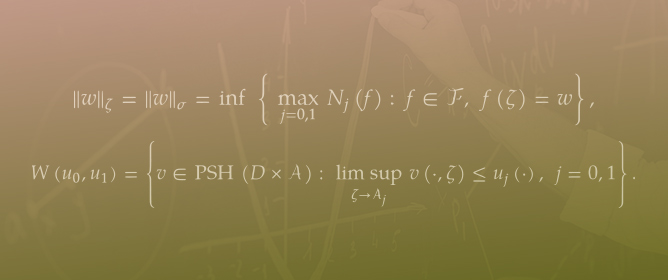Journal Description
Axioms
Axioms
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal of mathematics, mathematical logic and mathematical physics, published monthly online by MDPI. The European Society for Fuzzy Logic and Technology (EUSFLAT), International Fuzzy Systems Association (IFSA) and Union of Slovak Mathematicians and Physicists (JSMF) are affiliated with Axioms and their members receive discounts on the article processing charges.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High visibility: indexed within Scopus, SCIE (Web of Science), dblp, and other databases.
- Journal Rank: JCR - Q2 (Mathematics, Applied) / CiteScore - Q1 (Algebra and Number Theory)
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 20 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 2.9 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the first half of 2023).
- Recognition of Reviewers: reviewers who provide timely, thorough peer-review reports receive vouchers entitling them to a discount on the APC of their next publication in any MDPI journal, in appreciation of the work done.
Impact Factor:
2.0 (2022);
5-Year Impact Factor:
1.9 (2022)
Latest Articles
Bogdanov–Takens Bifurcation Analysis of a Learning-Process Model
Axioms 2023, 12(9), 853; https://doi.org/10.3390/axioms12090853 (registering DOI) - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
►
Show Figures
In this paper, as a complement to the works by Monterio and Notargiacomo, we analyze the dynamical behavior of a learning-process model in a case where the system admits a unique interior degenerate equilibrium. Meanwhile, we acquire the sufficient condition for the cusp
[...] Read more.
In this paper, as a complement to the works by Monterio and Notargiacomo, we analyze the dynamical behavior of a learning-process model in a case where the system admits a unique interior degenerate equilibrium. Meanwhile, we acquire the sufficient condition for the cusp of codimension 2 and verify that the system undergoes Bogdanov–Takens bifurcation around the cusp. Finally, we give a numerical simulation to support the theoretical results.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Enhanced Remora Optimization with Deep Learning Model for Intelligent PMSM Drives Temperature Prediction in Electric Vehicles
by
, , , and
Axioms 2023, 12(9), 852; https://doi.org/10.3390/axioms12090852 - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
One of the widespread electric motors for electric vehicles (EVs) is permanent magnet synchronous machine (PMSM) drives. It is because of the power density and high energy of the PMSM with moderate assembly cost. The widely adopted PMSM as the motor of choice
[...] Read more.
One of the widespread electric motors for electric vehicles (EVs) is permanent magnet synchronous machine (PMSM) drives. It is because of the power density and high energy of the PMSM with moderate assembly cost. The widely adopted PMSM as the motor of choice for EVs, together with variety of applications urges stringent monitoring of temperature to ignore high temperatures. Temperature monitoring of the PMSM is highly complex to accomplish because of complex measurement device for internal components of the PMSM. Temperature values beyond a certain range might result in additional maintenance costs together with major operational problems in PMSM. The latest developments in artificial intelligence (AI) and deep learning (DL) methods pave a way for accurate temperature prediction in PMSM drivers. With this motivation, this article introduces an enhanced remora optimization algorithm with stacked bidirectional long short-term memory (EROA-SBiLSTM) approach for temperature prediction of the PMSM drives. The presented EROA-SBiLSTM technique mainly focuses on effectual temperature prediction using DL and hyperparameter tuning schemes. To accomplish this, the EROA-SBiLSTM technique applies Pearson correlation coefficient analysis for observing the correlation among various features, and the p-value is utilized for determining the relevant level. Next, the SBiLSTM model is used to predict the level of temperature that exists in the PMSM drivers. Finally, the EROA based hyperparameter tuning process is carried out to adjust the SBiLSTM parameters optimally. The experimental outcome of the EROA-SBiLSTM technique is tested using electric motor temperature dataset from the Kaggle dataset. The comprehensive study specifies the betterment of the EROA-SBiLSTM technique.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Application of Machine Learning and Optimization Methods in Engineering Mathematics)
►▼
Show Figures
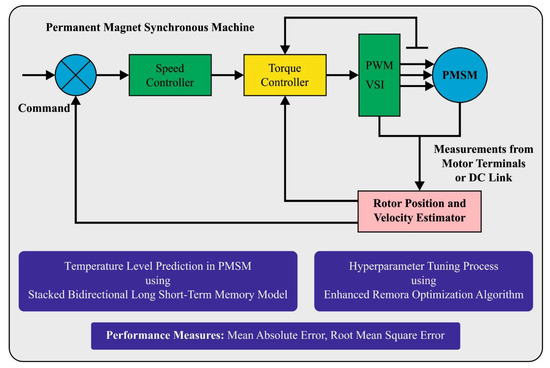
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Metrical Boundedness and Compactness of a New Operator between Some Spaces of Analytic Functions
by
Axioms 2023, 12(9), 851; https://doi.org/10.3390/axioms12090851 - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
The metrical boundedness and metrical compactness of a new operator from the weighted Bergman-Orlicz spaces to the weighted-type spaces and little weighted-type spaces of analytic functions are characterized.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Recent Advances in Functional Analysis and Operator Theory)
Open AccessArticle
Symbolic Regression Approaches for the Direct Calculation of Pipe Diameter
Axioms 2023, 12(9), 850; https://doi.org/10.3390/axioms12090850 - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
This study provides novel and accurate symbolic regression-based solutions for the calculation of pipe diameter when flow rate and pressure drop (head loss) are known, together with the length of the pipe, absolute inner roughness of the pipe, and kinematic viscosity of the
[...] Read more.
This study provides novel and accurate symbolic regression-based solutions for the calculation of pipe diameter when flow rate and pressure drop (head loss) are known, together with the length of the pipe, absolute inner roughness of the pipe, and kinematic viscosity of the fluid. PySR and Eureqa, free and open-source symbolic regression tools, are used for discovering simple and accurate approximate formulas. Three approaches are used: (1) brute force of computing power, which provides results based on raw input data; (2) an improved method where input parameters are transformed through the Lambert W-function; (3) a method where the results are based on inputs and the Colebrook equation transformed through new suitable dimensionless groups. The discovered models were simplified by the WolframAlpha simplify tool and/or the equivalent Matlab Symbolic toolbox. Novel models make iterative calculus redundant; they are simple for computer coding while the relative error remains lower compared with the solution through nomograms. The symbolic-regression solutions discovered by brute force computing power discard the kinematic viscosity of the fluid as an input parameter, implying that it has the least influence.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Methods and Applications of Advanced Statistical Analysis)
►▼
Show Figures
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
A Weighted Cosine-G Family of Distributions: Properties and Illustration Using Time-to-Event Data
Axioms 2023, 12(9), 849; https://doi.org/10.3390/axioms12090849 - 30 Aug 2023
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Modeling and predicting time-to-event phenomena in engineering, sports, and medical sectors are very crucial. Numerous models have been proposed for modeling such types of data sets. These models are introduced by adding one or more parameters to the traditional distributions. The addition of
[...] Read more.
Modeling and predicting time-to-event phenomena in engineering, sports, and medical sectors are very crucial. Numerous models have been proposed for modeling such types of data sets. These models are introduced by adding one or more parameters to the traditional distributions. The addition of new parameters to the traditional distributions leads to serious issues, such as estimation consequences and re-parametrization problems. To avoid such problems, this paper introduces a new method for generating new probability distributions without any additional parameters. The proposed method may be called a weighted cosine-G family of distributions. Different distributional properties of the weighted cosine-G family, along with the maximum likelihood estimators, are obtained. A special model of the weighted cosine-G family, by utilizing the Weibull model, is considered. The special model of the weighted cosine-G family may be called a weighted cosine-Weibull distribution. A simulation study of the weighted cosine-Weibull model is conducted to evaluate the performances of its estimators. Finally, the applications of the weighted cosine-Weibull distribution are shown by considering three data sets related to the time-to-event phenomena.
Full article
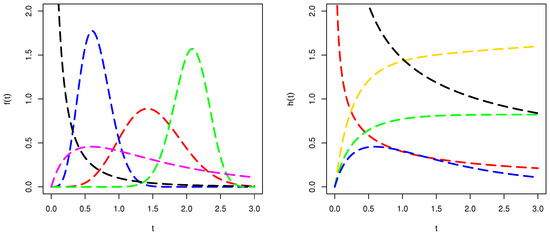
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Inertial Iterative Algorithms for Split Variational Inclusion and Fixed Point Problems
Axioms 2023, 12(9), 848; https://doi.org/10.3390/axioms12090848 - 30 Aug 2023
Abstract
This paper aims to present two inertial iterative algorithms for estimating the solution of split variational inclusion
This paper aims to present two inertial iterative algorithms for estimating the solution of split variational inclusion
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Nonlinear Functional Analysis in Natural Sciences)
►▼
Show Figures
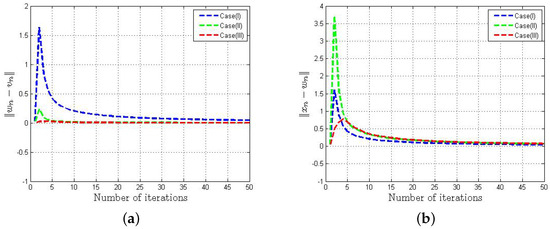
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Research on the Dynamic Mechanism of Technological Innovation Diffusion in Enterprise Communities Based on a Predation Diffusion Model
by
and
Axioms 2023, 12(9), 847; https://doi.org/10.3390/axioms12090847 - 30 Aug 2023
Abstract
In order to study the dynamic mechanism of the impact of technological innovation diffusion on enterprise population networks, a corresponding relationship between enterprise population networks and predatory models was established based on a predatory model. Without considering the impact of technological innovation diffusion,
[...] Read more.
In order to study the dynamic mechanism of the impact of technological innovation diffusion on enterprise population networks, a corresponding relationship between enterprise population networks and predatory models was established based on a predatory model. Without considering the impact of technological innovation diffusion, the stability of the enterprise population network was analyzed, and the results showed that it has the characteristic of local asymptotic stability at a positive equilibrium point. Considering the influence of technological innovation diffusion, the stability of the enterprise population network becomes complex, and its stability at the positive equilibrium point is also affected by the eigenvalue of the Laplacian matrix and technological innovation diffusion coefficient. The simulation experimental results indicate that in addition to the influence of technological innovation diffusion coefficient, the connection probability density of enterprise population networks has an important impact on stability. Only when the connection probability density is very small can the enterprise population network resist the impact of technological innovation diffusion and maintain stability.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Advances in Mathematical Methods in Economics)
►▼
Show Figures
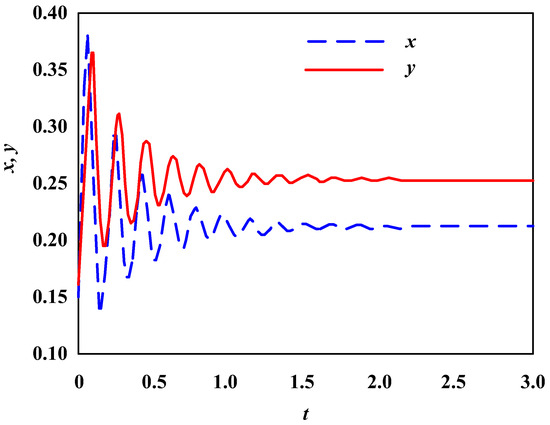
Figure 1
Open AccessEditorial
Preface to the Special Issue “A Themed Issue on Mathematical Inequalities, Analytic Combinatorics and Related Topics in Honor of Professor Feng Qi”
Axioms 2023, 12(9), 846; https://doi.org/10.3390/axioms12090846 - 30 Aug 2023
Abstract
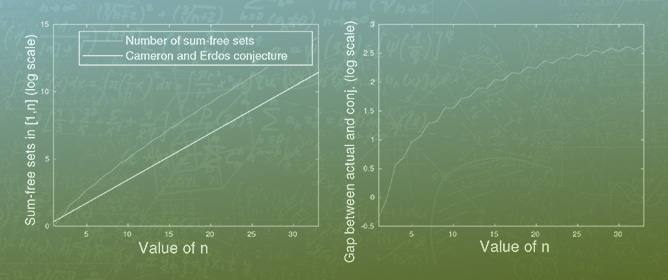
This Special Issue of the journal Axioms pays tribute to Professor Feng Qi’s significant contributions and provides some important recent advances in mathematics [...]
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue A Themed Issue on Mathematical Inequalities, Analytic Combinatorics and Related Topics in Honor of Professor Feng Qi)
Open AccessArticle
Derivative Formulas and Gradient of Functions with Non-Independent Variables
Axioms 2023, 12(9), 845; https://doi.org/10.3390/axioms12090845 - 30 Aug 2023
Abstract
Stochastic characterizations of functions subject to constraints result in treating them as functions with non-independent variables. By using the distribution function or copula of the input variables that comply with such constraints, we derive two types of partial derivatives of functions with non-independent
[...] Read more.
Stochastic characterizations of functions subject to constraints result in treating them as functions with non-independent variables. By using the distribution function or copula of the input variables that comply with such constraints, we derive two types of partial derivatives of functions with non-independent variables (i.e., actual and dependent derivatives) and argue in favor of the latter. Dependent partial derivatives of functions with non-independent variables rely on the dependent Jacobian matrix of non-independent variables, which is also used to define a tensor metric. The differential geometric framework allows us to derive the gradient, Hessian, and Taylor-type expansions of functions with non-independent variables.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Mathematical and Statistical Analysis Methods with Multidisciplinary Applications)
Open AccessArticle
The Maximum Domain for an Analytical Approximate Solution to a Nonlinear Differential Equation in the Neighborhood of a Moving Singular Point
by
and
Axioms 2023, 12(9), 844; https://doi.org/10.3390/axioms12090844 - 30 Aug 2023
Abstract
This paper presents the final stage in the study of the analytical approximate solution to a class of nonlinear differential equations unsolvable in quadrature in the general case in the neighborhood of a perturbed value of a moving singular point. An a priori
[...] Read more.
This paper presents the final stage in the study of the analytical approximate solution to a class of nonlinear differential equations unsolvable in quadrature in the general case in the neighborhood of a perturbed value of a moving singular point. An a priori error estimation is proven. The scope of application of the analytical approximate solution is extended; the formula for calculating this scope is obtained. The proof of the theorem is based on the application of elements of differential calculus. Theoretical results are supported by numerical calculations, which validate their reliability. The authors report a numerical comparison between the results, obtained in the paper, and the findings that were published earlier.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Mathematical Analysis)
►▼
Show Figures
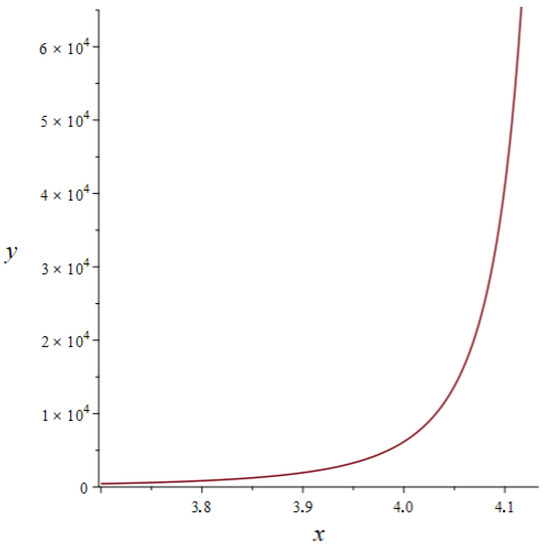
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Causality in Scalar-Einstein Waves
Axioms 2023, 12(9), 843; https://doi.org/10.3390/axioms12090843 - 30 Aug 2023
Abstract
A wavelike scalar-Einstein solution is found and indicating vectors constructed from the Bel-Robinson tensor are used to study which objects co-move with the wave and whether gravitational energy transfer is null. It is found that this Bel-Robinson energy criteria gives null energy transfer
[...] Read more.
A wavelike scalar-Einstein solution is found and indicating vectors constructed from the Bel-Robinson tensor are used to study which objects co-move with the wave and whether gravitational energy transfer is null. It is found that this Bel-Robinson energy criteria gives null energy transfer for both the vacuum plane wave and the scalar plane wave.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Applied Nonlinear Dynamical Systems in Mathematical Physics)
Open AccessArticle
Nonseparation Approach to General-Decay Synchronization of Quaternion-Valued Neural Networks with Mixed Time Delays
Axioms 2023, 12(9), 842; https://doi.org/10.3390/axioms12090842 - 30 Aug 2023
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
In this paper, the general-decay synchronization issue of a class of quaternion-valued neural networks with mixed time delays is investigated. Firstly, unlike some previous works where the quaternion-valued model is separated into four real-valued networks or two complex-valued networks, we consider the mixed-delayed
[...] Read more.
In this paper, the general-decay synchronization issue of a class of quaternion-valued neural networks with mixed time delays is investigated. Firstly, unlike some previous works where the quaternion-valued model is separated into four real-valued networks or two complex-valued networks, we consider the mixed-delayed quaternion-valued neural network model as a whole and introduce a novel nonlinear feedback controller for the corresponding response system. Then, by introducing a suitable Lyapunov–Krasovskii functional and employing a novel inequality technique, some easily verifiable sufficient conditions are obtained to ensure the general-decay synchronization for the considered drive-response networks. Finally, the feasibility of the established theoretical results is verified by carrying out Matlab numerical simulations.
Full article
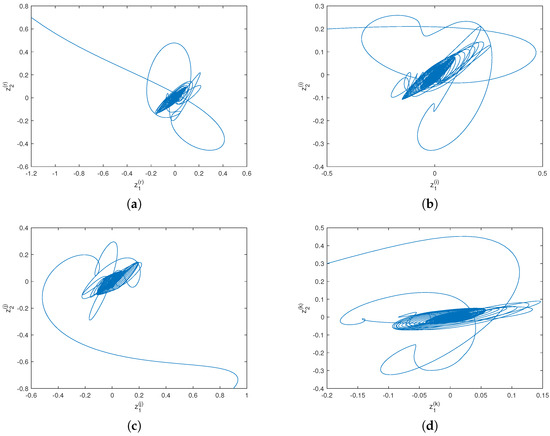
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
New Results for the Investigation of the Asymptotic Behavior of Solutions of Nonlinear Perturbed Differential Equations
by
and
Axioms 2023, 12(9), 841; https://doi.org/10.3390/axioms12090841 - 30 Aug 2023
Abstract
This study focuses on investigating the oscillatory properties of a particular class of perturbed differential equations in the noncanonical case. Our research aims to establish more effective criteria for evaluating the absence of positive solutions to the equation under study and subsequently investigate
[...] Read more.
This study focuses on investigating the oscillatory properties of a particular class of perturbed differential equations in the noncanonical case. Our research aims to establish more effective criteria for evaluating the absence of positive solutions to the equation under study and subsequently investigate its oscillatory behavior. We also perform a comparative analysis, contrasting the oscillation of the studied equation with another equation in the canonical case. To achieve this, we employ the Riccati technique along with other methods to obtain several sufficient criteria. Furthermore, we apply these new conditions to specific instances of the considered equation, assessing their performance. The significance of our work lies in its extension and broadening of the existing body of literature, contributing novel insights into this field of study.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Differential Equations and Related Topics)
►▼
Show Figures
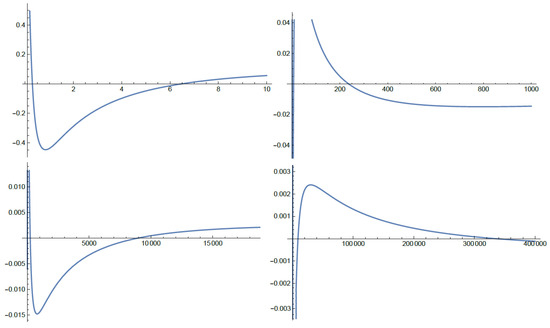
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Using Vector-Product Loop Algebra to Generate Integrable Systems
Axioms 2023, 12(9), 840; https://doi.org/10.3390/axioms12090840 - 29 Aug 2023
Abstract
A new three-dimensional Lie algebra and its loop algebra are proposed by us, whose commutator is a vector product. Based on this, a positive flow and a negative flow are obtained by introducing a new kind of spectral problem expressed by the vector
[...] Read more.
A new three-dimensional Lie algebra and its loop algebra are proposed by us, whose commutator is a vector product. Based on this, a positive flow and a negative flow are obtained by introducing a new kind of spectral problem expressed by the vector product, which reduces to a generalized KdV equation, a generalized Schrödinger equation, a sine-Gordon equation, and a sinh-Gordon equation. Next, the well-known Tu scheme is generalized for generating isospectral integrable hierarchies and non-isospectral integrable hierarchies. It is important that we make use of the variational method to create a new vector-product trace identity for which the Hamiltonian structure of the isospectral integrable hierarchy presented in the paper is worded out. Finally, we further enlarge the three-dimensional loop algebra into a six-dimensional loop algebra so that a new isospectral integrable hierarchy which is a type of extended integrable model is produced whose bi-Hamiltonian structure is also derived from the vector-product trace identity. This new approach presented in the paper possesses extensive applications in the aspect of generating integrable hierarchies of evolution equations.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Mathematical Physics)
Open AccessFeature PaperArticle
On the Total Positivity and Accurate Computations of r-Bell Polynomial Bases
Axioms 2023, 12(9), 839; https://doi.org/10.3390/axioms12090839 - 29 Aug 2023
Abstract
A new class of matrices defined in terms of r-Stirling numbers is introduced. These r-Stirling matrices are totally positive and determine the linear transformation between monomial and r-Bell polynomial bases. An efficient algorithm for the computation to high relative accuracy
[...] Read more.
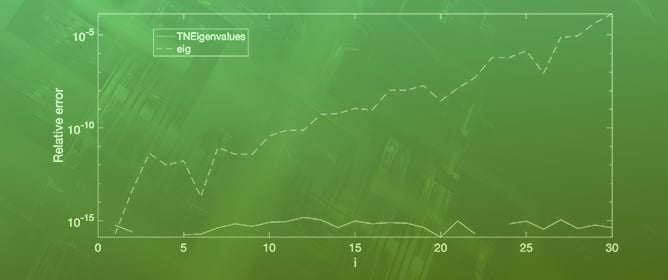
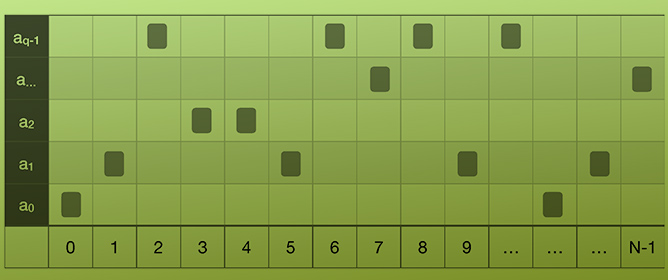
A new class of matrices defined in terms of r-Stirling numbers is introduced. These r-Stirling matrices are totally positive and determine the linear transformation between monomial and r-Bell polynomial bases. An efficient algorithm for the computation to high relative accuracy of the bidiagonal factorization of r-Stirling matrices is provided and used to achieve computations to high relative accuracy for the resolution of relevant algebraic problems with collocation, Wronskian, and Gramian matrices of r-Bell bases. The numerical experimentation confirms the accuracy of the proposed procedure.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Advances in Linear Algebra with Applications)
►▼
Show Figures
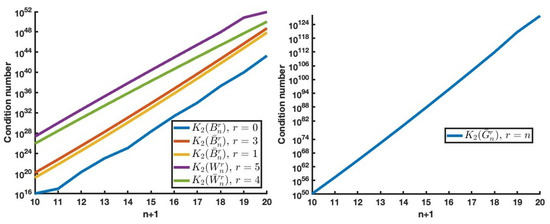
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Reliability Estimation of Inverse Weibull Distribution Based on Intuitionistic Fuzzy Lifetime Data
by
and
Axioms 2023, 12(9), 838; https://doi.org/10.3390/axioms12090838 - 29 Aug 2023
Abstract
As a commonly used model in reliability analysis, the inverse Weibull distribution (IWD) is widely applied in various scientific fields. This paper considers the reliability estimation of the IWD based on intuitionistic fuzzy lifetime data. Firstly, the related concepts of the fuzzy set
[...] Read more.
As a commonly used model in reliability analysis, the inverse Weibull distribution (IWD) is widely applied in various scientific fields. This paper considers the reliability estimation of the IWD based on intuitionistic fuzzy lifetime data. Firstly, the related concepts of the fuzzy set theory are reviewed, and the concepts of the intuitionistic fuzzy conditional density, intuitionistic fuzzy likelihood function, and intuitionistic fuzzy conditional expectation are obtained by extension. In classical estimations, the maximum likelihood estimators of parameters and reliability are derived. Due to the nonlinearity, the EM algorithm is used to obtain the maximum likelihood estimates. In the Bayesian estimation, the gamma prior is selected, and the Bayesian estimation of the parameters and reliability is conducted under the symmetric entropy and the scale square error loss function, respectively. Since the integrals are complicated, the Lindley approximation is used to approximate the Bayesian estimates. Then, the performance of these estimators is evaluated by the Monte Carlo simulation. The simulation results show that the Bayesian estimation is more suitable than the maximum likelihood estimation for the reliability estimation. Finally, a set of real data is used to prove the effectiveness of these proposed methods. Through these methods, the reliability of the intuitive fuzzy life data is accurately estimated, which provides an important reference for the reliability analysis in the scientific field.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Mathematical Methods in the Applied Sciences)
►▼
Show Figures
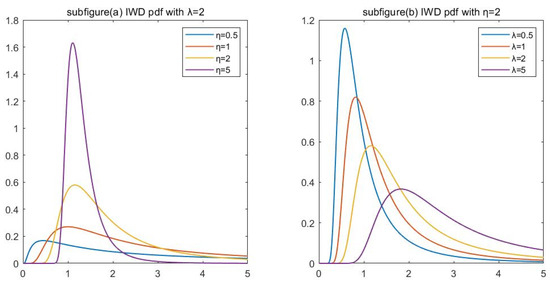
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
On the Geometry of the Riemannian Curvature Tensor of Nearly Trans-Sasakian Manifolds
Axioms 2023, 12(9), 837; https://doi.org/10.3390/axioms12090837 - 29 Aug 2023
Abstract
This paper presents the results of fundamental research into the geometry of the Riemannian curvature tensor of nearly trans-Sasakian manifolds. The components of the Riemannian curvature tensor on the space of the associated G-structure are counted, and the components of the Ricci tensor
[...] Read more.
This paper presents the results of fundamental research into the geometry of the Riemannian curvature tensor of nearly trans-Sasakian manifolds. The components of the Riemannian curvature tensor on the space of the associated G-structure are counted, and the components of the Ricci tensor are calculated. Some identities are obtained that are satisfied by the Riemannian curvature tensors and the Ricci tensor. A number of properties are proved that characterize nearly trans-Sasakian manifolds with a closed contact form. The structure of nearly trans-Sasakian manifolds with a closed contact form is obtained. Several classes are singled out in terms of second-order differential-geometric invariants, and their local structure is obtained. The k-nullity distribution of a nearly trans-Sasakian manifold is studied.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Mathematical Analysis in Application to Solving Mathematical and Technical Problems)
Open AccessArticle
Nonlinear Differential Equations of Flow Motion Considering Resistance Forces
Axioms 2023, 12(9), 836; https://doi.org/10.3390/axioms12090836 - 29 Aug 2023
Abstract
For a stationary potential 2D planar open high-velocity water flow of the ideal liquid, we propose a closed system of nonlinear equations considering the resistance forces to the flow from the channel bottom. Tangential stresses on jet interfaces are ignored. The resistance force
[...] Read more.
For a stationary potential 2D planar open high-velocity water flow of the ideal liquid, we propose a closed system of nonlinear equations considering the resistance forces to the flow from the channel bottom. Tangential stresses on jet interfaces are ignored. The resistance force components are expressed in terms of velocity components. In this case, the flow equations can be solved through the method of characteristics, and the surface forces are reduced to equivalent volumetric forces. The system of non-linear equations is solved in the velocity hodograph plane; further, the transition to the physical plane takes place. Since the value of the hydrodynamic pressure decreases downstream of the flow, the friction forces to the flow in the first approximation can be considered by using the integral laws of resistance. At that, the form of the equations of motion in the plane of the velocity hodograph does not change. This fact is proved in the article. An example of calculating the water flow is provided. The kinecity, ordinates, and velocities of the flow along its extreme line are calculated without considering resistance forces. Validation of the model in the real flow is performed. Acceptable accuracy relative to experimental data is obtained.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Mathematical Analysis in Application to Solving Mathematical and Technical Problems)
Open AccessArticle
Forecasting the S&P 500 Index Using Mathematical-Based Sentiment Analysis and Deep Learning Models: A FinBERT Transformer Model and LSTM
Axioms 2023, 12(9), 835; https://doi.org/10.3390/axioms12090835 - 29 Aug 2023
Abstract
Stock price prediction has been a subject of significant interest in the financial mathematics field. Recently, interest in natural language processing models has increased, and among them, transformer models, such as BERT and FinBERT, are attracting attention. This study uses a mathematical framework
[...] Read more.
Stock price prediction has been a subject of significant interest in the financial mathematics field. Recently, interest in natural language processing models has increased, and among them, transformer models, such as BERT and FinBERT, are attracting attention. This study uses a mathematical framework to investigate the effects of human sentiment on stock movements, especially in text data. In particular, FinBERT, a domain-specific language model based on BERT tailored for financial language, was employed for the sentiment analysis on the financial texts to extract sentiment information. In this study, we use “summary” text data extracted from The New York Times, representing concise summaries of news articles. Accordingly, we apply FinBERT to the summary text data to calculate sentiment scores. In addition, we employ the LSTM (Long short-term memory) methodology, one of the machine learning models, for stock price prediction using sentiment scores. Furthermore, the LSTM model was trained by stock price data and the estimated sentiment scores. We compared the predictive power of LSTM models with and without sentiment analysis based on error measures such as MSE, RMSE, and MAE. The empirical results demonstrated that including sentiment scores through the LSTM model led to improved prediction accuracy for all three measures. These findings indicate the significance of incorporating news sentiment into stock price predictions, shedding light on the potential impact of psychological factors on financial markets. By using the FinBERT transformer model, this study aimed to investigate the interplay between sentiment and stock price predictions, contributing to a deeper understanding of mathematical-based sentiment analysis in finance and its role in enhancing forecasting in financial mathematics. Furthermore, we show that using summary data instead of entire news articles is a useful strategy for mathematical-based sentiment analysis.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Mathematical and Computational Finance Analysis)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Enhancing Dynamic Parameter Adaptation in the Bird Swarm Algorithm Using General Type-2 Fuzzy Analysis and Mathematical Functions
by
and
Axioms 2023, 12(9), 834; https://doi.org/10.3390/axioms12090834 - 29 Aug 2023
Abstract
The pursuit of continuous improvement across diverse processes presents a pressing challenge. Precision in manufacturing, efficient delivery route planning, and accurate diagnostics are imperative, prompting the exploration of innovative solutions. Nature-inspired algorithms offer a pathway for enhancing these processes. In this study, we
[...] Read more.
The pursuit of continuous improvement across diverse processes presents a pressing challenge. Precision in manufacturing, efficient delivery route planning, and accurate diagnostics are imperative, prompting the exploration of innovative solutions. Nature-inspired algorithms offer a pathway for enhancing these processes. In this study, we address this challenge by dynamically adapting parameters in the Bird Swarm Algorithm using General Type-2 Fuzzy Systems, encompassing a range of rules and membership functions. Two complex case studies validate the effectiveness of our approach. The first evaluates Congress of Evolutionary Competition 2017 functions, while the second tackles the intricacies of Congress of Evolutionary Competition 2019 functions. Our methodology achieves an 97% improvement for Congress of Evolutionary Competition 2017 functions and a significant 70% enhancement for Congress of Evolutionary Competition 2019 functions. Notably, our results are benchmarked against the original method. Crucially, rigorous statistical analysis underscores the significant advancements facilitated by our proposed method. The comparison demonstrates clear and statistically significant improvements over the original approach. This study proves the marked impact of integrating General Type-2 Fuzzy Systems into the Bird Swarm Algorithm, presenting a promising avenue for addressing intricate optimization challenges in diverse domains.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Imprecision to Insights: Theoretical Advances in Fuzzy Uncertainty Modeling and Their Applications in New Frontiers)
►▼
Show Figures
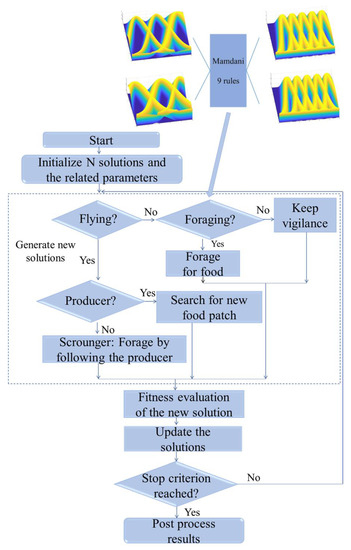
Figure 1

Journal Menu
► ▼ Journal Menu-
- Axioms Home
- Aims & Scope
- Editorial Board
- Reviewer Board
- Topical Advisory Panel
- Instructions for Authors
- Special Issues
- Topics
- Sections & Collections
- Article Processing Charge
- Indexing & Archiving
- Editor’s Choice Articles
- Most Cited & Viewed
- Journal Statistics
- Journal History
- Journal Awards
- Society Collaborations
- Conferences
- Editorial Office
Journal Browser
► ▼ Journal BrowserHighly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Algorithms, Axioms, Fractal Fract, Mathematics, Symmetry
Approximation Theory in Computer and Computational Sciences
Topic Editors: Faruk Özger, Asif Khan, Syed Abdul Mohiuddine, Zeynep Ödemiş ÖzgerDeadline: 20 September 2023
Topic in
Axioms, Computation, Dynamics, Mathematics, Symmetry
Structural Stability and Dynamics: Theory and Applications
Topic Editors: Harekrushna Behera, Chia-Cheng Tsai, Jen-Yi ChangDeadline: 30 September 2023
Topic in
Entropy, Fractal Fract, Dynamics, Mathematics, Computation, Axioms
Advances in Nonlinear Dynamics: Methods and Applications
Topic Editors: Ravi P. Agarwal, Maria Alessandra RagusaDeadline: 20 November 2023
Topic in
Algorithms, Axioms, Information, Mathematics, Symmetry
Fuzzy Number, Fuzzy Difference, Fuzzy Differential: Theory and Applications
Topic Editors: Changyou Wang, Dong Qiu, Yonghong ShenDeadline: 20 December 2023

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
Axioms
Advances in Mathematical Methods in Signal Processing and Its Applications
Guest Editor: Dobrea Dan-MariusDeadline: 20 September 2023
Special Issue in
Axioms
Advanced Approximation Techniques and Their Applications
Guest Editors: Roman Dmytryshyn, Tuncer AcarDeadline: 30 September 2023
Special Issue in
Axioms
Recent Advances in Complex Analysis and Applications
Guest Editor: Miodrag MateljevicDeadline: 20 October 2023
Special Issue in
Axioms
Optimization Algorithms and Applications
Guest Editor: Nodari VakhaniaDeadline: 31 October 2023
Topical Collections
Topical Collection in
Axioms
Mathematical Analysis and Applications
Collection Editor: Hari Mohan Srivastava
Topical Collection in
Axioms
Differential Equations and Dynamical Systems
Collection Editor: Feliz Manuel Minhós