-
 Driver Stress Detection from Physiological Signals by Virtual Reality Simulator
Driver Stress Detection from Physiological Signals by Virtual Reality Simulator -
 Leading Logistics Firms’ Re-Engineering through the Optimization of the Customer’s Social Media and Website Activity
Leading Logistics Firms’ Re-Engineering through the Optimization of the Customer’s Social Media and Website Activity -
 Reviewing Federated Learning Aggregation Algorithms; Strategies, Contributions, Limitations and Future Perspectives
Reviewing Federated Learning Aggregation Algorithms; Strategies, Contributions, Limitations and Future Perspectives -
 Visual Perception Based Intra Coding Algorithm for H.266/VVC
Visual Perception Based Intra Coding Algorithm for H.266/VVC -
 Digital Twins in the Marine Industry
Digital Twins in the Marine Industry
Journal Description
Electronics
Electronics
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal on the science of electronics and its applications published semimonthly online by MDPI. The Polish Society of Applied Electromagnetics (PTZE) is affiliated with Electronics and their members receive a discount on article processing charges.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within Scopus, SCIE (Web of Science), CAPlus / SciFinder, Inspec, and other databases.
- Journal Rank: JCR - Q2(Electrical and Electronic Engineering) CiteScore - Q2 (Electrical and Electronic Engineering)
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 15.8 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 2.7 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the first half of 2023).
- Recognition of Reviewers: reviewers who provide timely, thorough peer-review reports receive vouchers entitling them to a discount on the APC of their next publication in any MDPI journal, in appreciation of the work done.
- Companion journals for Electronics include: Magnetism, Signals, Network and Software.
Impact Factor:
2.9 (2022);
5-Year Impact Factor:
2.9 (2022)
Latest Articles
Human Action Recognition Based on Skeleton Information and Multi-Feature Fusion
Electronics 2023, 12(17), 3702; https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12173702 (registering DOI) - 01 Sep 2023
Abstract
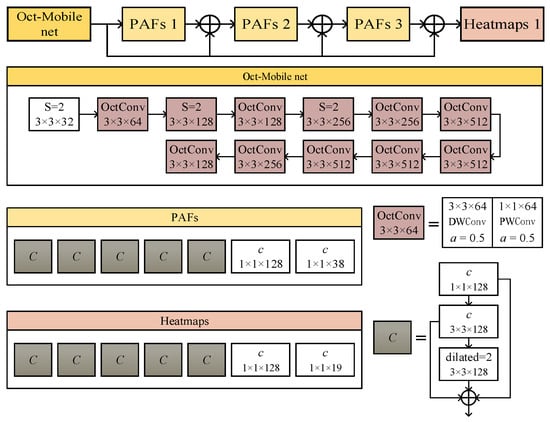
Action assessment and feedback can effectively assist fitness practitioners in improving exercise benefits. In this paper, we address key challenges in human action recognition and assessment by proposing innovative methods that enhance performance while reducing computational complexity. Firstly, we present Oct-MobileNet, a lightweight
[...] Read more.
Action assessment and feedback can effectively assist fitness practitioners in improving exercise benefits. In this paper, we address key challenges in human action recognition and assessment by proposing innovative methods that enhance performance while reducing computational complexity. Firstly, we present Oct-MobileNet, a lightweight backbone network, to overcome the limitations of the traditional OpenPose algorithm’s VGG19 network, which exhibits a large parameter size and high device requirements. Oct-MobileNet employs octave convolution and attention mechanisms to improve the extraction of high-frequency features from the human body contour, resulting in enhanced accuracy with reduced model computational burden. Furthermore, we introduce a novel approach for action recognition that combines skeleton-based information and multiple feature fusion. By extracting spatial geometric and temporal characteristics from actions, we employ a sliding window algorithm to integrate these features. Experimental results show the effectiveness of our approach, demonstrating its ability to accurately recognize and classify various human actions. Additionally, we address the evaluation of traditional fitness exercises, specifically focusing on the BaDunJin movements. We propose a multimodal information-based assessment method that combines pose detection and keypoint analysis. Label sequences are obtained through a pose detector and each frame’s keypoint coordinates are represented as pose vectors. Leveraging multimodal information, including label sequences and pose vectors, we explore action similarity and perform quantitative evaluations to help exercisers assess the quality of their exercise performance.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Human Computer Interaction in Intelligent System)
►
Show Figures
Open AccessCommunication
Brief Comparison of High-Side Gate Drivers for Series Capacitor Buck Converters
Electronics 2023, 12(17), 3701; https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12173701 (registering DOI) - 01 Sep 2023
Abstract
This short article is concerned with the floating high-side gate driver suitable for driving the high side MOSFET/IGBT switch in the series capacitor buck converter family or converters with similar topological features. Biasing the high-side driver in series capacitor buck converters presents an
[...] Read more.
This short article is concerned with the floating high-side gate driver suitable for driving the high side MOSFET/IGBT switch in the series capacitor buck converter family or converters with similar topological features. Biasing the high-side driver in series capacitor buck converters presents an engineering challenge. To alleviate the problem, a modified high-side driver with a voltage lift circuit for driving a high-side switch is proposed. The suggested solution, while being simple and low cost, has several benefits over the earlier propositions. The primary advantage of the proposed circuit is that it relies on a regulated supply to recharge its boot capacitor so to properly bias the high-side driver. Moreover, the proposed driver can operate in a wide range of input voltages while self-adjusting the correct voltage lift according to the operating point of a particular phase of the series buck converter. Thus, any number of phases can be implemented, avoiding cross-coupling effects and providing the high-switch with gating pulses of same amplitude.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue New Trends in Power Electronics for Microgrids)
►▼
Show Figures
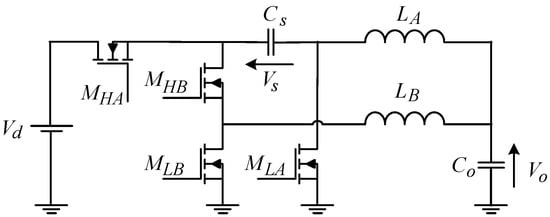
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Enhancing Efficiency in Hierarchical Reinforcement Learning through Topological-Sorted Potential Calculation
Electronics 2023, 12(17), 3700; https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12173700 (registering DOI) - 01 Sep 2023
Abstract
Hierarchical reinforcement learning (HRL) offers a hierarchical structure for organizing tasks, enabling agents to learn and make decisions autonomously in complex environments. However, traditional HRL approaches face limitations in effectively handling complex tasks. Reward machines, which specify high-level goals and associated rewards for
[...] Read more.
Hierarchical reinforcement learning (HRL) offers a hierarchical structure for organizing tasks, enabling agents to learn and make decisions autonomously in complex environments. However, traditional HRL approaches face limitations in effectively handling complex tasks. Reward machines, which specify high-level goals and associated rewards for sub-goals, have been introduced to address these limitations by facilitating the agent’s understanding and reasoning with respect to the task hierarchy. In this paper, we propose a novel approach to enhance HRL performance through topologically sorted potential calculation for reward machines. By leveraging the topological structure of the task hierarchy, our method efficiently determines potentials for different sub-goals. This topological sorting enables the agent to prioritize actions leading to the accomplishment of higher-level goals, enhancing the learning process. To assess the efficacy of our approach, we conducted experiments in the grid-world environment with OpenAI-Gym. The results showcase the superiority of our proposed method over traditional HRL techniques and reward machine-based reinforcement learning approaches in terms of learning efficiency and overall task performance.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Advances in Theories and Applications of Multi-Agent Systems)
►▼
Show Figures
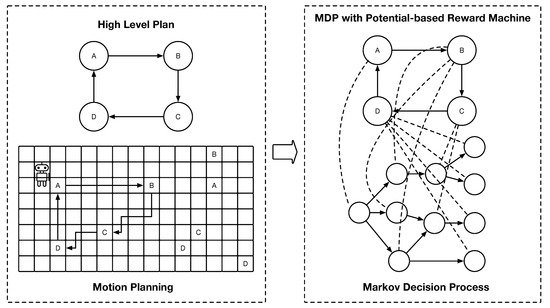
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Edge–Cloud Collaboration-Based Plug and Play and Topology Identification for Microgrids: The Case of Jingshan Microgrid Project in Hubei, China
by
, , , , , , , and
Electronics 2023, 12(17), 3699; https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12173699 (registering DOI) - 01 Sep 2023
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The rapid advancement of renewable energy technologies necessitates innovative solutions for the efficient deployment and management of microgrid systems. This paper presents a detailed study on the implementation of edge–cloud collaboration-based plug and play (PnP) and topology identification for microgrids, focusing on the
[...] Read more.
The rapid advancement of renewable energy technologies necessitates innovative solutions for the efficient deployment and management of microgrid systems. This paper presents a detailed study on the implementation of edge–cloud collaboration-based plug and play (PnP) and topology identification for microgrids, focusing on the Jingshan AC/DC Microgrid Cluster System (JS-MCS) in Hubei, China. Firstly, the paper elucidates the structure of JS-MCS’s physical system and integral information system, comprising the cloud platform, communication network, edge unit, and terminal unit. The following sections introduce the methods of PnP, describing the overall procedure and specific implementations between cloud and edge and cloud and terminal. Then, a novel approach for topology identification is further explored based on correlation analysis. An exemplary analysis of the studied system, JS-MCS, accentuates practical insights into the application of PnP and topology identification methods.
Full article
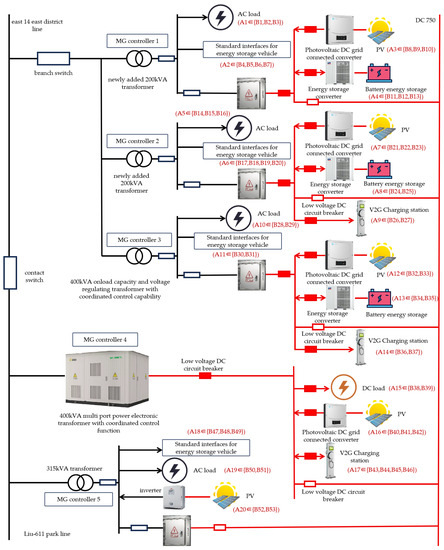
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
A Method of User Travel Mode Recognition Based on Convolutional Neural Network and Cell Phone Signaling Data
by
, , , , , , , and
Electronics 2023, 12(17), 3698; https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12173698 (registering DOI) - 01 Sep 2023
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
As urbanization accelerates, traffic congestion in cities has become a problem. Therefore, accurately identifying urban residents’ travel patterns is crucial for urban traffic planning and intelligent transportation systems. In this study, a convolutional neural network (CNN) approach based on multichannel feature extraction using
[...] Read more.
As urbanization accelerates, traffic congestion in cities has become a problem. Therefore, accurately identifying urban residents’ travel patterns is crucial for urban traffic planning and intelligent transportation systems. In this study, a convolutional neural network (CNN) approach based on multichannel feature extraction using mobile phone signaling data to identify user travel modes is proposed. Here, a trajectory generation method was designed for five types of travel modes. By designing a spatiotemporal threshold screening method, anomalies were identified and processed, combined with the feature analysis method, key points in the signaling extracted, the travel trajectory sliced, and travel sub-trajectory data generated. Next, in the travel mode identification stage, road network information was introduced to improve localization accuracy, and the method for calculating feature values improved. A user travel feature dataset was generated by calculating the feature values, and the travel modes represented by each class were classified and recognized based on the CNN method. Satisfactory results were achieved through experiments using mobile phone signaling and field research data in Kunming, China. The experimental results showed that analysis based on mobile phone signaling data could classify, identify, and obtain different travel category modes. This method’s accuracy was 84.7%. The method provided a feasible way of identifying travel patterns in the context of smart cities and big data, providing strong support for urban transport planning and management, and has the potential for wider application.
Full article
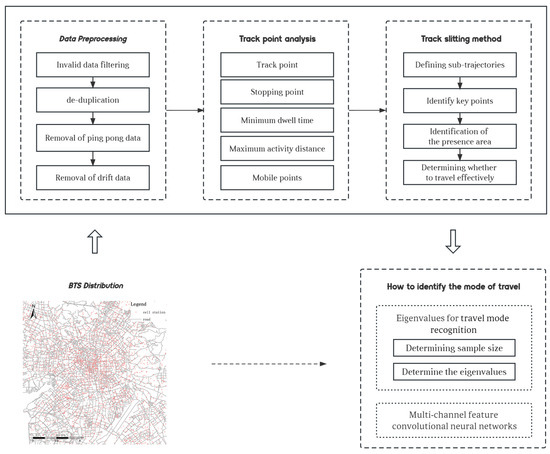
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Black-Box Watermarking and Blockchain for IP Protection of Voiceprint Recognition Model
Electronics 2023, 12(17), 3697; https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12173697 (registering DOI) - 01 Sep 2023
Abstract
Deep neural networks are widely used for voiceprint recognition, whilst voiceprint recognition models are vulnerable to attacks. Existing protection schemes for voiceprint recognition models are insufficient to withstand various robustness attacks and cannot prevent model theft. This paper proposes a black-box voiceprint recognition
[...] Read more.
Deep neural networks are widely used for voiceprint recognition, whilst voiceprint recognition models are vulnerable to attacks. Existing protection schemes for voiceprint recognition models are insufficient to withstand various robustness attacks and cannot prevent model theft. This paper proposes a black-box voiceprint recognition model protection framework that combines active and passive protection. It embeds key information into the Mel spectrogram to generate trigger samples that are difficult to detect and remove and injects them into the host model as watermark W, thereby enhancing the copyright protection performance of the voiceprint recognition model. To restrict the use of the model by unauthorized users, the index number corresponding to the model and the encrypted model information are stored on the blockchain, and then, an exclusive smart contract is designed to restrict access to the model. Experimental results show that this framework effectively protects voiceprint recognition model copyrights and restricts unauthorized access.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Advances in Multimodal Intelligence and Image/Video Processing)
►▼
Show Figures
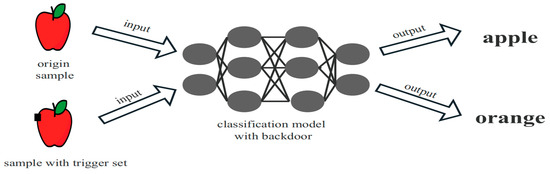
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Research and Implementation of High-Efficiency and Low-Complexity LDPC Coding Algorithm
Electronics 2023, 12(17), 3696; https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12173696 (registering DOI) - 01 Sep 2023
Abstract
* Corresponding authors: guojunxiong@cdu [...]
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Wireless Communication and Multimedia Technology – Theory and Applications)
Open AccessArticle
A Multi-Stage Adaptive Copy-Paste Data Augmentation Algorithm Based on Model Training Preferences
Electronics 2023, 12(17), 3695; https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12173695 (registering DOI) - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
Datasets play an important role in the field of object detection. However, the production of the dataset is influenced by objective environment and human subjectivity, resulting in class imbalanced or even long-tailed distribution in the datasets. At present, the optimization methods based on
[...] Read more.
Datasets play an important role in the field of object detection. However, the production of the dataset is influenced by objective environment and human subjectivity, resulting in class imbalanced or even long-tailed distribution in the datasets. At present, the optimization methods based on data augmentation still rely on subjective parameter adjustments, which is tedious. In this paper, we propose a multi-stage adaptive Copy-Paste augmentation (MSACP) algorithm. This algorithm divides model training into multiple training stages, each stage forming unique training preferences for that stage. Based on these training preferences, the class information of the training set is adaptively adjusted, which not only alleviates the problem of class imbalance in training, but also expands different sample sizes for categories with insufficient information at different training stages. Experimental verification of the traffic sign dataset Tsinghua–Tencent 100K (TT100K) was carried out and showed that the proposed method not only can improve the class imbalance in the dataset, but can also improve the detection performance of models. By using MSACP to transplant the trained optimal weights to an embedded platform, and combining YOLOv3-tiny, the model’s accuracy in detecting traffic signs in autonomous driving scenarios was improved, verifying the effectiveness of the MSACP algorithm in practical applications.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Deep Learning in Image Processing and Pattern Recognition)
►▼
Show Figures
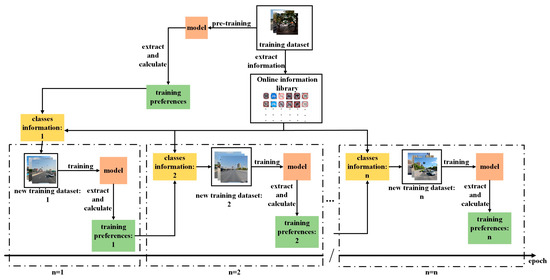
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Validation of a Biomechanical Injury and Disease Assessment Platform Applying an Inertial-Based Biosensor and Axis Vector Computation
Electronics 2023, 12(17), 3694; https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12173694 (registering DOI) - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
Inertial kinetics and kinematics have substantial influences on human biomechanical function. A new algorithm for Inertial Measurement Unit (IMU)-based motion tracking is presented in this work. The primary aims of this paper are to combine recent developments in improved biosensor technology with mainstream
[...] Read more.
Inertial kinetics and kinematics have substantial influences on human biomechanical function. A new algorithm for Inertial Measurement Unit (IMU)-based motion tracking is presented in this work. The primary aims of this paper are to combine recent developments in improved biosensor technology with mainstream motion-tracking hardware to measure the overall performance of human movement based on joint axis-angle representations of limb rotation. This work describes an alternative approach to representing three-dimensional rotations using a normalized vector around which an identified joint angle defines the overall rotation, rather than a traditional Euler angle approach. Furthermore, IMUs allow for the direct measurement of joint angular velocities, offering the opportunity to increase the accuracy of instantaneous axis of rotation estimations. Although the axis-angle representation requires vector quotient algebra (quaternions) to define rotation, this approach may be preferred for many graphics, vision, and virtual reality software applications. The analytical method was validated with laboratory data gathered from an infant dummy leg’s flexion and extension knee movements and applied to a living subject’s upper limb movement. The results showed that the novel approach could reasonably handle a simple case and provide a detailed analysis of axis-angle migration. The described algorithm could play a notable role in the biomechanical analysis of human joints and offers a harbinger of IMU-based biosensors that may detect pathological patterns of joint disease and injury.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Recent Advanced Applications of Computational Biology and Biomedical Informatics Based on AI)
►▼
Show Figures
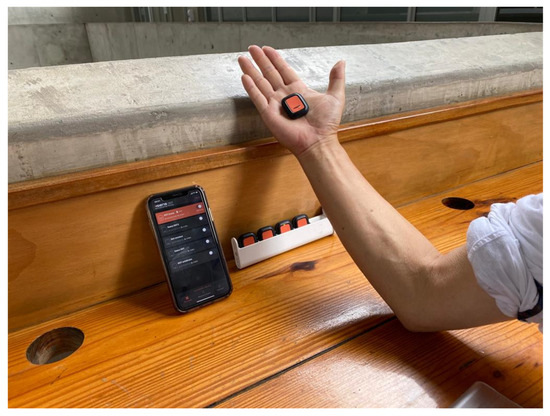

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Enhancing Image Clarity: A Non-Local Self-Similarity Prior Approach for a Robust Dehazing Algorithm
Electronics 2023, 12(17), 3693; https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12173693 (registering DOI) - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
When light propagates in foggy weather, it is affected and scattered by suspended particles in the air. As a result, images taken in this environment often suffer from blurring, reduced contrast, loss of details, and other issues. The primary challenge in dehazing images
[...] Read more.
When light propagates in foggy weather, it is affected and scattered by suspended particles in the air. As a result, images taken in this environment often suffer from blurring, reduced contrast, loss of details, and other issues. The primary challenge in dehazing images is to estimate the transmission coefficient map in the atmospheric degradation model. In this paper, we propose a dehazing algorithm based on the optimization of the “haze-line” prior and non-local self-similarity prior. First, we divided the input haze image into small blocks and used the nearest neighbor classification algorithm to cluster the small patches, which were referred to as “patch-lines”. Based on the characteristics of these “patch-lines”, we could estimate the transmission coefficient map for the image. We then applied the transmission map to a weighted least squares filter to smooth it. Finally, we calculated the clear image using the haze degradation model. The experimental results demonstrate that our algorithm enhanced the image contrast and preserved the fine details, both qualitatively and quantitatively.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Advances in Image Processing and Detection)
►▼
Show Figures
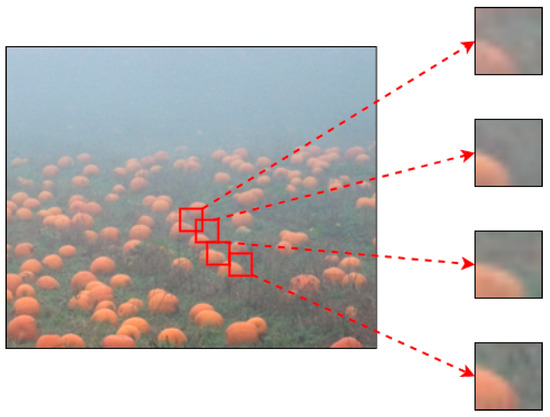
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Seismic Image Identification and Detection Based on Tchebichef Moment Invariant
Electronics 2023, 12(17), 3692; https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12173692 (registering DOI) - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
The research focuses on the analysis of seismic data, specifically targeting the detection, edge segmentation, and classification of seismic images. These processes are fundamental in image processing and are crucial in understanding the stratigraphic structure and identifying oil and natural gas resources. However,
[...] Read more.
The research focuses on the analysis of seismic data, specifically targeting the detection, edge segmentation, and classification of seismic images. These processes are fundamental in image processing and are crucial in understanding the stratigraphic structure and identifying oil and natural gas resources. However, there is a lack of sufficient resources in the field of seismic image detection, and interpreting 2D seismic image slices based on 3D seismic data sets can be challenging. In this research, image segmentation involves image preprocessing and the use of a U-net network. Preprocessing techniques, such as Gaussian filter and anisotropic diffusion, are employed to reduce blur and noise in seismic images. The U-net network, based on the Canny descriptor is used for segmentation. For image classification, the ResNet-50 and Inception-v3 models are applied to classify different types of seismic images. In image detection, Tchebichef invariants are computed using the Tchebichef polynomials’ recurrence relation. These invariants are then used in an optimized multi-class SVM network for detecting and classifying various types of seismic images. The promising results of the SVM model based on Tchebichef invariants suggest its potential to replace Hu moment invariants (HMIs) and Zernike moment invariants (ZMIs) for seismic image detection. This approach offers a more efficient and dependable solution for seismic image analysis in the future.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Advances in Digital Signal and Image Processing, Techniques, and Computations with Multidisciplinary Applications)
Open AccessArticle
Dynamic Power Reduction in TCAM Using Advanced Selective Pre-Charging of Match Lines
by
and
Electronics 2023, 12(17), 3691; https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12173691 (registering DOI) - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
In this paper, we propose a power-efficient memory operation, selective match line precharge, based on an analysis of power consumption in ternary content-addressable memory (TCAM). A statistical study reveals that, on average, 58% of power dissipation related to the match line operation is
[...] Read more.
In this paper, we propose a power-efficient memory operation, selective match line precharge, based on an analysis of power consumption in ternary content-addressable memory (TCAM). A statistical study reveals that, on average, 58% of power dissipation related to the match line operation is saved by deactivating the unnecessary swing of match lines. The improvement has been simulated and proved using 180 nm CMOS technology.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Mixed Signal Circuit Design, Volume II)
►▼
Show Figures
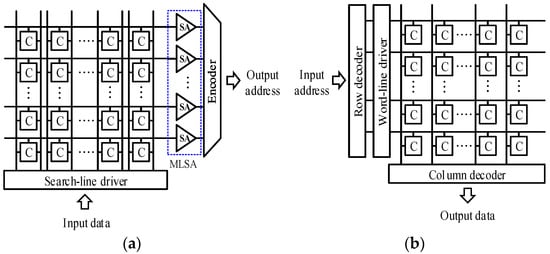
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Echo Preprocessing-Based Smeared Spectrum Interference Suppression
Electronics 2023, 12(17), 3690; https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12173690 (registering DOI) - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
Self-protection deceptive interferences (SPDI) are widely used in electronic countermeasures. Smeared spectrum (SMSP) interference, as a typical SPDI, can form a large number of dense false targets at the receiver output to affect effective target detection. Therefore, the suppression of SMSP interference is
[...] Read more.
Self-protection deceptive interferences (SPDI) are widely used in electronic countermeasures. Smeared spectrum (SMSP) interference, as a typical SPDI, can form a large number of dense false targets at the receiver output to affect effective target detection. Therefore, the suppression of SMSP interference is a compelling issue. The existing SMSP interference suppression methods inevitably result in energy loss of the target due to signal processing. This paper proposes a novel interference suppression method based on echo preprocessing to address this problem. Firstly, the pulse compression (PC) and the coherent integration (CI) characteristics of SMSP interference in the pulse Doppler radar are obtained through the derivation of formulas. Then, echo preprocessing is introduced, and the steps of interference suppression are listed in detail. Finally, the SMSP interference is suppressed because the preprocessed interference forms a center-shifting and range-scaling in the distance dimension after PC, and CI gain cannot be further obtained. The proposed method does not lose the energy of the true target because it does not involve filtering and reconstruction processing. Simulations show that the target detection probability of the proposed method can reach 100% via peak search after the interference suppression when the signal-to-noise ratio is greater than −10 dB and the jamming-to-signal ratio (JSR) is less than 35 dB. Compared with three representative methods in the recent literature, the proposed method has better robustness and higher JSR tolerance.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Artificial Intelligence (AI) Based Radar Signal Processing and Radar Imaging)
►▼
Show Figures
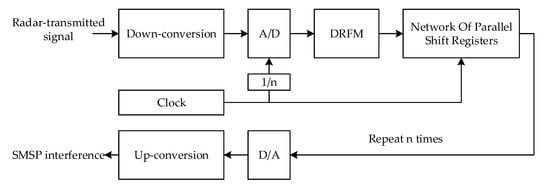
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
ABLA: Application-Based Load-Balanced Approach for Adaptive Mapping of Datacenter Networks
by
, , , , , , , and
Electronics 2023, 12(17), 3689; https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12173689 (registering DOI) - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
Cloud-based services are growing more rapidly than ever, and so does the management challenge on their providers’ side. Cloud-based datacenter networks are built with nodes of huge processing power, connected by high bandwidth capacities to carry their interior traffic requirements. However, such cloud
[...] Read more.
Cloud-based services are growing more rapidly than ever, and so does the management challenge on their providers’ side. Cloud-based datacenter networks are built with nodes of huge processing power, connected by high bandwidth capacities to carry their interior traffic requirements. However, such cloud networks still have limits that are imposed not necessarily by their physical components, but by the schemes of resource management being deployed. Traditionally, for an institute to provide services, it needs to have its own datacenter facility that interconnects its servers through a topology that matches its desired administrative policies and scaling objectives. With the theme of cloud-based IaaS, such datacenter topologies can be created virtually over the cloud. Nowadays, a significant part of those institutes who provide us with our daily services have their infrastructures hosted over cloud ones. Therefore, resources of such cloud networks need to be efficiently utilized, in order to keep their performance and hosting prices competitive. A typical datacenter network mainly consists of server nodes and network links. Besides the resources of the server nodes, the network bandwidth resources are considered a crucial key determinant for the whole datacenter performance. Indeed, a server without sufficient bandwidth capacities is almost useless. Proposals in the literature present schemes for resource utilization on either side of the problem at a time: the nodes or the links. Working in isolation can never deliver efficient mapping solutions. ABLA is an Application-Based, and Load balancing Approach for adaptive mapping proposal. ABLA’s methodology tackles both sides of the datacenter, the nodes and links. It starts by (1) breaking down the node’s resource requirement for the requested applications to be hosted over the virtual server machines besides (2) reading the topological connectivity and bandwidth requirements for each virtual node to all other nodes in the virtual datacenter topology. Compared to other models in the literature, the simulation results show that our proposed ABLA model provides for complete mapping services via load-balanced hosting networks. This allows for competitive hosting prices, with higher performance and service satisfaction rates.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue State-of-the-Art Technology in Cloud and Network Infrastructure)
►▼
Show Figures
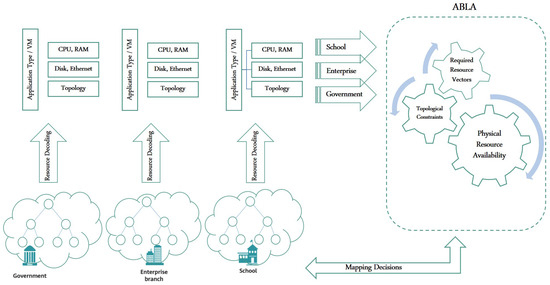
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
A Symmetric Key and Elliptic Curve Cryptography-Based Protocol for Message Encryption in Unmanned Aerial Vehicles
by
, , , , , and
Electronics 2023, 12(17), 3688; https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12173688 (registering DOI) - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
Unmanned aerial vehicles have found applications in fields such as environmental monitoring and the military. Although the collected data in some of these application domains are sensitive, public channels are deployed during the communication process. Therefore, many protocols have been presented to preserve
[...] Read more.
Unmanned aerial vehicles have found applications in fields such as environmental monitoring and the military. Although the collected data in some of these application domains are sensitive, public channels are deployed during the communication process. Therefore, many protocols have been presented to preserve the confidentiality and integrity of the exchanged messages. However, numerous security and performance challenges have been noted in the majority of these protocols. In this paper, an elliptic curve cryptography (ECC) and symmetric key-based protocol is presented. The choice of ECC was informed by its relatively shorter key sizes compared to other asymmetric encryption algorithms such as the Rivest–Shamir–Adleman (RSA) algorithm. Security analysis showed that this protocol provides mutual authentication, session key agreement, untraceability, anonymity, forward key secrecy, backward key secrecy, and biometric privacy. In addition, it is robust against smart card loss, password guessing, known secret session temporary information (KSSTI), privileged insider, side-channeling, impersonation, denial-of-service (DoS), and man-in-the-middle (MitM) attacks. The comparative performance evaluation showed that it has relatively low computation, storage, and communication complexities.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Protocols and Mechanisms for Emerging Network Technologies)
►▼
Show Figures
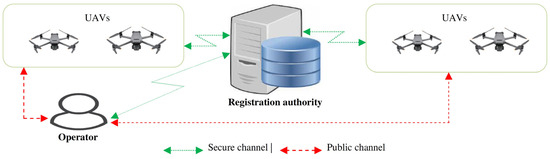
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Leveraging Memory Copy Overlap for Efficient Sparse Matrix-Vector Multiplication on GPUs
by
and
Electronics 2023, 12(17), 3687; https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12173687 (registering DOI) - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
Sparse matrix-vector multiplication (SpMV) is central to many scientific, engineering, and other applications, including machine learning. Compressed Sparse Row (CSR) is a widely used sparse matrix storage format. SpMV using the CSR format on GPU computing platforms is widely studied, where the access
[...] Read more.
Sparse matrix-vector multiplication (SpMV) is central to many scientific, engineering, and other applications, including machine learning. Compressed Sparse Row (CSR) is a widely used sparse matrix storage format. SpMV using the CSR format on GPU computing platforms is widely studied, where the access behavior of GPU is often the performance bottleneck. The Ampere GPU architecture recently from NVIDIA provides a new asynchronous memory copy instruction, memcpy_async, for more efficient data movement in shared memory. Leveraging the capability of this new memcpy_async instruction, we first propose the CSR-Partial-Overlap to carefully overlap the data copy from global memory to shared memory and computation, allowing us to take full advantage of the data transfer time. In addition, we design the dynamic batch partition and the dynamic threads distribution to achieve effective load balancing, avoid the overhead of fixing up partial sums, and improve thread utilization. Furthermore, we propose the CSR-Full-Overlap based on the CSR-Partial-Overlap, which takes the overlap of data transfer from host to device and SpMV kernel execution into account as well. The CSR-Full-Overlap unifies the two major overlaps in SpMV and hides the computation as much as possible in the two important access behaviors of the GPU. This allows CSR-Full-Overlap to achieve the best performance gains from both overlaps. As far as we know, this paper is the first in-depth study of how memcpy_async can be potentially applied to help accelerate SpMV computation in GPU platforms. We compare CSR-Full-Overlap to the current state-of-the-art cuSPARSE, where our experimental results show an average 2.03x performance gain and up to 2.67x performance gain.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Computer Science & Engineering)
►▼
Show Figures
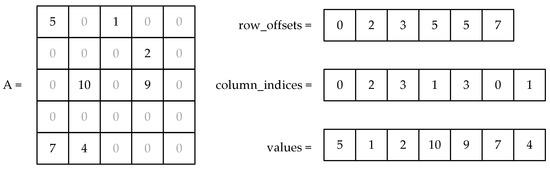
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Contactless Multi-User Virtual Hair Design Synthesis
by
and
Electronics 2023, 12(17), 3686; https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12173686 - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
This study introduces a virtual reality (VR)-based remote hair design training system that addresses the limitations of physical presence. By leveraging virtual environments and eliminating the need for tangible tools, this system allows hairstylists and learners to collaborate and master hair-design techniques from
[...] Read more.
This study introduces a virtual reality (VR)-based remote hair design training system that addresses the limitations of physical presence. By leveraging virtual environments and eliminating the need for tangible tools, this system allows hairstylists and learners to collaborate and master hair-design techniques from a distance. In this approach, a section of a user’s hair was derived from their photograph, and during the training, the most compatible 3D hair model was integrated with the user’s 3D avatar using the recommended matching procedure. This aligned hairstyle was subsequently incorporated into a 3D model for hair simulation. Further, VR HMD interaction mapping was used for hair cutting and styling. A collaborative environment for hair design has been crafted, enabling multiple participants to partake in remote hairstyle education. This system offers cost-effective training, enhances cooperative learning, and aligns with the requirements of contact-free education. In essence, this research has transformed remote hair design training with immersive VR technology. To verify the system’s accuracy, tests were conducted, and the results showcased enhancements in the matching procedure.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Use of Extended Reality (XR) Spectrum for Education and Training: Trends, Applications and Impact)
►▼
Show Figures
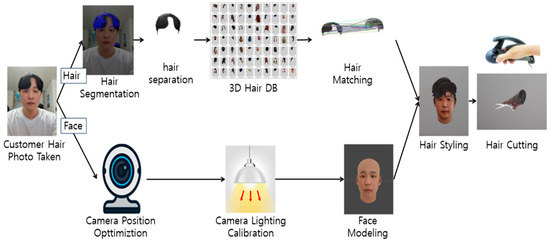
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Stability Analysis and Control Strategy Optimization of a Paralleled IPOS Phase-Shifted Full-Bridge Converters System Based on Droop Control
Electronics 2023, 12(17), 3685; https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12173685 - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
The application of high-power DC equipment further increases the power supply scale of DC systems. But, it is difficult for a single converter to support high transmission power, so multiple converters must operate in parallel for efficient power transmission. In a parallel system
[...] Read more.
The application of high-power DC equipment further increases the power supply scale of DC systems. But, it is difficult for a single converter to support high transmission power, so multiple converters must operate in parallel for efficient power transmission. In a parallel system comprising many IPOS phase-shifting full-bridge converters, current sharing can be realized via droop control. However, the stability of the parallel system using current-sharing control will appear poor in light load conditions, so it is necessary to analyze the stability of parallel systems in light load conditions. Firstly, a single IPOS phase-shifted full-bridge control system is modeled; on this basis, the state space model of the n-module paralleled IPOS phase-shifted full-bridge converters system is derived. Then, the influence of load power and the number of parallel IPOS phase-shifted full-bridge converters on the system stability is analyzed via eigenvalue analysis, and an optimal control strategy based on a particle swarm optimization algorithm is proposed. The control parameters are optimized for the parallel system of eight IPOS phase-shifted full-bridge converters. Finally, the above results are simulated to verify the accuracy of the stability analysis and the feasibility of the optimized control strategy.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Power Quality Conditioning and Stability Enhancement of More-Electronics Power Systems, Volume II)
►▼
Show Figures
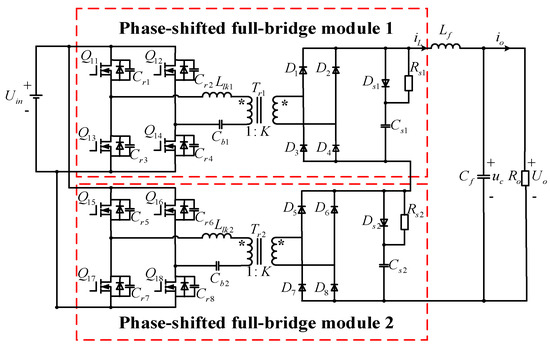
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Harmonic Resonance Analysis and Impedance Remodeling Method of Multi-Inverter Grid-Connected System
Electronics 2023, 12(17), 3684; https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12173684 - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
The harmonic and resonant characteristics of a multi-inverter grid-connected system can negatively affect power quality when weak grid conditions are present. In this paper, firstly, harmonic currents are modeled for the inverter, the correctness of low-frequency harmonics and high-frequency harmonics are verified in
[...] Read more.
The harmonic and resonant characteristics of a multi-inverter grid-connected system can negatively affect power quality when weak grid conditions are present. In this paper, firstly, harmonic currents are modeled for the inverter, the correctness of low-frequency harmonics and high-frequency harmonics are verified in closed loop, and the characteristics of harmonic currents are analyzed when the parameters are varied. Secondly, the resonant characteristics of the inverter with feed-forward link are analyzed, and a multi-inverter grid-connected equivalent model based on the triple-decomposition conductance is developed and analyzed in conjunction with the resonant modal analysis method. Then, a harmonic resonance impedance reshaping method is proposed to suppress the background harmonics using improved weighted average current control (WACC), suppress the system resonance based on the point of common coupling (PCC) paralleling virtual conductance method, and improve the stability margin of the system combined with impedance reshaping resonance suppression method. Finally, simulations and comparison of results with different suppression methods verify the superiority and effectiveness of the proposed method.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Application of Power Electronics Technology in Energy System)
►▼
Show Figures
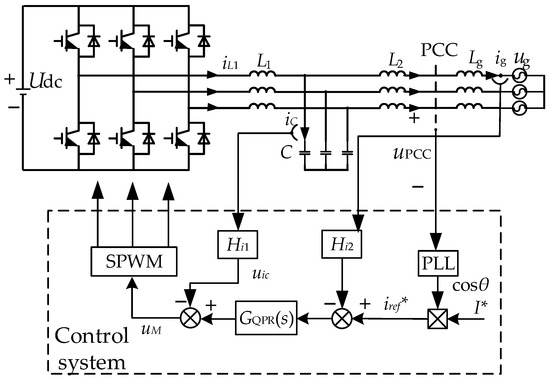
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Wind Power Group Prediction Model Based on Multi-Task Learning
Electronics 2023, 12(17), 3683; https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12173683 - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
Large-scale wind power grid connection increases the uncertainty of the power system, which reduces the economy and security of power system operations. Wind power prediction technology provides the wind power sequence for a period of time in the future, which provides key technical
[...] Read more.
Large-scale wind power grid connection increases the uncertainty of the power system, which reduces the economy and security of power system operations. Wind power prediction technology provides the wind power sequence for a period of time in the future, which provides key technical support for the reasonable development of the power generation plan and the arrangement of spare capacity. For large-scale wind farm groups, we propose a cluster model of wind power prediction based on multi-task learning, which can directly output the power prediction results of multiple wind farms. Firstly, the spatial and temporal feature matrix is constructed based on the meteorological forecast data provided by eight wind farms, and the dimensionality of each attribute is reduced by the principal component analysis algorithm to form the spatial fusion feature set. Then, a network structure with bidirectional gated cycle units is constructed, and a multi-output network structure is designed based on the Multi-gate Mixture-of-Experts (MMoE) framework to design the wind power group prediction model. Finally, the data provided by eight wind farms in Jilin, China, was used for experimental analysis, and the predicted average normalized root mean square error is 0.1754, meaning the prediction precision meets the scheduling requirement, which verifies the validity of the wind power prediction model.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Advances in Power System Dynamics, Stability, Control and Dispatch with Large-Scale Renewable Energy Penetrated)
►▼
Show Figures
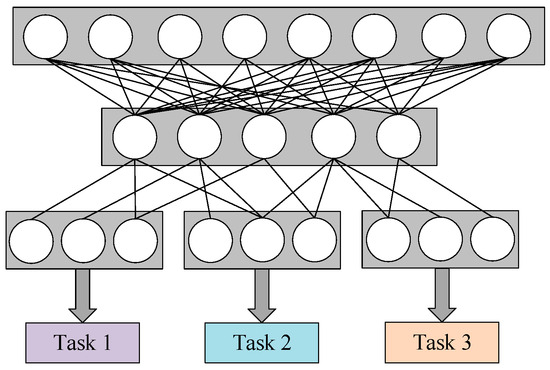
Figure 1

Journal Menu
► ▼ Journal Menu-
- Electronics Home
- Aims & Scope
- Editorial Board
- Reviewer Board
- Topical Advisory Panel
- Instructions for Authors
- Special Issues
- Topics
- Sections & Collections
- Article Processing Charge
- Indexing & Archiving
- Editor’s Choice Articles
- Most Cited & Viewed
- Journal Statistics
- Journal History
- Journal Awards
- Society Collaborations
- Conferences
- Editorial Office
Journal Browser
► ▼ Journal BrowserHighly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Applied Sciences, Energies, Mathematics, Electronics, Algorithms
Distributed Optimization for Control
Topic Editors: Honglei Xu, Lingyun WangDeadline: 20 September 2023
Topic in
Energies, Applied Sciences, Sensors, Electronics, Sci
Modeling and Optimizing Operation of Energy Internet
Topic Editors: Qiuye Sun, Rui Wang, Lei LiuDeadline: 30 September 2023
Topic in
Coatings, Electronics, Energies, Sensors, Telecom
Condition Monitoring and Diagnostic Methods for Power Equipment in New Energy Power Systems
Topic Editors: Shuaibing Li, Guoqiang Gao, Guochang Li, Yi Cui, Jiefeng Liu, Guangya Zhu, Jin LiDeadline: 15 October 2023
Topic in
Applied Sciences, Designs, Electronics, Energies, Machines
Designs and Drive Control of Electromechanical Machines
Topic Editors: Kan Liu, Wei HuDeadline: 31 October 2023

Conferences
27 October–10 November 2023
The 4th International Electronic Conference on Applied Sciences (ASEC2023)

Special Issues
Special Issue in
Electronics
Blockchain-Enabled Trust Management
Guest Editors: Xiaofeng Lu, Yongkai FanDeadline: 1 September 2023
Special Issue in
Electronics
Supercapacitor Applications
Guest Editor: Nihal KularatnaDeadline: 15 September 2023
Special Issue in
Electronics
Dependability of Emerging Computing Paradigms and Technologies in IoT-Oriented Circuits, Architectures and Algorithms
Guest Editors: Marcello Traiola, Elena-Ioana Vǎtǎjelu, Angeliki KritikakouDeadline: 30 September 2023
Special Issue in
Electronics
Power Electronic Converters in a Multiphase Drive Systems
Guest Editors: Kotb Tawfiq, Mohamed N. Ibrahim, Hegazy RezkDeadline: 16 October 2023
Topical Collections
Topical Collection in
Electronics
Millimeter and Terahertz Wireless Communications
Collection Editor: Yosef Pinhasi
Topical Collection in
Electronics
Application of Advanced Computing, Control and Processing in Engineering
Collection Editors: Sudip Chakraborty, Robertas Damaševičius, Sergio Greco
Topical Collection in
Electronics
Deep Learning for Computer Vision: Algorithms, Theory and Application
Collection Editors: Jungong Han, Guiguang Ding
Topical Collection in
Electronics
New Technologies for Biomedical Circuits and Systems
Collection Editors: S. Abdollah Mirbozorgi, Nima TaheriNejad