-
 Exerting Forces and Wall Load during Duodenoscopy for ERCP: An Experimental Measurement in an Artificial Model
Exerting Forces and Wall Load during Duodenoscopy for ERCP: An Experimental Measurement in an Artificial Model -
 Mesenchymal Stromal Cell Therapy in Lung Transplantation
Mesenchymal Stromal Cell Therapy in Lung Transplantation -
 Using Micro-Electrode-Array Recordings and Retinal Disease Models to Elucidate Visual Functions: Simultaneous Recording of Local Electroretinograms and Ganglion Cell Action Potentials Reveals the Origin of Retinal Oscillatory Potentials
Using Micro-Electrode-Array Recordings and Retinal Disease Models to Elucidate Visual Functions: Simultaneous Recording of Local Electroretinograms and Ganglion Cell Action Potentials Reveals the Origin of Retinal Oscillatory Potentials -
 Orthotopic Ferret Tracheal Transplantation Using a Recellularized Bioengineered Graft Produces Functional Epithelia
Orthotopic Ferret Tracheal Transplantation Using a Recellularized Bioengineered Graft Produces Functional Epithelia -
 Synthetic Inflammation Imaging with PatchGAN Deep Learning Networks
Synthetic Inflammation Imaging with PatchGAN Deep Learning Networks
Journal Description
Bioengineering
Bioengineering
is an international, scientific, peer-reviewed, open access journal on the science and technology of bioengineering, published monthly online by MDPI. The Society for Regenerative Medicine (Russian Federation) (RPO) is affiliated with Bioengineering and its members receive discounts on the article processing charges.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within Scopus, SCIE (Web of Science), PubMed, PMC, CAPlus / SciFinder, Inspec, and other databases.
- Journal Rank: JCR - Q2 (Engineering, Biomedical)
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 15.6 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 3.5 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the first half of 2023).
- Recognition of Reviewers: reviewers who provide timely, thorough peer-review reports receive vouchers entitling them to a discount on the APC of their next publication in any MDPI journal, in appreciation of the work done.
Impact Factor:
4.6 (2022)
Latest Articles
Production of Astaxanthin Using CBFD1/HFBD1 from Adonis aestivalis and the Isopentenol Utilization Pathway in Escherichia coli
Bioengineering 2023, 10(9), 1033; https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10091033 (registering DOI) - 01 Sep 2023
Abstract
Astaxanthin is a powerful antioxidant and is used extensively as an animal feed additive and nutraceutical product. Here, we report the use of the β-carotene hydroxylase (CBFD1) and the β-carotene ketolase (HBFD1) from Adonis aestivalis, a flowering plant, to produce astaxanthin in
[...] Read more.
Astaxanthin is a powerful antioxidant and is used extensively as an animal feed additive and nutraceutical product. Here, we report the use of the β-carotene hydroxylase (CBFD1) and the β-carotene ketolase (HBFD1) from Adonis aestivalis, a flowering plant, to produce astaxanthin in E. coli equipped with the P. agglomerans β-carotene pathway and an over-expressed 4-methylerythritol-phosphate (MEP) pathway or the isopentenol utilization pathway (IUP). Introduction of the over-expressed MEP pathway and the IUP resulted in a 3.2-fold higher carotenoid content in LB media at 36 h post-induction compared to the strain containing only the endogenous MEP. However, in M9 minimal media, the IUP pathway dramatically outperformed the over-expressed MEP pathway with an 11-fold increase in total carotenoids produced. The final construct split the large operon into two smaller operons, both with a T7 promoter. This resulted in slightly lower productivity (70.0 ± 8.1 µg/g·h vs. 53.5 ± 3.8 µg/g·h) compared to the original constructs but resulted in the highest proportion of astaxanthin in the extracted carotenoids (73.5 ± 0.2%).
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Advances in Microbial Biosynthesis of Plant Natural Products)
►
Show Figures
Open AccessBrief Report
FD-2, an Anticervical Stenosis Device for Patients Undergoing Radical Trachelectomy or Cervical Conization
Bioengineering 2023, 10(9), 1032; https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10091032 (registering DOI) - 01 Sep 2023
Abstract
This study aimed to introduce FD-2, a newly developed anticervical stenosis device for patients with cervical cancer undergoing radical trachelectomy. Using ethylene-vinyl acetate copolymers, we developed FD-2 to prevent uterine cervical stenosis after radical trachelectomy. The tensile test and extractables and leachables testing
[...] Read more.
This study aimed to introduce FD-2, a newly developed anticervical stenosis device for patients with cervical cancer undergoing radical trachelectomy. Using ethylene-vinyl acetate copolymers, we developed FD-2 to prevent uterine cervical stenosis after radical trachelectomy. The tensile test and extractables and leachables testing were performed to evaluate FD-2’s safety as a medical device. FD-2 was indwelled in three patients with cervical cancer during radical trachelectomy and its utility was preliminarily evaluated. FD-2 consists of a head (fish-born-like structure), neck (connecting bridges), and body (tubular structure); the head is identical to FD-1, an intrauterine contraceptive device. FD-2 passed the tensile test and extractables and leachables testing. The average time required for the application or removal of FD-2 in cervical cancer patients was less than 10 s. The median duration of FD-2 indwelling was 8 weeks. No complications, including abdominal pain, pelvic infections, or hemorrhages, associated with FD-2 indwelling were reported. At the 3–12-month follow-up after the radical trachelectomy, no patients developed cervical stenosis or experienced dysmenorrhea. In conclusion, we developed FD-2, a novel device that can be used for preventing cervical stenosis after radical trachelectomy for uterine cervical cancer.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Bioengineering Approaches for the Treatment of Cancer)
►▼
Show Figures
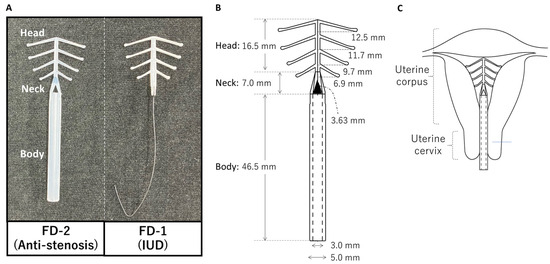
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
New Approach for Generating Synthetic Medical Data to Predict Type 2 Diabetes
by
, , , , and
Bioengineering 2023, 10(9), 1031; https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10091031 (registering DOI) - 01 Sep 2023
Abstract
The lack of medical databases is currently the main barrier to the development of artificial intelligence-based algorithms in medicine. This issue can be partially resolved by developing a reliable high-quality synthetic database. In this study, an easy and reliable method for developing a
[...] Read more.
The lack of medical databases is currently the main barrier to the development of artificial intelligence-based algorithms in medicine. This issue can be partially resolved by developing a reliable high-quality synthetic database. In this study, an easy and reliable method for developing a synthetic medical database based only on statistical data is proposed. This method changes the primary database developed based on statistical data using a special shuffle algorithm to achieve a satisfactory result and evaluates the resulting dataset using a neural network. Using the proposed method, a database was developed to predict the risk of developing type 2 diabetes 5 years in advance. This dataset consisted of data from 172,290 patients. The prediction accuracy reached 94.45% during neural network training of the dataset.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Machine Learning Technology in Biomedical Engineering)
►▼
Show Figures
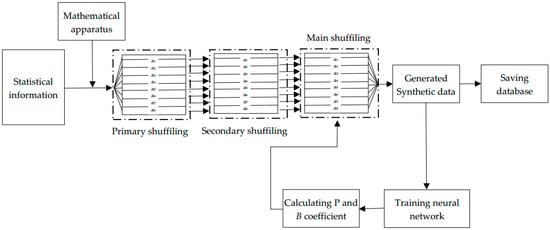
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
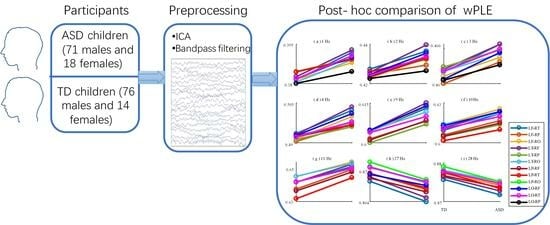
EEG Connectivity Diversity Differences between Children with Autism and Typically Developing Children: A Comparative Study
Bioengineering 2023, 10(9), 1030; https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10091030 (registering DOI) - 01 Sep 2023
Abstract
Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) is a neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by deficits in social interaction and communication, and repetitive or stereotyped behaviors. Previous studies have reported altered brain connectivity in ASD children compared to typically developing children. In this study, we investigated the diversity
[...] Read more.
Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) is a neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by deficits in social interaction and communication, and repetitive or stereotyped behaviors. Previous studies have reported altered brain connectivity in ASD children compared to typically developing children. In this study, we investigated the diversity of connectivity patterns between children with ASD and typically developing children using phase lag entropy (PLE), a measure of the variability of phase differences between two time series. We also developed a novel wavelet-based PLE method for the calculation of PLE at specific scales. Our findings indicated that the diversity of connectivity in ASD children was higher than that in typically developing children at Delta and Alpha frequency bands, both within brain regions and across hemispheric brain regions. These findings provide insight into the underlying neural mechanisms of ASD and suggest that PLE may be a useful tool for investigating brain connectivity in ASD.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Monitoring and Analysis of Human Biosignals)
►▼
Show Figures
Graphical abstract
Open AccessReview
Effects of tDCS on Foot Biomechanics: A Narrative Review and Clinical Applications
Bioengineering 2023, 10(9), 1029; https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10091029 - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
In recent years, neuro-biomechanical enhancement techniques, such as transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS), have been widely used to improve human physical performance, including foot biomechanical characteristics. This review aims to summarize research on the effects of tDCS on foot biomechanics and its clinical
[...] Read more.
In recent years, neuro-biomechanical enhancement techniques, such as transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS), have been widely used to improve human physical performance, including foot biomechanical characteristics. This review aims to summarize research on the effects of tDCS on foot biomechanics and its clinical applications, and further analyze the underlying ergogenic mechanisms of tDCS. This review was performed for relevant papers until July 2023 in the following databases: Web of Science, PubMed, and EBSCO. The findings demonstrated that tDCS can improve foot biomechanical characteristics in healthy adults, including proprioception, muscle strength, reaction time, and joint range of motion. Additionally, tDCS can be effectively applied in the field of foot sports medicine; in particular, it can be combined with functional training to effectively improve foot biomechanical performance in individuals with chronic ankle instability (CAI). The possible mechanism is that tDCS may excite specific task-related neurons and regulate multiple neurons within the system, ultimately affecting foot biomechanical characteristics. However, the efficacy of tDCS applied to rehabilitate common musculoskeletal injuries (e.g., CAI and plantar fasciitis) still needs to be confirmed using a larger sample size. Future research should use multimodal neuroimaging technology to explore the intrinsic ergogenic mechanism of tDCS.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Biomechanics, Health, Disease and Rehabilitation)
Open AccessArticle
Continuous Motion Estimation of Knee Joint Based on a Parameter Self-Updating Mechanism Model
Bioengineering 2023, 10(9), 1028; https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10091028 - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
Estimation of continuous motion of human joints using surface electromyography (sEMG) signals has a critical part to play in intelligent rehabilitation. Traditional methods always use sEMG signals as inputs to build regression or biomechanical models to estimate continuous joint motion variables. However, it
[...] Read more.
Estimation of continuous motion of human joints using surface electromyography (sEMG) signals has a critical part to play in intelligent rehabilitation. Traditional methods always use sEMG signals as inputs to build regression or biomechanical models to estimate continuous joint motion variables. However, it is challenging to accurately estimate continuous joint motion in new subjects due to the non-stationarity and individual differences in sEMG signals, which greatly limits the generalisability of the method. In this paper, a continuous motion estimation model for the human knee joint with a parameter self-updating mechanism based on the fusion of particle swarm optimization (PSO) and deep belief network (DBN) is proposed. According to the original sEMG signals of different subjects, the method adaptively optimized the parameters of the DBN model and completed the optimal reconstruction of signal feature structure in high-dimensional space to achieve the optimal estimation of continuous joint motion. Extensive experiments were conducted on knee joint motions. The results suggested that the average root mean square errors (RMSEs) of the proposed method were 9.42° and 7.36°, respectively, which was better than the results obtained by common neural networks. This finding lays a foundation for the human–robot interaction (HRI) of the exoskeleton robots based on the sEMG signals.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Monitoring and Analysis of Human Biosignals)
►▼
Show Figures
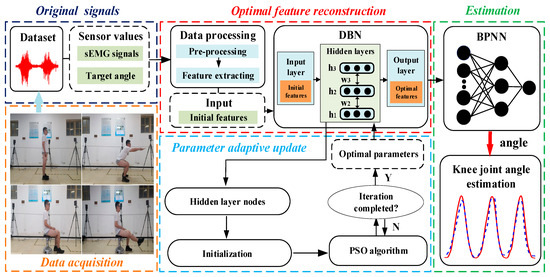
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Research on Mental Workload of Deep-Sea Oceanauts Driving Operation Tasks from EEG Data
Bioengineering 2023, 10(9), 1027; https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10091027 - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
A person’s present mental state is closely associated with the frequency and temporal domain features of spontaneous electroencephalogram (EEG) impulses, which directly reflect neurophysiological signals of brain activity. EEG signals are employed in this study to measure the mental workload of drivers while
[...] Read more.
A person’s present mental state is closely associated with the frequency and temporal domain features of spontaneous electroencephalogram (EEG) impulses, which directly reflect neurophysiological signals of brain activity. EEG signals are employed in this study to measure the mental workload of drivers while they are operating a vehicle. A technique based on the quantum genetic algorithm (QGA) is suggested for improving the kernel function parameters of the multi-class support vector machine (MSVM). The performance of the algorithm based on the quantum genetic algorithm is found to be superior to that of other ways when other methods and the quantum genetic algorithm are evaluated for the parameter optimization of kernel function via simulation. A multi-classification support vector machine based on the quantum genetic algorithm (QGA-MSVM) is applied to identify the mental workload of oceanauts through the collection and feature extraction of EEG signals during driving simulation operation experiments in a sea basin area, a seamount area, and a hydrothermal area. Even with a limited data set, QGA-MSVM is able to accurately identify the cognitive burden experienced by ocean sailors, with an overall accuracy of 91.8%.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Advances of Artificial Intelligence for Sustainable Engineering and Medical Applications: Machine Learning and Optimization)
►▼
Show Figures
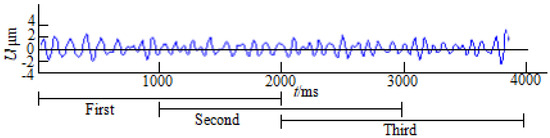
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Multitask Attention-Based Neural Network for Intraoperative Hypotension Prediction
Bioengineering 2023, 10(9), 1026; https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10091026 - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
Timely detection and response to Intraoperative Hypotension (IOH) during surgery is crucial to avoid severe postoperative complications. Although several methods have been proposed to predict IOH using machine learning, their performance still has space for improvement. In this paper, we propose a ResNet-BiLSTM
[...] Read more.
Timely detection and response to Intraoperative Hypotension (IOH) during surgery is crucial to avoid severe postoperative complications. Although several methods have been proposed to predict IOH using machine learning, their performance still has space for improvement. In this paper, we propose a ResNet-BiLSTM model based on multitask training and attention mechanism for IOH prediction. We trained and tested our proposed model using bio-signal waveforms obtained from patient monitoring of non-cardiac surgery. We selected three models (WaveNet, CNN, and TCN) that process time-series data for comparison. The experimental results demonstrate that our proposed model has optimal MSE (43.83) and accuracy (0.9224) compared to other models, including WaveNet (51.52, 0.9087), CNN (318.52, 0.5861), and TCN (62.31, 0.9045), which suggests that our proposed model has better regression and classification performance. We conducted ablation experiments on the multitask and attention mechanisms, and the experimental results demonstrated that the multitask and attention mechanisms improved MSE and accuracy. The results demonstrate the effectiveness and superiority of our proposed model in predicting IOH.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Monitoring and Analysis of Human Biosignals, Volume II)
►▼
Show Figures
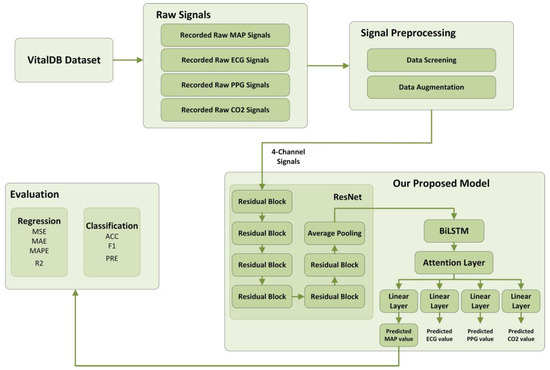
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Development of a New Wearable Device for the Characterization of Hand Tremor
by
, , , , , , and
Bioengineering 2023, 10(9), 1025; https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10091025 - 30 Aug 2023
Abstract
Rest tremor (RT) is observed in subjects with Parkinson’s disease (PD) and Essential Tremor (ET). Electromyography (EMG) studies have shown that PD subjects exhibit alternating contractions of antagonistic muscles involved in tremors, while the contraction pattern of antagonistic muscles is synchronous in ET
[...] Read more.
Rest tremor (RT) is observed in subjects with Parkinson’s disease (PD) and Essential Tremor (ET). Electromyography (EMG) studies have shown that PD subjects exhibit alternating contractions of antagonistic muscles involved in tremors, while the contraction pattern of antagonistic muscles is synchronous in ET subjects. Therefore, the RT pattern can be used as a potential biomarker for differentiating PD from ET subjects. In this study, we developed a new wearable device and method for differentiating alternating from a synchronous RT pattern using inertial data. The novelty of our approach relies on the fact that the evaluation of synchronous or alternating tremor patterns using inertial sensors has never been described so far, and current approaches to evaluate the tremor patterns are based on surface EMG, which may be difficult to carry out for non-specialized operators. This new device, named “RT-Ring”, is based on a six-axis inertial measurement unit and a Bluetooth Low-Energy microprocessor, and can be worn on a finger of the tremulous hand. A mobile app guides the operator through the whole acquisition process of inertial data from the hand with RT, and the prediction of tremor patterns is performed on a remote server through machine learning (ML) models. We used two decision tree-based algorithms, XGBoost and Random Forest, which were trained on features extracted from inertial data and achieved a classification accuracy of 92% and 89%, respectively, in differentiating alternating from synchronous tremor segments in the validation set. Finally, the classification response (alternating or synchronous RT pattern) is shown to the operator on the mobile app within a few seconds. This study is the first to demonstrate that different electromyographic tremor patterns have their counterparts in terms of rhythmic movement features, thus making inertial data suitable for predicting the muscular contraction pattern of tremors.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic Machine Learning and Biomedical Sensors)
►▼
Show Figures
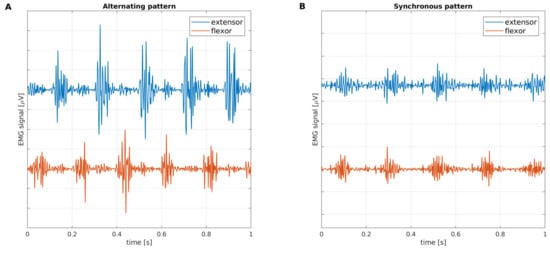
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Predicting Respiratory Rate from Electrocardiogram and Photoplethysmogram Using a Transformer-Based Model
Bioengineering 2023, 10(9), 1024; https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10091024 - 30 Aug 2023
Abstract
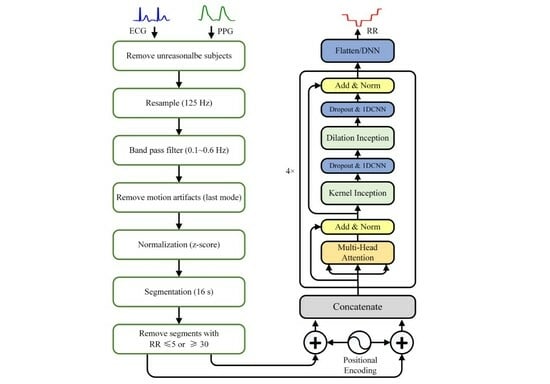
The respiratory rate (RR) serves as a critical physiological parameter in the context of both diagnostic and prognostic evaluations. Due to the challenges of direct measurement, RR is still predominantly measured through the traditional manual counting-breaths method in clinic practice. Numerous algorithms and
[...] Read more.
The respiratory rate (RR) serves as a critical physiological parameter in the context of both diagnostic and prognostic evaluations. Due to the challenges of direct measurement, RR is still predominantly measured through the traditional manual counting-breaths method in clinic practice. Numerous algorithms and machine learning models have been developed to predict RR using physiological signals, such as electrocardiogram (ECG) or/and photoplethysmogram (PPG) signals. Yet, the accuracy of these existing methods on available datasets remains limited, and their prediction on new data is also unsatisfactory for actual clinical applications. In this paper, we proposed an enhanced Transformer model with inception blocks for predicting RR based on both ECG and PPG signals. To evaluate the generalization capability on new data, our model was trained and tested using subject-level ten-fold cross-validation using data from both BIDMC and CapnoBase datasets. On the test set, our model achieved superior performance over five popular deep-learning-based methods with mean absolute error (1.2) decreased by 36.5% and correlation coefficient (0.85) increased by 84.8% compared to the best results of these models. In addition, we also proposed a new pipeline to preprocess ECG and PPG signals to improve model performance. We believe that the development of the TransRR model is expected to further expedite the clinical implementation of automatic RR estimation.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Artificial Intelligence for Biomedical Signal Processing)
►▼
Show Figures
Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
The Use of a CAD/CAM Thermoformed Splints System in Closed Reduction of Condylar Fractures
by
, , , , and
Bioengineering 2023, 10(9), 1023; https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10091023 - 29 Aug 2023
Abstract
(1) Background: Mandibular fractures are very common. Common indications of closed treatment for mandibular fractures are non-displaced or minimally displaced simple fractures in adult compliant patients with good dentition, the absence of occlusal disruption, and fractures in growing children. In closed treatment, the
[...] Read more.
(1) Background: Mandibular fractures are very common. Common indications of closed treatment for mandibular fractures are non-displaced or minimally displaced simple fractures in adult compliant patients with good dentition, the absence of occlusal disruption, and fractures in growing children. In closed treatment, the mandible is maintained in centric occlusion with a maxillomandibular fixation (MMF) with orthodontic elastics. Many methods of MMF have been described, often using orthodontic appliances. In recent years, CAD-CAM technology has improved many procedures used in maxillofacial surgery and orthodontics. The device we present is manufactured following a digital workflow, and was designed specifically for MMF. (2) Materials: Two patients with mandibular fractures were treated with an MMF method whose procedure comprised scanning of the dental arches, followed by construction of thermoformed splints on which buttons for the elastics and retention holes are made. The splints were fixed on the dental arches with composite resin at the level of the holes, and were kept in place for the period of healing of the fracture, with the intermaxillary elastics hooked to the buttons. (3) Results: The application time of the splints was very quick. The splints remained stable for the necessary time, without causing particular discomfort to the patients. (4) Conclusions: From our experience, this technique has proved to be reliable and reproducible and could represent a valid tool in the closed treatment of mandibular fractures.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Recent Advances in the Treatment of Dental Diseases)
►▼
Show Figures
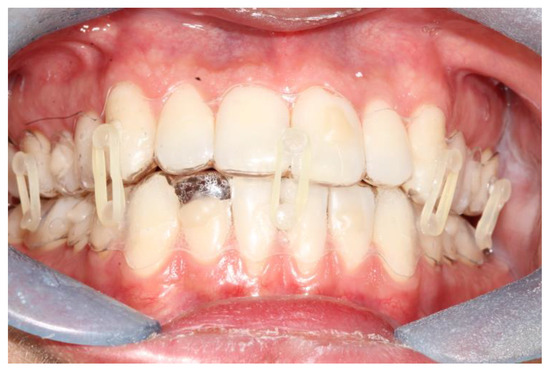
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Technical Evaluation of a New Medical Device Based on Rigenase in the Treatment of Chronic Skin Lesions
by
, , , , , and
Bioengineering 2023, 10(9), 1022; https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10091022 - 29 Aug 2023
Abstract
Chronic wound is characterized by slow healing time, persistence, and abnormal healing progress. Therefore, serious complications can lead at worst to the tissue removal. In this scenario, there is an urgent need for an ideal dressing capable of high absorbency, moisture retention and
[...] Read more.
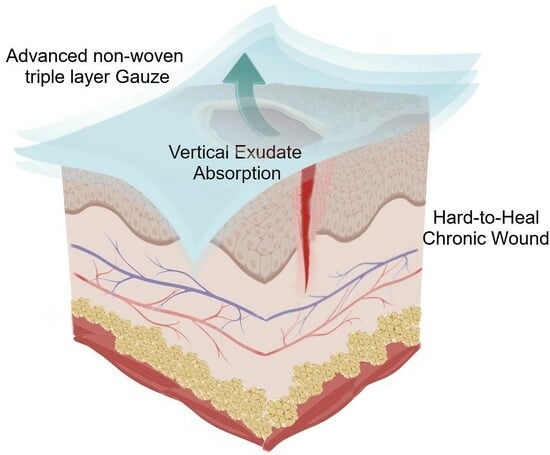
Chronic wound is characterized by slow healing time, persistence, and abnormal healing progress. Therefore, serious complications can lead at worst to the tissue removal. In this scenario, there is an urgent need for an ideal dressing capable of high absorbency, moisture retention and antimicrobial properties. Herein we investigate the technical properties of a novel advanced non-woven triple layer gauze imbibed with a cream containing Rigenase, an aqueous extract of Triticum vulgare used for the treatment of skin injuries. To assess the applicability of this system we analyzed the dressing properties by wettability, dehydration, absorbency, Water Vapor Transmission Rate (WVTR), lateral diffusion and microbiological tests. The dressing showed an exudate absorption up to 50%. It created a most environment allowing a proper gaseous exchange as attested by the WVTR and a controlled dehydration rate. The results candidate the new dressing as an ideal medical device for the treatment of the chronic wound repairing process. It acts as a mechanical barrier providing a good management of the bacterial load and proper absorption of abundant wound exudate. Finally, its vertical transmission minimizes horizontal diffusion and side effects on perilesional skin as maceration and bacterial infection.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Biomaterials for Chronic Wound Healing)
►▼
Show Figures
Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Intelligent Grapevine Disease Detection Using IoT Sensor Network
by
, , , , , , and
Bioengineering 2023, 10(9), 1021; https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10091021 - 29 Aug 2023
Abstract
The Internet of Things (IoT) has gained significance in agriculture, using remote sensing and machine learning to help farmers make high-precision management decisions. This technology can be applied in viticulture, making it possible to monitor disease occurrence and prevent them automatically. The study
[...] Read more.
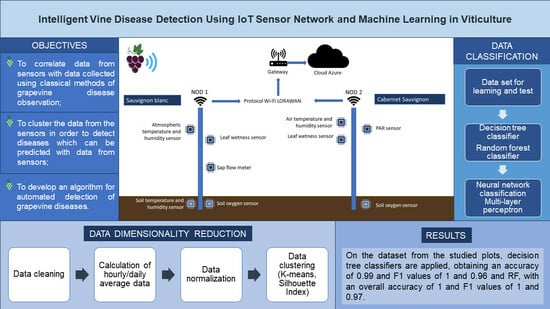
The Internet of Things (IoT) has gained significance in agriculture, using remote sensing and machine learning to help farmers make high-precision management decisions. This technology can be applied in viticulture, making it possible to monitor disease occurrence and prevent them automatically. The study aims to achieve an intelligent grapevine disease detection method, using an IoT sensor network that collects environmental and plant-related data. The focus of this study is the identification of the main parameters which provide early information regarding the grapevine’s health. An overview of the sensor network, architecture, and components is provided in this paper. The IoT sensors system is deployed in the experimental plots located within the plantations of the Research Station for Viticulture and Enology (SDV) in Murfatlar, Romania. Classical methods for disease identification are applied in the field as well, in order to compare them with the sensor data, thus improving the algorithm for grapevine disease identification. The data from the sensors are analyzed using Machine Learning (ML) algorithms and correlated with the results obtained using classical methods in order to identify and predict grapevine diseases. The results of the disease occurrence are presented along with the corresponding environmental parameters. The error of the classification system, which uses a feedforward neural network, is 0.05. This study will be continued with the results obtained from the IoT sensors tested in vineyards located in other regions.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue IoT Technology in Bioengineering Applications)
►▼
Show Figures
Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Self-Reporting Theranostic: Nano Tool for Arterial Thrombosis
by
, , , , , and
Bioengineering 2023, 10(9), 1020; https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10091020 - 29 Aug 2023
Abstract
Arterial thrombosis (AT) originates through platelet-mediated thrombus formation in the blood vessel and can lead to heart attack, stroke, and peripheral vascular diseases. Restricting the thrombus growth and its simultaneous monitoring by visualisation is an unmet clinical need for a better AT prognosis.
[...] Read more.
Arterial thrombosis (AT) originates through platelet-mediated thrombus formation in the blood vessel and can lead to heart attack, stroke, and peripheral vascular diseases. Restricting the thrombus growth and its simultaneous monitoring by visualisation is an unmet clinical need for a better AT prognosis. As a proof-of-concept, we have engineered a nanoparticle-based theranostic (combined therapy and monitoring) platform that has the potential to monitor and restrain the growth of a thrombus concurrently. The theranostic nanotool is fabricated using biocompatible super-paramagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (SPIONs) as a core module tethered with the anti-platelet agent Abciximab (ReoPro) on its surface. Our in vitro feasibility results indicate that ReoPro-conjugated SPIONS (Tx@ReoPro) can effectively prevent thrombus growth by inhibiting fibrinogen receptors (GPIIbIIIa) on the platelet surface, and simultaneously, it can also be visible through non-invasive magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) for potential reporting of the real-time thrombus status.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Biosynthesis of Nanoparticle/Exosome/ECV/Microparticles)
►▼
Show Figures
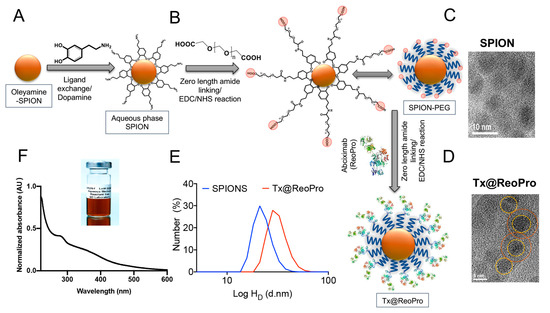
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Functionalized 3D-Printed PLA Biomimetic Scaffold for Repairing Critical-Size Bone Defects
by
, , , , , , , and
Bioengineering 2023, 10(9), 1019; https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10091019 - 29 Aug 2023
Abstract
The treatment of critical-size bone defects remains a complicated clinical challenge. Recently, bone tissue engineering has emerged as a potential therapeutic approach for defect repair. This study examined the biocompatibility and repair efficacy of hydroxyapatite-mineralized bionic polylactic acid (PLA) scaffolds, which were prepared
[...] Read more.
The treatment of critical-size bone defects remains a complicated clinical challenge. Recently, bone tissue engineering has emerged as a potential therapeutic approach for defect repair. This study examined the biocompatibility and repair efficacy of hydroxyapatite-mineralized bionic polylactic acid (PLA) scaffolds, which were prepared through a combination of 3D printing technology, plasma modification, collagen coating, and hydroxyapatite mineralization coating techniques. Physicochemical analysis, mechanical testing, and in vitro and animal experiments were conducted to elucidate the impact of structural design and microenvironment on osteogenesis. Results indicated that the PLA scaffold exhibited a porosity of 84.1% and a pore size of 350 μm, and its macrostructure was maintained following functionalization modification. The functionalized scaffold demonstrated favorable hydrophilicity and biocompatibility and promoted cell adhesion, proliferation, and the expression of osteogenic genes such as ALP, OPN, Col-1, OCN, and RUNX2. Moreover, the scaffold was able to effectively repair critical-size bone defects in the rabbit radius, suggesting a novel strategy for the treatment of critical-size bone defects.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Multiscale Mechanical Behavior of Biomaterials)
►▼
Show Figures
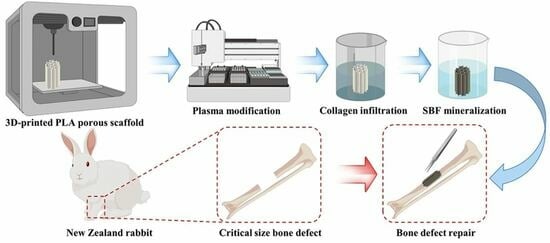
Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Comparison of Mid-Infrared Handheld and Benchtop Spectrometers to Detect Staphylococcus epidermidis in Bone Grafts
by
, , , , , , , , , , , and
Bioengineering 2023, 10(9), 1018; https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10091018 - 29 Aug 2023
Abstract
Bone analyses using mid-infrared spectroscopy are gaining popularity, especially with handheld spectrometers that enable on-site testing as long as the data quality meets standards. In order to diagnose Staphylococcus epidermidis in human bone grafts, this study was carried out to compare the effectiveness
[...] Read more.
Bone analyses using mid-infrared spectroscopy are gaining popularity, especially with handheld spectrometers that enable on-site testing as long as the data quality meets standards. In order to diagnose Staphylococcus epidermidis in human bone grafts, this study was carried out to compare the effectiveness of the Agilent 4300 Handheld Fourier-transform infrared with the Perkin Elmer Spectrum 100 attenuated-total-reflectance infrared spectroscopy benchtop instrument. The study analyzed 40 non-infected and 10 infected human bone samples with Staphylococcus epidermidis, collecting reflectance data between 650 cm−1 and 4000 cm−1, with a spectral resolution of 2 cm−1 (Agilent 4300 Handheld) and 0.5 cm−1 (Perkin Elmer Spectrum 100). The acquired spectral information was used for spectral and unsupervised classification, such as a principal component analysis. Both methods yielded significant results when using the recommended settings and data analysis strategies, detecting a loss in bone quality due to the infection. MIR spectroscopy provides a valuable diagnostic tool when there is a tissue shortage and time is of the essence. However, it is essential to conduct further research with larger sample sizes to verify its pros and cons thoroughly.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Applications of Computational Modeling in Biomedical Image and Signal Processing)
►▼
Show Figures
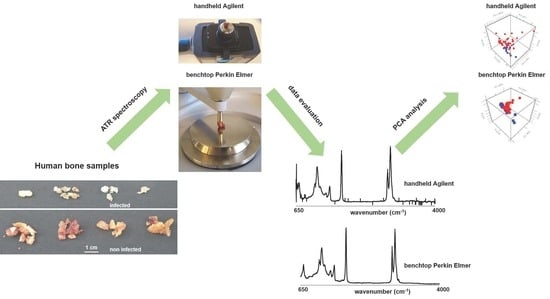
Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Waste Activated Sludge-High Rate (WASHR) Treatment Process: A Novel, Economically Viable, and Environmentally Sustainable Method to Co-Treat High-Strength Wastewaters at Municipal Wastewater Treatment Plants
Bioengineering 2023, 10(9), 1017; https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10091017 - 29 Aug 2023
Abstract
High-strength wastewaters from a variety of sources, including the food industry, domestic septage, and landfill leachate, are often hauled to municipal wastewater treatment plants (WWTPs) for co-treatment. Due to their high organic loadings, these wastewaters can cause process upsets in both a WWTP’s
[...] Read more.
High-strength wastewaters from a variety of sources, including the food industry, domestic septage, and landfill leachate, are often hauled to municipal wastewater treatment plants (WWTPs) for co-treatment. Due to their high organic loadings, these wastewaters can cause process upsets in both a WWTP’s liquid and solids treatment trains and consume organic treatment capacity, leaving less capacity available to service customers in the catchment area. A novel pre-treatment method, the Waste Activated Sludge-High Rate (WASHR) process, is proposed to optimize the co-treatment of high-strength wastewaters. The WASHR process combines the contact stabilization and sequencing batch reactor processes. It utilizes waste activated sludge from a municipal WWTP as its biomass source, allowing for a rapid start-up. Bench-scale treatment trials of winery wastewater confirm the WASHR process can reduce loadings on the downstream WWTP’s liquid and solids treatment trains. A case study approach is used to confirm the economic viability and environmental sustainability of the WASHR process compared to direct co-treatment, using life-cycle cost analyses and greenhouse gas emissions estimates.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Advanced Bioremediation Technologies and Processes)
►▼
Show Figures
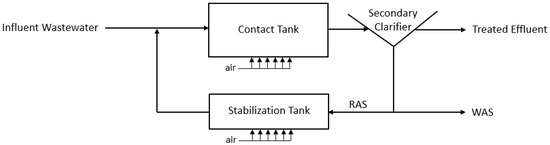
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
The Development of a Permanent Implantable Spacer with the Function of Size Adjustability for Customizing Treat Regurgitant Heart Valve Disease
by
, , , , , , , , , , and
Bioengineering 2023, 10(9), 1016; https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10091016 - 28 Aug 2023
Abstract
The Pivot Mandu is an innovative device featuring a leak-tight adjustable 3D balloon spacer, incorporating inner mesh support, an outer e-PTFE layer, and a compliant balloon in the middle layer with a specialized detachable system. To assess its feasibility, proof of concept was
[...] Read more.
The Pivot Mandu is an innovative device featuring a leak-tight adjustable 3D balloon spacer, incorporating inner mesh support, an outer e-PTFE layer, and a compliant balloon in the middle layer with a specialized detachable system. To assess its feasibility, proof of concept was rigorously evaluated through bench testing and survival porcine animal experiments. The results demonstrated successful remote inflation of the balloon system, with the balloon spacer exhibiting sustained patent and functional integrity over an extended observation period of up to 6 months. A noteworthy feature of the newly designed 3D balloon spacer is its capability for easy size adjustment during procedures, enhancing its adaptability and practicality in clinical settings. This three-layered 3D balloon spacer, with its established long-term patency, exhibits highly encouraging outcomes that hold promise in overcoming the current limitations of spacer devices for heart valve diseases. Given the compelling results from preclinical investigations, the translation of the Pivot Mandu into human trials is strongly warranted.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue New Devices and Preclinical Assessment for the Treatment of Mitral and Tricuspid Regurgitation)
►▼
Show Figures
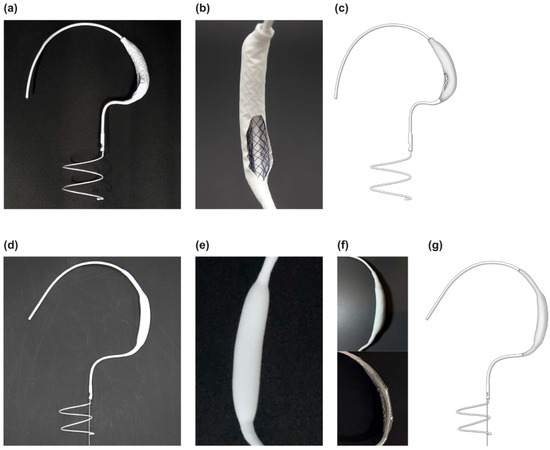
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
3D-Vision-Transformer Stacking Ensemble for Assessing Prostate Cancer Aggressiveness from T2w Images
by
and
Bioengineering 2023, 10(9), 1015; https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10091015 - 28 Aug 2023
Abstract
Vision transformers represent the cutting-edge topic in computer vision and are usually employed on two-dimensional data following a transfer learning approach. In this work, we propose a trained-from-scratch stacking ensemble of 3D-vision transformers to assess prostate cancer aggressiveness from T2-weighted images to help
[...] Read more.
Vision transformers represent the cutting-edge topic in computer vision and are usually employed on two-dimensional data following a transfer learning approach. In this work, we propose a trained-from-scratch stacking ensemble of 3D-vision transformers to assess prostate cancer aggressiveness from T2-weighted images to help radiologists diagnose this disease without performing a biopsy. We trained 18 3D-vision transformers on T2-weighted axial acquisitions and combined them into two- and three-model stacking ensembles. We defined two metrics for measuring model prediction confidence, and we trained all the ensemble combinations according to a five-fold cross-validation, evaluating their accuracy, confidence in predictions, and calibration. In addition, we optimized the 18 base ViTs and compared the best-performing base and ensemble models by re-training them on a 100-sample bootstrapped training set and evaluating each model on the hold-out test set. We compared the two distributions by calculating the median and the 95% confidence interval and performing a Wilcoxon signed-rank test. The best-performing 3D-vision-transformer stacking ensemble provided state-of-the-art results in terms of area under the receiving operating curve (0.89 [0.61–1]) and exceeded the area under the precision–recall curve of the base model of 22% (p < 0.001). However, it resulted to be less confident in classifying the positive class.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Clinical Diagnosis and Treatment Inspired by Artificial Intelligence)
►▼
Show Figures
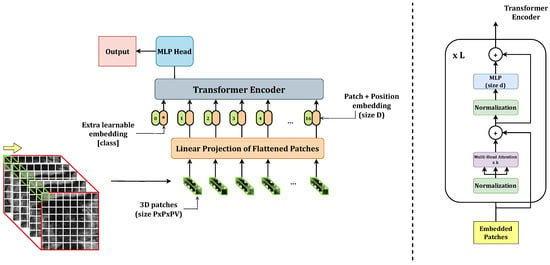
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Localized Refractive Changes Induced by Symmetric and Progressive Asymmetric Intracorneal Ring Segments Assessed with a 3D Finite-Element Model
Bioengineering 2023, 10(9), 1014; https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10091014 - 27 Aug 2023
Abstract
To build a representative 3D finite element model (FEM) for intracorneal ring segment (ICRS) implantation and to investigate localized optical changes induced by different ICRS geometries, a hyperelastic shell FEM was developed to compare the effect of symmetric and progressive asymmetric ICRS designs
[...] Read more.
To build a representative 3D finite element model (FEM) for intracorneal ring segment (ICRS) implantation and to investigate localized optical changes induced by different ICRS geometries, a hyperelastic shell FEM was developed to compare the effect of symmetric and progressive asymmetric ICRS designs in a generic healthy and asymmetric keratoconic (KC) cornea. The resulting deformed geometry was assessed in terms of average curvature via a biconic fit, sagittal curvature (K), and optical aberrations via Zernike polynomials. The sagittal curvature map showed a locally restricted flattening interior to the ring (Kmax −11 to −25 dpt) and, in the KC cornea, an additional local steepening on the opposite half of the cornea (Kmax up to +1.9 dpt). Considering the optical aberrations present in the model of the KC cornea, the progressive ICRS corrected vertical coma (−3.42 vs. −3.13 µm); horizontal coma (−0.67 vs. 0.36 µm); and defocus (2.90 vs. 2.75 µm), oblique trefoil (−0.54 vs. −0.08 µm), and oblique secondary astigmatism (0.48 vs. −0.09 µm) aberrations stronger than the symmetric ICRS. Customized ICRS designs inspired by the underlying KC phenotype have the potential to achieve more tailored refractive corrections, particularly in asymmetric keratoconus patterns.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Biomedical Imaging and Analysis of the Eye)
►▼
Show Figures
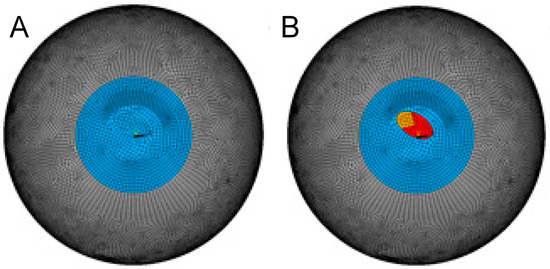
Figure 1

Journal Menu
► ▼ Journal Menu-
- Bioengineering Home
- Aims & Scope
- Editorial Board
- Reviewer Board
- Topical Advisory Panel
- Instructions for Authors
- Special Issues
- Topics
- Sections & Collections
- Article Processing Charge
- Indexing & Archiving
- Editor’s Choice Articles
- Most Cited & Viewed
- Journal Statistics
- Journal History
- Journal Awards
- Society Collaborations
- Conferences
- Editorial Office
Journal Browser
► ▼ Journal BrowserHighly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Applied Biosciences, Bioengineering, Biomolecules, JCDD, JCM, Micromachines, Reports
Usefulness and Clinical Applications of 3D Printing in Cardiovascular Diseases 2.0
Topic Editors: Zhonghua Sun, Massimo Chessa, Israel Valverde, Alexander Van De BruaeneDeadline: 31 October 2023
Topic in
Applied Biosciences, Bioengineering, Energies, Pollutants, Molecules
Sustainable Approaches for Biofuels from Waste Materials
Topic Editors: Md Sohrab Hossain, Venugopal BalakrishnanDeadline: 31 December 2023
Topic in
Energies, Processes, Bioengineering, ChemEngineering, Clean Technol.
Chemical and Biochemical Processes for Energy Sources
Topic Editors: Venko N. Beschkov, Konstantin PetrovDeadline: 31 January 2024
Topic in
Applied Sciences, Bioengineering, Electronics, Healthcare, JCM
Applied System on Biomedical Engineering, Healthcare and Sustainability 2023
Topic Editors: Teen-Hang Meen, Chun-Yen Chang, Charles Tijus, Po-Lei Lee, Kuei-Shu HsuDeadline: 31 March 2024

Conferences
27 October–10 November 2023
The 4th International Electronic Conference on Applied Sciences (ASEC2023)

Special Issues
Special Issue in
Bioengineering
Fundamentals and Applications of Fluid Mechanics and Acoustics in Biomedical Engineering
Guest Editors: Ephraim Gutmark, Iris LittleDeadline: 1 September 2023
Special Issue in
Bioengineering
Advances in Dental and Maxillofacial Tissue Engineering
Guest Editors: Apostolos Tsolakis, Lisa DeLouiseDeadline: 15 September 2023
Special Issue in
Bioengineering
3D Cell Culture in Disease Modeling and Tissue Regeneration
Guest Editors: Pasquale Marrazzo, Aijun Wang, Chengfei ZhangDeadline: 30 September 2023
Special Issue in
Bioengineering
Wound Healing and Regenerative Medicine
Guest Editors: Geoffrey C. Gurtner, Kellen ChenDeadline: 15 October 2023
Topical Collections
Topical Collection in
Bioengineering
Nanoparticles for Therapeutic and Diagnostic Applications
Collection Editor: Wassana Yantasee
Topical Collection in
Bioengineering
Feature Papers in Advanced Computational Technologies for Biosignal Processing
Collection Editors: Yunfeng Wu, Shi Qiu, Behnaz Ghoraani
Topical Collection in
Bioengineering
Extracellular Matrix in Engineered Microenvironments for 3D Cell Culture, Tissue Reconstruction, and Disease Modelling In Vitro - 2nd Edition
Collection Editor: Anna E. Guller