-
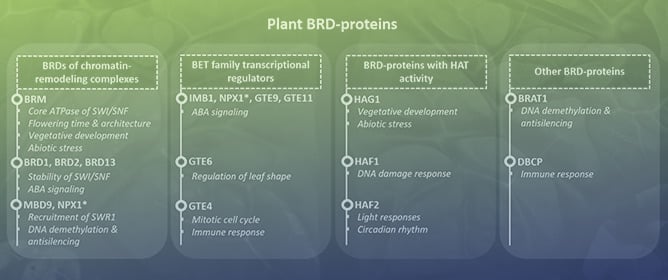 Spotlight on Plant Bromodomain Proteins
Spotlight on Plant Bromodomain Proteins -
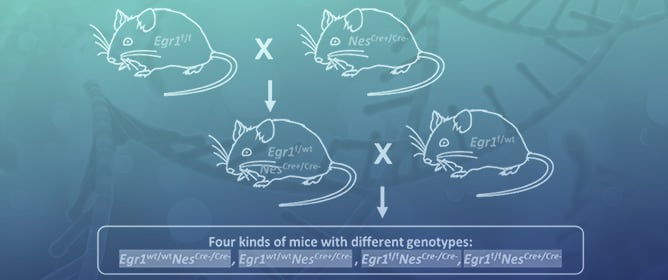 Sex-Linked Growth Disorder and Aberrant Pituitary Gene Expression in Nestin-Cre-Mediated Egr1 Conditional Knockout Mice
Sex-Linked Growth Disorder and Aberrant Pituitary Gene Expression in Nestin-Cre-Mediated Egr1 Conditional Knockout Mice -
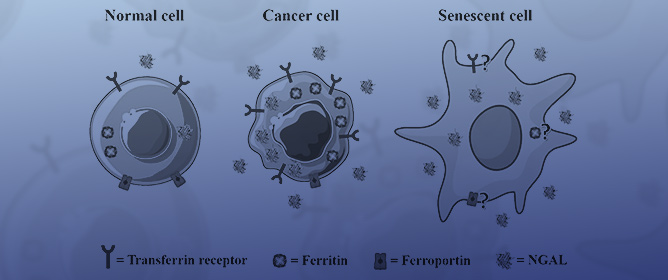 Iron Metabolism in Cancer and Senescence: A Cellular Perspective
Iron Metabolism in Cancer and Senescence: A Cellular Perspective -
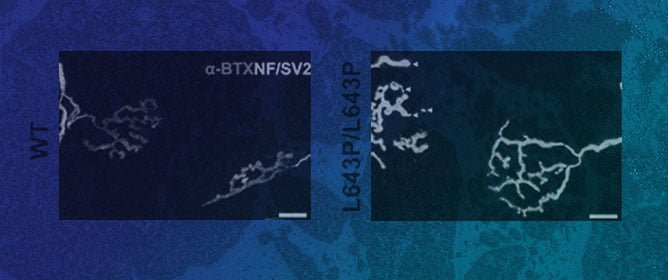 A Novel Mfn2 Mutation Causes a Motor Phenotype but Not Peripheral Neuropathy in Mice
A Novel Mfn2 Mutation Causes a Motor Phenotype but Not Peripheral Neuropathy in Mice -
 Gender Differences in Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Gender Differences in Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Journal Description
Biology
Biology
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal of biological sciences published monthly online by MDPI. The Spanish Society for Nitrogen Fixation (SEFIN) and Federation of European Laboratory Animal Science Associations (FELASA) are affiliated with Biology, and their members receive discounts on the article processing charges.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within Scopus, SCIE (Web of Science), PubMed, PMC, PubAg, CAPlus / SciFinder, and other databases.
- Journal Rank: JCR - Q2 (Biology) / CiteScore - Q1 (General Agricultural and Biological Sciences)
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 18.8 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 2.5 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the first half of 2023).
- Recognition of Reviewers: reviewers who provide timely, thorough peer-review reports receive vouchers entitling them to a discount on the APC of their next publication in any MDPI journal, in appreciation of the work done.
- Companion journal: Foundations.
Impact Factor:
4.2 (2022);
5-Year Impact Factor:
4.4 (2022)
Latest Articles
Carbon Fluxes in Potato (Solanum tuberosum) Remain Stable in Cell Cultures Exposed to Nutritional Phosphate Deficiency
Biology 2023, 12(9), 1190; https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12091190 (registering DOI) - 01 Sep 2023
Abstract
Nutritional phosphate deficiency is a major limitation to plant growth. Here, we monitored fluxes in pathways supporting respiratory metabolism in potato (Solanum tuberosum) cell cultures growing in control or limiting phosphate conditions. Sugar uptake was quantified using [U-14C]sucrose as
[...] Read more.
Nutritional phosphate deficiency is a major limitation to plant growth. Here, we monitored fluxes in pathways supporting respiratory metabolism in potato (Solanum tuberosum) cell cultures growing in control or limiting phosphate conditions. Sugar uptake was quantified using [U-14C]sucrose as precursor. Carbohydrate degradation through glycolysis and respiratory pathways was estimated using the catabolism of [U-14C]sucrose to 14CO2. Anaplerotic carbon flux was assessed by labeling with NaH14CO3. The data showed that these metabolic fluxes displayed distinct patterns over culture time. However, phosphate depletion had relatively little impact on the various fluxes. Sucrose uptake was higher during the first six days of culture, followed by a decline, which was steeper in Pi-sufficient cells. Anaplerotic pathway flux was more important at day three and decreased thereafter. In contrast, the flux between sucrose and CO2 was at a maximum in the mid-log phase of the culture, with a peak at Day 6. Metabolization of [U-14C]sucrose into neutral, basic and acidic fractions was also unaffected by phosphate nutrition. Hence, the well-documented changes in central metabolism enzymes activities in response to Pi deficiency do not drastically modify metabolic fluxes, but rather result in the maintenance of the carbon fluxes that support respiration.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Plant Science)
►
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
Integration of Omics Data and Network Models to Unveil Negative Aspects of SARS-CoV-2, from Pathogenic Mechanisms to Drug Repurposing
Biology 2023, 12(9), 1196; https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12091196 (registering DOI) - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) caused the COVID-19 health emergency, affecting and killing millions of people worldwide. Following SARS-CoV-2 infection, COVID-19 patients show a spectrum of symptoms ranging from asymptomatic to very severe manifestations. In particular, bronchial and pulmonary cells, involved
[...] Read more.
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) caused the COVID-19 health emergency, affecting and killing millions of people worldwide. Following SARS-CoV-2 infection, COVID-19 patients show a spectrum of symptoms ranging from asymptomatic to very severe manifestations. In particular, bronchial and pulmonary cells, involved at the initial stage, trigger a hyper-inflammation phase, damaging a wide range of organs, including the heart, brain, liver, intestine and kidney. Due to the urgent need for solutions to limit the virus’ spread, most efforts were initially devoted to mapping outbreak trajectories and variant emergence, as well as to the rapid search for effective therapeutic strategies. Samples collected from hospitalized or dead COVID-19 patients from the early stages of pandemic have been analyzed over time, and to date they still represent an invaluable source of information to shed light on the molecular mechanisms underlying the organ/tissue damage, the knowledge of which could offer new opportunities for diagnostics and therapeutic designs. For these purposes, in combination with clinical data, omics profiles and network models play a key role providing a holistic view of the pathways, processes and functions most affected by viral infection. In fact, in addition to epidemiological purposes, networks are being increasingly adopted for the integration of multiomics data, and recently their use has expanded to the identification of drug targets or the repositioning of existing drugs. These topics will be covered here by exploring the landscape of SARS-CoV-2 survey-based studies using systems biology approaches derived from omics data, paying particular attention to those that have considered samples of human origin.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Multi-Omics Data Integration in Complex Diseases)
►▼
Show Figures
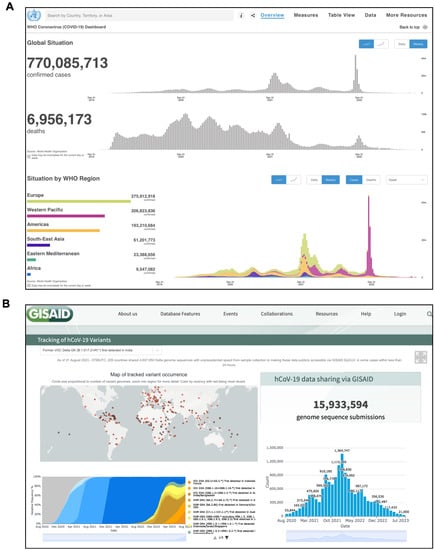
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
A Bacillus subtilis Strain ZJ20 with AFB1 Detoxification Ability: A Comprehensive Analysis
by
, , , , , , , , , , , and
Biology 2023, 12(9), 1195; https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12091195 (registering DOI) - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
As a class I carcinogen, aflatoxin can cause serious damage to various tissues and organs through oxidative stress injuries. The liver, as the target organ of AFB1, is the most seriously damaged. Biological methods are commonly used to degrade AFB1
[...] Read more.
As a class I carcinogen, aflatoxin can cause serious damage to various tissues and organs through oxidative stress injuries. The liver, as the target organ of AFB1, is the most seriously damaged. Biological methods are commonly used to degrade AFB1. In our study, the aflatoxin B1-degrading strain ZJ20 was screened from AFB1-contaminated feed and soil, and the degradation of AFB1 by ZJ20 was investigated. The whole genome of strain ZJ20 was analyzed, revealing the genomic complexity of strain ZJ20. The 16S rRNA analysis of strain ZJ20 showed 100% identity to Bacillus subtilis IAM 12118. Through whole gene functional annotation, it was determined that ZJ20 has high antioxidant activity and enzymatic activity; more than 100 CAZymes and 11 gene clusters are involved in the production of secondary metabolites with antimicrobial properties. In addition, B. subtilis ZJ20 was predicted to contain a cluster of genes encoding AFB1-degrading enzymes, including chitinase, laccase, lactonase, and manganese oxidase. The comprehensive analysis of B. subtilis provides a theoretical basis for the subsequent development of the biological functions of ZJ20 and the combinatorial enzyme degradation of AFB1.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Microbiology)
►▼
Show Figures
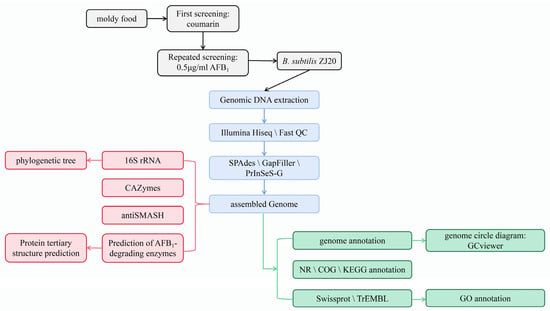
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
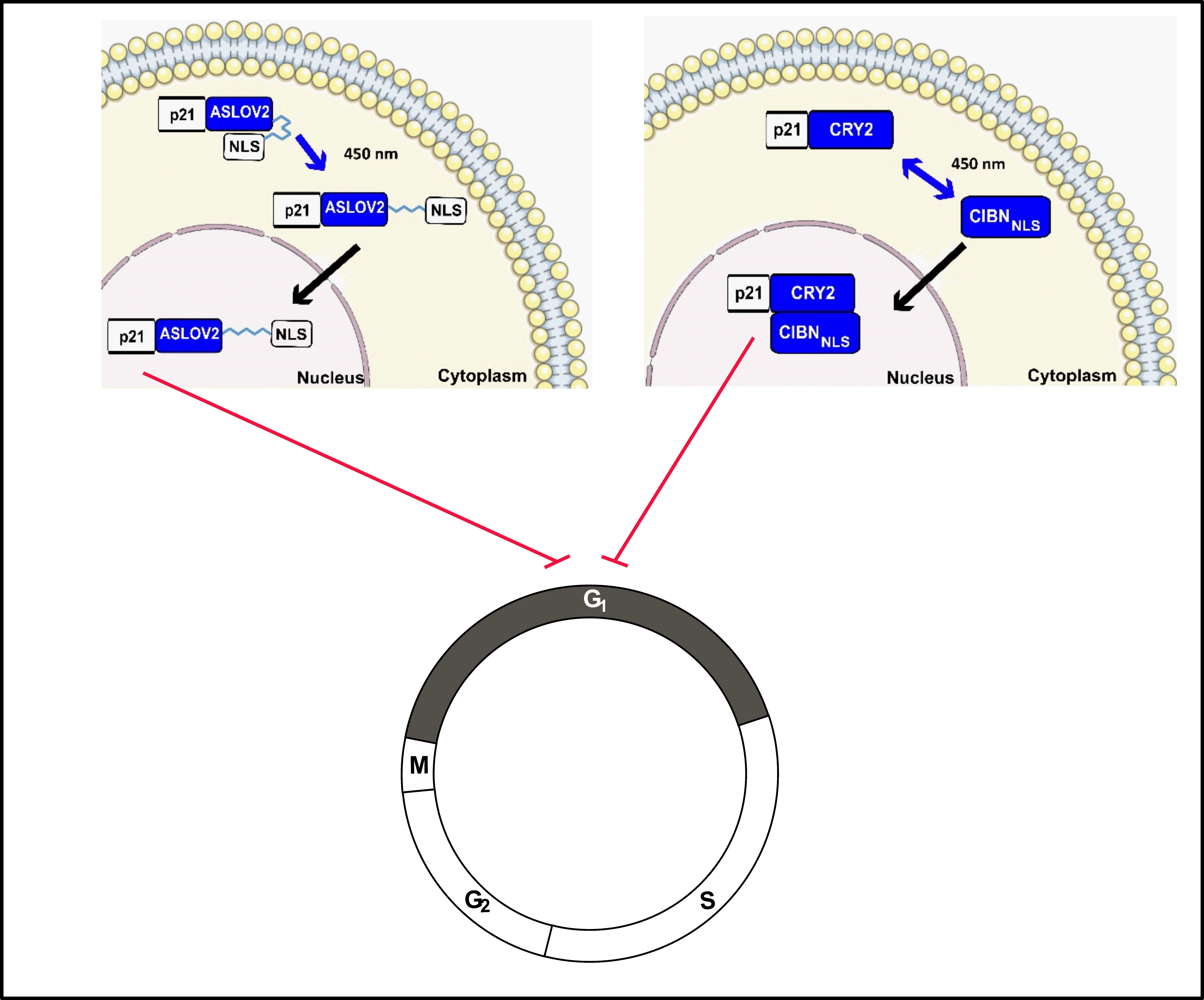
Cell Cycle Control by Optogenetically Regulated Cell Cycle Inhibitor Protein p21
by
, , , , and
Biology 2023, 12(9), 1194; https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12091194 (registering DOI) - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
The progression through the cell cycle phases is driven by cyclin-dependent kinases and cyclins as their regulatory subunits. As nuclear protein, the cell cycle inhibitor p21/CDKN1A arrests the cell cycle at the growth phase G1 by inhibiting the activity of cyclin-dependent kinases. The
[...] Read more.
The progression through the cell cycle phases is driven by cyclin-dependent kinases and cyclins as their regulatory subunits. As nuclear protein, the cell cycle inhibitor p21/CDKN1A arrests the cell cycle at the growth phase G1 by inhibiting the activity of cyclin-dependent kinases. The G1 phase correlates with increased cell size and cellular productivity. Here, we applied an optogenetic approach to control the subcellular localization of p21 and its nuclear functions. To generate light-controllable p21, appropriate fusions with the blue light switch cryptochrome 2/CIBN and the AsLOV-based light-inducible nuclear localization signal, LINuS, were used. Both systems, p21-CRY2/CIB1 and p21-LINuS, increased the amounts of cells arrested in the G1 phase correlating with the increased cell-specific productivity of the reporter-protein-secreted alkaline phosphatase. Varying the intervals of blue LED light exposure and the light dose enable the fine-tuning of the systems. Light-controllable p21 implemented in producer cell lines could be applied to steer the uncoupling of cell proliferation and cell cycle arrest at the G1 phase optimizing the production of biotherapeutic proteins.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Cell Biology)
►▼
Show Figures
Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Seasonality Is the Main Determinant of Microbial Diversity Associated to Snow/Ice around Concordia Station on the Antarctic Polar Plateau
by
, , , , and
Biology 2023, 12(9), 1193; https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12091193 (registering DOI) - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
The French–Italian Concordia Research Station, situated on the Antarctic Polar Plateau at an elevation of 3233 m above sea level, offers a unique opportunity to study the presence and variation of microbes introduced by abiotic or biotic vectors and, consequently, appraise the amplitude
[...] Read more.
The French–Italian Concordia Research Station, situated on the Antarctic Polar Plateau at an elevation of 3233 m above sea level, offers a unique opportunity to study the presence and variation of microbes introduced by abiotic or biotic vectors and, consequently, appraise the amplitude of human impact in such a pristine environment. This research built upon a previous work, which explored microbial diversity in the surface snow surrounding the Concordia Research Station. While that study successfully characterized the bacterial assemblage, detecting fungal diversity was hampered by the low DNA content. To address this knowledge gap, in the present study, we optimized the sampling by increasing ice/snow collected to leverage the final DNA yield. The V4 variable region of the 16S rDNA and Internal Transcribed Spacer (ITS1) rDNA was used to evaluate bacterial and fungal diversity. From the sequencing, we obtained 3,352,661 and 4,433,595 reads clustered in 930 and 3182 amplicon sequence variants (ASVs) for fungi and bacteria, respectively. Amplicon sequencing revealed a predominance of Basidiomycota (49%) and Ascomycota (42%) in the fungal component; Bacteroidota (65.8%) is the main representative among the bacterial phyla. Basidiomycetes are almost exclusively represented by yeast-like fungi. Our findings provide the first comprehensive overview of both fungal and bacterial diversity in the Antarctic Polar Plateau’s surface snow/ice near Concordia Station and to identify seasonality as the main driver of microbial diversity; we also detected the most sensitive microorganisms to these factors, which could serve as indicators of human impact in this pristine environment and aid in planetary protection for future exploration missions.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Multi-Omics of Extremophilic Organisms)
►▼
Show Figures
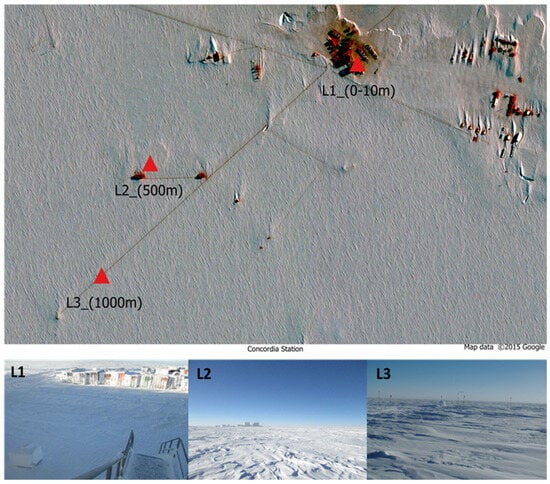
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Cytochrome P450s-Involved Enhanced Metabolism Contributes to the High Level of Nicosulfuron Resistance in Digitaria sanguinalis from China
Biology 2023, 12(9), 1192; https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12091192 - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
Large crabgrass (Digitaria sanguinalis (L.) Scop.) is one of the major malignant grass weeds in Chinese maize (Zea mays L.) fields, and it has recently developed resistance to the acetolactate synthase (ALS)-inhibiting herbicide nicosulfuron. This study focused on a suspected nicosulfuron-resistant
[...] Read more.
Large crabgrass (Digitaria sanguinalis (L.) Scop.) is one of the major malignant grass weeds in Chinese maize (Zea mays L.) fields, and it has recently developed resistance to the acetolactate synthase (ALS)-inhibiting herbicide nicosulfuron. This study focused on a suspected nicosulfuron-resistant (R) population (LJ-01) of D. sanguinalis, collected from Lujiang County in Anhui Province, China, to explore the resistance level and potential resistance mechanism. Whole-plant dose–response testing confirmed that the LJ-01 population evolved a high level of resistance to nicosulfuron (11.5-fold) compared to the susceptible (S) population, DY-02. The ALS gene sequencing and relative expression assay of the R plants indicated that target gene mutation and overexpression were not responsible for the resistance phenotype. However, pretreatment with malathion, a known cytochrome P450 monooxygenase (P450) inhibitor, alleviated the resistance of the R population to nicosulfuron by approximately 36%. High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) analysis revealed that the R plants metabolized nicosulfuron faster than the S plants. Moreover, cross-resistance testing suggested that the R population exhibited low levels of resistance to thifensulfuron-methyl and pyrazosulfuron-ethyl, but it remained susceptible to rimsulfuron. Multiple resistance patterns showed that the R population evolved low resistance to the photosystem inhibitors bromoxynil octanoate and atrazine and sensitivity to the acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACCase) inhibitor cyhalofop-butyl and the 4-hydroxyphenylpyruvate dioxygenase (HPPD) inhibitors tembotrione, mesotrione, and topramezone. This study reports, for the first time, the simultaneous resistance to ALS and different photosystem inhibitors in D. sanguinalis. The nicosulfuron resistance observed in the R population could primarily be attributed to an enhanced metabolism involving P450 enzymes.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Current Advances in Weed Biology, Ecology and Management)
►▼
Show Figures
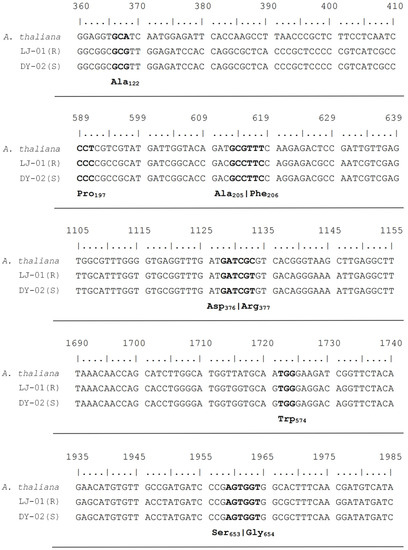
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Effect of Environmental Variables on African Penguin Vocal Activity: Implications for Acoustic Censusing
by
, , , , , , , , , , and
Biology 2023, 12(9), 1191; https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12091191 - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
Global biodiversity is in rapid decline, and many seabird species have disproportionally poorer conservation statuses than terrestrial birds. A good understanding of population dynamics is necessary for successful conservation efforts, making noninvasive, cost-effective monitoring tools essential. Here, we set out to investigate whether
[...] Read more.
Global biodiversity is in rapid decline, and many seabird species have disproportionally poorer conservation statuses than terrestrial birds. A good understanding of population dynamics is necessary for successful conservation efforts, making noninvasive, cost-effective monitoring tools essential. Here, we set out to investigate whether passive acoustic monitoring (PAM) could be used to estimate the number of animals within a set area of an African penguin (Spheniscus demersus) colony in South Africa. We were able to automate the detection of ecstatic display songs (EDSs) in our recordings, thus facilitating the handling of large datasets. This allowed us to show that calling rate increased with wind speed and humidity but decreased with temperature, and to highlight apparent abundance variations between nesting habitat types. We then showed that the number of EDSs in our recordings positively correlated with the number of callers counted during visual observations, indicating that the density could be estimated based on calling rate. Our observations suggest that increasing temperatures may adversely impact penguin calling behaviour, with potential negative consequences for population dynamics, suggesting the importance of effective conservation measures. Crucially, this study shows that PAM could be successfully used to monitor this endangered species’ populations with minimal disturbance.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Aquatic Conservation and Protection Management)
►▼
Show Figures
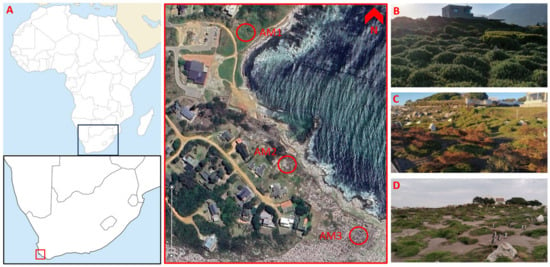
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Bull Shark (Carcharhinus leucas) Occurrence along Beaches of South-Eastern Australia: Understanding Where, When and Why
Biology 2023, 12(9), 1189; https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12091189 - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
Unprovoked shark bites have increased over the last three decades, yet they are still relatively rare. Bull sharks are globally distributed throughout rivers, estuaries, nearshore areas and continental shelf waters, and are capable of making long distance movements between tropical and temperate regions.
[...] Read more.
Unprovoked shark bites have increased over the last three decades, yet they are still relatively rare. Bull sharks are globally distributed throughout rivers, estuaries, nearshore areas and continental shelf waters, and are capable of making long distance movements between tropical and temperate regions. As this species is implicated in shark bites throughout their range, knowledge of the environmental drivers of bull shark movements are important for better predicting the likelihood of their occurrence at ocean beaches and potentially assist in reducing shark bites. Using the largest dataset of acoustically tagged bull sharks in the world, we examined the spatial ecology of 233 juvenile and large (including sub-adult and adult) bull sharks acoustically tagged and monitored over a 5.5-year period (2017–2023) using an array of real-time acoustic listening stations off 21 beaches along the coast of New South Wales, Australia. Bull sharks were detected more in coastal areas of northern NSW (<32° S) but they travelled southwards during the austral summer and autumn. Juveniles were not detected on shark listening stations until they reached 157 cm and stayed north of 31.98° S (Old Bar). Intra-specific diel patterns of occurrence were observed, with juveniles exhibiting higher nearshore presence between 20:00 and 03:00, whilst the presence of large sharks was greatest from midday through to 04:00. The results of generalised additive models revealed that large sharks were more often found when water temperatures were higher than 20 °C, after >45 mm of rain and when swell heights were between 1.8 and 2.8 m. Understanding the influence that environmental variables have on the occurrence of bull sharks in the coastal areas of NSW will facilitate better education and could drive shark smart behaviour amongst coastal water users.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Understanding and Managing Human–Shark Interactions in an Environmentally Aware World)
►▼
Show Figures
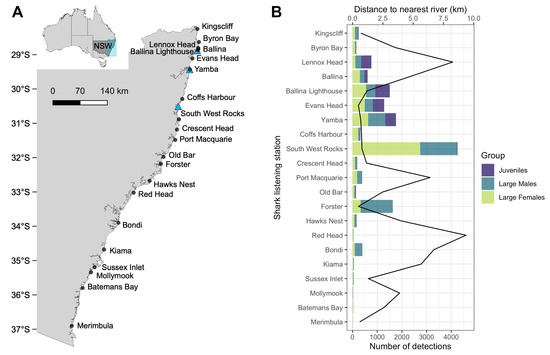
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Nlrp3 Deficiency Alleviates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Acute Kidney Injury via Suppressing Renal Inflammation and Ferroptosis in Mice
Biology 2023, 12(9), 1188; https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12091188 - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
The nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain-like receptor protein 3 (NLRP3) inflammasome is a vital component of many inflammatory responses. Here, we intended to investigate the involvement of NLRP3 in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced sepsis-associated acute kidney injury (S-AKI) and explore its mechanisms. For the first time, we
[...] Read more.
The nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain-like receptor protein 3 (NLRP3) inflammasome is a vital component of many inflammatory responses. Here, we intended to investigate the involvement of NLRP3 in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced sepsis-associated acute kidney injury (S-AKI) and explore its mechanisms. For the first time, we validated elevated NLRP3 expression in the renal tissues of S-AKI patients by immunohistochemistry analysis. Through LPS injection in both wild-type and Nlrp3−/− mice, a S-AKI model was developed. It was found that LPS-induced kidney injury, including an abnormal morphology in a histological examination, abnormal renal function in a laboratory examination, and an increase in the expression of AKI biomarkers, was dramatically reversed in Nlrp3-deficient mice. Nlrp3 deletion alleviated renal inflammation, as evidenced by the suppression of the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines. A combinative analysis of RNA sequencing and the FerrDb V2 database showed that Nlrp3 knockout regulated multiple metabolism pathways and ferroptosis in LPS-induced S-AKI. Further qPCR coupled with Prussian blue staining demonstrated that Nlrp3 knockout inhibited murine renal ferroptosis, indicating a novel mechanism involving S-AKI pathogenesis by NLRP3. Altogether, the aforementioned findings suggest that Nlrp3 deficiency alleviates LPS-induced S-AKI by reducing renal inflammation and ferroptosis. Our data highlight that NLRP3 is a potential therapeutic target for S-AKI.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Immune Response Regulation in Animals)
►▼
Show Figures
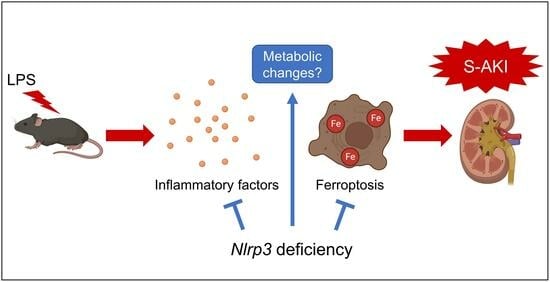
Graphical abstract
Open AccessReview
Biodiversity of Skin Microbiota as an Important Biomarker for Wound Healing
by
, , , , and
Biology 2023, 12(9), 1187; https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12091187 - 30 Aug 2023
Abstract
Cutaneous wound healing is a natural and complex repair process that is implicated within four stages. However, microorganisms (e.g., bacteria) can easily penetrate through the skin tissue from the wound bed, which may lead to disbalance in the skin microbiota. Although commensal and
[...] Read more.
Cutaneous wound healing is a natural and complex repair process that is implicated within four stages. However, microorganisms (e.g., bacteria) can easily penetrate through the skin tissue from the wound bed, which may lead to disbalance in the skin microbiota. Although commensal and pathogenic bacteria are in equilibrium in normal skin, their imbalance in the wound area can cause the delay or impairment of cutaneous wounds. Moreover, skin microbiota is in constant crosstalk with the immune system and epithelial cells, which has significance for the healing of a wound. Therefore, understanding the major bacteria species in the cutaneous wound as well as their communication with the immune system has gained prominence in a way that allows for the emergence of a new perspective for wound healing. In this review, the major bacteria isolated from skin wounds, the role of the crosstalk between the cutaneous microbiome and immune system to heal wounds, the identification techniques of these bacteria populations, and the applied therapies to manipulate the skin microbiota are investigated.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Microbial Diversity and Microbial Resistance)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Discovery of TBX20 as a Novel Gene Underlying Atrial Fibrillation
by
, , , , , , , , , , and
Biology 2023, 12(9), 1186; https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12091186 - 30 Aug 2023
Abstract
Atrial fibrillation (AF), the most prevalent type of sustained cardiac dysrhythmia globally, confers strikingly enhanced risks for cognitive dysfunction, stroke, chronic cardiac failure, and sudden cardiovascular demise. Aggregating studies underscore the crucial roles of inherited determinants in the occurrence and perpetuation of AF.
[...] Read more.
Atrial fibrillation (AF), the most prevalent type of sustained cardiac dysrhythmia globally, confers strikingly enhanced risks for cognitive dysfunction, stroke, chronic cardiac failure, and sudden cardiovascular demise. Aggregating studies underscore the crucial roles of inherited determinants in the occurrence and perpetuation of AF. However, due to conspicuous genetic heterogeneity, the inherited defects accounting for AF remain largely indefinite. Here, via whole-genome genotyping with genetic markers and a linkage assay in a family suffering from AF, a new AF-causative locus was located at human chromosome 7p14.2-p14.3, a ~4.89 cM (~4.43-Mb) interval between the markers D7S526 and D7S2250. An exome-wide sequencing assay unveiled that, at the defined locus, the mutation in the TBX20 gene, NM_001077653.2: c.695A>G; p.(His232Arg), was solely co-segregated with AF in the family. Additionally, a Sanger sequencing assay of TBX20 in another family suffering from AF uncovered a novel mutation, NM_001077653.2: c.862G>C; p.(Asp288His). Neither of the two mutations were observed in 600 unrelated control individuals. Functional investigations demonstrated that the two mutations both significantly reduced the transactivation of the target gene KCNH2 (a well-established AF-causing gene) and the ability to bind the promoter of KCNH2, while they had no effect on the nuclear distribution of TBX20. Conclusively, these findings reveal a new AF-causative locus at human chromosome 7p14.2-p14.3 and strongly indicate TBX20 as a novel AF-predisposing gene, shedding light on the mechanism underlying AF and suggesting clinical significance for the allele-specific treatment of AF patients.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Editorial Board Members’ Collection Series: "Pathology of Cancer and Cardiovascular Disease")
►▼
Show Figures
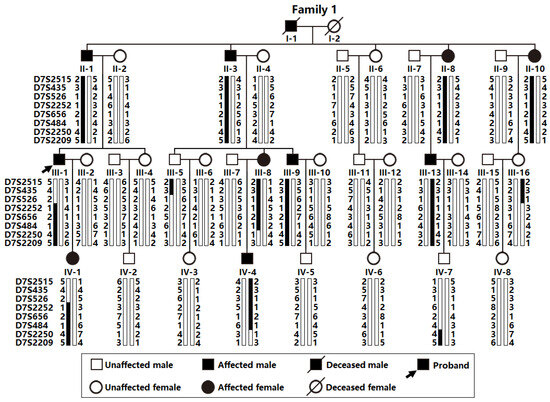
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Hyperglycemia and Hyperlipidemia with Kidney or Liver Transplantation: A Review
by
and
Biology 2023, 12(9), 1185; https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12091185 - 29 Aug 2023
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Although solid organ transplantation in persons with diabetes mellitus is often associated with hyperglycemia, the risk of hyperlipidemia in all organ transplant recipients is often underestimated. The diagnosis of diabetes often predates transplantation; however, in a moderate percentage of allograft recipients, perioperative hyperglycemia
[...] Read more.
Although solid organ transplantation in persons with diabetes mellitus is often associated with hyperglycemia, the risk of hyperlipidemia in all organ transplant recipients is often underestimated. The diagnosis of diabetes often predates transplantation; however, in a moderate percentage of allograft recipients, perioperative hyperglycemia occurs triggered by antirejection regimens. Post-transplant prescription of glucocorticoids, calcineurin inhibitors and mTOR inhibitors are associated with increased lipid concentrations. The existence of diabetes mellitus prior to or following a liver transplant is associated with shorter times of useful allograft function. A cycle involving Smad, TGF beta, m-TOR and toll-like receptors has been identified in the contribution of rejection and aging of allografts. Glucocorticoids (prednisone) and calcineurin inhibitors (cyclosporine and tacrolimus) induce hyperglycemia associated with insulin resistance. Azathioprine, mycophenolate and prednisone are associated with lipogenesis. mTOR inhibitors (rapamycin) are used to decrease doses of atherogenic agents used for immunosuppression. Post-transplant medication management must balance immune suppression and glucose and lipid control. Concerns regarding rejection often override those relative to systemic and organ vascular aging and survival. This review focuses attention on the underlying mechanism of relationships between glycemia/lipidemia control, transplant rejection and graft aging.
Full article
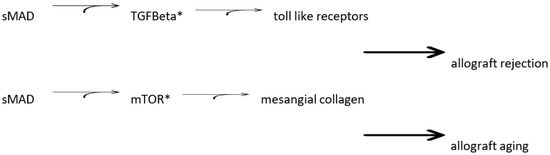
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Protective Effect of Daidzein against Diethylnitrosamine/Carbon Tetrachloride-Induced Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Male Rats
by
, , , , , , and
Biology 2023, 12(9), 1184; https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12091184 - 29 Aug 2023
Abstract
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the second-largest cause of death among all cancer types. Many drugs have been used to treat the disease for a long time but have been mostly discontinued because of their side effects or the development of resistance in the
[...] Read more.
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the second-largest cause of death among all cancer types. Many drugs have been used to treat the disease for a long time but have been mostly discontinued because of their side effects or the development of resistance in the patients with HCC. The administration of DZ orally is a great focus to address the clinical crisis. Daidzein (DZ) is a prominent isoflavone polyphenolic chemical found in soybeans and other leguminous plants. It has various pharmacological effects, including anti-inflammatory, antihemolytic, and antioxidant. This present study investigates the protective effect of DZ on chemically induced HCC in rat models. The DZ was administered orally four weeks before HCC induction and continued during treatment. Our study included four treatment groups: control (group 1, without any treatment), HCC-induced rats (group II), an HCC group treated with DZ at 20 mg/kg (group III), and an HCC group treated with DZ at 40 mg/kg (group IV). HCC rats showed elevation in all the HCC markers (AFP, GPC3, and VEGF), liver function markers (ALP, ALT, and AST), inflammatory markers (IL-6, TNF-α, and CRP), and lipid markers concomitant with a decrease in antioxidant enzymes and protein. However, groups III and IV demonstrated dose-dependent alleviation in the previous parameters resulting from HCC. In addition, the high dose of DZ reduces many hepatological changes in HCC rats. All study parameters improved with DZ administration. Due to its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory characteristics, DZ is a promising HCC treatment option for clinical use.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic Advances in Anti-Cancer Drugs)
►▼
Show Figures
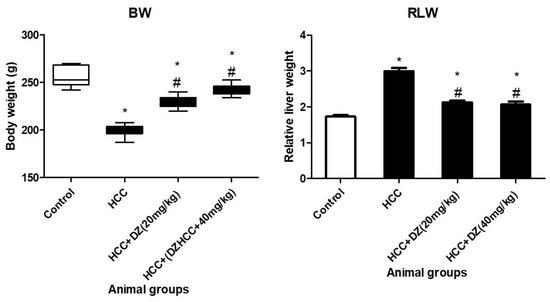
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
From Chaos to Opportunity: Decoding Cancer Heterogeneity for Enhanced Treatment Strategies
by
, , , , , , , , , , , and
Biology 2023, 12(9), 1183; https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12091183 - 29 Aug 2023
Abstract
Cancer manifests as a multifaceted disease, characterized by aberrant cellular proliferation, survival, migration, and invasion. Tumors exhibit variances across diverse dimensions, encompassing genetic, epigenetic, and transcriptional realms. This heterogeneity poses significant challenges in prognosis and treatment, affording tumors advantages through an increased propensity
[...] Read more.
Cancer manifests as a multifaceted disease, characterized by aberrant cellular proliferation, survival, migration, and invasion. Tumors exhibit variances across diverse dimensions, encompassing genetic, epigenetic, and transcriptional realms. This heterogeneity poses significant challenges in prognosis and treatment, affording tumors advantages through an increased propensity to accumulate mutations linked to immune system evasion and drug resistance. In this review, we offer insights into tumor heterogeneity as a crucial characteristic of cancer, exploring the difficulties associated with measuring and quantifying such heterogeneity from clinical and biological perspectives. By emphasizing the critical nature of understanding tumor heterogeneity, this work contributes to raising awareness about the importance of developing effective cancer therapies that target this distinct and elusive trait of cancer.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Cancer Biology)
►▼
Show Figures
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Transcriptome Responses to Different Environments in Intertidal Zones in the Peanut Worm Sipunculus nudus
Biology 2023, 12(9), 1182; https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12091182 - 29 Aug 2023
Abstract
The peanut worm (Sipunculus nudus) is an important intertidal species worldwide. Species living in the same aquaculture area might suffer different environmental impacts. To increase knowledge of the molecular mechanisms underlying the response to environmental fluctuations, we performed a transcriptome analysis
[...] Read more.
The peanut worm (Sipunculus nudus) is an important intertidal species worldwide. Species living in the same aquaculture area might suffer different environmental impacts. To increase knowledge of the molecular mechanisms underlying the response to environmental fluctuations, we performed a transcriptome analysis of S. nudus from different intertidal zones using a combination of the SMRT platform and the Illumina sequencing platform. (1) A total of 105,259 unigenes were assembled, and 23,063 unigenes were perfectly annotated. The results of the PacBio Iso-Seq and IIIumina RNA-Seq enriched the genetic database of S. nudus. (2) A total of 830 DEGs were detected in S. nudus from the different groups. In particular, 33 DEGs had differential expression in the top nine KEGG pathways related to pathogens, protein synthesis, and cellular immune response and signaling. The results indicate that S. nudus from different zones experience different environmental stresses. (3) Several DEGs (HSPA1, NFKBIA, eEF1A, etc.) in pathways related to pathogens (influenza A, legionellosis, measles, and toxoplasmosis) had higher expression in groups M and L. HSPA1 was clearly enriched in most of the pathways, followed by NFKBIA. The results show that the peanut worms from the M and L tidal flats might have suffered more severe environmental conditions. (4) Some DEGs (MKP, MRAS, and HSPB1) were upregulated in peanut worms from the H tidal flat, and these DEGs were mainly involved in the MAPK signaling pathway. These results indicate that the MAPK pathway may play a vital role in the immune response of the peanut worm to the effects of different intertidal flats. This study provides a valuable starting point for further studies to elucidate the molecular basis of the response to different environmental stresses in S. nudus.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Impacts of Climate Change on the Marine Biota: From Molecules to Ecosystems)
►▼
Show Figures
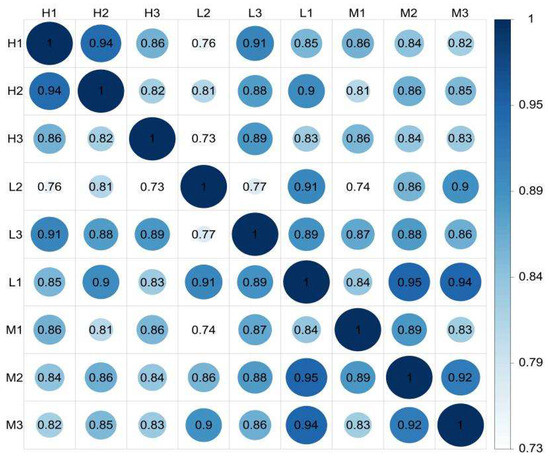
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Measurement of Salivary Cortisol in Two New World Primate Species
Biology 2023, 12(9), 1181; https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12091181 - 29 Aug 2023
Abstract
Glucocorticoids (GCs) are mammalian steroid hormones involved in a variety of physiological processes, including metabolism, the immune response, and cardiovascular functions. Due to their link to the physiological stress response, GC measurement is a valuable tool for conservation and welfare assessment in animal
[...] Read more.
Glucocorticoids (GCs) are mammalian steroid hormones involved in a variety of physiological processes, including metabolism, the immune response, and cardiovascular functions. Due to their link to the physiological stress response, GC measurement is a valuable tool for conservation and welfare assessment in animal populations. GC levels can be measured from different matrices, such as urine and feces. Moreover, especially in captive settings, measuring GCs from saliva samples proved particularly useful as those samples can be collected non-invasively and easily from trained animals. Salivary GC levels can be measured using a variety of analytical methods, such as enzyme immunoassays. However, it is crucial to validate the analytical method for each specific application and species when using a new matrix. Using high-pressure liquid chromatography and a cortisol enzyme immunoassay, we show that the main glucocorticoids secreted in the saliva of squirrel monkeys and brown capuchin monkeys are cortisol and cortisone. Our biological validation found the expected salivary cortisol level to decline throughout the day. Our findings support the reliability of salivary cortisol measurements and their potential to be used as a valid tool in research and welfare assessment for these non-human primates.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Research on Primate Endocrinology)
►▼
Show Figures
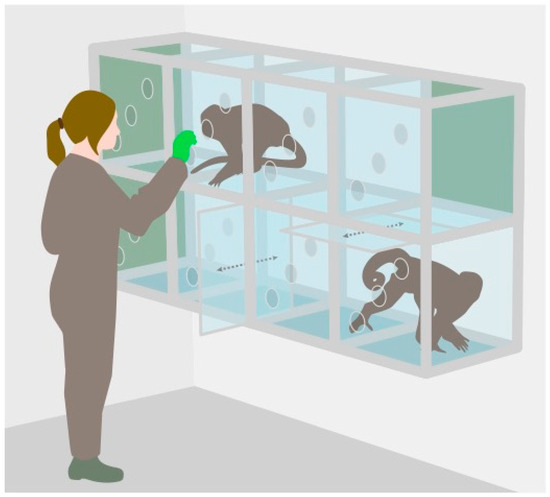
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Tree Physiological Variables as a Proxy of Heavy Metal and Platinum Group Elements Pollution in Urban Areas
by
, , , , and
Biology 2023, 12(9), 1180; https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12091180 - 29 Aug 2023
Abstract
Physiological variables (the content of chlorophyll, flavonoids and nitrogen, together with Fv/Fm) and the content of ten heavy metals (As, Cd, Cu, Hg, Mn, Ni, Pb, Sb, V and Zn) and two platinum group elements (PGEs: Pd and Rh)
[...] Read more.
Physiological variables (the content of chlorophyll, flavonoids and nitrogen, together with Fv/Fm) and the content of ten heavy metals (As, Cd, Cu, Hg, Mn, Ni, Pb, Sb, V and Zn) and two platinum group elements (PGEs: Pd and Rh) were measured in the leaves of 50 individuals of Ligustrum lucidum trees regularly distributed in the city of Logroño (Northern Spain). Three of these variables increased with increasing physiological vitality (chlorophyll, nitrogen and Fv/Fm), whereas flavonoids increased in response to different abiotic stresses, including pollution. Our aim was to test their adequacy as proxies for the pollution due to heavy metals and PGEs. The three vitality indicators generally showed high values typical of healthy plants, and they did not seem to be consistently affected by the different pollutants. In fact, the three vitality variables were positively correlated with the first factor of a PCA that was dominated by heavy metals (mainly Pb, but also Sb, V and Ni). In addition, Fv/Fm was negatively correlated with the second factor of the PCA, which was dominated by PGEs, but the trees showing Fv/Fm values below the damage threshold did not coincide with those showing high PGE content. Regarding flavonoid content, it was negatively correlated with PCA factors dominated by heavy metals, which did not confirm its role as a protectant against metal stress. The relatively low levels of pollution usually found in the city of Logroño, together with the influence of other environmental factors and the relative tolerance of Ligustrum lucidum to modest atmospheric pollution, probably determined the only slight response of the physiological variables to heavy metals and PGEs.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Biological Response of Plants to Environmental Changes)
►▼
Show Figures
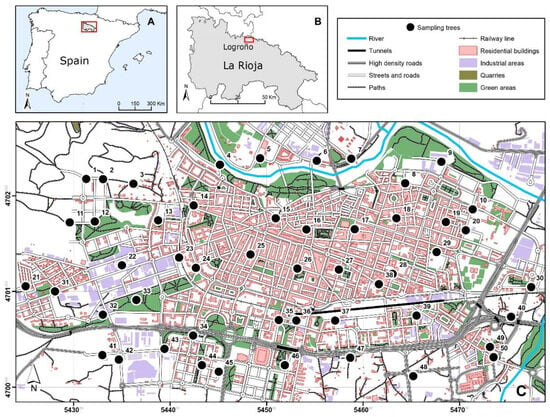
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
World Spread of Tropical Soda Apple (Solanum viarum) under Global Change: Historical Reconstruction, Niche Shift, and Potential Geographic Distribution
Biology 2023, 12(9), 1179; https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12091179 - 29 Aug 2023
Abstract
Solanum viarum has become extensively invasive owing to international trade, climate change, and land–use change. As it is classified as a quarantine weed by countries such as the U.S. and Mexico, it is critical to understand the prevailing historical dispersal, ecological niche dynamics,
[...] Read more.
Solanum viarum has become extensively invasive owing to international trade, climate change, and land–use change. As it is classified as a quarantine weed by countries such as the U.S. and Mexico, it is critical to understand the prevailing historical dispersal, ecological niche dynamics, and distribution patterns. We reconstructed the historical invasion countries and analyzed the ecological niche shift of S. viarum. Using MaxEnt based on the conservativeness of ecological niches, we studied variations in the potential geographical distributions (PGDs) of S. viarum in ecosystems and variations in suitability probabilities along latitudinal gradients. The invasion history in six continents involved three phases: lag (before 1980), spread (1980–2010), and equilibrium (2010–present). The ecological niche remains conserved. The area of S. viarum PGDs had increased by 259 km2; the PGDs will expand to reach a maximum in the 2050s, SSP5–8.5. The PGDs of S. viarum will migrate to higher latitudes under the same future climate scenarios. The latitudes subject to high threats range from 20° to 30° in forest and cropland ecosystems, 15.5° to 27.5° (northern hemisphere) and 33.1° to 42.8° (southern hemisphere) in grassland ecosystems, and 20° to 35° in urban ecosystems. Global change has led to an increased threat of S. viarum at high latitudes. These findings provide a theoretical basis to monitor and control S. viarum.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Risk Assessment for Biological Invasions)
►▼
Show Figures
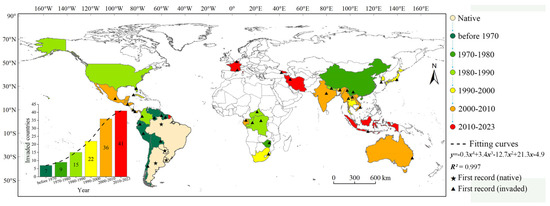
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic Modeling of Extracellular Vesicles
Biology 2023, 12(9), 1178; https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12091178 - 29 Aug 2023
Abstract
Extracellular vesicles (EVs) are lipid membrane bound-cell-derived structures that are a key player in intercellular communication and facilitate numerous cellular functions such as tumor growth, metastasis, immunosuppression, and angiogenesis. They can be used as a drug delivery platform because they can protect drugs
[...] Read more.
Extracellular vesicles (EVs) are lipid membrane bound-cell-derived structures that are a key player in intercellular communication and facilitate numerous cellular functions such as tumor growth, metastasis, immunosuppression, and angiogenesis. They can be used as a drug delivery platform because they can protect drugs from degradation and target specific cells or tissues. With the advancement in the technologies and methods in EV research, EV-therapeutics are one of the fast-growing domains in the human health sector. Therapeutic translation of EVs in clinics requires assessing the quality, safety, and efficacy of the EVs, in which pharmacokinetics is very crucial. We report here the application of physiologically based pharmacokinetic (PBPK) modeling as a principal tool for the prediction of absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion of EVs. To create a PBPK model of EVs, researchers would need to gather data on the size, shape, and composition of the EVs, as well as the physiological processes that affect their behavior in the body. The PBPK model would then be used to predict the pharmacokinetics of drugs delivered via EVs, such as the rate at which the drug is absorbed and distributed throughout the body, the rate at which it is metabolized and eliminated, and the maximum concentration of the drug in the body. This information can be used to optimize the design of EV-based drug delivery systems, including the size and composition of the EVs, the route of administration, and the dose of the drug. There has not been any dedicated review article that describes the PBPK modeling of EV. This review provides an overview of the absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion (ADME) phenomena of EVs. In addition, we will briefly describe the different computer-based modeling approaches that may help in the future of EV-based therapeutic research.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Extracellular Vesicles: Multifaceted Biological Nanoparticles in Health and Disease (Volume II))
►▼
Show Figures
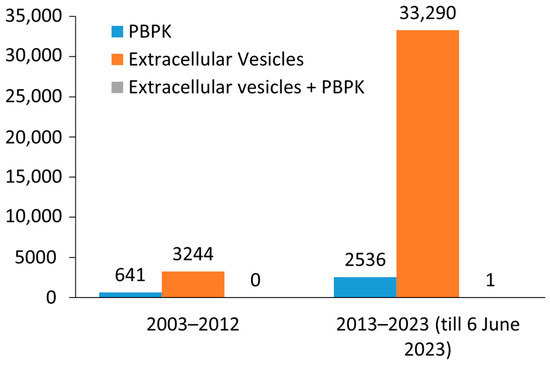
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Emergence and Progression of Behavioral Motor Deficits and Skeletal Muscle Atrophy across the Adult Lifespan of the Rat
by
, , , , , and
Biology 2023, 12(9), 1177; https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12091177 - 28 Aug 2023
Abstract
The facultative loss of muscle mass and function during aging (sarcopenia) poses a serious threat to our independence and health. When activities of daily living are impaired (clinical phase), it appears that the processes leading to sarcopenia have been ongoing in humans for
[...] Read more.
The facultative loss of muscle mass and function during aging (sarcopenia) poses a serious threat to our independence and health. When activities of daily living are impaired (clinical phase), it appears that the processes leading to sarcopenia have been ongoing in humans for decades (preclinical phase). Here, we examined the natural history of sarcopenia in male outbred rats to compare the occurrence of motor behavioral deficits with the degree of muscle wasting and to explore the muscle-associated processes of the preclinical and clinical phases, respectively. Selected metrics were validated in female rats. We used the soleus muscle because of its long duty cycles and its importance in postural control. Results show that gait and coordination remain intact through middle age (40–60% of median lifespan) when muscle mass is largely preserved relative to body weight. However, the muscle shows numerous signs of remodeling with a shift in myofiber-type composition toward type I. As fiber-type prevalence shifted, fiber-type clustering also increased. The number of hybrid fibers, myofibers with central nuclei, and fibers expressing embryonic myosin increased from being barely detectable to a significant number (5–10%) at late middle age. In parallel, TGFβ1, Smad3, FBXO32, and MuRF1 mRNAs increased. In early (25-month-old) and advanced (30-month-old) aging, gait and coordination deteriorate with the progressive loss of muscle mass. In late middle age and early aging due to type II atrophy (>50%) followed by type I atrophy (>50%), the number of myofibers did not correlate with this process. In advanced age, atrophy is accompanied by a decrease in SCs and βCatenin mRNA, whereas several previously upregulated transcripts were downregulated. The re-expression of embryonic myosin in myofibers and the upregulation of mRNAs encoding the γ-subunit of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor, the neuronal cell adhesion molecule, and myogenin that begins in late middle age suggest that one mechanism driving sarcopenia is the disruption of neuromuscular connectivity. We conclude that sarcopenia in rats, as in humans, has a long preclinical phase in which muscle undergoes extensive remodeling to maintain muscle mass and function. At later time points, these adaptive mechanisms fail, and sarcopenia becomes clinically manifest.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Medical Biology)
►▼
Show Figures
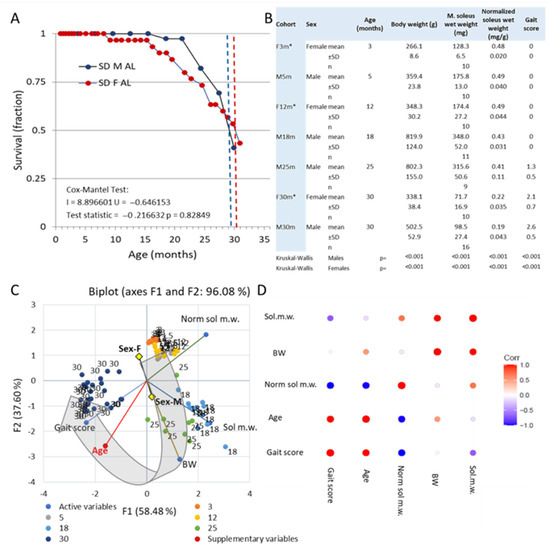
Figure 1

Journal Menu
► ▼ Journal Menu-
- Biology Home
- Aims & Scope
- Editorial Board
- Reviewer Board
- Topical Advisory Panel
- Instructions for Authors
- Special Issues
- Topics
- Sections & Collections
- Article Processing Charge
- Indexing & Archiving
- Editor’s Choice Articles
- Most Cited & Viewed
- Journal Statistics
- Journal History
- Journal Awards
- Society Collaborations
- Conferences
- Editorial Office
Journal Browser
► ▼ Journal BrowserHighly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Biology, Biomedicines, Cancers, Current Oncology, Onco
Targeting Signaling Networks for Cancer Therapy
Topic Editors: Renato Bassan, Jose-Maria Ribera, Linlin GuoDeadline: 5 September 2023
Topic in
Cancers, Biology, Current Oncology, IJMS, JCM
Advances in Molecular and Cellular Studies in Oral Diseases
Topic Editors: Bing Liu, Ming ZhongDeadline: 20 September 2023
Topic in
Biology, Cells, IJMS, Organoids
Pluripotent Stem Cells
Topic Editors: Dongsheng Guo, Xianming Wang, Yuelin Zhang, Linpeng Li, Kepin WangDeadline: 1 October 2023
Topic in
IJERPH, JCM, Biology, Diagnostics, Dentistry Journal
Diagnosis of Craniofacial Changes: Conventional Approaches and Novel Methodologies
Topic Editors: Nikolaos Gkantidis, Carlalberta VernaDeadline: 20 October 2023

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
Biology
Taxonomy and Ecology of Freshwater Diatoms
Guest Editor: Saúl BlancoDeadline: 1 September 2023
Special Issue in
Biology
Metabolism of Hematopoietic Stem Cells during Development and Aging
Guest Editor: Tasleem ArifDeadline: 15 September 2023
Special Issue in
Biology
Chemical Contaminants and Environmental Health
Guest Editors: Song Cui, Xuebin Qi, Zulin Zhang, Yongzhen Ding, Ping LiDeadline: 30 September 2023
Special Issue in
Biology
Physiological and Pathophysiological Responses to Biomaterials 2.0: From Nano- to Microscale Effects and Interactions
Guest Editors: Amilcare Barca, Marta Madaghiele, Stefania SciallaDeadline: 15 October 2023
Topical Collections
Topical Collection in
Biology
Abiotic Stress Tolerance in Cereals
Collection Editor: Dorothea Bartels
Topical Collection in
Biology
Crop Improvement Now and Beyond
Collection Editors: Pierre Devaux, Pierre Sourdille
Topical Collection in
Biology
Gap Junctions and Connexins in Physiology, Pharmacology and Disease
Collection Editors: Yi Zhu, Sebastian Curti, Xinbo Li
Topical Collection in
Biology
Molecular Mechanisms of Aging
Collection Editors: Serena Dato, Giuseppina Rose, Paolina Crocco









.jpg)







