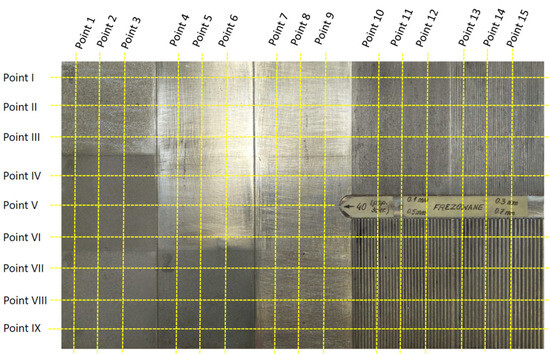
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Study on Heating Performance and Flexural Strength Properties of Electrically Conductive Mortar
Appl. Sci. 2023, 13(17), 9903; https://doi.org/10.3390/app13179903 (registering DOI) - 01 Sep 2023
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The use of electrically conductive mortar (ECM) is a relatively new construction material technology developed to obtain high conductivity and mechanical strength. This study presents an experimental investigation on the heating performance and flexural strength properties of ECM mixed with carbon fiber (CF)
[...] Read more.
The use of electrically conductive mortar (ECM) is a relatively new construction material technology developed to obtain high conductivity and mechanical strength. This study presents an experimental investigation on the heating performance and flexural strength properties of ECM mixed with carbon fiber (CF) and steel fiber (SF), which are conductive fibers. Furthermore, the internal microstructure of the ECM was analyzed with a scanning electron microscope (SEM) and thermogravimetric analysis was carried out using a thermogravimetric analyzer (TGA) device. The results of the experiment showed that the incorporation of SF had little effect on heating performance. In the case of CF, however, it was found that as the fiber contents and applied voltages increased, the heating performance increased. In particular, the maximum heating temperature of the ECM-CF125 specimen was 145.1 °C at an applied voltage of 30 V and an electrode spacing of 40 mm, which was about 7.3 times higher than the initial temperature (20 °C). In addition, the flexural strength of ECM mixed with SF was higher than that of plain mortar (PM), whereas the ECM-CF125 specimen showed a greater tendency to significantly decrease. It was confirmed that the hydration products and internal microstructures of the specimens were unaffected by repetitive electrical heating, and the ECM maintained stable electrical conductivity.
Full article
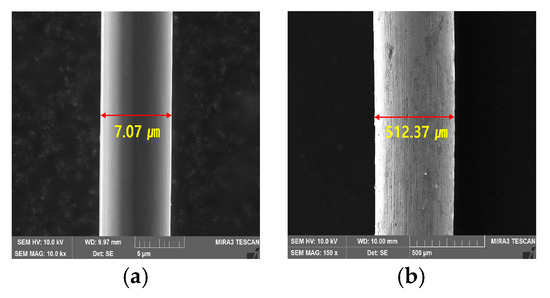
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Simulated Prediction of Roof Water Breakout for High-Intensity Mining under Reservoirs in Mining Areas in Western China
Appl. Sci. 2023, 13(17), 9902; https://doi.org/10.3390/app13179902 (registering DOI) - 01 Sep 2023
Abstract
China is rich in coal resources under water bodies. However, the safety prediction of high-intensity mining under water bodies has long been one of the problems encountered by the coal industry. It is of great significance to realize safe mining under water bodies,
[...] Read more.
China is rich in coal resources under water bodies. However, the safety prediction of high-intensity mining under water bodies has long been one of the problems encountered by the coal industry. It is of great significance to realize safe mining under water bodies, improve the recovery rate of coal resources and protect reservoir resources. Therefore, this article takes the No. 5 coal seam and No. 11 mining area of the Wangwa Coal Mine as the research object, and integrates physical simulation, numerical simulation, theoretical analysis, and other methods to study the development height of water-conducting fracture zones in fully mechanized top coal caving mining. Solid–liquid coupling physical simulation tests reveal the failure characteristics of overlying strata in goaf and the seepage law of reservoir water under the influence of mining. By comparing the monitoring data of borehole leakage, the measured data obtained by borehole monitoring with the height data of the water-conducting fracture zone obtained by the traditional empirical formula of three-under standard, the error between the two is as high as −29.39%. In this case, the variance correction coefficient is used to correct the empirical formula, and on this basis, in order to effectively protect the surface water dam and water body, the mining height of the coal seam in the working face with limited height mining is inversely derived. The research results provide a basis for the safety prediction of high-intensity mining under the reservoir dam in the ecologically fragile areas of western China and a scientific guarantee for the formulation of safety measures under such conditions.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic Dynamic Disaster Control, Mine Multi-Source Disaster Monitoring and Intelligent Analysis)
►▼
Show Figures
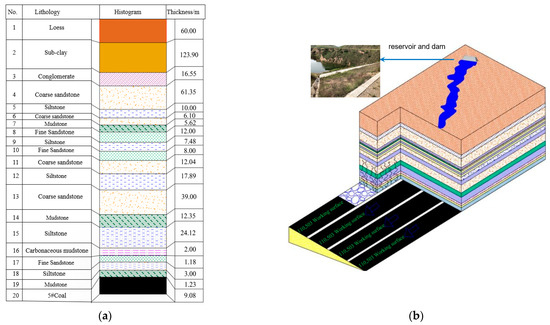
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Enhancing User Engagement in Shared Autonomous Vehicles: An Innovative Gesture-Based Windshield Interaction System
by
, , , , , and
Appl. Sci. 2023, 13(17), 9901; https://doi.org/10.3390/app13179901 (registering DOI) - 01 Sep 2023
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
With the rapid advancement of autonomous vehicles, a transformative transportation paradigm is emerging in the automotive industry, necessitating a re-evaluation of how users engage with and utilize these evolving settings. This research paper introduces an innovative interaction system tailored for shared autonomous vehicles,
[...] Read more.
With the rapid advancement of autonomous vehicles, a transformative transportation paradigm is emerging in the automotive industry, necessitating a re-evaluation of how users engage with and utilize these evolving settings. This research paper introduces an innovative interaction system tailored for shared autonomous vehicles, focusing on its development and comprehensive evaluation. The proposed system uses the car’s windshield as an interactive display surface, enabling infotainment and real-time information about the surrounding environment. The integration of two gesture-based interfaces forms a central component of the system. Through a study involving twenty subjects, we analyzed and compared the user experience facilitated by these interfaces. The study outcomes demonstrated that the subjects exhibited similar behaviors and responses across both interfaces, thus validating the potential of these interaction systems for future autonomous vehicles. These findings collectively emphasize the transformative nature of the proposed system and its ability to enhance user engagement and interaction within the context of autonomous transportation.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Handgrip Strength as a Distinguishing Factor of People Training Martial Arts
Appl. Sci. 2023, 13(17), 9900; https://doi.org/10.3390/app13179900 (registering DOI) - 01 Sep 2023
Abstract
Jujutsu is a close-contact grappling combat sport. Karate is a long-distance combat sport, primarily using strikes and kicks. Well-designed strength characteristics should be capable of differentiating between participants of martial arts and combat sports, especially if, due to training preferences, they develop particular
[...] Read more.
Jujutsu is a close-contact grappling combat sport. Karate is a long-distance combat sport, primarily using strikes and kicks. Well-designed strength characteristics should be capable of differentiating between participants of martial arts and combat sports, especially if, due to training preferences, they develop particular preferences for grappling or striking that differentiate them, as is the case in jujutsu and karate. One hundred and seventy-eight participants were tested for their age, weight, years of training, style (modern jujutsu, Polish and German groups, karate Kyokushin, karate Shotokan), skill level (Kyu or Dan grade), gender, and handgrip strength (HGS). An analysis of variance utilizing age, weight, years of training, martial art, gender, and skill in explaining HGS showed that variance in skill level and the interaction between skills and weight were significant. Furthermore, a post-hoc Tukey’s HSD test based on skills separated practitioners with the second Kyu from those with the sixth Dan grade. There were two groups identified when a similar analysis was conducted for the interaction between skill and weight. The first one encompassed all athletes below the fifth grade, whereas the second one comprised the remaining practitioners. Principal component analysis with gender as a grouping variable showed that women formed a partly separated group of athletes, with the most differentiating factors being age and years of training. When the grouping variable was skill level, the most influential variables were weight, HGS, and age. Finally, utilizing martial arts as a grouping variable showed that age, years of training, and skill were the essential variables. Our study has demonstrated that by utilizing HGS in combination with such characteristics as weight, age, years of training, gender, Dan grade, and martial arts, it is possible to identify differences between people training distinct martial styles, those with varying skills, and those representing opposite sexes. However, the differentiation is only sometimes apparent.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Applied Biosciences and Bioengineering)
►▼
Show Figures
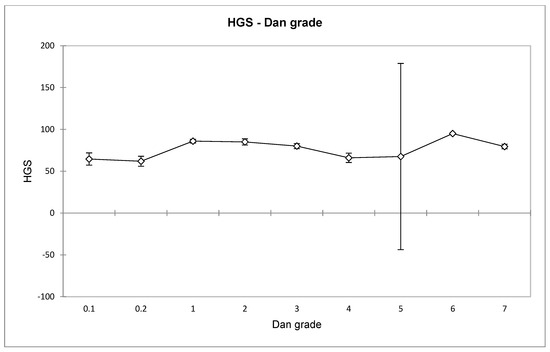
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Controllable Friction of an Epoxy Composite via Thermal Treatment
Appl. Sci. 2023, 13(17), 9899; https://doi.org/10.3390/app13179899 (registering DOI) - 01 Sep 2023
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Smart surfaces with controllable friction have generated considerable attention lately. However, most composites prepared with traditional fillers cannot achieve “real-time” friction conversion. Herein, a new smart surface was designed to achieve different friction coefficients (0.65 and 0.12). Different coefficients of friction were reversibly
[...] Read more.
Smart surfaces with controllable friction have generated considerable attention lately. However, most composites prepared with traditional fillers cannot achieve “real-time” friction conversion. Herein, a new smart surface was designed to achieve different friction coefficients (0.65 and 0.12). Different coefficients of friction were reversibly and precisely controlled via heating. Via friction and heating, 1H,1H,2H,2H-perfluorohexyl hexadecane (PHHD), a kind of phase-change material—paraffin wax—was released from the microcapsules, and a stable and complete film was formed. It changed the interface from “solid-solid” to “solid-liquid” in a dry friction state. The composite contains microcapsules that prevent phase separation between PHHD and matrix, which enables the composite to have a long service time and switchable friction performance. In addition, this composite can maintain its extraordinary ability even in harsh environments like UV irradiation. By demonstrating switchable friction based on changes in the interactions between contact interfaces, this work provides a new principle for designing smart tribological composites.
Full article
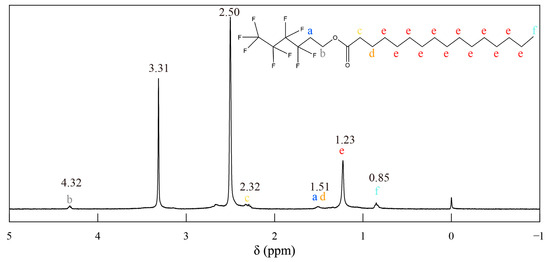
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
A Novel Way of Optimizing Headlight Distributions Based on Real-Life Traffic and Eye Tracking Data Part 3: Driver Gaze Behaviour on Real Roads and Optimized Light Distribution
Appl. Sci. 2023, 13(17), 9898; https://doi.org/10.3390/app13179898 (registering DOI) - 01 Sep 2023
Abstract
In order to find optimized headlight distributions based on real traffic data, a three-step approach has been chosen. The complete investigations are too extensive to fit into a single paper; this paper is the last of a three part series. Over the three
[...] Read more.
In order to find optimized headlight distributions based on real traffic data, a three-step approach has been chosen. The complete investigations are too extensive to fit into a single paper; this paper is the last of a three part series. Over the three papers, a novel way to optimize automotive headlight distributions based on real-life traffic and eye tracking data is presented. Across all three papers, a total of 119 test subjects participated in the studies with over 15,000 km of driving, including recordings of gaze behaviour, light data, detection distances, and other objects in traffic. In this third paper, driver gaze behaviour is recorded while driving a 128 km round course, covering urban roads, country roads, and motorways. This gaze behaviour is then analysed and compared to prior work covering driver gaze behaviour. Comparing the gaze distributions with roadway object distributions from part two of this series, Analysis of Real-World Traffic Data in Germany and combining them with the idealized baseline headlight distribution from part one, different optimized headlight distributions can be generated. These headlight distributions can be optimized for different driving requirements based on the data that is used and weighting the different road types differently. The resulting headlight distribution is then compared to a standard light distribution in terms of the required luminous flux, angular distribution, and overall shape. Nonetheless, it is the overall approach that has been taken that we see as the primary novel outcome of this investigation, even more than the actual distribution resulting from this effort.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Smart Lighting and Visual Safety)
►▼
Show Figures
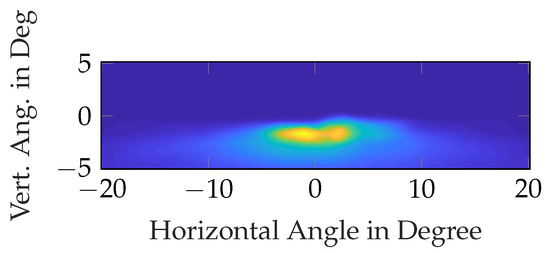
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Experimental Study on the Effect of the Freeze–Thaw Cycle in an Acidic Environment on the Mechanical Properties of Grout-Reinforced Rock Specimens
Appl. Sci. 2023, 13(17), 9897; https://doi.org/10.3390/app13179897 (registering DOI) - 01 Sep 2023
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
A new type of grouting material—FCM (fast cementing material)—is being used in coastal and offshore infrastructure projects, such as harbor and tunnel rehabilitation. In order to investigate how this material performs under different conditions, the compressive strength, failure mode, and surface microscopic changes
[...] Read more.
A new type of grouting material—FCM (fast cementing material)—is being used in coastal and offshore infrastructure projects, such as harbor and tunnel rehabilitation. In order to investigate how this material performs under different conditions, the compressive strength, failure mode, and surface microscopic changes of different fracture penetration degrees and different crack angles of grout-reinforced specimens formed by the FCM and sandstone were investigated in an acidic environment with pH = 1.1 and after freeze–thaw cycles of 5, 10, 20, and 30 times. In addition, through the preliminary determination of FCM grouting material fluidity and setting time, it was determined that the water-material ratio in this test is 0.3, and the sandstone used has good uniformity. The results show that the strength of the original rock can be matched or even exceeded by the solid grout of FCM and sandstone. Acidic environments and freeze–thaw cycles will erode the specimens, mainly on the surface of the specimens. The fracture penetration degree and crack angle determine the degree of strength reduction of the specimens. The compressive strength of the specimens decreases most rapidly within 10 freeze–thaw cycles. After soaking in acidic solution and a freeze–thaw cycle in an acidic environment, particle shedding occurs on the surface of the grout material and a “honeycomb” area appears on the surface of the sandstone. As the freeze–thaw cycle increases, the particle-shedding area and the honeycomb area increase continuously.
Full article
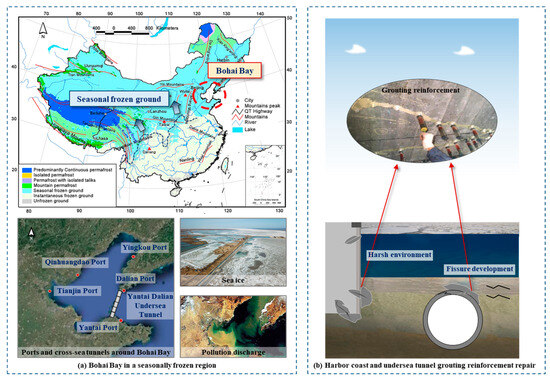
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Performance Evaluation of an API Stock Exchange Web System on Cloud Docker Containers
by
Appl. Sci. 2023, 13(17), 9896; https://doi.org/10.3390/app13179896 (registering DOI) - 01 Sep 2023
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
This study aims to identify the most effective input parameters for performance modelling of container-based web systems. We introduce a method using queueing Petri nets to model web system performance for containerized structures, leveraging prior measurement data for resource demand estimation. This approach
[...] Read more.
This study aims to identify the most effective input parameters for performance modelling of container-based web systems. We introduce a method using queueing Petri nets to model web system performance for containerized structures, leveraging prior measurement data for resource demand estimation. This approach eliminates intrusive interventions in the production system. Our research evaluates the accuracy of various formal estimation methods, pinpointing the most suitable for container environments. With the use of a stock exchange web system benchmark for data collection and simulation verification, our findings reveal that the proposed method ensures precise response time parameter accuracy for such architectural configurations.
Full article
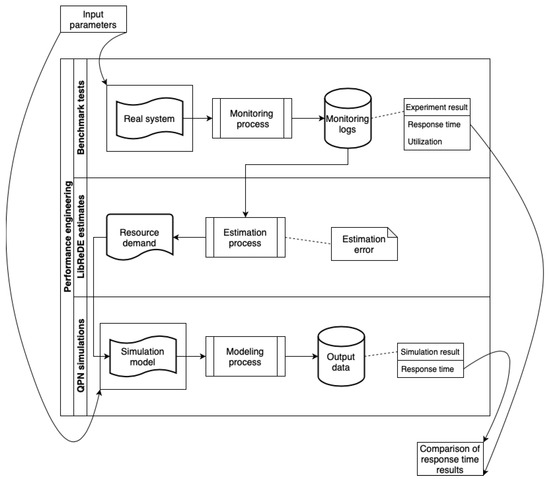
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Smart Logistics Warehouse Moving-Object Tracking Based on YOLOv5 and DeepSORT
by
and
Appl. Sci. 2023, 13(17), 9895; https://doi.org/10.3390/app13179895 (registering DOI) - 01 Sep 2023
Abstract
The future development of Industry 4.0 places paramount importance on human-centered/-centric factors in the production, design, and management of logistic systems, which has led to the emergence of Industry 5.0. However, effectively integrating human-centered/-centric factors in logistics scenarios has become a challenge. A
[...] Read more.
The future development of Industry 4.0 places paramount importance on human-centered/-centric factors in the production, design, and management of logistic systems, which has led to the emergence of Industry 5.0. However, effectively integrating human-centered/-centric factors in logistics scenarios has become a challenge. A pivotal technological solution for dealing with such a challenge is to distinguish and track moving objects such as humans and goods. Therefore, an algorithm model combining YOLOv5 and DeepSORT for logistics warehouse object tracking is designed, where YOLOv5 is selected as the object-detection algorithm and DeepSORT distinguishes humans from goods and environments. The evaluation metrics from the MOT Challenge affirm the algorithm’s robustness and efficacy. Through rigorous experimental tests, the combined algorithm demonstrates rapid convergence (within 30 ms), which holds promising potential for applications in real-world logistics warehouses.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Sustainable, Human-Centred/Centric and Resilient Production and Logistic Systems Design and Management)
►▼
Show Figures
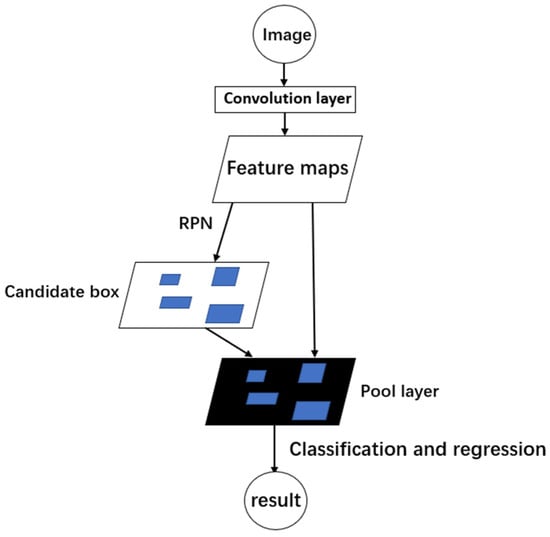
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Development and Initial Characterisation of a Localised Elastin Degradation Ex Vivo Porcine Aortic Aneurysm Model
Appl. Sci. 2023, 13(17), 9894; https://doi.org/10.3390/app13179894 (registering DOI) - 01 Sep 2023
Abstract
Aortic aneurysms (AA) occur in 4.8% of people causing 150,000 deaths annually. While endovascular aneurysm repairs reduce surgical morbidity, device-related failures (leak/displacement) are frequent highlighting the need for test models that better represent the mural geometry and compliance changes in human AAs. We
[...] Read more.
Aortic aneurysms (AA) occur in 4.8% of people causing 150,000 deaths annually. While endovascular aneurysm repairs reduce surgical morbidity, device-related failures (leak/displacement) are frequent highlighting the need for test models that better represent the mural geometry and compliance changes in human AAs. We aimed to develop and characterise an ex vivo porcine aortic model of AA. The optimal duration of tissue elastase exposure to emulate AA changes in elastin microstructure and content was determined using porcine aortic rings. Elastase-induced changes were quantified morphologically, and mechanical properties assessed via ring tensile testing. Subsequent experiments tested the potential for localised elastase treatment in a 1 cm segment of porcine aorta using a specially designed 3D printed rig. The effect on pressure-diameter behaviour was investigated via inflation-extension testing. Elastase treatment produced time dependent decreases in elastin, resulting in an increased tensile modulus and circumferential length in the ring samples in the final phase of the J-shaped tissue stress-strain curves. In whole aortic segments, localised elastase-induced luminal degradation was successfully limited to a central region. The degree of elastin degradation achieved was sufficient to cause localised dilation with respect to controls under physiological pressures. Localised elastin degradation in porcine aortic segments is feasible and emulates the changes seen clinically in aortic aneurysms.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Application of Biomechanics in Cardiovascular Diseases)
►▼
Show Figures
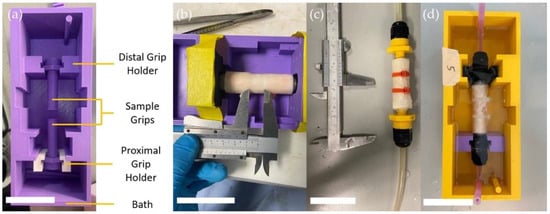
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Metabolic and Developmental Changes in Insects as Stress-Related Response to Electromagnetic Field Exposure
Appl. Sci. 2023, 13(17), 9893; https://doi.org/10.3390/app13179893 (registering DOI) - 01 Sep 2023
Abstract
(1) Background: The growing ubiquity of electromagnetic fields (EMF) due to rapid technological progress raises concerns about potential health implications. While laboratory experiments have generated inconclusive findings about adverse effects, EMFs have demonstrated efficacy in magnetotherapy. Earlier studies indicate that an EMF can
[...] Read more.
(1) Background: The growing ubiquity of electromagnetic fields (EMF) due to rapid technological progress raises concerns about potential health implications. While laboratory experiments have generated inconclusive findings about adverse effects, EMFs have demonstrated efficacy in magnetotherapy. Earlier studies indicate that an EMF can trigger stress responses in organisms, the outcomes of which are dependent on the intensity of the EMF. (2) Methods: This study aims to explore the effects of extremely low-frequency EMF (50 Hz, 1 mT, or 7 mT) on metamorphosis and metabolism rates, which are indicators of stress, across different developmental stages of Tenebrio molitor, including adults, pupae, and larvae. (3) Results: Our findings reveal that exposure to EMF leads to accelerated weight loss, increased adult metabolism, and higher mortality; however, EMF exposure appears to have no impact on sugar levels or the rate and success of metamorphosis. Notably, significant changes were only observed under the influence of a strong EMF (7 mT), while the weaker EMF (1 mT) did not yield statistically significant outcomes. (4) Conclusion: The obtained results suggest that an extremely low-frequency EMF can be considered a stressor, with its effects contingent upon the specific parameters of exposure and the developmental stage of the experimental model.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Novel Advances and Applications in Bio-Electromagnetics and Biomedical Engineering)
►▼
Show Figures
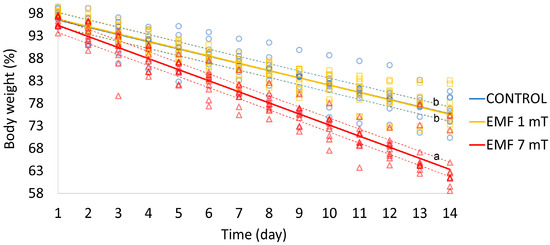
Figure 1
Open AccessEditorial
Special Issue on New Trends in Telecommunications Engineering
Appl. Sci. 2023, 13(17), 9892; https://doi.org/10.3390/app13179892 (registering DOI) - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
This collection of research papers explores various aspects of antenna design and high-speed wireless communication, delving into the forefront of technology for modern telecommunications [...]
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue New Trends in Telecommunications Engineering)
Open AccessArticle
Stability Analysis of Lane-Keeping Assistance System for Trucks under Crosswind Conditions
Appl. Sci. 2023, 13(17), 9891; https://doi.org/10.3390/app13179891 (registering DOI) - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
To enhance the control accuracy of lane-keeping assistance systems for trucks encountering crosswind-induced lateral deviations to improve the lateral stability of the vehicle, this study proposes a control strategy based on a linear quadratic regulator (LQR) using a path-tracking preview model. First, the
[...] Read more.
To enhance the control accuracy of lane-keeping assistance systems for trucks encountering crosswind-induced lateral deviations to improve the lateral stability of the vehicle, this study proposes a control strategy based on a linear quadratic regulator (LQR) using a path-tracking preview model. First, the lateral deviation is calculated using the path-tracking preview model. Then, an observer for the vehicle’s sideslip angle is designed using a vehicle lateral tracking deviation model and a Kalman filter controller, and this is used to solve the deviation of the sideslip angle. Finally, a feedforward controller is designed based on the LQR controller and a linear two-degrees-of-freedom vehicle model to eliminate steady-state errors arising from LQR optimization, thereby obtaining the steering angle of the vehicle when subjected to crosswind conditions. Comparing the test results of the sideslip angle, yaw rate, and lateral acceleration demonstrates that this strategy effectively improves the control accuracy of lane-keeping under crosswind conditions. The proposed method is validated through hardware-in-the-loop experiments on a test bench, yielding results consistent with simulations.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Automotive Safety and Security Engineering: From Theories to Practices)
Open AccessArticle
Facial Emotion Recognition for Photo and Video Surveillance Based on Machine Learning and Visual Analytics
Appl. Sci. 2023, 13(17), 9890; https://doi.org/10.3390/app13179890 (registering DOI) - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
Modern video surveillance systems mainly rely on human operators to monitor and interpret the behavior of individuals in real time, which may lead to severe delays in responding to an emergency. Therefore, there is a need for continued research into the designing of
[...] Read more.
Modern video surveillance systems mainly rely on human operators to monitor and interpret the behavior of individuals in real time, which may lead to severe delays in responding to an emergency. Therefore, there is a need for continued research into the designing of interpretable and more transparent emotion recognition models that can effectively detect emotions in safety video surveillance systems. This study proposes a novel technique incorporating a straightforward model for detecting sudden changes in a person’s emotional state using low-resolution photos and video frames from surveillance cameras. The proposed technique includes a method of the geometric interpretation of facial areas to extract features of facial expression, the method of hyperplane classification for identifying emotional states in the feature vector space, and the principles of visual analytics and “human in the loop” to obtain transparent and interpretable classifiers. The experimental testing using the developed software prototype validates the scientific claims of the proposed technique. Its implementation improves the reliability of abnormal behavior detection via facial expressions by 0.91–2.20%, depending on different emotions and environmental conditions. Moreover, it decreases the error probability in identifying sudden emotional shifts by 0.23–2.21% compared to existing counterparts. Future research will aim to improve the approach quantitatively and address the limitations discussed in this paper.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Advanced Technologies for Emotion Recognition)
Open AccessArticle
Research on High-Speed Vibration and Structure Optimization of Multiwire Sawing Machine
Appl. Sci. 2023, 13(17), 9889; https://doi.org/10.3390/app13179889 (registering DOI) - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
To improve the sawing stability and slicing quality of an existing multi-wire saw under severe vibrations using a high wire speed, its structure is optimized to improve its structural stiffness, so that it can still maintain good operation stability under higher wire speed.
[...] Read more.
To improve the sawing stability and slicing quality of an existing multi-wire saw under severe vibrations using a high wire speed, its structure is optimized to improve its structural stiffness, so that it can still maintain good operation stability under higher wire speed. First, a finite element simulation model is established based on the shape, structural and material characteristics of the multi-wire saw, and then a transient dynamic simulation calculation is carried out using finite element software to obtain the vibration characteristics of the machine, which is verified with the measured data. The results show that the error between the calculated and the measured value is less than 11.46%, which verifies the accuracy of the simulation. On this basis, a multi-objective optimization design method based on the response surface is used to optimize the structure of the whole machine, and the optimized model is simulated again to evaluate its optimization effect. The results show that the amplitude of the optimized machine at a 2400 m/min wire speed is equivalent to that of the original machine at a 1500 m/min wire speed, and the wire speed is increased by 60% year-on-year with the same operation stability, which can guide research on high-speed multi-wire saws and machine tool vibration control strategies.
Full article
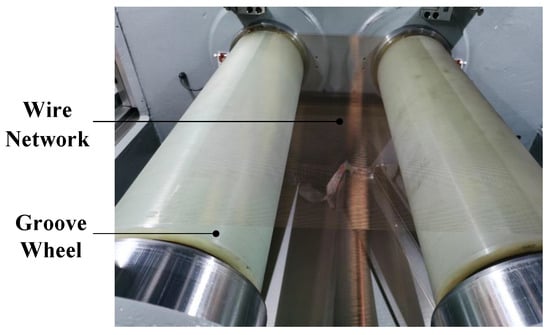
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Short-Term Wind Power Forecasting Based on VMD and a Hybrid SSA-TCN-BiGRU Network
Appl. Sci. 2023, 13(17), 9888; https://doi.org/10.3390/app13179888 (registering DOI) - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
Wind power generation is a renewable energy source, and its power output is influenced by multiple factors such as wind speed, direction, meteorological conditions, and the characteristics of wind turbines. Therefore, accurately predicting wind power is crucial for the grid operation and maintenance
[...] Read more.
Wind power generation is a renewable energy source, and its power output is influenced by multiple factors such as wind speed, direction, meteorological conditions, and the characteristics of wind turbines. Therefore, accurately predicting wind power is crucial for the grid operation and maintenance management of wind power plants. This paper proposes a hybrid model to improve the accuracy of wind power prediction. Accurate wind power forecasting is critical for the safe operation of power systems. To improve the accuracy of wind power prediction, this paper proposes a hybrid model incorporating variational modal decomposition (VMD), a Sparrow Search Algorithm (SSA), and a temporal-convolutional-network-based bi-directional gated recurrent unit (TCN-BiGRU). The model first uses VMD to break down the raw power data into several modal components, and then it builds an SSA-TCN-BIGRU model for each component for prediction, and finally, it accumulates all the predicted components to obtain the wind power prediction results. The proposed short-term wind power prediction model was validated using measured data from a wind farm in China. The proposed VMD-SSA-TCN-BiGRU forecasting framework is compared with benchmark models to verify its practicability and reliability. Compared with the TCN-BiGRU, the symmetric mean absolute percentage error, the mean absolute error, and the root mean square error of the VMD-SSA-TCN-BiGRU model reduced by 34.36%, 49.14%, and 55.94%.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue State-of-the-Art of Power Systems)
►▼
Show Figures
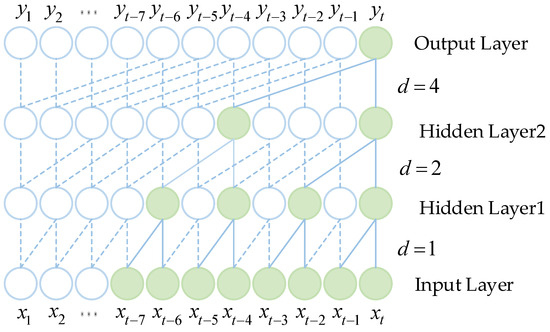
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Spatiotemporal Changes in the Hydrochemical Characteristics and the Assessment of Groundwater Suitability for Drinking and Irrigation in the Mornag Coastal Region, Northeastern Tunisia
Appl. Sci. 2023, 13(17), 9887; https://doi.org/10.3390/app13179887 (registering DOI) - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
Hydrogeochemical properties and groundwater quality assessment are very important for the effective management of water resources in arid and semiarid regions. The present investigation is a spatiotemporal analysis of groundwater quality using both chemical analysis and water quality indices (WQIs) in the Mornag
[...] Read more.
Hydrogeochemical properties and groundwater quality assessment are very important for the effective management of water resources in arid and semiarid regions. The present investigation is a spatiotemporal analysis of groundwater quality using both chemical analysis and water quality indices (WQIs) in the Mornag Basin in northeastern Tunisia. The results exhibit that the Mornag shallow aquifer is dominated by chloride–sodium–potassium water facies, which progress over time toward chloride–sulfate–calcium and magnesium water facies. This may highlight that the mineralization of groundwater, which increases in the direction of groundwater flow, is primarily controlled by a natural process resulting from the dissolution of evaporative minerals and cation exchange with clay minerals relatively abundant in the study area. The anthropogenic activities represented by the return flow of irrigation water, the recharge by wastewater, and climate change also have a key role in groundwater contamination. The temporal evolution in %Na and SAR over the last three years in the Mornag aquifer shows an increasing trend that makes them unsuitable for irrigation. These findings highlight the need for assessing water quality in mapping local water resource vulnerability to pollution and developing sustainable water resources management.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic Advances in Well and Borehole Hydraulics and Hydrogeology)
Open AccessArticle
AI in Gravitational Wave Analysis, an Overview
Appl. Sci. 2023, 13(17), 9886; https://doi.org/10.3390/app13179886 (registering DOI) - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
Gravitational wave research presents a range of intriguing challenges, each of which has driven significant progress in the field. Key research problems include glitch classification, glitch cancellation, gravitational wave denoising, binary black hole signal detection, gravitational wave bursts, and minor issues that contribute
[...] Read more.
Gravitational wave research presents a range of intriguing challenges, each of which has driven significant progress in the field. Key research problems include glitch classification, glitch cancellation, gravitational wave denoising, binary black hole signal detection, gravitational wave bursts, and minor issues that contribute to the overall understanding of gravitational wave phenomena. This paper explores the applications of artificial intelligence, deep learning, and machine learning techniques in addressing these challenges. The main goal of the paper is to provide an effective view of AI and deep learning usage for gravitational wave analysis. Thanks to the advancements in artificial intelligence and machine learning techniques, aided by GPUs and specialized software frameworks, these techniques have played a key role over the last decade in the identification, classification, and cancellation of gravitational wave signals, as presented in our results. This paper provides a comprehensive exploration of the adoption rate of these techniques, with reference to the software and hardware involved, their effectiveness, and potential limitations, offering insights into the advancements in the analysis of gravitational wave data.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Gravitational Wave Observatory: The Realm of Applied Science)

Journal Menu
► ▼ Journal Menu-
- Applied Sciences Home
- Aims & Scope
- Editorial Board
- Reviewer Board
- Topical Advisory Panel
- Instructions for Authors
- Special Issues
- Topics
- Sections & Collections
- Article Processing Charge
- Indexing & Archiving
- Editor’s Choice Articles
- Most Cited & Viewed
- Journal Statistics
- Journal History
- Journal Awards
- Society Collaborations
- Conferences
- Editorial Office
Journal Browser
► ▼ Journal BrowserHighly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Applied Sciences, Energies, Mathematics, Electronics, Algorithms
Distributed Optimization for Control
Topic Editors: Honglei Xu, Lingyun WangDeadline: 20 September 2023
Topic in
Applied Sciences, Energies, Fluids, Materials, Mathematics
Fluid Mechanics
Topic Editors: Vasily Novozhilov, Cunlu ZhaoDeadline: 30 September 2023
Topic in
Energies, Processes, Electronics, Applied Sciences, WEVJ
Energy Management and Efficiency in Electric Motors, Drives, Power Converters and Related Systems
Topic Editors: Mario Marchesoni, Alfonso DamianoDeadline: 15 October 2023
Topic in
Applied Sciences, Coatings, Materials, Metals, Nanomaterials
Cutting-Edge Research Trends in (Non)Metallic Materials: Design, Testing and Application
Topic Editors: Petrica Vizureanu, Andrei Victor Sandu, Madalina Simona Baltatu, Dumitru Doru Burduhos NergisDeadline: 31 October 2023

Conferences
27 October–10 November 2023
The 4th International Electronic Conference on Applied Sciences (ASEC2023)

Special Issues
Special Issue in
Applied Sciences
Novel Approaches for Improving Food Quality
Guest Editors: Agnieszka Ciurzyńska, Monika JanowiczDeadline: 1 September 2023
Special Issue in
Applied Sciences
Real-Time Diagnosis Algorithms in Biomedical Applications and Decision Support Tools
Guest Editor: Alfredo RosadoDeadline: 16 September 2023
Special Issue in
Applied Sciences
AI, Machine Learning and Deep Learning in Signal Processing
Guest Editors: Jongweon Kim, Yongseok LeeDeadline: 30 September 2023
Special Issue in
Applied Sciences
Emerging Technologies for Air Quality Improvement
Guest Editor: Thomas MaggosDeadline: 15 October 2023
Topical Collections
Topical Collection in
Applied Sciences
Advances in Automation and Robotics
Collection Editors: Manuel Armada, Roemi Fernandez
Topical Collection in
Applied Sciences
Optical Design and Engineering
Collection Editors: Zhi-Ting Ye, Pin Han, Chun Hung Lai, Yi Chin Fang
Topical Collection in
Applied Sciences
Electromagnetic Antennas for HF, VHF, and UHF Band Applications
Collection Editors: Keum Cheol Hwang, Jae-Young Chung