-
 Smart Adaptive Homes and Their Potential to Improve Space Efficiency and Personalisation
Smart Adaptive Homes and Their Potential to Improve Space Efficiency and Personalisation -
 Can the Hemp Industry Improve the Sustainability Performance of the Australian Construction Sector?
Can the Hemp Industry Improve the Sustainability Performance of the Australian Construction Sector? -
 Metal–Organic Frameworks (MOFs) Based Electrospun Nanofiber Membrane for Passive Indoor Moisture Control
Metal–Organic Frameworks (MOFs) Based Electrospun Nanofiber Membrane for Passive Indoor Moisture Control -
 Urban Microclimate, Outdoor Thermal Comfort, and Socio-Economic Mapping: A Case Study of Philadelphia, PA
Urban Microclimate, Outdoor Thermal Comfort, and Socio-Economic Mapping: A Case Study of Philadelphia, PA -
 Analysis and Design of Confined Masonry Structures: Review and Future Research Directions
Analysis and Design of Confined Masonry Structures: Review and Future Research Directions
Journal Description
Buildings
Buildings
is an international, scientific, peer-reviewed, open access journal on building science, building engineering and architecture published monthly online by MDPI. The International Council for Research and Innovation in Building and Construction (CIB) is affiliated with Buildings and their members receive a discount on the article processing charges.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within Scopus, SCIE (Web of Science), Inspec, and other databases.
- Journal Rank: JCR - Q2 (Engineering, Civil) / CiteScore - Q1 (Architecture)
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 13.8 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 2.8 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the first half of 2023).
- Recognition of Reviewers: reviewers who provide timely, thorough peer-review reports receive vouchers entitling them to a discount on the APC of their next publication in any MDPI journal, in appreciation of the work done.
- Companion Journal: Architecture.
Impact Factor:
3.8 (2022);
5-Year Impact Factor:
3.8 (2022)
Latest Articles
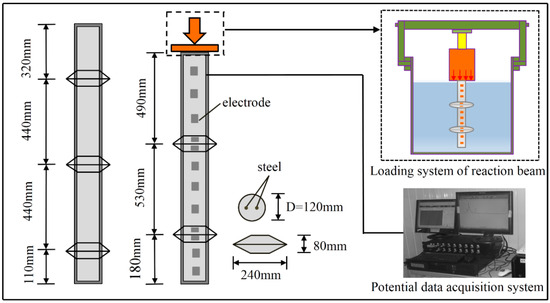
Study on the Force Model of Squeezed Branch Piles Based on Surface Potential Characteristics
Buildings 2023, 13(9), 2231; https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings13092231 (registering DOI) - 01 Sep 2023
Abstract
Squeezed branch piles, which boast the advantages of great bearing capacity, small settlement, and good stability, are an important infrastructure in the foundation of buildings, and their safety state is related to the safety of the entire structure. As a non-destructive testing method,
[...] Read more.
Squeezed branch piles, which boast the advantages of great bearing capacity, small settlement, and good stability, are an important infrastructure in the foundation of buildings, and their safety state is related to the safety of the entire structure. As a non-destructive testing method, surface potential can be used to effectively evaluate the damaged state of a pile foundation without destroying its stability. On this basis, in this study, the characteristics of surface potential change during settlement and deformation of squeezed branch piles under graded loading were tested and analyzed with the aid of a self-made loading system of reaction beams and an LB-IV multi-channel potential data acquisition system. The results show that: Under graded loading, squeezed branch piles can produce surface potential signals whose intensity can well reflect the settlement and local failure characteristics of the pile foundation; The potential signals change in advance of load; and they fluctuate violently before local fracturing of squeezed branch piles. The unstable fluctuation of the potential signal can be regarded as a precursor to the fracturing of squeezed branch piles. The research results have positive theoretical significance and important application value for assessing the stability of both branch piles and their stress states on site and monitoring and forecasting the disaster of pile foundation instability.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Monitoring and Prevention of Dynamic Disasters in Deep Underground Engineering)
►
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Shrinkage and Consolidation Characteristics of Chitosan-Amended Soft Soil—A Sustainable Alternate Landfill Liner Material
by
, , , and
Buildings 2023, 13(9), 2230; https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings13092230 (registering DOI) - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
Kuttanad is a region that lies in the southwest part of Kerala, India, and possesses soft soil, which imposes constraints on many civil engineering applications owing to low shear strength and high compressibility. Chemical stabilizers such as cement and lime have been extensively
[...] Read more.
Kuttanad is a region that lies in the southwest part of Kerala, India, and possesses soft soil, which imposes constraints on many civil engineering applications owing to low shear strength and high compressibility. Chemical stabilizers such as cement and lime have been extensively utilized in the past to address compressibility issues. However, future civilizations will be extremely dependent on the development of sustainable materials and practices such as the use of bio-enzymes, calcite precipitation methods, and biological materials as a result of escalating environmental concerns due to carbon emissions of conventional stabilizers. One such alternative is the utilization of biopolymers. The current study investigates the effect of chitosan (biopolymer extracted from shrimp shells) in improving the consolidation and shrinkage characteristics of these soft soils. The dosages adopted are 0.5%, 1%, 2%, and 4%. One-dimensional fixed ring consolidation tests indicate that consolidation characteristics are improved upon the addition of chitosan up to an optimum dosage of 2%. The coefficient of consolidation increases up to seven times that of untreated soil, indicating the acceleration of the consolidation process by incorporating chitosan. The shrinkage potential is reduced by 11% after amendment with 4% chitosan and all the treated samples exhibit zero signs of curling. Based on the findings from consolidation and shrinkage data, carbon emission assessments are carried out for a typical landfill liner amended with an optimum dosage of chitosan. In comparison to conventional stabilizers like cement and lime, the results indicate that chitosan minimized carbon emissions by 7.325 times and 8.754 times, respectively.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Energy Efficiency and Sustainability in Construction and Building Materials)
►▼
Show Figures
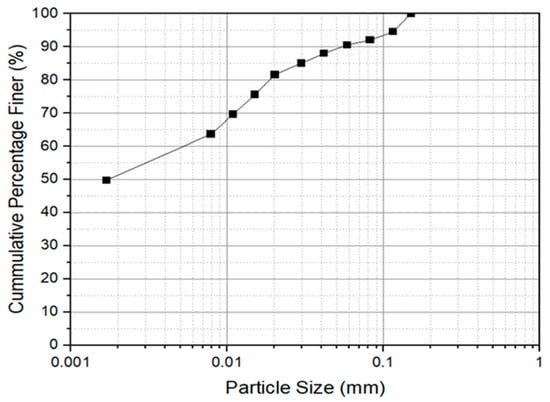
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Stakeholders’ Perceptions of Digital Collaboration in Delivering a Mixed-Use Housing Development Project: A Case Study in Australia
Buildings 2023, 13(9), 2229; https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings13092229 (registering DOI) - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
The paper presents an analysis of collaborative processes in delivering mixed-use housing developments, with a focus on the adoption and roles of digital collaboration to address complex challenges. Extending the collaborative practice (CP) model, the research utilises a qualitative approach and an instrumental
[...] Read more.
The paper presents an analysis of collaborative processes in delivering mixed-use housing developments, with a focus on the adoption and roles of digital collaboration to address complex challenges. Extending the collaborative practice (CP) model, the research utilises a qualitative approach and an instrumental case study involving nine semi-structured interviews with key stakeholders from an award-winning mixed-use housing development in Australia. The study identifies key collaboration elements, such as early project establishment, a well-defined brief, and an adaptive integrated digital plan relevant to the interdisciplinary team. The scarcity of successful “extreme” mixed-use cases globally highlights the need for a core conceptual model for collaboration in complex housing developments, focused on digital collaboration, to support future projects in the sector. The research emphasises social innovation in mixed-use housing developments and highlights the importance of effective digital collaboration for addressing environmental, economic, and social sustainability needs. Contributions to the field extend both theoretical and empirical aspects of the CP model, critically exploring the potential of digital collaboration in mixed-use housing projects. The findings reveal critical elements for establishing a digital collaboration plan, leveraging technology to enhance stakeholder experiences and project delivery. The research is especially relevant in the post-COVID era, where digital collaboration gains significance for the industry.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Application of BIM through the Life Cycle of Buildings)
Open AccessReview
A Bibliometric Analysis and Visualization of Building Decarbonization Research
by
and
Buildings 2023, 13(9), 2228; https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings13092228 (registering DOI) - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
The building sector is responsible for approximately 40% of global energy consumption and carbon emissions, making it a key area of focus in addressing the urgent global challenge of climate change and in achieving the 1.5-degree target. This study concentrated on building decarbonization,
[...] Read more.
The building sector is responsible for approximately 40% of global energy consumption and carbon emissions, making it a key area of focus in addressing the urgent global challenge of climate change and in achieving the 1.5-degree target. This study concentrated on building decarbonization, using bibliometric and network visualization analyses based on a dataset of 2494 publications retrieved from the Web of Science up to 25 June 2023. Findings revealed a rapid growth in publications, with China being the largest contributor (approximately 31%). Notably, the journals of Cleaner Production and Applied Energy emerged as the most influential journal in this field. Although leadership teams and authors have gained prominence, cross-national collaboration and communication among them remain limited. Furthermore, an analysis of keywords and co-citations revealed that the main research themes and hotspots encompass “energy”, “life cycle assessment”, “storage”, and related “models” and decarbonization “strategies”. As the field progresses, a clear trend toward multidisciplinary integration and diversified research directions and content was observed. Researchers can further concentrate their efforts on countries with historically limited research but substantial emissions, and enhance international collaboration and interdisciplinary integration. Overall, this study offers valuable insights for researchers and facilitates future investigations in the field of building decarbonization.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Building Energy, Physics, Environment, and Systems)
►▼
Show Figures
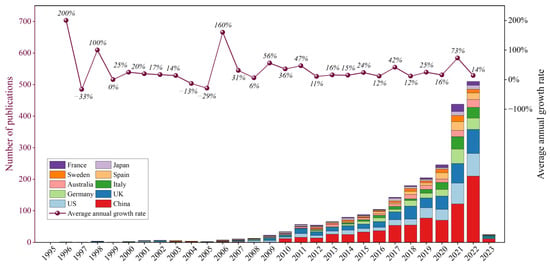
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Reflections from the 2019 Durrës Earthquakes: An Earthquake Engineering Evaluation for Masonry Typologies
by
, , , , and
Buildings 2023, 13(9), 2227; https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings13092227 (registering DOI) - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
Two earthquakes struck the NW region of Albanian territory on 21 September 2019 (Mw = 5.6) and on 26 November 2019 (Mw = 6.4). The epicenters of the seismic activity were located offshore NW Durrës, one of Albania’s most populated cities,
[...] Read more.
Two earthquakes struck the NW region of Albanian territory on 21 September 2019 (Mw = 5.6) and on 26 November 2019 (Mw = 6.4). The epicenters of the seismic activity were located offshore NW Durrës, one of Albania’s most populated cities, located 30 km from the capital Tirana. Various aftershocks followed subsequently. While there were no reported injuries, a number of buildings sustained significant damage near the epicenter following the initial event. Subsequently, during the second event, there was loss of life and extensive damage to civilian structures, resulting in multiple collapses. This study focuses on the earthquake damages observed in residential and public buildings in the earthquake-affected region. The earthquakes predominantly affected low-rise masonry buildings, while the newly constructed RC structures built according to the latest seismic rules were almost unaffected. The commonly encountered building typologies in the region, together with photos showing the amount of destruction are presented here. As observed by the authors during the reconnaissance visit to the stricken area, examples of various damage patterns are presented, along with a technically substantiated description of the reasons for those damages. Although modern buildings during recent earthquakes in the region show acceptable performance, the detailed surveys from the Durrës Earthquakes showed that there is still an important level of deficiency in current masonry buildings built by conventional methods and materials. This problem may reoccur in future earthquakes that may hit other rural regions of Albania, which must be focused on systematically in the near future.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Advanced Research and Prospect of Buildings Seismic Performance)
►▼
Show Figures
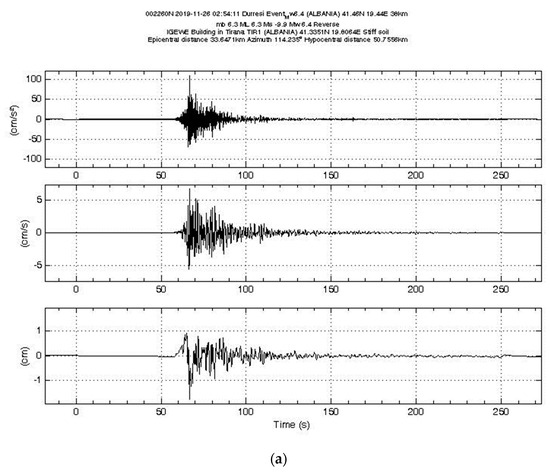
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
A Preliminary Study Was Conducted on the Compressive Strength and Flow Performance of Environmentally Friendly UHPC-SCA
Buildings 2023, 13(9), 2226; https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings13092226 (registering DOI) - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
This research paper explores using marine shells as coarse aggregates in producing seawater sea sand UHPC-CA. The study examined factors such as coarse aggregates (granite, oyster shell, and cone shell), fine aggregates (sea sand and river sand), fiber types, and content. The research
[...] Read more.
This research paper explores using marine shells as coarse aggregates in producing seawater sea sand UHPC-CA. The study examined factors such as coarse aggregates (granite, oyster shell, and cone shell), fine aggregates (sea sand and river sand), fiber types, and content. The research findings indicate that different coarse aggregates and fibers influence the flow performance of UHPC-SCA. The study identified the cone shell as the best coarse shell aggregate and 1.5% steel fiber as the optimal fiber and inclusion amount. The compressive strength of this combination reached 106 MPa, which is comparable to the granite stone UHPC-CA of the same particle size.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Eco-Friendly Building Materials: Recycled Waste and Sustainable Design)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Impact of Continuous Cable-Strut Joints on the Anti-Progressive-Collapse Performance of Suspended-Dome Structures
Buildings 2023, 13(9), 2225; https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings13092225 (registering DOI) - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
In suspended-dome structures, cable-strut joints can be categorized into discontinuous joints and continuous joints. In calculations, the discontinuous joints can be treated as hinge joints. However, in the event of a cable breakage, the continuous joints might experience slip and detachment phenomena. Simplifying
[...] Read more.
In suspended-dome structures, cable-strut joints can be categorized into discontinuous joints and continuous joints. In calculations, the discontinuous joints can be treated as hinge joints. However, in the event of a cable breakage, the continuous joints might experience slip and detachment phenomena. Simplifying continuous cable-strut joints as hinge joints for calculation purposes can result in a significant discrepancy from the actual load-bearing state of the continuous joints. In fact, under the scenario of cable rupture, the continuous cable-strut joints might undergo slip and detachment. This could influence the formation of new tension paths within the cable support system, thereby affecting the anti-collapse performance of the suspended-dome structure. Therefore, this paper investigates the influence of the slippage and detachment of continuous cable-strut joints on the anti-progressive collapse performance of suspended-dome structures through joint tests, numerical simulations, and theoretical analyses. Firstly, two cable-strut joint test models were constructed. Apart from the difference that one uses a discontinuous cable-strut joint and the other a continuous cable-strut joint, all other conditions were kept identical. Research was conducted on the hoop cable failure test. The results indicate that the slippage and detachment of continuous joints hinder the formation of new tension paths in the lower cable-strut system. Structures using continuous cable-strut joints have lower anti-collapse capabilities compared to those using discontinuous cable-strut joints. Secondly, a simplified numerical simulation algorithm for cable-strut joints’ slippage and detachment is proposed. This algorithm only considers the support of struts to the upper structure and uses an Abaqus subroutine to achieve an equivalent simulation of the slippage and detachment phenomena of continuous joints during the finite element computation process. Then, using this algorithm, a progressive collapse analysis of suspended domes using continuous cable-strut joints was carried out. It was found that for suspended domes with continuous cable-strut joints, the slippage and detachment of the cable-strut joints are extremely detrimental to forming new tension paths, making the structure more susceptible to a progressive collapse. Lastly, using the resistance index, a quantitative analysis was conducted on the anti-collapse carrying capacity of suspended domes using both continuous and discontinuous cable-strut joints.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Building Structures)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Noise Perception and Health Effects on Population: A Cross-Sectional Study on COVID-19 Lockdown by Noise Sources for Spanish Dwellings
by
, , , and
Buildings 2023, 13(9), 2224; https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings13092224 - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
An online questionnaire on the subjective response to noise was created to collect national experiences from households during the first COVID-19 wave (from 14 March to 21 June). In this study, different noise sources (general noise, but also noise from neighbors, common areas,
[...] Read more.
An online questionnaire on the subjective response to noise was created to collect national experiences from households during the first COVID-19 wave (from 14 March to 21 June). In this study, different noise sources (general noise, but also noise from neighbors, common areas, facilities, premises, and traffic) and self-declared health effects (stress, lack of concentration, sleep disturbance, anxiety, irritability, or their absence) reported from 582 participants were analyzed (before and during quarantine). A descriptive and statistical analysis between variables was established to observe relational trends for the two periods. The results associated stress and sleep disturbance with most of the noise sources before the pandemic. Sleep disturbance was not significant in confinement, maybe due to habit changes and staying home. Uncertainty linked to the pandemic could explain why stress showed significance during quarantine. Irritability showed an inverse relation with noise sources since their values were greater for declared noise sources and more annoying before the pandemic in all cases. Finally, anxiety showed an association with fewer noise sources, maybe also conditioned by other factors. However, the extreme situation and the uncertainty generated, the presence of cohabitants at home, and building factors (such as acoustic insulation) conditioned the households’ experience.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Acoustics and Noise Control in Buildings)
►▼
Show Figures
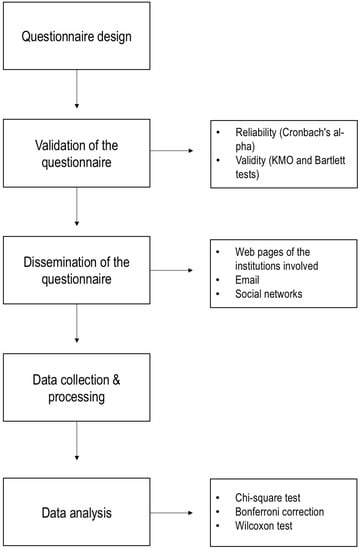
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Dynamics of Structures, Frames, and Plates with Viscoelastic Dampers or Layers: A Literature Review
Buildings 2023, 13(9), 2223; https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings13092223 - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
The paper is devoted to a review of recent achievements in the field of dynamic analysis of structures and structural elements, such as beams and plates, with embedded viscoelastic (VE) dampers and/or layers. The general characteristics of VE materials, their rheological models, and
[...] Read more.
The paper is devoted to a review of recent achievements in the field of dynamic analysis of structures and structural elements, such as beams and plates, with embedded viscoelastic (VE) dampers and/or layers. The general characteristics of VE materials, their rheological models, and methods of parameters identification are discussed. New formulations of dynamic problems for systems with VE elements are also reviewed. The methods of determination of dynamic characteristics, together with the methods of analysis of steady-state and transient vibrations of such systems, are also discussed. Both linear and geometrically non-linear vibrations are considered. The paper ends with a review of the methods of sensitivity and uncertainty analysis, and the methods of optimization, for structures with VE elements.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Dynamics Analysis of Structures with Viscoelastic Elements)
►▼
Show Figures
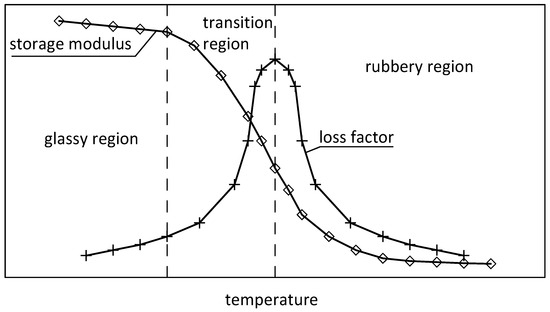
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Research on the Correlations between Spatial Morphological Indices and Carbon Emission during the Operational Stage of Built Environments for Old Communities in Cold Regions
Buildings 2023, 13(9), 2222; https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings13092222 - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
The escalation of the urban population and energy demands has exacerbated the carbon emission intensity at the operational stage of urban old communities. The spatial elements of the built environments comprising building groups, roads and landscape, and the spatial morphology of these elements,
[...] Read more.
The escalation of the urban population and energy demands has exacerbated the carbon emission intensity at the operational stage of urban old communities. The spatial elements of the built environments comprising building groups, roads and landscape, and the spatial morphology of these elements, are endowed not only with human activities but also impact local microclimates and overall carbon emissions. Nonetheless, little attention has been paid to the correlation mechanism between the spatial morphology of the urban built environments and carbon emissions. In this paper, the aim is to combine carbon emissions simulation and statistical analysis to find the correlation between the spatial morphological indices and carbon emissions and to bridge the gaps. Thus, guided by the principles of urban energy modeling, this research adopts a parametric process of “information model construction–carbon emission simulation–statistical analysis”. First, taking 60 typical samples of an old community in Jinan, China, as objects, morphological indices such as density, texture and layout are analyzed through regression analysis to highlight their impacts on carbon emissions. Then, a carbon emission prediction model based on spatial morphological indices is established and verified. The results show that the floor area ratio (FAR), building coverage ratio (BCR), enclosure degree (ED), shape factor (SF) and average road aspect ratio (AS) have significant impacts on carbon emissions during the operational stage. Among these indices, the FAR and the ED are identified as the pivotal influencers. The findings confirm the important role of spatial morphological design of old communities in cold regions in improving urban carbon reduction potential, and they provide theoretical underpinnings and empirical data as references for urban morphology design formulated within the context of low-carbon objectives.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Collection Performance-Based Urban Design: Integrated Urban Analytics, Simulation and Climate-Responsive Design)
►▼
Show Figures
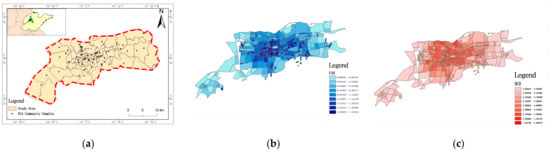
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Design Methodology of U-Shaped Infilled Composite Beams with Angled Shear Connectors Using Finite Element Analysis
Buildings 2023, 13(9), 2221; https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings13092221 - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
A composite beam is a structural member that behaves as a single unit by using shear connectors between a concrete slab and an I-shaped steel girder. The composite ratio is crucial and is determined by the shear connectors’ ability to withstand the horizontal
[...] Read more.
A composite beam is a structural member that behaves as a single unit by using shear connectors between a concrete slab and an I-shaped steel girder. The composite ratio is crucial and is determined by the shear connectors’ ability to withstand the horizontal shear forces between the concrete and steel girder. In this study, a U-shaped composite beam was designed, which differs from conventional composite beams as it allows the use of a steel girder as a formwork. Moreover, angle-type shear connectors, instead of stud-type connectors, were employed. Based on this design, large-scale U-shaped composite beams with angle-type shear connectors were fabricated, and load tests were conducted to analyze the behavior after composite action and the influence of shear connector spacing. Additionally, the strength of the angle-type shear connectors used in this paper was evaluated through finite element analysis. Finally, a strength evaluation method for composite beams of this configuration is proposed.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Modeling and Simulation of Reinforced Concrete Structures)
►▼
Show Figures
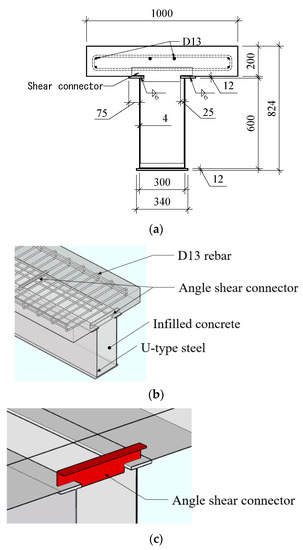
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Seismic Performance Analysis of Corrugated Steel Plate Shear Wall Connected with Beams Only
Buildings 2023, 13(9), 2220; https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings13092220 - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
This paper studied the seismic performance of corrugated steel plate shear walls with vertical corrugated steel plates connected with beams only (CboSPSWs). A numerical model of a CboSPSW was developed. Then, a series of parametric analyses were conducted to determine the effects of
[...] Read more.
This paper studied the seismic performance of corrugated steel plate shear walls with vertical corrugated steel plates connected with beams only (CboSPSWs). A numerical model of a CboSPSW was developed. Then, a series of parametric analyses were conducted to determine the effects of the related parameters on the hysteretic performance of CboSPSWs, including the height–thickness ratio, aspect ratio, corrugation angle, stiffness of the free-edge stiffener, and surrounding frame stiffness. In addition, the limit of the stiffness of the free-edge stiffener of the CboSPSW was investigated. Finally, the serviceability of the existing design method, the Plate-Frame Interaction model (PFI), for CboSPSWs was examined. The results show that CboSPSWs have high values of strength and initial stiffness as well as good and stable energy dissipation capacities. The ultimate strength of the corrugated steel plate (CSP) can be improved significantly by free-edge stiffeners. When the flexural stiffness ratio exceeds 1.0, the increase of the average stress of the CSPs close to the beams is less than 20%, and the tension field develops fully in the CSPs in CboSPSWs. The PFI model can predict the shear strength and initial stiffness values of the hysteretic curves of CboSPSWs with good accuracy, which can be used in the design and plastic analyses of CboSPSWs.
Full article
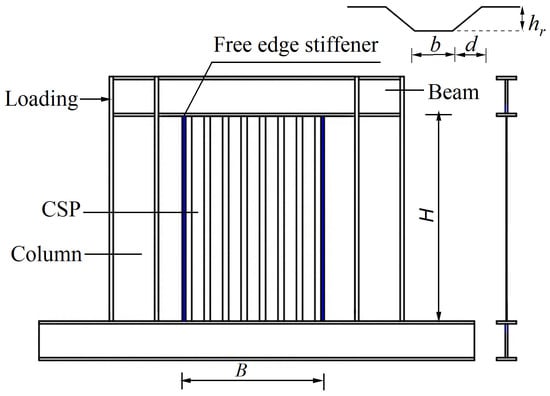
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Investigating the Source of Claims with the Importance of BIM Application on Reducing Construction Disputable Claims in KSA
Buildings 2023, 13(9), 2219; https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings13092219 - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
The construction industry in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA) is a significant sector in the Middle East, with annual expenditures surpassing USD 120 billion. It employs approximately 15% of the workforce and consumes more than 14% of the country’s energy resources. However,
[...] Read more.
The construction industry in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA) is a significant sector in the Middle East, with annual expenditures surpassing USD 120 billion. It employs approximately 15% of the workforce and consumes more than 14% of the country’s energy resources. However, the Saudi construction sector encounters numerous challenges, including a deficiency in skilled labor, escalating costs, disputes, and material shortages. This study aims to investigate the origins of construction disputes in KSA and emphasize the significance of employing Building Information Modeling (BIM) applications to diminish the factors causing claims in both commercial and residential construction projects. The methodology employed comprises a comprehensive literature review and a field survey consisting of interview sessions. This study analyzes a total of 50 contributing factors to the causes of claims, along with conducting a field survey interview session involving 35 participants. The findings reveal seven substantial sources that give rise to construction claims in the KSA, impacting 75 projects, as discussed in this study. Furthermore, the research critically evaluates the advantages of utilizing BIM technology to mitigate construction disputes in the KSA. The data analysis results indicate that the reliance on traditional project management approaches is one of the catalysts for the emergence of disputes in the construction industry, particularly in the KSA.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Building Information Modelling (BIM) Applications in Construction Management)
►▼
Show Figures
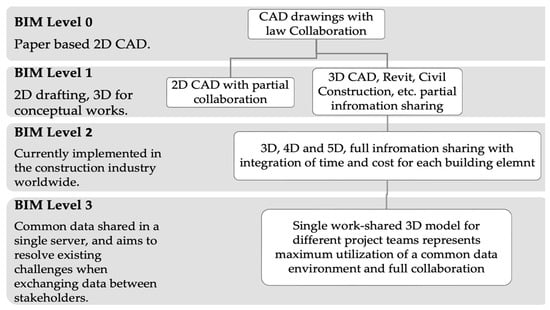
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Impact of Engineering Changes on Value Movement in Fund Flow: Monte Carlo-System Dynamics Modeling Approach
Buildings 2023, 13(9), 2218; https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings13092218 - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
A healthy fund flow system is crucial for the successful construction of any project. Project fund flow management has made significant progress, increasingly aligning with real-world applications. However, due to the uncertainties associated with Engineering Changes (ECs) in projects, the actual fund flow
[...] Read more.
A healthy fund flow system is crucial for the successful construction of any project. Project fund flow management has made significant progress, increasingly aligning with real-world applications. However, due to the uncertainties associated with Engineering Changes (ECs) in projects, the actual fund flow may still deviate from expectations. These systems still require improvements and corrections of flaws to enhance the efficiency of construction projects and reduce exposure to risks associated with ECs. Construction projects are complex and involve many processes. Each process represents a specific part of the project; therefore, an EC in one area can impact resource scheduling and fund balance. In our analysis, we found that ECs are directly related to fund demands and may result in the need for more materials, labor, and duration. Furthermore, ECs can alter construction progress and payment schedules, exacerbating project risks. As a result, effective management of fund flexibility becomes highly necessary. To explore the impact of ECs on the value dynamics of fund flow, it is important to understand and describe the stochastic paths of fund flow and discern the dynamic changes at each stage. Given this, we introduced a system dynamics model based on the Monte Carlo simulation. This model adeptly characterizes project risks and quantifies uncertainty variables, thereby making the simulation more aligned with reality. Moreover, the model illuminates the intricate relationship between project risk and project productivity, highlighting the origins of fund flow fluctuations. It is imperative to identify project risks early and address ECs promptly and effectively. Through sensitivity analysis and strategies, we ensure the stability of fund flow. This study offers a pivotal framework for understanding and managing fund flow in projects, emphasizing the central role of system dynamics in this process.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Advanced Construction Management for Modular and Off-Site Building Construction)
►▼
Show Figures
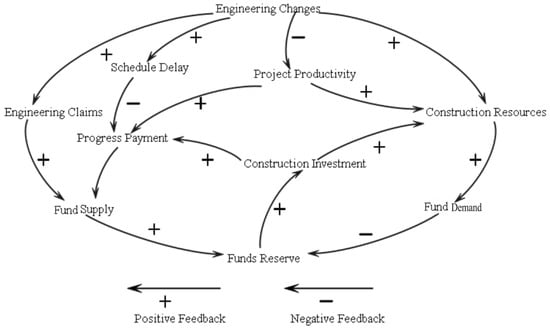
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Effect of Crushing Method on the Properties of Produced Recycled Concrete Aggregates
Buildings 2023, 13(9), 2217; https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings13092217 - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
Construction and Demolition Waste (C&DW) is generated around the world and its quantity will increase in the future. Recycling has become the favored method of dealing with concrete waste but, to avoid its downcycling, it is important to develop a recycling process which
[...] Read more.
Construction and Demolition Waste (C&DW) is generated around the world and its quantity will increase in the future. Recycling has become the favored method of dealing with concrete waste but, to avoid its downcycling, it is important to develop a recycling process which is able to produce high-grade recycled concrete aggregates (RCA). To that end, studying the influence of the production process on the properties of RCA can prove to be a crucial step toward a more circular construction industry. In this study, the influence of the crushing method is investigated. Samples of five laboratory-made concretes have been crushed using the most common mechanical crushing methods (impact crusher and jaw crusher), and the particle size distribution, morphology, hardened cement paste content and water absorption of the produced RCA have been measured and analyzed. The findings indicate that the use of impact crushers results in the production of RCA possessing more spherical geometric characteristics, albeit with a broader particle size distribution and a relatively higher content of fine particles as compared to those obtained from jaw crushers. Additionally, it is observed that the employed crushing technique seemingly exerts no discernible impact on the hardened cement paste content and the water absorption in the context of the studied concretes.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Sustainable Development: Recycle and Reuse of Waste Materials in Construction Industry)
►▼
Show Figures
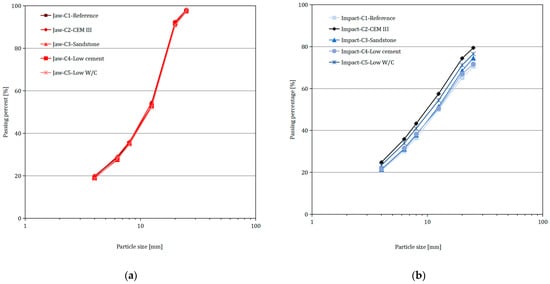
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Antecedents and Consequences of Sustainable Project Management: Evidence from the Construction Industry in China
Buildings 2023, 13(9), 2216; https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings13092216 - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
SPM (sustainable project management) is vital to enhancing the success of projects. Despite several studies dealing with the connection between SPM and project success, this nexus is still insufficiently addressed. Steered by institutional theory and resource-based value theory, the purpose of this article
[...] Read more.
SPM (sustainable project management) is vital to enhancing the success of projects. Despite several studies dealing with the connection between SPM and project success, this nexus is still insufficiently addressed. Steered by institutional theory and resource-based value theory, the purpose of this article is to investigate not only the link between SPM and SPS (sustainable project success), but also the mediating effect of SPP (sustainable project planning) on this connection, and the antecedent role of the institutional pressures (mimetic isomorphism pressure, MIP; normative isomorphism pressure, NIP) on SPM. To test the proposed hypotheses, this article applies PLS-SEM (partial least squares structural equation modeling) and recruited 365 project professionals who have experience in participating in SPM projects in China’s construction industry. The results confirm that both MIP and NIP significantly affect SPM, with NIP being the most significant. Moreover, the findings evidence that SPM had a significantly positive impact on SPS and SPP, and SPP had a significantly positive effect on SPS. Furthermore, the results also evidence that SPP mediates the effect of SPM on SPS. These findings provide empirical evidence for construction companies to understand SPM in the Chinese construction industry. They may also help policymakers to formulate proper policies to promote SPM to achieve sustainable development.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Construction Management, and Computers & Digitization)
►▼
Show Figures
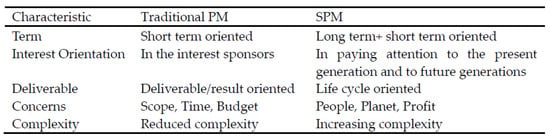
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Analysis of Variables Affecting Indoor Thermal Comfort in Mediterranean Climates Using Machine Learning
Buildings 2023, 13(9), 2215; https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings13092215 - 30 Aug 2023
Abstract
To improve the energy efficiency and performance of buildings, it is essential to understand the factors that influence indoor thermal comfort. Through an extensive analysis of various variables, actions can be developed to enhance the thermal sensation of the occupants, promoting sustainability and
[...] Read more.
To improve the energy efficiency and performance of buildings, it is essential to understand the factors that influence indoor thermal comfort. Through an extensive analysis of various variables, actions can be developed to enhance the thermal sensation of the occupants, promoting sustainability and economic benefits in conditioning systems. This study identifies eight key variables: indoor air temperature, mean radiant temperature, indoor globe temperature, CO2, age, outdoor temperature, indoor humidity, and the running mean temperature, which are relevant for predicting thermal comfort in Mediterranean office buildings. The proposed methodology effectively analyses the relevance of these variables, using five techniques and two different databases, Mediterranean climate buildings published by ASHRAE and a study conducted in Seville, Spain. The results indicate that the extended database to 21 variables improves the quality of the metrics by 5%, underscoring the importance of a comprehensive approach in the analysis. Among the evaluated techniques, random forest emerges as the most successful, offering superior performance in terms of accuracy and other metrics, and this method is highlighted as a technique that can be used to assist in the design and operation or control of a building’s conditioning system or in tools that recommend adaptive measures to improve thermal comfort.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Strategies to Promote Resilience, Energy Efficiency and Sustainability of the Indoor and Built Environment)
►▼
Show Figures
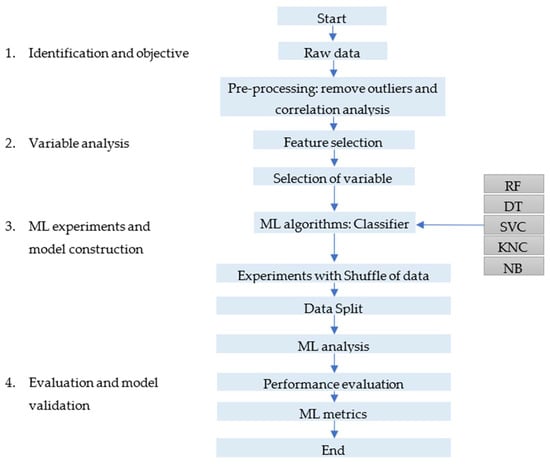
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Optimal Cable Force Adjustment for Long-Span Concrete-Filled Steel Tube Arch Bridges: Real-Time Correction and Reliable Results
Buildings 2023, 13(9), 2214; https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings13092214 - 30 Aug 2023
Abstract
For complex structures, the existing optimization method for suspender cable forces involves extensive matrix operations during the solution process, requiring high computational power and time. As a result, obtaining a more accurate solution becomes challenging. To address this issue and improve the stress
[...] Read more.
For complex structures, the existing optimization method for suspender cable forces involves extensive matrix operations during the solution process, requiring high computational power and time. As a result, obtaining a more accurate solution becomes challenging. To address this issue and improve the stress distribution of suspenders in the completed state, while minimizing the need for frequent cable force adjustments and grid beam elevation changes during construction, a novel method for cable force optimization is proposed. In this study, the Pingnan Third Bridge, which is the world’s longest large span arch bridge with a span of 575 m, is taken as the engineering background. This study combines finite element analysis and multi-objective optimization methods to develop a cable force optimization approach for real-time correction during the panel girder lifting of long-span concrete-filled steel tube (CFST) arch bridges. The optimization method involves treating the panel girder weight and displacement during construction as parameter variables, and considering the displacement and unevenness of the panel girder in the completed state as constraint conditions. The objective equation is defined based on the displacement and cable force during the lifting construction process and, through optimization, the cable forces and displacements of each lifting section are calculated. The results demonstrate the feasibility of integrating optimization theory into the cable force optimization process during panel girder lifting. In this study, we have taken into account the characteristics of real-world engineering and focused on specific key points to reduce the order of the influence matrix. Consequently, the computational costs are reduced, facilitating the development of a multi-objective tension optimization program. By minimizing segment displacement variations and ensuring even cable force distribution in the completed state, the method ensures that the bridge meets the required completion requirements without the need for repetitive iterations or cumbersome calculations. It provides higher optimization efficiency and superior outcomes, offering significant value for cable force calculations during suspender construction of similar bridge types and guiding construction processes.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Construction Process Monitoring and Structural Damage Identification for Buildings and Bridges)
►▼
Show Figures
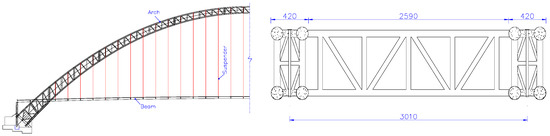
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Towards Intergenerational Transfer to Raise Awareness about the Benefits and Co-Benefits of Energy Retrofits in Residential Buildings
Buildings 2023, 13(9), 2213; https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings13092213 - 30 Aug 2023
Abstract
The LES Project (LES-Llavor Energètica i Salut. Del cole a casa i a la societat, in English: Energy and Health Seed. From school to home and society) is seen as an opportunity to increase the visibility of the role of science and women
[...] Read more.
The LES Project (LES-Llavor Energètica i Salut. Del cole a casa i a la societat, in English: Energy and Health Seed. From school to home and society) is seen as an opportunity to increase the visibility of the role of science and women scientists in their actual contexts and to present architectural research as essential in mitigating climate change and improving people’s health. The goal of this research was to reach the greatest range of people possible through intergenerational transfer. However, the main receptors and drivers were students aged between 8 and 10 years old who were responsible for transmitting energy and environmental conditioning concepts and their interrelations with strategic performance in buildings. Awareness was raised through scientific workshops implemented in primary schools that had energy and air quality deficiencies and opportunities, and the concepts were extrapolated to housing. Two schools in different socioeconomic districts (vulnerable and middle-income families) were selected as a strategy to provide details about the perceptions of energy benefits in both schools’ families. The results of the experience were highly satisfactory. Children from 8 to 10 years old were interested and ready to understand and transfer key concepts about energy efficiency and health improvement through the transformation of the buildings surrounding them. The dissemination of the project and social awareness reached the primary students of the two schools selected for the project and the entire educational community (students, teachers, families and all of society). Currently, we are working on a second stage that will allow for a broad volume of replicability of the workshops, with schoolteachers taking the lead in these actions. For this purpose, LES has the support of the Department of Education of the Generalitat de Catalunya.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Innovative Sustainable Architectural Design, Building Technologies and Structural Retrofitting)
►▼
Show Figures
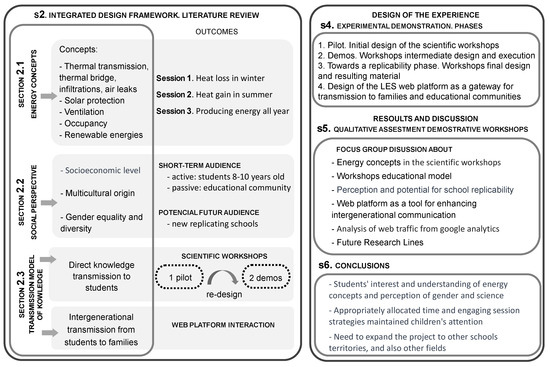
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Integrating BIM–IoT and Autonomous Mobile Robots for Construction Site Layout Printing
Buildings 2023, 13(9), 2212; https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings13092212 - 30 Aug 2023
Abstract
The traditional methods of marking construction site layouts using manual techniques such as chalk lines are prone to human errors, resulting in discrepancies between blueprints and actual layouts. This has serious implications for project delivery, construction, costs and, eventually, project success. However, this
[...] Read more.
The traditional methods of marking construction site layouts using manual techniques such as chalk lines are prone to human errors, resulting in discrepancies between blueprints and actual layouts. This has serious implications for project delivery, construction, costs and, eventually, project success. However, this issue can be resolved through autonomous robots and construction automation in line with Industry 4.0 and 5.0 goals. Construction automation enables workers to concentrate on the construction phase and not worry about manual site markups. This leads to an enhancement in their productivity. This study aims to improve the floor layout printing technique by introducing a framework that integrates building information modeling (BIM) and the Internet of Things (IoT), i.e., BIM–IoT and autonomous mobile robots (AMR). The development process focuses on three key components: a marking tool, an IoT-based AMR and BIM. The BIM-based tools extract and store coordinates on the cloud platform. The AMR, developed using ESP32 and connected to the Google Firestore cloud platform, leverages IoT technology to retrieve the data and draw site layout lines accordingly. Further, this research presents a prototype of an automated robot capable of accurately printing construction site layouts. A design science research (DSR) method is employed in this study that includes a comprehensive review of the existing literature and usage of AMRs in construction layout printing. Subsequently building upon the extant literature, an AMR is developed and experiments are conducted to evaluate the system’s performance. The experiment reveals that the system’s precision falls within a range of ±15 mm and its angle accuracy is within ±4 degrees. Integrating robotic automation, IoT and BIM technologies enhances the efficiency and precision of construction layout printing. The findings provide insights into the potential benefits of deploying AMRs in construction projects, reducing site layout errors and improving construction productivity. This study also adds to the body of knowledge around construction automation in line with Industry 4.0 and 5.0 endeavors.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Innovative Processes and Quality Management Methods in the Building and Construction Industry)
►▼
Show Figures
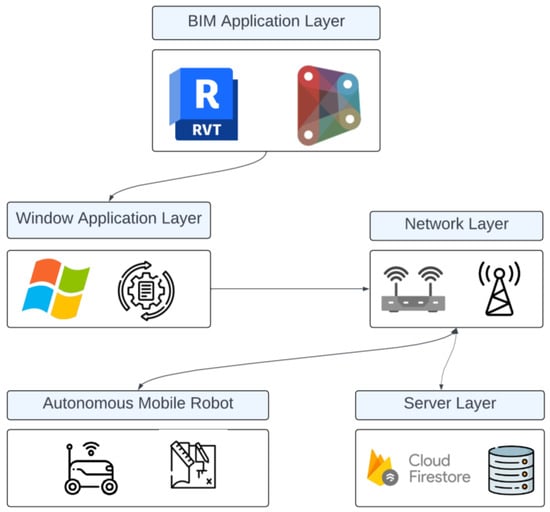
Figure 1

Journal Menu
► ▼ Journal Menu-
- Buildings Home
- Aims & Scope
- Editorial Board
- Reviewer Board
- Topical Advisory Panel
- Instructions for Authors
- Special Issues
- Topics
- Sections & Collections
- Article Processing Charge
- Indexing & Archiving
- Editor’s Choice Articles
- Most Cited & Viewed
- Journal Statistics
- Journal History
- Journal Awards
- Society Collaborations
- Conferences
- Editorial Office
Journal Browser
► ▼ Journal BrowserHighly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Buildings, COVID, Energies, Environments, IJERPH, Sustainability
Advanced Ventilation in and beyond the COVID-19 Pandemic
Topic Editors: John Z Lin, Zhaosong Fang, Sheng Zhang, Jian Liu, Yong Cheng, Chao HuanDeadline: 20 October 2023
Topic in
Buildings, Designs, Energies, Infrastructures, Sustainability
Resilient Civil Infrastructure
Topic Editors: De-Cheng Feng, Ji-Gang Xu, Xuyang CaoDeadline: 31 October 2023
Topic in
Buildings, JMSE, Materials, Remote Sensing, Sensors, Sustainability, Infrastructures, Mathematics
Development of Monitoring, Analysis and Maintenance Technics of Infrastructures
Topic Editors: Chunxu Qu, Jinhe Gao, Rui Zhang, Ziguang Jia, Jiaxiang LiDeadline: 20 November 2023
Topic in
Applied Sciences, Buildings, CivilEng, Materials, Remote Sensing, Sensors
Structural Health Monitoring Based on Materials, Mathematical Methods, and Sensing Technology
Topic Editors: Chongshi Gu, Lei Tang, Meng YangDeadline: 20 December 2023

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
Buildings
Advances in the Indoor Environments and Respiratory Health
Guest Editor: Ju-Hyeong ParkDeadline: 1 September 2023
Special Issue in
Buildings
Bioclimatic Layers of Built Environment
Guest Editor: Marie DavidováDeadline: 10 September 2023
Special Issue in
Buildings
Assessment and Retrofit of Buildings
Guest Editors: Andreas Kappos, Leonidas Alexandros S. KourisDeadline: 30 September 2023
Special Issue in
Buildings
Innovative Structures and Materials: Analysis, Design and Application
Guest Editors: Gaochuang Cai, Amir Si Larbi, Konstantinos Daniel TsavdaridisDeadline: 20 October 2023
Topical Collections
Topical Collection in
Buildings
Construction Management – Future Innovations, Methods, Techniques and Technologies
Collection Editors: Agnieszka Leśniak, Krzysztof Zima
Topical Collection in
Buildings
Structural Analysis for Earthquake-Resistant Design of Buildings
Collection Editors: Daniele Perrone, Emanuele Brunesi
Topical Collection in
Buildings
Virtual Reality and Mixed Reality in Architecture, Engineering, Construction, and Operation and Maintenance (AECOM) Building Sector
Collection Editor: Svetlana J. Olbina
Topical Collection in
Buildings
Non-linear Modelling and Analysis of Buildings
Collection Editors: Maria Polese, Marco Gaetani d'Aragona