Journal Description
Energies
Energies
is a peer-reviewed, open access journal of related scientific research, technology development, engineering policy, and management studies related to the general field of energy, from technologies of energy supply, conversion, dispatch, and final use to the physical and chemical processes behind such technologies. Energies is published semimonthly online by MDPI. The European Biomass Industry Association (EUBIA), Association of European Renewable Energy Research Centres (EUREC), Institute for Chemical Processing of Coal (IChPW), International Society for Porous Media (InterPore), CYTED and others are affiliated with Energies and their members receive a discount on the article processing charges.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within Scopus, SCIE (Web of Science), Ei Compendex, RePEc, Inspec, CAPlus / SciFinder, and other databases.
- Journal Rank: CiteScore - Q1 (Engineering (miscellaneous))
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 15.7 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 2.9 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the first half of 2023).
- Recognition of Reviewers: reviewers who provide timely, thorough peer-review reports receive vouchers entitling them to a discount on the APC of their next publication in any MDPI journal, in appreciation of the work done.
- Sections: published in 41 topical sections.
- Testimonials: See what our editors and authors say about Energies.
- Companion journals for Energies include: Fuels, Gases, Nanoenergy Advances and Solar.
Impact Factor:
3.2 (2022);
5-Year Impact Factor:
3.3 (2022)
Latest Articles
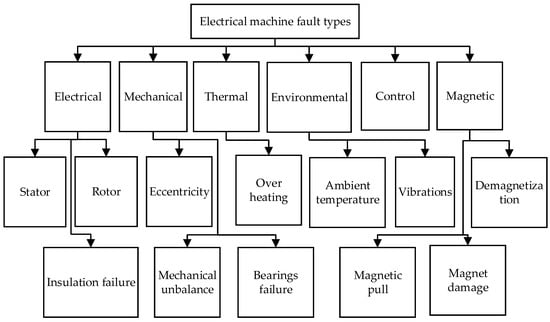
State-of-the-Art Techniques for Fault Diagnosis in Electrical Machines: Advancements and Future Directions
Energies 2023, 16(17), 6345; https://doi.org/10.3390/en16176345 (registering DOI) - 01 Sep 2023
Abstract
Electrical machines are prone to various faults and require constant monitoring to ensure safe and dependable functioning. A potential fault in electrical machinery results in unscheduled downtime, necessitating the prompt assessment of any abnormal circumstances in rotating electrical machines. This paper provides an
[...] Read more.
Electrical machines are prone to various faults and require constant monitoring to ensure safe and dependable functioning. A potential fault in electrical machinery results in unscheduled downtime, necessitating the prompt assessment of any abnormal circumstances in rotating electrical machines. This paper provides an in-depth analysis as well as the most recent trends in the application of condition monitoring and fault detection techniques in the disciplines of electrical machinery. It first investigates the evolution of traditional monitoring techniques, followed by signal-based techniques such as spectrum, vibration, and temperature analysis, and the most recent trends in its signal processing techniques for assessing faults. Then, it investigates and details the implementation and evolution of modern approaches that employ intelligence-based techniques such as neural networks and support vector machines. All these applicable and state-of-art techniques in condition monitoring and fault diagnosis aid in predictive maintenance and identification and have the highly reliable operation of a motor drive system. Furthermore, this paper focuses on the possible transformational impact of electrical machine condition monitoring by thoroughly analyzing each of the monitoring techniques, their corresponding pros and cons, their approaches, and their applicability. It offers strong and useful insights into proactive maintenance measures, improved operating efficiency, and specific recommendations for future applications in the field of diagnostics.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Novel Approaches to Electrical Machine Fault Diagnosis: Volume II)
►
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
Biogas Steam Reforming in Wastewater Treatment Plants: Opportunities and Challenges
Energies 2023, 16(17), 6343; https://doi.org/10.3390/en16176343 (registering DOI) - 01 Sep 2023
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Hydrogen as an energy vector is going to play an important role in the global energy mix. On the other hand, wastewater management has become a worldwide concern, as urban settlements have been considerably increasing for decades. Consequently, biodigestion to produce biogas (rich
[...] Read more.
Hydrogen as an energy vector is going to play an important role in the global energy mix. On the other hand, wastewater management has become a worldwide concern, as urban settlements have been considerably increasing for decades. Consequently, biodigestion to produce biogas (rich in methane) in water treatment plants could be an interesting starting point to obtain a valuable gas that can be converted into hydrogen through steam reforming. The aim of this work was to review the main aspects concerning steam reforming of biogas from wastewater treatment plants. For this purpose, the whole chain, from water treatment to hydrogen production and purification, was considered, paying attention to the main challenges and new technologies for its optimization. Thus, a wide range of possibilities is offered, from direct energy use of syngas to high purification of hydrogen (mainly through pressure swing adsorption or membrane reactors), presenting advantages and disadvantages. In any case, the role of catalysts seems to be essential, and aspects such as hydrogen sulfide and coke deposition control should be addressed. In conclusion, biogas steam reforming applied to wastewater treatment plants is a reality, with serious possibilities for its global implementation at the industrial level, according to techno-economic assessment.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
A Method to Obtain Lightning Peak Current in Indonesia
Energies 2023, 16(17), 6342; https://doi.org/10.3390/en16176342 (registering DOI) - 01 Sep 2023
Abstract
Lightning is a modern societal problem that continues to increase in line with technological growth. Today’s infrastructure is very vulnerable to disturbances caused by weather conditions. The most influential weather phenomenon in this regard is the weather produced by cumulonimbus (CB) clouds. Almost
[...] Read more.
Lightning is a modern societal problem that continues to increase in line with technological growth. Today’s infrastructure is very vulnerable to disturbances caused by weather conditions. The most influential weather phenomenon in this regard is the weather produced by cumulonimbus (CB) clouds. Almost every year, tanks and refineries in Indonesia explode due to lightning strikes. Furthermore, there have been several instances of outages in transmission and distribution lines, as well as lightning-related fatalities in mining areas. Lightning characteristics are widely used as important data for designing lightning protection systems. However, in Indonesia, there is still a need to obtain proper lightning characteristic data. Indonesia is a maritime country located in the tropics, making its geographical conditions highly conducive to the formation of cumulonimbus (CB) clouds. Therefore, this paper presents direct lightning peak-current measurements using magnetic tape, which has been installed in several provinces in Indonesia. The paper reports the local lightning characteristics for these provinces and presents a method for obtaining lightning data. To efficiently collect lightning data on a large scale, we propose a measurement system consisting of a lightning-event counter and magnetic tape. While magnetic tape has been widely used in laboratory testing, this research discusses its application and measurement results in natural lightning conditions in the field. The novel lightning characteristics obtained for several provinces in Indonesia are expected to assist professionals in designing lightning protection systems that match the local lightning characteristics, ultimately minimizing the impact of lightning damage.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic High Voltage Engineering)
►▼
Show Figures
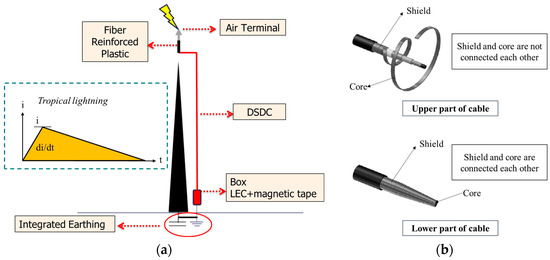
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Influence of the Skin and Proximity Effects on the Thermal Field in a System of Two Parallel Round Conductors
Energies 2023, 16(17), 6341; https://doi.org/10.3390/en16176341 (registering DOI) - 01 Sep 2023
Abstract
This paper presents a semi-analytical method for determining the distribution of the thermal field in a system of two parallel round conductors, taking into account the skin and proximity effects. The method of a suitably constructed Green’s function was applied to find an
[...] Read more.
This paper presents a semi-analytical method for determining the distribution of the thermal field in a system of two parallel round conductors, taking into account the skin and proximity effects. The method of a suitably constructed Green’s function was applied to find an analytical expression for the eigenfunctions describing the temperature distributions. In turn, the relevant integrals, which cannot be determined analytically, were calculated numerically. The foundation of the method is the knowledge of the current density distribution in the conductors. As a result, the steady-state distribution of the temperature field in the conductors for various parameter values can be determined. The obtained numerical results were positively verified using the finite element method. Using the developed method, the share of skin and proximity effects in the temperature rise and steady-state current rating was evaluated. Closed analytical formulas were obtained for the AC case with the skin effect taken into account. When the skin depth is smaller than the wire radius, the skin effect has quite a large impact on the conductor temperature. The impact of the proximity effect is much smaller but clearly noticeable when the distance between the wires is smaller than five times the wire radius. In addition, the influence of the value of the heat transfer coefficient on the thermal field of the conductors was also examined.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Linear and Nonlinear Electric Circuits: Theoretical Analysis and Applications—2nd Edition)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Determinants of Corporate Fossil Energy Assets Impairment and Measurement of Stranded Assets Risk
Energies 2023, 16(17), 6340; https://doi.org/10.3390/en16176340 (registering DOI) - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Climate change and transition risks have become major issues concerning the sustainable development of human society today. And the stranded fossil energy assets generated in this context are gradually becoming an important factor affecting corporate development and the stability of financial markets. Based
[...] Read more.
Climate change and transition risks have become major issues concerning the sustainable development of human society today. And the stranded fossil energy assets generated in this context are gradually becoming an important factor affecting corporate development and the stability of financial markets. Based on the data of China’s A-share listed companies in the high-carbon industry from 1998 to 2021, a two-way fixed-effects model is used to study the determinants of corporate fossil energy asset impairment. Furthermore, a “two-stage estimation approach” is used to measure the risk of stranding corporate fossil energy assets The results show that: (1) climate transition risks are a significant cause of stranded corporate fossil energy assets; (2) the stranded risk of Chinese companies’ fossil energy assets has been oscillating upward over the past two decades; (3) the stranded risk has increased significantly after the “double carbon” target. Based on the above conclusions, this paper puts forward relevant suggestions from both government and enterprise perspectives.
Full article
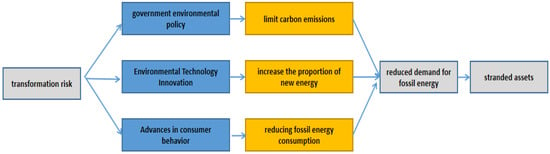
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
A Nonlinear Controller for Point-to-Point Position Control
Energies 2023, 16(17), 6339; https://doi.org/10.3390/en16176339 - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Position control algorithms can be classified into two groups: point-to-point control and continuous path control. For point-to-point control implemented in programmable logic controllers, the speed setpoint is mostly the only setpoint transmitted to the industrial converter. Incorrect settings of the position controller in
[...] Read more.
Position control algorithms can be classified into two groups: point-to-point control and continuous path control. For point-to-point control implemented in programmable logic controllers, the speed setpoint is mostly the only setpoint transmitted to the industrial converter. Incorrect settings of the position controller in PLC may lead to position overshoot or oscillations, which are unacceptable in position control applications. The speed control structure in the industrial converter usually has a fixed structure which does not allow the implementation of advanced speed controller. Moreover, standard library blocks for position control encounter difficulties in diagnostics and tuning. To address these limitations, this paper proposes a novel solution for position control that achieves time-optimal speed trajectory during acceleration and enhanced capabilities during deceleration. The proposed controller was verified by simulations of positioning of zinc ingot feeder unit drive and compared with a standard P-controller. Experimental results confirmed the performance of the proposed controller with the industrial application of a feeder unit.
Full article
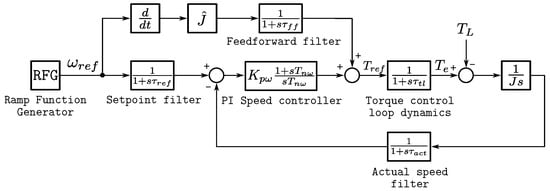
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Dynamic Dose-Based Emergency Evacuation Model for Enhancing Nuclear Power Plant Emergency Response Strategies
Energies 2023, 16(17), 6338; https://doi.org/10.3390/en16176338 (registering DOI) - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
The safe evacuation of residents near a nuclear power plant during a nuclear accident is vital for emergency response planning. To tackle this challenge, considering the dynamic dispersion of radioactive materials in the atmosphere and its impact on evacuation routes under different meteorological
[...] Read more.
The safe evacuation of residents near a nuclear power plant during a nuclear accident is vital for emergency response planning. To tackle this challenge, considering the dynamic dispersion of radioactive materials in the atmosphere and its impact on evacuation routes under different meteorological conditions is crucial. This paper develops a dynamic dose-based emergency evacuation model (DDEEM), which is an efficient and optimized nuclear accident evacuation model based on dynamic radiological dose calculation, utilizing an improved A* algorithm to determine optimal evacuation routes. The DDEEM takes into account the influence of radiological plume dispersion and path selection on evacuation effectiveness. This study employs the DDEEM to assess radiological consequences and evacuation strategies for students residing 5
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Advanced Multi-Physics Modeling, Simulation, and Optimization for Nuclear Technology)
►▼
Show Figures
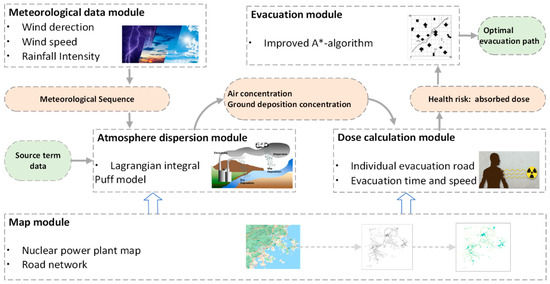
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Predicting Residential Photovoltaic Adoption Intention of Potential Prosumers in Thailand: A Theory of Planned Behavior Model
Energies 2023, 16(17), 6337; https://doi.org/10.3390/en16176337 - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
The current study investigates economic expectations and socio-psychological factors influencing individuals’ residential photovoltaic (RPV) adoption intentions in Thailand. The theory of planned behavior (TPB) and the diffusion of innovation theory provide a framework for our predictor selection. We obtained the data from a
[...] Read more.
The current study investigates economic expectations and socio-psychological factors influencing individuals’ residential photovoltaic (RPV) adoption intentions in Thailand. The theory of planned behavior (TPB) and the diffusion of innovation theory provide a framework for our predictor selection. We obtained the data from a nationwide survey on electricity prosumer infrastructure. RPV non-users (N = 760) were asked to rate their RPV knowledge, attitudes, perceived behavioral controls (PBCs), norms, and innovativeness. They then read scenarios describing the current RPV installation cost and payback rate. They rated their adoption intention and specified their intended system capacity, affordable installation cost, and desirable payback period. The gaps between the actual and desired installation costs and the internal rate of return were calculated. These economic expectation gaps, attitudes based on financial benefits, PBC based on perceived financial barriers, social norms, and innovativeness significantly predicted the adoption intention. On the other hand, perceived knowledge, attitudes based on environmental and image benefits, and PBC based on anticipated troubles and inconveniences failed to predict intention. The implications of the TPB model for RPV adoption were discussed.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic Energy Management and Sustainable Development from Economic, Social and Environmental Aspects)
►▼
Show Figures
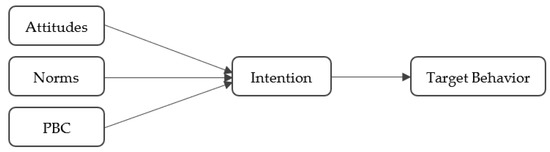
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Optimization Design and Comparative Analysis of Enhanced Heat Transfer and Anti-Vibration Performance of Twisted-Elliptic-Tube Heat Exchanger: A Case Study
Energies 2023, 16(17), 6336; https://doi.org/10.3390/en16176336 - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
The intercooler is a crucial component of the rich gas compressor. Due to the shortcomings of the conventional segmental baffle intercooler, an optimization design of the novel industrial-grade twisted-elliptic-tube intercooler is proposed. This study aims to compare the heat-transfer performance of these two
[...] Read more.
The intercooler is a crucial component of the rich gas compressor. Due to the shortcomings of the conventional segmental baffle intercooler, an optimization design of the novel industrial-grade twisted-elliptic-tube intercooler is proposed. This study aims to compare the heat-transfer performance of these two types of intercoolers in a delayed coking unit at Sinopec. During the plant revamp operation, the original segmental baffle intercooler was replaced by the novel twisted-elliptic-tube intercooler. Experimental determination and comparison analysis of the industrial locale operation of the two types of intercoolers before and after the revamps were conducted. The evaluation results show that the novel twisted-elliptic-tube intercooler has a higher cooling capacity, with a 13.2% increase, compared to the conventional intercooler. Under identical operating conditions, the overall heat-transfer coefficients increase by 87.8%. Moreover, the heat-transfer area and gas pressure drop decrease by 37.4% and 36.9%, respectively. The tube bundles’ vibration and loud noise problems of the old intercooler are eliminated. The average exit temperature of the enriched gas that requires cooling is 38.4 °C, which is 7.3 °C lower than that of the conventional intercooler. These outcomes indicate that utilizing this innovative twisted-elliptic-tube heat exchanger can provide substantial advantages in terms of high heat-transfer efficiency and exceptional anti-vibration performance.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section J1: Heat and Mass Transfer)
►▼
Show Figures
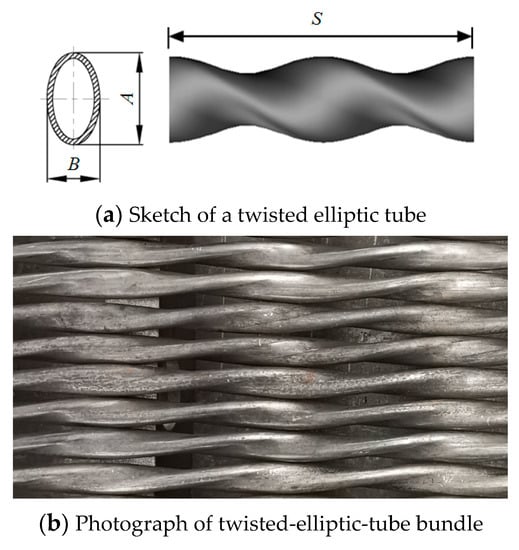
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Analysis of the Seismic Performance of ±500 kV Flexible DC Converter Valves
Energies 2023, 16(17), 6335; https://doi.org/10.3390/en16176335 - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The converter valve is the core equipment of flexible DC transmission, but it has been severely damaged in previous earthquakes. Therefore, the seismic performance of its structure has a significant impact on the safety and reliability of power transmission. To study the seismic
[...] Read more.
The converter valve is the core equipment of flexible DC transmission, but it has been severely damaged in previous earthquakes. Therefore, the seismic performance of its structure has a significant impact on the safety and reliability of power transmission. To study the seismic performance of ±500 kV flexible DC converter valves and identify weak links in the supporting valve tower, this article first established a refined finite-element model of a valve tower based on its physical structure; then modal analysis on the valve tower was conducted; finally, time-domain analysis of the valve tower under three seismic excitations, namely Wenchuan, EI Centro, and artificial, was conducted, and the equivalent stress and directional displacement cloud maps of the key parts of the valve tower were obtained. The research results indicate that the dynamic characteristics of the valve tower are relatively complex, with low fundamental frequency and diverse natural vibration modes. Under earthquake action, the predominant frequency of EI Centro waves is close to the fundamental frequency of the valve tower, which is prone to resonance and causes significant damage to the valve structure. The improved design of the valve tower meets the seismic strength requirements of level 8 seismic intensity.
Full article
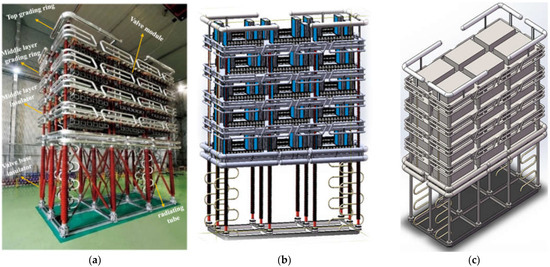
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Battery Energy Storage Systems for the New Electricity Market Landscape: Modeling, State Diagnostics, Management, and Viability—A Review
by
, , , and
Energies 2023, 16(17), 6334; https://doi.org/10.3390/en16176334 - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Renewable energy penetration and distributed generation are key for the transition towards more sustainable societies, but they impose a substantial challenge in terms of matching generation with demand due to the intermittent and unpredictable nature of some of these renewable energy sources. Thus,
[...] Read more.
Renewable energy penetration and distributed generation are key for the transition towards more sustainable societies, but they impose a substantial challenge in terms of matching generation with demand due to the intermittent and unpredictable nature of some of these renewable energy sources. Thus, the role of energy storage in today’s and future electricity markets is undisputed. Batteries stand out among the different alternatives for energy storage. The R&D effort into different battery chemistries contributes to reducing the investment associated with battery systems. However, optimizing their operation according to the users’ and the electricity markets’ needs is the turning point to finally make these systems attractive. This review delves into the topic of battery management systems from a battery-technology-independent perspective, and it also explores more fundamental but related aspects, such as battery modeling or state estimation. The techno-economic part of battery energy storage systems is also covered in this document to understand their real potential and viability.
Full article
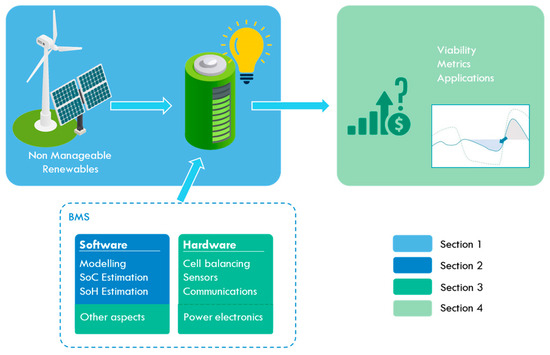
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Prediction of Carbon Price in EU-ETS Using a Geometric Brownian Motion Model and Its Application to Analyze the Economic Competitiveness of Carbon Capture and Storage
by
and
Energies 2023, 16(17), 6333; https://doi.org/10.3390/en16176333 - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
To achieve carbon neutrality, many countries and regions are making efforts to promote the commercialization of greenhouse gas (GHG) mitigation technologies using emissions trading systems (ETSs). Accurate predictions of when the cost of GHG reduction technologies will become competitive below carbon prices could
[...] Read more.
To achieve carbon neutrality, many countries and regions are making efforts to promote the commercialization of greenhouse gas (GHG) mitigation technologies using emissions trading systems (ETSs). Accurate predictions of when the cost of GHG reduction technologies will become competitive below carbon prices could be invaluable to engineers and policy makers. In this study, carbon price movement in the EU-ETS was analyzed using a geometric Brownian motion (GBM) model. Using daily price data for the last 10 years, it tested whether the price pattern of the latter three years could be predicted by applying the first seven years of data to the GBM model. The results showed that the GBM model could well predict the upper and lower bounds of the actual carbon price. Based on the acceptable predictability of the GBM model, simulations were performed using carbon price data over the last decade, showing that carbon prices would reach around 200 EUR/tCO2 by the start of 2026. This is higher than the cost of CO2 avoided evaluated from the costs of commercial-scale carbon capture facilities for coal-fired power plants. This means that carbon capture technologies in the coal-fired power sector could become economically competitive within the next several years.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Energy-Environment-Economy Analysis of Carbon Emissions and the Carbon Trading System)
►▼
Show Figures
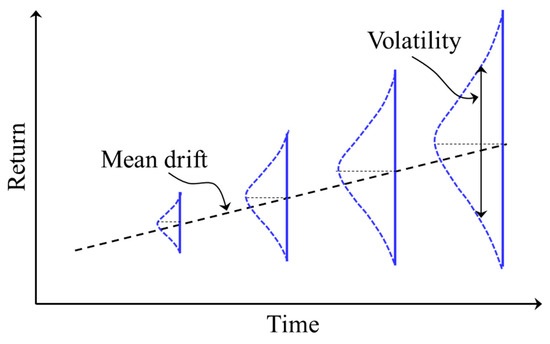
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
A Survey of Time-Series Prediction for Digitally Enabled Maintenance of Electrical Grids
Energies 2023, 16(17), 6332; https://doi.org/10.3390/en16176332 - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
The maintenance of electrical grids is crucial for improving their reliability, performance, and cost-effectiveness. It involves employing various strategies to ensure smooth operation and address potential issues. With the advancement of digital technologies, utilizing time-series prediction has emerged as a valuable approach to
[...] Read more.
The maintenance of electrical grids is crucial for improving their reliability, performance, and cost-effectiveness. It involves employing various strategies to ensure smooth operation and address potential issues. With the advancement of digital technologies, utilizing time-series prediction has emerged as a valuable approach to enhance maintenance practices in electrical systems. The utilization of various recorded data from electrical grid components plays a crucial role in digitally enabled maintenance. However, the comprehensive exploration of time-series data prediction for maintenance is still lacking. This review paper extensively explores different time series that can be utilized to support maintenance efforts in electrical grids with regard to different maintenance strategies and grid components. The digitization of the electrical grids has enabled the collection of diverse time-series data from various network components. In this context, the paper provides an overview of how these time-series and historical-fault data can be utilized for maintenance purposes in electrical grids. Various maintenance levels and time series used for maintenance purposes in different components of the electrical grid are presented.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section F1: Electrical Power System)
►▼
Show Figures
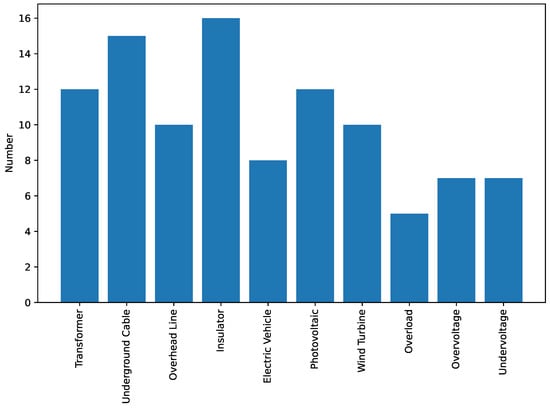
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Review of Methods for Evaluating the Energy Efficiency of Vehicles with Conventional and Alternative Power Plants
Energies 2023, 16(17), 6331; https://doi.org/10.3390/en16176331 - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The evaluation of the energy efficiency of vehicles in operating conditions is used to solve management and control tasks in intelligent transport systems. The modern world fleet is characterized by an increase in the share of vehicles with alternative power plants (hybrid, electric,
[...] Read more.
The evaluation of the energy efficiency of vehicles in operating conditions is used to solve management and control tasks in intelligent transport systems. The modern world fleet is characterized by an increase in the share of vehicles with alternative power plants (hybrid, electric, and hydrogen fuel cells). At the same time, vehicles with conventional power plants (internal combustion engines) remain in operation. A wide range of modern power plants determines the relevance of studying the advantages and limitations of existing methods of evaluating the vehicle energy efficiency, delineating the application scope and highlighting promising directions for their further development. The article systematizes the methods of evaluation and management of the energy efficiency of vehicles with conventional and alternative power plants. Special attention is paid to the assessment of energy consumption per unit of transport work at the stage of vehicle operation, taking into account various operational factors. The concept of a 3D morphological model of the transport system for evaluating the energy efficiency of vehicles is presented. An algorithm for the optimization of the current transport system configuration according to the criterion of an increase in the energy efficiency indicator is given.
Full article
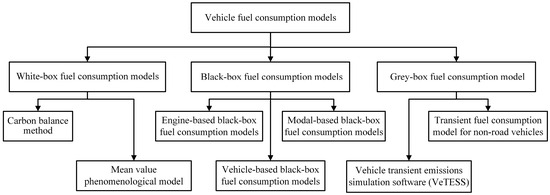
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Design and Implementation of a Dual-Axis Solar Tracking System
by
and
Energies 2023, 16(17), 6330; https://doi.org/10.3390/en16176330 - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
A dual-axis solar tracking system with a novel and simple structure was designed and constructed, as documented in this paper. The photoelectric method was utilized to perform the tracking. The solar radiation values of the designed system and a fixed panel system were
[...] Read more.
A dual-axis solar tracking system with a novel and simple structure was designed and constructed, as documented in this paper. The photoelectric method was utilized to perform the tracking. The solar radiation values of the designed system and a fixed panel system were theoretically estimated and compared, showing that the proposed system is more efficient in collecting solar energy than a fixed solar panel with a 30° tilted fixed surface facing south. The experimental results verified the validity of the prediction as well as the efficiency of the proposed solar tracking system. In a comparison of the data obtained from the measurements, 24.6% more energy was seen to have been obtained in the dual-axis solar tracking system compared to the fixed system. This study possesses potential value in small- and medium-sized photovoltaic applications.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Innovative Design and Research on Solar Thermal Systems)
►▼
Show Figures
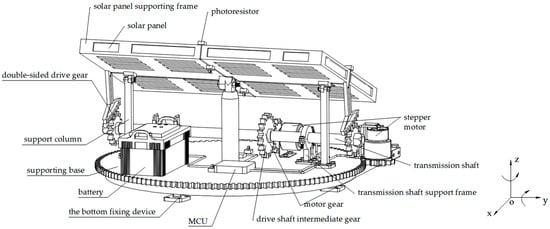
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
A Review of Energy Efficiency Interventions in Public Buildings
Energies 2023, 16(17), 6329; https://doi.org/10.3390/en16176329 - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
This research provides a comprehensive exploration of energy efficiency dynamics in non-residential public buildings such as schools, swimming pools, hospitals, and museums. Recognizing the distinct energy consumption patterns of each building type, the study accentuates the unique challenges they present, with a particular
[...] Read more.
This research provides a comprehensive exploration of energy efficiency dynamics in non-residential public buildings such as schools, swimming pools, hospitals, and museums. Recognizing the distinct energy consumption patterns of each building type, the study accentuates the unique challenges they present, with a particular focus on the continuous and intensive energy demands of hospitals and the unparalleled energy needs of swimming pools. Through an extensive review of various case studies, the research unveils prevailing energy consumption trends, highlighting the role of metrics in assessing energy efficiency and the inherent challenges these metrics face in ensuring uniformity and direct comparability. A core element of this analysis emphasizes the dual nature of technical retrofitting, categorizing interventions into passive and active measures. The research delves into the sustainability imperatives of energy interventions, exploring the economic motivations underpinning retrofit decisions, and the intricate relationship between advanced technological solutions and the behavioral tendencies of building operators and users. Additionally, the study uncovers the influence of external determinants such as climatic factors and government policies in shaping energy consumption in public buildings. In synthesizing these findings, the paper offers insightful recommendations, emphasizing the need for an integrated approach that harmonizes technological innovations with informed operational habits, aiming to optimize energy efficiency in public non-residential buildings.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic Building Energy Efficiency)
►▼
Show Figures
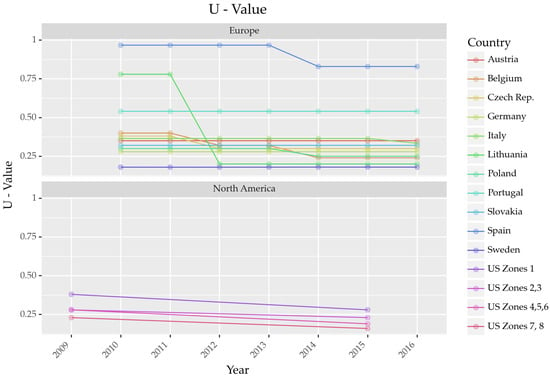
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Remaining Useful Life Prediction of Lithium-Ion Batteries by Using a Denoising Transformer-Based Neural Network
Energies 2023, 16(17), 6328; https://doi.org/10.3390/en16176328 - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
In this study, we introduce a novel denoising transformer-based neural network (DTNN) model for predicting the remaining useful life (RUL) of lithium-ion batteries. The proposed DTNN model significantly outperforms traditional machine learning models and other deep learning architectures in terms of accuracy and
[...] Read more.
In this study, we introduce a novel denoising transformer-based neural network (DTNN) model for predicting the remaining useful life (RUL) of lithium-ion batteries. The proposed DTNN model significantly outperforms traditional machine learning models and other deep learning architectures in terms of accuracy and reliability. Specifically, the DTNN achieved an
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Experiment and Simulation of Energy Storage Systems and Renewable Energy Materials)
►▼
Show Figures
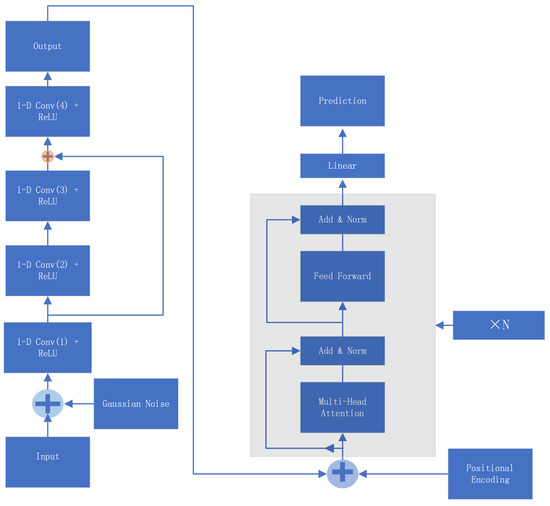
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Enhancing Energy Efficiency and Building Performance through BEMS-BIM Integration
Energies 2023, 16(17), 6327; https://doi.org/10.3390/en16176327 - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
This paper presents a comprehensive analysis of the potential benefits and feasibility of integrating Building Energy Management Systems (BEMSs) with Building Information Modeling (BIM) in, but not limited to, the construction and building management sectors. By examining advantages, challenges, and real-world case studies,
[...] Read more.
This paper presents a comprehensive analysis of the potential benefits and feasibility of integrating Building Energy Management Systems (BEMSs) with Building Information Modeling (BIM) in, but not limited to, the construction and building management sectors. By examining advantages, challenges, and real-world case studies, this study offers valuable insights into the impact of BEMS-BIM integration on building operations. The research methodology includes a literature review and bibliometric analysis to understand the subject domain and identify prevalent keywords. Additionally, case studies demonstrate the effectiveness of BEMS-BIM integration in real-world scenarios. This study investigates the possibilities and challenges of BIM to the BEMS methodology for energy-efficient industrial buildings, emphasizing the importance of addressing uncertainties and enhancing software interoperability. This research highlights the potential of BEMS-BIM integration to revolutionize building performance, enhance sustainability, and contribute to a greener and more efficient future for the construction and building management industries.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Energy Efficiency of the Buildings Ⅱ)
►▼
Show Figures
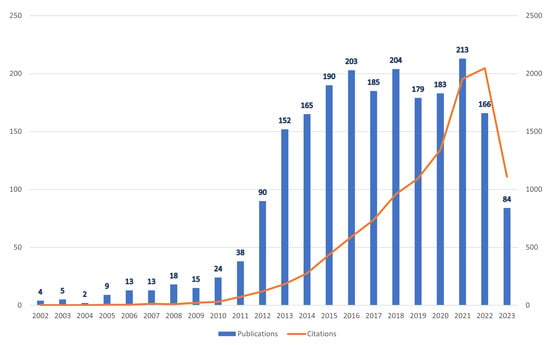
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Large-Scale Ex Situ Tests for CO2 Storage in Coal Beds
by
, , , , , and
Energies 2023, 16(17), 6326; https://doi.org/10.3390/en16176326 - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
This publication discusses the experiments and findings of project ROCCS (Establishing a Research Observatory to Unlock European Coal Seams for Carbon Dioxide Storage), which aimed to investigate the potential for carbon dioxide storage in coal seams. The project involved large-scale ex situ laboratory
[...] Read more.
This publication discusses the experiments and findings of project ROCCS (Establishing a Research Observatory to Unlock European Coal Seams for Carbon Dioxide Storage), which aimed to investigate the potential for carbon dioxide storage in coal seams. The project involved large-scale ex situ laboratory tests, where CO2 was injected into an experimental coal seam using a high-pressure reactor at the Central Mining Institute in Poland. The reactor simulated underground conditions, and the experimental coal seam measured 3.05 m in length with a cross-section of 0.4 × 0.4 m. Parameters such as gas flow, temperatures, and pressures were monitored during the experiments. In the study conducted, the sorption capacity of coal from the Polish mine “Piast-Ziemowit” for CO2, at a sorption pressure of 30 bar, was determined to be 4.8% by weight relative to the raw coal mass. The data collected from these ex situ tests can support the design of a potential commercial-scale CO2 storage installation.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Carbon Dioxide Capture, Utilization and Storage (CCUS) Ⅱ)
►▼
Show Figures
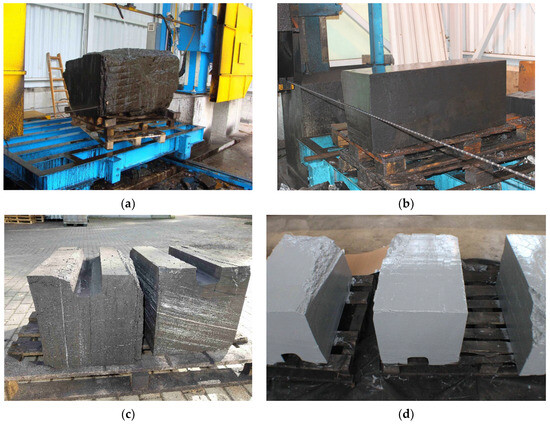
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Investigation of the Impact of Biochar Application on Foaming Slags with Varied Compositions in Electric Arc Furnace-Based Steel Production
by
and
Energies 2023, 16(17), 6325; https://doi.org/10.3390/en16176325 - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
This paper investigates the influence of biochar, either as an individual component or in combination with high-temperature coke, on the slag foaming behavior. High-temperature coke serves as a reference. Three scenarios were considered to study the slag foaming behavior, each characterized by different
[...] Read more.
This paper investigates the influence of biochar, either as an individual component or in combination with high-temperature coke, on the slag foaming behavior. High-temperature coke serves as a reference. Three scenarios were considered to study the slag foaming behavior, each characterized by different slag chemical compositions. The results indicate that biochar can promote steady foaming for specific slags when the basicity (CaO/SiO2) falls within a range of 1.2 to 3.4. Experimental findings also reveal that stable foaming can be achieved when a mixture containing biochar and coke with a ratio of 1:1 is employed, with a minimum slag basicity of 1.0 and FeO content of 25 wt.%. The foaming range obtained using different FeO contents (15 wt.% to 40 wt.%) in the mixture surpasses the range observed with the individual application of coke or biochar. The X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis showed that unrelated to the carbon source applied, the general pattern was that the phases larnite (Ca2SiO4) or dicalcium silicate were detected for slag foams with high basicity. Monticellite (CaMgSiO4) and magnesium iron oxide (Fe2MgO4) were predominant in slag foam samples, with the highest MgO content. The presence of monticellite and merwinite (Ca3MgSi2O8) occurred in samples with the lowest basicity. Eventually, the application of the mixture of coke and biochar showed the potential to obtain stable foaming across a wide range of slag compositions.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Recent Progress in Biomass Pyrolysis and High Value Utilization of Pyrolytic Carbon)
►▼
Show Figures
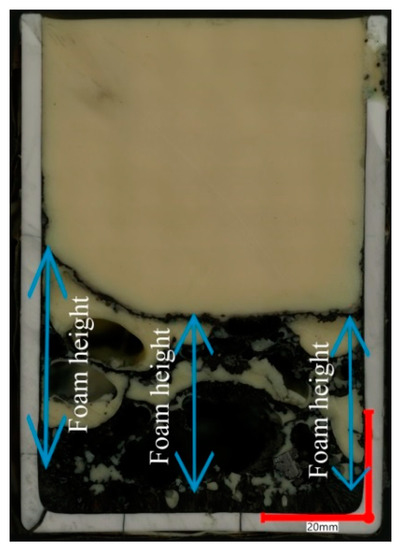
Figure 1

Journal Menu
► ▼ Journal Menu-
- Energies Home
- Aims & Scope
- Editorial Board
- Reviewer Board
- Topical Advisory Panel
- Instructions for Authors
- Special Issues
- Topics
- Sections & Collections
- Article Processing Charge
- Indexing & Archiving
- Editor’s Choice Articles
- Most Cited & Viewed
- Journal Statistics
- Journal History
- Journal Awards
- Society Collaborations
- Conferences
- Editorial Office
Journal Browser
► ▼ Journal BrowserHighly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Energies, Geosciences, JMSE, Minerals, Water
Basin Analysis and Modelling
Topic Editors: Jingshou Liu, Wenlong Ding, Ruyue Wang, Lei Gong, Ke Xu, Ang LiDeadline: 20 September 2023
Topic in
Batteries, Designs, Energies, Materials, Sustainability
Materials for Energy Harvesting and Storage
Topic Editors: Xia Lu, Xueyi LuDeadline: 30 September 2023
Topic in
Coatings, Electronics, Energies, Sensors, Telecom
Condition Monitoring and Diagnostic Methods for Power Equipment in New Energy Power Systems
Topic Editors: Shuaibing Li, Guoqiang Gao, Guochang Li, Yi Cui, Jiefeng Liu, Guangya Zhu, Jin LiDeadline: 15 October 2023
Topic in
Catalysts, Energies, Hydrogen, Molecules, Nanomaterials
Hydrogen Generation, Storage, and Utilization
Topic Editors: In-Hwan Lee, Duy Thanh Tran, Vandung DaoDeadline: 31 October 2023

Conferences
27 October–10 November 2023
The 4th International Electronic Conference on Applied Sciences (ASEC2023)

Special Issues
Special Issue in
Energies
Smart Energy Management for Electric and Hybrid Electric Vehicles
Guest Editor: Daniela ChrenkoDeadline: 6 September 2023
Special Issue in
Energies
Water–Food–Energy Nexus for a Sustainable Use and Management of Natural Resources, Byproducts and Wastes in Agri-Food Systems
Guest Editors: Wei Liao, Attilio Toscano, Francesca ValentiDeadline: 20 September 2023
Special Issue in
Energies
Smart Energy Management and Power Electronic Systems
Guest Editor: Kambiz TehraniDeadline: 30 September 2023
Special Issue in
Energies
The Advances in Wave Energy Extraction Systems
Guest Editor: Mário José Gonçalves Cavaco MendesDeadline: 13 October 2023
Topical Collections
Topical Collection in
Energies
Electric and Hybrid Vehicles Collection
Collection Editor: K. T. Chau
Topical Collection in
Energies
Advances in Heat Transfer Enhancement
Collection Editors: Sergio Nardini, Bernardo Buonomo







.jpg)






