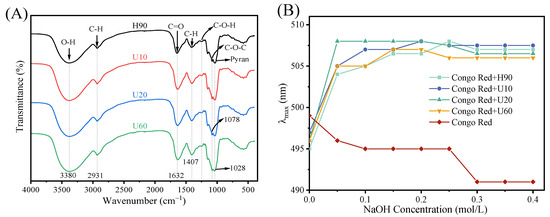
-
 Sweeteners’ Influence on In Vitro α-Glucosidase Inhibitory Activity, Cytotoxicity, Stability and In Vivo Bioavailability of the Anthocyanins from Lingonberry Jams
Sweeteners’ Influence on In Vitro α-Glucosidase Inhibitory Activity, Cytotoxicity, Stability and In Vivo Bioavailability of the Anthocyanins from Lingonberry Jams -
 Food Front-of-Pack Labelling and the Nutri-Score Nutrition Label—Poland-Wide Cross-Sectional Expert Opinion Study
Food Front-of-Pack Labelling and the Nutri-Score Nutrition Label—Poland-Wide Cross-Sectional Expert Opinion Study -
 Are the Blueberries We Buy Good Quality? Comparative Study of Berries Purchased from Different Outlets
Are the Blueberries We Buy Good Quality? Comparative Study of Berries Purchased from Different Outlets
Journal Description
Foods
Foods
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal on food science published semimonthly online by MDPI. The Italian Society of Food Sciences (SISA) and Spanish Nutrition Foundation (FEN) are affiliated with Foods and their members receive discounts on the article processing charges.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within Scopus, SCIE (Web of Science), PubMed, PMC, FSTA, AGRIS, PubAg, and other databases.
- Journal Rank: JCR - Q1 (Food Science & Technology) / CiteScore - Q1 (Health Professions (miscellaneous))
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 15.9 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 2.9 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the first half of 2023).
- Recognition of Reviewers: reviewers who provide timely, thorough peer-review reports receive vouchers entitling them to a discount on the APC of their next publication in any MDPI journal, in appreciation of the work done.
Impact Factor:
5.2 (2022);
5-Year Impact Factor:
5.5 (2022)
Latest Articles
Lentinula edodes Sing Polysaccharide: Extraction, Characterization, Bioactivities, and Emulsifying Applications
Foods 2023, 12(17), 3289; https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12173289 (registering DOI) - 01 Sep 2023
Abstract
In the present work, the optimization of extraction, emulsifying properties, and biological activities of polysaccharides from Lentinula edodes Sing (LES) were studied. The results showed LES polysaccharides extracted by hot water or ultrasonication are a group of β-glucan. Among all the samples, the
[...] Read more.
In the present work, the optimization of extraction, emulsifying properties, and biological activities of polysaccharides from Lentinula edodes Sing (LES) were studied. The results showed LES polysaccharides extracted by hot water or ultrasonication are a group of β-glucan. Among all the samples, the one extracted by hot water showed the best emulsifying capacity. In addition, the results demonstrated that LES polysaccharide had strong scavenging activities in vitro on DPPH and ABTS radicals, which reached the highest level for the one extracted by 90 min ultrasonication (p < 0.05). Overall, Lentinula edodes Sing polysaccharides (LESPs) may have potential applications as emulsifying agents in food industries.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Preparation, Characterization and Application of the Delivery System for Food Products)
►
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
Essential Oils and Their Combination with Lactic Acid Bacteria and Bacteriocins to Improve the Safety and Shelf Life of Foods: A Review
by
, , , , , , and
Foods 2023, 12(17), 3288; https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12173288 (registering DOI) - 01 Sep 2023
Abstract
The use of plant extracts (e.g., essential oils and their active compounds) represents an interesting alternative to chemical additives and preservatives applied to delay the alteration and oxidation of foods during their storage. Essential oils (EO) are nowadays considered valuable sources of food
[...] Read more.
The use of plant extracts (e.g., essential oils and their active compounds) represents an interesting alternative to chemical additives and preservatives applied to delay the alteration and oxidation of foods during their storage. Essential oils (EO) are nowadays considered valuable sources of food preservatives as they provide a healthier alternative to synthetic chemicals while serving the same purpose without affecting food quality parameters. The natural antimicrobial molecules found in medicinal plants represent a possible solution against drug-resistant bacteria, which represent a global health problem, especially for foodborne infections. Several solutions related to their application on food have been described, such as incorporation in active packaging or edible film and direct encapsulation. However, the use of bioactive concentrations of plant derivatives may negatively impact the sensorial characteristics of the final product, and to solve this problem, their application has been proposed in combination with other hurdles, including biocontrol agents. Biocontrol agents are microbial cultures capable of producing natural antimicrobials, including bacteriocins, organic acids, volatile organic compounds, and hydrolytic enzymes. The major effect of bacteriocins or bacteriocin-producing LAB (lactic acid bacteria) on food is obtained when their use is combined with other preservation methods. The combined use of EOs and biocontrol agents in fruit and vegetables, meat, and dairy products is becoming more and more important due to growing concerns about potentially dangerous and toxic synthetic additives. The combination of these two hurdles can improve the safety and shelf life (inactivation of spoilage or pathogenic microorganisms) of the final products while maintaining or stabilizing their sensory and nutritional quality. This review critically describes and collects the most updated works regarding the application of EOs in different food sectors and their combination with biocontrol agents and bacteriocins.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Natural Antimicrobial Agents Utilized in Food Preservation)
►▼
Show Figures
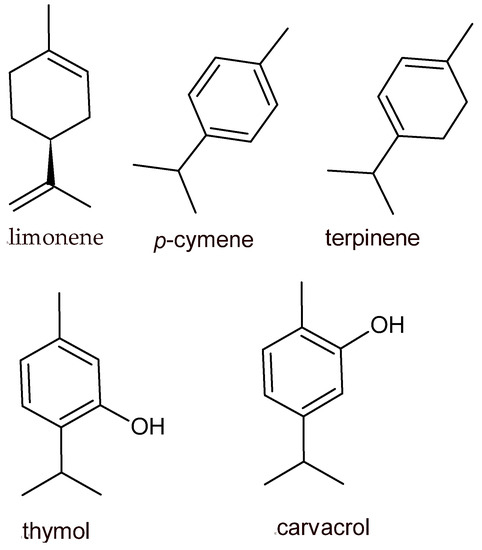
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Three-Dimensional Printing of Foods: A Critical Review of the Present State in Healthcare Applications, and Potential Risks and Benefits
Foods 2023, 12(17), 3287; https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12173287 (registering DOI) - 01 Sep 2023
Abstract
Three-dimensional printing is one of the most precise manufacturing technologies with a wide variety of applications. Three-dimensional food printing offers potential benefits for food production in terms of modifying texture, personalized nutrition, and adaptation to specific consumers’ needs, among others. It could enable
[...] Read more.
Three-dimensional printing is one of the most precise manufacturing technologies with a wide variety of applications. Three-dimensional food printing offers potential benefits for food production in terms of modifying texture, personalized nutrition, and adaptation to specific consumers’ needs, among others. It could enable innovative and complex foods to be presented attractively, create uniquely textured foods tailored to patients with dysphagia, and support sustainability by reducing waste, utilizing by-products, and incorporating eco-friendly ingredients. Notable applications to date include, but are not limited to, printing novel shapes and complex geometries from candy, chocolate, or pasta, and bio-printed meats. The main challenges of 3D printing include nutritional quality and manufacturing issues. Currently, little research has explored the impact of 3D food printing on nutrient density, bioaccessibility/bioavailability, and the impact of matrix integrity loss on diet quality. The technology also faces challenges such as consumer acceptability, food safety and regulatory concerns. Possible adverse health effects due to overconsumption or the ultra-processed nature of 3D printed foods are major potential pitfalls. This review describes the state-of-the-art of 3D food printing technology from a nutritional perspective, highlighting potential applications and current limitations of this technology, and discusses the potential nutritional risks and benefits of 3D food printing.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Food Engineering and Technology)
►▼
Show Figures
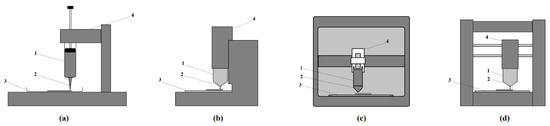
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Valorisation of Side Stream Products through Green Approaches: The Rapeseed Meal Case
by
, , , , , and
Foods 2023, 12(17), 3286; https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12173286 (registering DOI) - 01 Sep 2023
Abstract
Rapeseed meal (RSM) is a by-product of rapeseed oil extraction and is a rich source of bioactive compounds, including proteins and antioxidants. This study compared two methods for extracting antioxidants from RSM: conventional ethanol Soxhlet extraction and supercritical CO2 extraction. These procedures
[...] Read more.
Rapeseed meal (RSM) is a by-product of rapeseed oil extraction and is a rich source of bioactive compounds, including proteins and antioxidants. This study compared two methods for extracting antioxidants from RSM: conventional ethanol Soxhlet extraction and supercritical CO2 extraction. These procedures were applied to both native RSM and RSM after protein removal to evaluate their bio-compound composition and potential applications. HPLC-DAD, NMR, and GC/MS analyses revealed a rich polyphenolic profile in the extracts, including the presence of sinapic acid. The concentration of sinapic acid varied depending on the extraction method used. The anti-radical activity of the extracts was also analysed using the DPPH assay, which confirmed the potential of RSM as a source of antioxidants for use in cosmetics, food, and pharmaceutical formulations.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Green Extraction Techniques of Bioactive Compounds from Food By-Products)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Consumers’ Trust in Different Sources of Information Related to Food Hazards and Their Judgment of Government Performance—A Cross-Sectional Study in Brazil
Foods 2023, 12(17), 3285; https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12173285 (registering DOI) - 01 Sep 2023
Abstract
Trust in institutions is fundamental for the stability and proper functioning of democracies, particularly in matters of high public sensitivity, such as food safety. This study aimed to assess trust levels in different sources of information and respondents’ evaluation of the performance of
[...] Read more.
Trust in institutions is fundamental for the stability and proper functioning of democracies, particularly in matters of high public sensitivity, such as food safety. This study aimed to assess trust levels in different sources of information and respondents’ evaluation of the performance of government agencies responsible for controlling food-related hazards. Individuals interviewed in three environments (hospitals/clinics, supermarkets, universities, N = 1000) answered a face-to-face questionnaire in the Federal District of Brazil, and another population (health surveillance employees at the municipal, state and federal levels; N = 1017) answered the questionnaire online. About 60% of the population interviewed considered government performance to be low/very low. Scientists/universities, medical doctors (MD)/health professionals, and nongovernmental organizations (NGOs) were judged to be the most reliable sources of information on food hazards, while the food industry, supermarkets and social media inspired the lowest trust. Individuals from the hospitals/clinics group had significantly higher trust in MD/health professionals, media and websites than the two other Federal District groups. In general, income and education were the most predictive factors for the results, being negatively associated with assessment of government performance and trust in most information sources. In the Federal District, there was a negative association between trust levels in the government and worry about pesticides and genetically modified food, but a positive association between trust in NGOs and worry on these hazards. The results point to the need for the implementation of more effective communication strategies by institutions in which the population has low trust levels, such as government and food companies.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Sensory and Consumer Sciences)
►▼
Show Figures
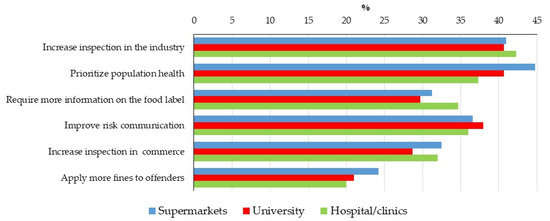
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
A Predictive Model to Correlate Amino Acids and Aromatic Compounds in Calabrian Honeys
Foods 2023, 12(17), 3284; https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12173284 (registering DOI) - 01 Sep 2023
Abstract
To better understand the biochemistry of the organoleptic properties of honey influencing its commercial value, a predictive model for correlating amino acid profiles to aromatic compounds was built. Because the amino acid composition of different varieties of honey plays a key role as
[...] Read more.
To better understand the biochemistry of the organoleptic properties of honey influencing its commercial value, a predictive model for correlating amino acid profiles to aromatic compounds was built. Because the amino acid composition of different varieties of honey plays a key role as a precursor of specific aroma bouquets, it is necessary to relate the amino acid typesetting to aromatic molecules. A selection of unifloral honeys produced in Calabria, South Italy, were used, and a new methodology based on the use of HILIC-UHPLC-ESI-MS/MS and HS-SPME-GC-MS combined with multivariate processing has been developed. This study, carried out for the first time on honey, shows its excellent potential as a modern analytical tool for a rapid multicomponent analysis of food-quality indicators. Data obtained showed strong positive linear correlations between aldehydes and isoleucine, valine, leucine, and phenylalanine. Furans are correlated with isoleucine, leucine, and phenylalanine; hydrocarbons with serine, glutamic acid, and aspartic acid; and ketones with serine, alanine, glutamine, histidine, asparagine, and lysine. Alcohols were more associated with tyrosine than esters with arginine. Proline, tryptophan, and threonine showed poor correlations with all the classes of aroma compounds.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Identification, Characterization and Quantification of Food Compounds Using Chromatography and Mass Spectrometry)
►▼
Show Figures
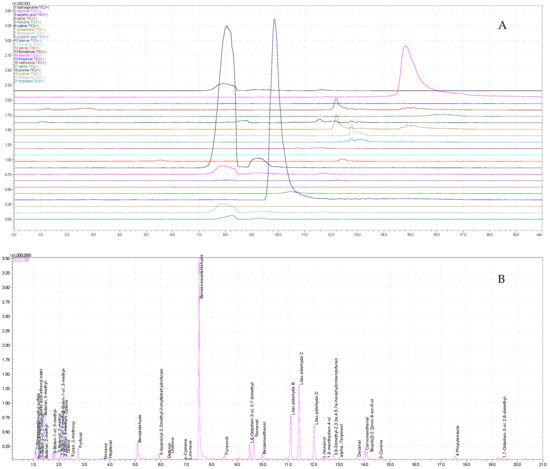
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Sunflower and Palm Kernel Meal Present Bioaccessible Compounds after Digestion with Antioxidant Activity
by
, , , , , and
Foods 2023, 12(17), 3283; https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12173283 (registering DOI) - 01 Sep 2023
Abstract
Sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.) and African palm kernel (Elaeis guineensis Jacq.) are among the most cultivated in the world regarding oil extraction. The oil industry generates a large amount of meal as a by-product, which can be a source of nutrients
[...] Read more.
Sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.) and African palm kernel (Elaeis guineensis Jacq.) are among the most cultivated in the world regarding oil extraction. The oil industry generates a large amount of meal as a by-product, which can be a source of nutrients and bioactive compounds. However, the physiological effects of bioactive compounds in such matrices are only valid if they remain bioavailable and bioactive after simulated gastrointestinal digestion. This study evaluated the chemical composition and antioxidant and prebiotic potential of de-oiled sunflower (DS) and de-oiled palm kernel (DP) meal after in vitro digestion. The DS sample had the highest protein content and the best chemical score, in which lysine was the limiting amino acid. Digested samples showed increased antioxidant activity, measured by in vitro methods. The digested DS sample showed a better antioxidant effect compared to DP. Moreover, both samples managed to preserve DNA supercoiling in the presence of the oxidizing agent. The insoluble fractions after digestion stimulated the growth of prebiotic bacterium, similar to inulin. In conclusion, simulated gastrointestinal digestion promoted in both matrices an increase in protein bioaccessibility and antioxidant capacity, pointing to a metabolic modulation favorable to the organism.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Bioactive Peptides as Natural Antioxidants in Food Industry)
►▼
Show Figures
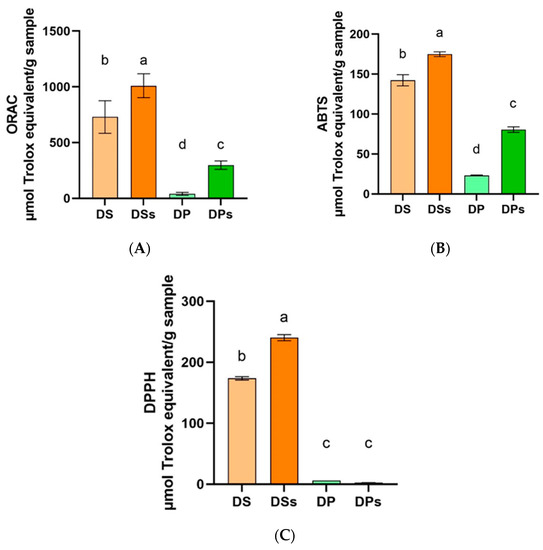
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Processing-Induced Markers in Proteins of Commercial Plant-Based Drinks in Relation to Compositional Aspects
by
, , , and
Foods 2023, 12(17), 3282; https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12173282 (registering DOI) - 01 Sep 2023
Abstract
The consumption of plant-based drinks is increasing, but they represent a product category normally with lower protein content as compared with bovine milk. Furthermore, the products are highly processed and, therefore, the proteins in this product category may carry a significant processing history.
[...] Read more.
The consumption of plant-based drinks is increasing, but they represent a product category normally with lower protein content as compared with bovine milk. Furthermore, the products are highly processed and, therefore, the proteins in this product category may carry a significant processing history. In the present study, a series of 17 freshly produced, commercially available plant-based drinks were benchmarked according to protein-quality parameters. The plant-based drinks represented different plant sources, as well as some mixed products, and were investigated relative to composition, aggregate sizes, presence of non-reducible proteins complexes, and level of processing-induced markers in the proteins. Processing-induced changes in the proteins were determined by a newly developed cocktail method, determining markers related to Maillard and dehydroalanine pathways, as well as intact lysine by triple quadrupole-multiple reaction monitoring-mass spectrometry. It was found that all drinks contained non-reducible protein complexes, but specifically, oat-based drinks represented the largest span contents of processing-induced markers within the proteins, which may relate to their inherent processing histories. Furthermore, it was shown that in products containing added sugar, Maillard reaction-related processing markers were increased over the dehydroalanine pathway.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Food Proteins and Bioactive Peptides: Novel Sources, Characteristic and Application)
►▼
Show Figures
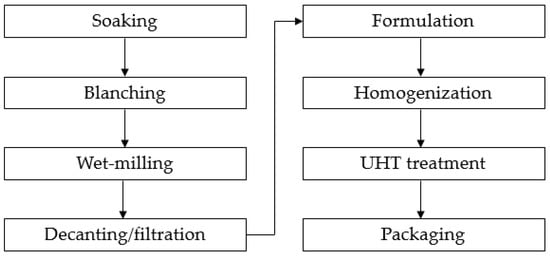
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Utilization of Algae Extracts as Natural Antibacterial and Antioxidants for Controlling Foodborne Bacteria in Meat Products
by
, , , , , , , , , , and
Foods 2023, 12(17), 3281; https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12173281 (registering DOI) - 01 Sep 2023
Abstract
Padina pavonica, Hormophysa cuneiformis, and Corallina officinalis are three types of algae that are assumed to be used as antibacterial agents. Our study’s goal was to look into algal extracts’ potential to be used as food preservative agents and to evaluate
[...] Read more.
Padina pavonica, Hormophysa cuneiformis, and Corallina officinalis are three types of algae that are assumed to be used as antibacterial agents. Our study’s goal was to look into algal extracts’ potential to be used as food preservative agents and to evaluate their ability to inhibit pathogenic bacteria in several meat products (pastirma, beef burger, luncheon, minced meat, and kofta) from the local markets in Alexandria, Egypt. By testing their antibacterial activity, results demonstrated that Padina pavonica showed the highest antibacterial activity towards Bacillus cereus, Staphylococcus aureus, Escherichia coli, Streptococcus pyogenes, Salmonella spp., and Klebsiella pneumoniae. Padina pavonica extract also possesses most phenolic and flavonoid content overall. It has 24 mg gallic acid equivalent/g and 7.04 mg catechol equivalent/g, respectively. Moreover, the algae extracts were tested for their antioxidant activity, and the findings were measured using ascorbic acid as a benchmark. The IC50 of ascorbic acid was found to be 25.09 μg/mL, while Padina pavonica exhibited an IC50 value of 267.49 μg/mL, Corallina officinalis 305.01 μg/mL, and Hormophysa cuneiformis 325.23 μg/mL. In this study, Padina pavonica extract was utilized in three different concentrations (Treatment 1 g/100 g, Treatment 2 g/100 g, and Treatment 3 g/100 g) on beef burger as a model. The results showed that as the concentration of the extract increased, the bacterial inhibition increased over time. Bacillus cereus was found to be the most susceptible to the extract, while Streptococcus pyogenes was the least. In addition, Padina pavonica was confirmed to be a safe compound through cytotoxicity testing. After conducting a sensory evaluation test, it was confirmed that Padina pavonica in meat products proved to be a satisfactory product.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Food Biotechnology)
►▼
Show Figures
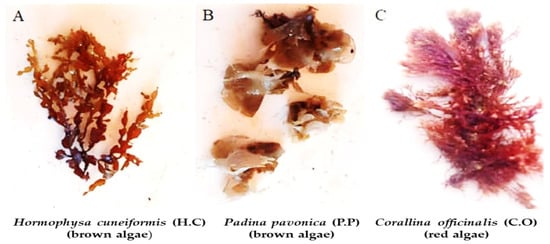
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
The Relationship between “Zero Waste” and Food: Insights from Social Media Trends
Foods 2023, 12(17), 3280; https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12173280 (registering DOI) - 01 Sep 2023
Abstract
Zero waste (ZW), the concept of reducing waste production, is now becoming a lifestyle trend. Social media is strengthening this by popularizing the movement and connecting related communities. ZW and food are closely related, since food waste is a significant sustainability issue; however,
[...] Read more.
Zero waste (ZW), the concept of reducing waste production, is now becoming a lifestyle trend. Social media is strengthening this by popularizing the movement and connecting related communities. ZW and food are closely related, since food waste is a significant sustainability issue; however, the exact relationship between ZW and food communication on social networks is not clear. This study analyzed user communication on the social networking site Twitter between July 2008 and April 2023 to determine how members communicated and shared topics related to ZW and food; an analysis of hashtag frequency was also conducted. During the study period, a total of 50,650 tweets with both #zerowaste and #food hashtags were recorded, written by 21,271 unique users from all over the world. Topic analysis identified the nine related topics: ZW lifestyle, leftover recipes, ZW events, food rescue, climate change, packaging, ZW stores, composting, and ZW restaurants; visual analysis indicated that these topics were closely connected, suggesting common membership of these communities. Overall, our results provide insight into the ZW and food communities on Twitter, which may be useful for marketers, influencers, and government agencies to create targeted content and facilitate wider adoption of a ZW lifestyle.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Solution for Sustainable Food System by Using Application of Green Technologies)
►▼
Show Figures
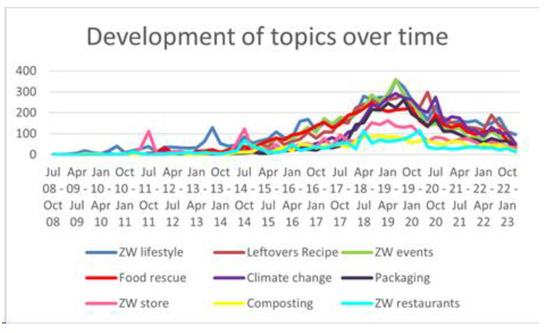
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Utilization of Food-Derived β-Glucans to Prevent and Treat Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)
Foods 2023, 12(17), 3279; https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12173279 (registering DOI) - 01 Sep 2023
Abstract
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) has become the most common chronic liver disease nowadays. Currently, there is no officially approved drug to treat NAFLD. In view of the increasing global prevalence of NAFLD and an absence of treatments, the development of effective treatments
[...] Read more.
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) has become the most common chronic liver disease nowadays. Currently, there is no officially approved drug to treat NAFLD. In view of the increasing global prevalence of NAFLD and an absence of treatments, the development of effective treatments is of utmost importance. β-glucan, a natural bioactive polysaccharide, has demonstrated hepatoprotective effects in NAFLD prevention and treatment. This review solely focuses on gathering the published preclinical animal studies that demonstrated the anti-liver injury, anti-steatotic, anti-inflammatory, anti-fibrotic, and antioxidant activities of β-glucan. The impact of β-glucan on gut microbiota and its metabolites including short-chain fatty acids and bile acids as the underlying mechanism for its bioactive beneficial effect on NAFLD is also explored. Given the limited knowledge of β-glucan on anti-fibrotic activity, bile acid metabolism, and gut microbiota function, additional relevant research is highly encouraged to lay a solid foundation for the use of food-derived β-glucan as a functional food for NAFLD. It is envisaged that further investigation of food-derived β-glucan in human clinical studies should be carried out for its wider utilization.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Biosynthesis, Structure and Utilization of Food-Derived Natural Polysaccharides)
►▼
Show Figures
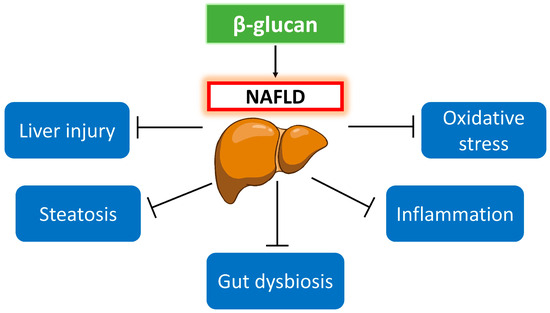
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Systematic Investigation of the Effect of Lactobacillus acidophilus TW01 on Potential Prevention of Particulate Matter (PM)2.5-Induced Damage Using a Novel In Vitro Platform
by
and
Foods 2023, 12(17), 3278; https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12173278 (registering DOI) - 01 Sep 2023
Abstract
Exposure to ambient particulate matter (PM) and cigarette smoking (CS) is a risk factor for respiratory/lung infections and metabolic disorders. Lung–gut axis disruption involving the upregulation of oxidative stress, systemic inflammation, and gut barrier dysfunction by PM is one of the potential mechanisms.
[...] Read more.
Exposure to ambient particulate matter (PM) and cigarette smoking (CS) is a risk factor for respiratory/lung infections and metabolic disorders. Lung–gut axis disruption involving the upregulation of oxidative stress, systemic inflammation, and gut barrier dysfunction by PM is one of the potential mechanisms. Thus, we designed a novel in vitro platform for pre-selecting probiotics with potentially protective effects against PM-induced lung damage through the lung–gut axis to reduce animal usage. The results showed that a high dose of Lactobacillus acidophilus TW01 (1 × 108 CFU/mL) inhibited reactive oxygen species (ROS) production. This strain could also reduce respiratory epithelial cell death induced by cigarette smoke extraction (CSE), as well as promoting Caco-2 cell migration in 1 × 106 CFU/mL. Although further animal experiments are needed to validate the in vitro findings, L. acidophilus TW01 is a promising probiotic strain for the potential prevention of PM2.5-induced damage.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Probiotics: Selection, Cultivation, Evaluation and Application)
►▼
Show Figures
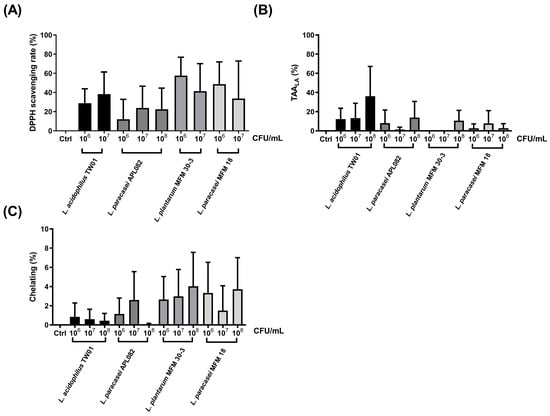
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Exploiting Potential Probiotic Lactic Acid Bacteria Isolated from Chlorella vulgaris Photobioreactors as Promising Vitamin B12 Producers
by
, , , , , , , and
Foods 2023, 12(17), 3277; https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12173277 (registering DOI) - 01 Sep 2023
Abstract
Lactic acid bacteria (LAB) have been documented as potential vitamin B12 producers and may constitute an exogenous source of cobalamin for the microalga Chlorella vulgaris, which has been described as being able to perform vitamin uptake. Hence, there is an interest in
[...] Read more.
Lactic acid bacteria (LAB) have been documented as potential vitamin B12 producers and may constitute an exogenous source of cobalamin for the microalga Chlorella vulgaris, which has been described as being able to perform vitamin uptake. Hence, there is an interest in discovering novel B12-producing probiotic LAB. Therefore, the purpose of the current work was to perform a phenotype–genotype analysis of the vitamin B12 biosynthesis capacity of LAB isolated from C. vulgaris bioreactors, and investigate their probiotic potential. Among the selected strains, Lactococcus lactis E32, Levilactobacillus brevis G31, and Pediococcus pentosaceus L51 demonstrated vitamin B12 biosynthesis capacity, with the latter producing the highest (28.19 ± 2.27 pg mL−1). The genomic analysis confirmed the presence of pivotal genes involved in different steps of the biosynthetic pathway (hemL, cbiT, cobC, and cobD). Notably, P. pentosaceus L51 was the only strain harboring cobA, pduU, and pduV genes, which may provide evidence for the presence of the cobalamin operon. All strains demonstrated the capability to withstand harsh gastrointestinal conditions, although P. pentosaceus L51 was more resilient. The potential for de novo cobalamin biosynthesis and remarkable probiotic features highlighted that P. pentosaceus L51 may be considered the most promising candidate strain for developing high-content vitamin B12 formulations.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Microorganisms and Their Importance in the Food Industry: Safety, Quality and Health Properties)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Antibacterial Activity and Transcriptomic Analysis of Hesperetin against Alicyclobacillus acidoterrestris Vegetative Cells
by
, , , , , and
Foods 2023, 12(17), 3276; https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12173276 (registering DOI) - 01 Sep 2023
Abstract
The aim of this research was to investigate the antimicrobial characteristics and mechanism of hesperetin against Alicyclobacillus acidoterrestris vegetative cells. The results presented show that hesperetin had effective antimicrobial activity on Alicyclobacillus acidoterrestris vegetative cells, minimum inhibition concentration (MIC) of 0.0625 g/L, and
[...] Read more.
The aim of this research was to investigate the antimicrobial characteristics and mechanism of hesperetin against Alicyclobacillus acidoterrestris vegetative cells. The results presented show that hesperetin had effective antimicrobial activity on Alicyclobacillus acidoterrestris vegetative cells, minimum inhibition concentration (MIC) of 0.0625 g/L, and minimum bacterial concentration (MBC) greater than 2 g/L. Moreover, treatment of hesperetin caused significant damage to cell integrity, preventing the growth of Alicyclobacillus acidoterrestris vegetative cells, enhancing the leakage of nucleic acid and proteins, and destroying the vegetative cell morphology. To further investigate the mechanism, transcriptomic analysis was carried out, and 3056 differentially expressed genes (DEGs) were detected. Gene ontology (GO) enrichment analysis revealed that hesperetin inhibits Alicyclobacillus acidoterrestris by affecting the intracellular nitrogen metabolism and amino acid metabolism. The Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) enrichment analysis explained that hesperetin was also able to prevent the growth of Alicyclobacillus acidoterrestris by affecting the processes of nutrient transport, energy metabolism, and flagella motility. These results provide new insights into the antimicrobial effects and mechanism of hesperetin against Alicyclobacillus acidoterrestris, which provides a new method for inactive Alicyclobacillus acidoterrestris in the juice industry.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Food Microbiology)
►▼
Show Figures
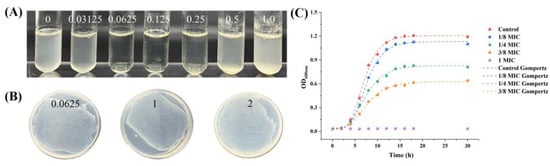
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Improving the Technology of Primary Purification of the Safflower Oil Using Secondary Products of Processing on a Biological Basis
by
, , , , , , , , , and
Foods 2023, 12(17), 3275; https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12173275 - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
Safflower oil is a very valuable product for the body and human health. It is rich in macro- and microelements, vitamins and minerals, and also has antioxidant properties. The primary purification of safflower oil is an important stage of its production and directly
[...] Read more.
Safflower oil is a very valuable product for the body and human health. It is rich in macro- and microelements, vitamins and minerals, and also has antioxidant properties. The primary purification of safflower oil is an important stage of its production and directly affects the quality of the final product and its storage ability. Purifying safflower oil using a combination of filtration and sedimentation processes in an experimental cone-shaped centrifuge is a new direction in its processing. The purpose of this study was to determine the effects of flax fiber as a filter material for safflower oil. The Akmai variety of the safflower was tested. The results showed that the quality indicators of safflower oil before and after filtration through flax fiber are different. The amount of unsaturated fatty acids such as oleic (18.31 ± 0.874%) and cis-linoleic acid (82.52 ± 1.854%) increased, as well as the content of arginine (2.1), tyrosine (0.57), methionine (0.4), cystine (2.5), tryptophan (2.6), and other amino acids (in oil g per 100 g of protein). The increase in the total amount of phenols (322.12 ± 6 mgEAG/kg of oil) was observed, which directly caused the higher antioxidant activity (42.65 ± 8%) of the safflower oil. These results demonstrate that flax fiber can enrich safflower oil. To find the optimal conditions for safflower oil centrifugation in a cone-shaped sedimentary-filtering centrifuge, the thickness of the flax fiber and the distance between the inner and outer perforated filter rotor were tested. It was found that the optimal and effective thickness of the flax fiber is 1.5 × 107 nm, while the thickness of the sediment is 0.5 × 107 nm.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Advances in Processing Technology and the Storage Quality of Edible Oils)
►▼
Show Figures
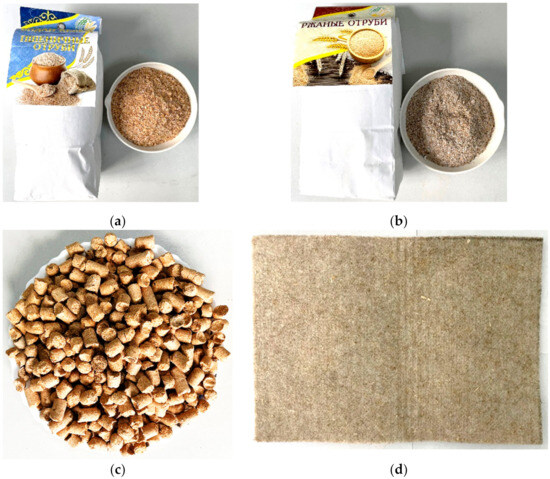

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Production and Characterization of Novel Fabs Generated from Different Phage Display Libraries as Probes for Immunoassays for Gluten Detection in Food
by
, , , , and
Foods 2023, 12(17), 3274; https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12173274 - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
Gluten is the main fraction of wheat proteins. It is widely used in the food industry because of the properties that are generated in the dough, but it is also able to trigger diseases like allergies, autoimmunity processes (such as celiac disease), and
[...] Read more.
Gluten is the main fraction of wheat proteins. It is widely used in the food industry because of the properties that are generated in the dough, but it is also able to trigger diseases like allergies, autoimmunity processes (such as celiac disease), and intolerances in sensitized persons. The most effective therapy for these diseases is the total avoidance of gluten in the diet because it not only prevents damage but also enhances tissue healing. To ensure the absence of gluten in food products labeled as gluten-free, accurate detection systems, like immunoassays, are required. In this work, four recombinant Fab antibody fragments, selected by phage display technology, were produced and tested for specificity and accuracy against gluten in experimental flour mixtures and commercial food products. A high-affinity probe (Fab-C) was identified and characterized. An indirect ELISA test was developed based on Fab-C that complied with the legal detection limits and could be applied in the assessment of gluten-free diets.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Food Analytical Methods)
►▼
Show Figures
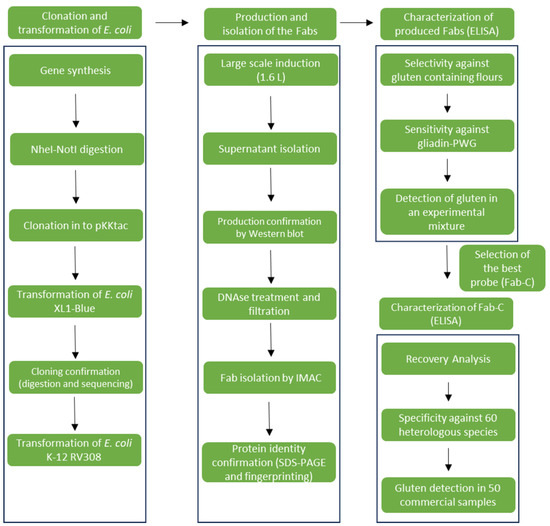
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Effect of Sodium Nitrite, Nisin and Lactic Acid on the Prevalence and Antibiotic Resistance Patterns of Listeria monocytogenes Naturally Present in Poultry
by
, , , and
Foods 2023, 12(17), 3273; https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12173273 - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
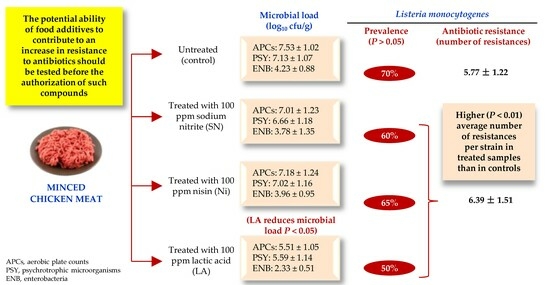
The impact of treating minced chicken meat with sodium nitrite (SN, 100 ppm), nisin (Ni, 10 ppm) and lactic acid (LA, 3000 ppm) on the levels of some microbial groups indicating hygiene quality were investigated. Specifically, aerobic plate counts and culture-based counts of
[...] Read more.
The impact of treating minced chicken meat with sodium nitrite (SN, 100 ppm), nisin (Ni, 10 ppm) and lactic acid (LA, 3000 ppm) on the levels of some microbial groups indicating hygiene quality were investigated. Specifically, aerobic plate counts and culture-based counts of psychrotrophic microorganisms and enterobacteria were obtained. Additionally, the prevalence of Listeria monocytogenes and the resistance of 245 isolates from this bacterium to 15 antibiotics were documented. L. monocytogenes was isolated using the ISO 11290-1:2017 method and confirmed with polymerase chain reaction using the lmo1030 gene. Antibiotic resistance was established using the disc diffusion technique (EUCAST and CLSI criteria). Twenty-four hours after treatment, the microbial load (log10 cfu/g) was reduced (p < 0.05) relative to controls in those samples treated with LA, with counts of 5.51 ± 1.05 (LA-treated samples) vs. 7.53 ± 1.02 (control) for APC, 5.59 ± 1.14 (LA) vs. 7.13 ± 1.07 (control) for psychrotrophic microorganisms and 2.33 ± 0.51 (LA) vs. 4.23 ± 0.88 (control) for enterobacteria. L. monocytogenes was detected in 70% (control samples), 60% (samples receiving SN), 65% (Ni) and 50% (LA) (p > 0.05) of samples. All strains showed resistance to multiple antimicrobials (between 3 and 12). In all, 225 isolates (91.8%) showed a multi-drug resistant (MDR) phenotype, and one isolate (0.4%) showed an extensively drug-resistant (XDR) phenotype. The mean number of resistances per strain was lower (p < 0.01) in the control samples, at 5.77 ± 1.22, than in those receiving treatment, at 6.39 ± 1.51. It is suggested that the use of food additives might increase the prevalence of resistance to antibiotics in L. monocytogenes, although additional studies would be necessary to verify this finding by analyzing a higher number of samples and different foodstuffs and by increasing the number of antimicrobial compounds and concentrations to be tested.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Food Microbiology)
►▼
Show Figures
Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Controlled Release of Phycocyanin in Simulated Gastrointestinal Conditions Using Alginate-Agavins-Polysaccharide Beads
by
, , , , , , and
Foods 2023, 12(17), 3272; https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12173272 - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
C-phycocyanin (CPC) is an antioxidant protein that, when purified, is photosensitive and can be affected by environmental and gastrointestinal conditions. This can impact its biological activity, requiring an increase in the effective amount to achieve a therapeutic effect. Therefore, the aim of this
[...] Read more.
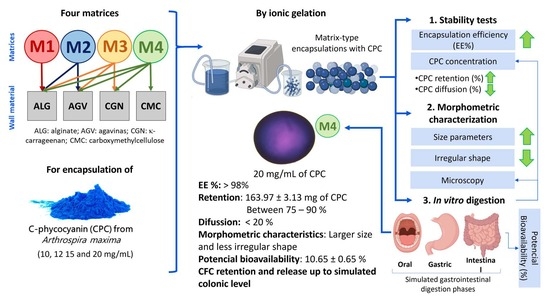
C-phycocyanin (CPC) is an antioxidant protein that, when purified, is photosensitive and can be affected by environmental and gastrointestinal conditions. This can impact its biological activity, requiring an increase in the effective amount to achieve a therapeutic effect. Therefore, the aim of this study was to develop a microencapsulate of a complex matrix, as a strategy to protect and establish a matrix for the controlled release of CPC based on polysaccharides such as agavins (AGV) using ionic gelation. Four matrices were formulated: M1 (alginate: ALG), M2 (ALG and AGV), M3 (ALG, AGV, and κ-carrageenan: CGN), and M4 (ALG, AGV, CGN, and carboxymethylcellulose: CMC) with increasing concentrations of CPC. The retention and diffusion capacities of C-phycocyanin provided by each matrix were evaluated, as well as their stability under simulated gastrointestinal conditions. The results showed that the encapsulation efficiency of the matrix-type encapsulates with complex composites increased as more components were added to the mixtures. CMC increased the retention due to the hydrophobicity that it provides by being in the polysaccharide matrix; CGN enabled the controlled diffusive release; and AGV provided protection of the CPC beads under simulated gastrointestinal conditions. Therefore, matrix M4 exhibited an encapsulation efficiency for CPC of 98% and a bioaccessibility of 10.65 ± 0.65% after the passage of encapsulates through in vitro digestion.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Advances in Encapsulation and Controlled Release of Food Bioactive Components)
►▼
Show Figures
Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Are Chokeberry Products Safe for Health? Evaluation of the Content of Contaminants and Health Risk
by
, , , and
Foods 2023, 12(17), 3271; https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12173271 - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
The health-promoting properties of chokeberry fruit have been confirmed in numerous scientific studies. It has been shown that the consumption of these fruits, due to the high content of bioactive compounds, has beneficial effects in neurodegenerative diseases, in addition to having hypolipemic, hypotensive,
[...] Read more.
The health-promoting properties of chokeberry fruit have been confirmed in numerous scientific studies. It has been shown that the consumption of these fruits, due to the high content of bioactive compounds, has beneficial effects in neurodegenerative diseases, in addition to having hypolipemic, hypotensive, hypoglycemic, and anti-inflammatory properties. However, different conditions and methods of fruit cultivation, as well as methods of juice and fiber production, may result in a high content of toxic substances, which reduce the health value of chokeberry products. Many substances are environmental pollutants. In this study, for the first time, we examined the content of toxic elements (As, Hg, Cd, Pb), nitrates, and nitrites in all chokeberry juices (organic, conventional, from concentrate, and not from fruit concentrate) without additives and in all chokeberry fibers available in Poland. In addition, risk indicators of adverse health effects were calculated. The median content of the contaminants tested in juices was 0.461 µg/kg for As, 1.170 µg/kg for Cd, 0.427 µg/kg for Hg, 1.404 µg/kg for Pb, 4.892 mg/kg for NO2−, and 41.788 mg/kg for NO3−. These values did not exceed the permissible standards for the calculated indicators. There were also no statistically significant differences in the content of Cd, Hg, and Pb, as well as nitrates (III) and nitrates (V), in the tested juices depending on the method of cultivation and juice production. However, statistically significant differences in As content were found between juices from conventional and organic cultivation (1.032 µg/kg vs. 0.458 µg/kg) and juices from concentrate and not from concentrate (1.164 µg/kg vs. 0.460 µg/kg). There were no statistically significant differences with respect to impurities in fibers. It is shown that the consumption of chokeberry juice and fiber in the amount normally consumed does not pose a health risk associated with the intake of toxic substances; in the case of long-term fiber consumption, the Pb content should be monitored. In particular, organic juices and those not from fruit concentrate are recommended due to the lower As content.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Food Risk Assessment and Control of Food Hazards)
Open AccessArticle
The Effect of Vice–Virtue Bundles on Consumers’ Purchase Intentions for Vice Packaged Foods: Evidence from Randomized Experiments
Foods 2023, 12(17), 3270; https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12173270 - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
Packaged foods have significantly expanded their market presence, with the utilization of vice–virtue bundles gaining momentum, particularly in the realm of vice-packaged foods. Consequently, understanding how consumers respond to vice-packaged food with vice–virtue bundles (i.e., vice-packaged food combined with virtue ingredients) becomes crucial.
[...] Read more.
Packaged foods have significantly expanded their market presence, with the utilization of vice–virtue bundles gaining momentum, particularly in the realm of vice-packaged foods. Consequently, understanding how consumers respond to vice-packaged food with vice–virtue bundles (i.e., vice-packaged food combined with virtue ingredients) becomes crucial. This research investigates this issue through four experiments employing a one-way between-subjects design, incorporating distinct stimuli and measures, and involving samples from diverse sources. In Experiment 1 (n = 172), Experiment 2 (n = 169), and the follow-up experiment (n = 153), variance analysis, chi-square test, and mediating analysis demonstrate that consumers are more inclined to purchase vice-packaged food with vice–virtue bundles owing to the perception of it being healthier than vice packaged food with vice–virtue bundles. Furthermore, Experiment 3 (n = 249) employs moderated mediation analysis, uncovering that both the heightened purchase intention for vice-packaged food with vice–virtue bundles and the mediating effect of perceived healthiness are attenuated among consumers with prevention (vs. promotion) focus. Beyond contributing to theories on packaged food consumption, vice–virtue bundles, and regulatory focus theory, these findings hold practical implications for packaged food marketing, promoting rational food choices, and enhancing healthier diets.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Sensory and Consumer Sciences)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1

Journal Menu
► ▼ Journal Menu-
- Foods Home
- Aims & Scope
- Editorial Board
- Reviewer Board
- Topical Advisory Panel
- Instructions for Authors
- Special Issues
- Topics
- Sections & Collections
- Article Processing Charge
- Indexing & Archiving
- Editor’s Choice Articles
- Most Cited & Viewed
- Journal Statistics
- Journal History
- Journal Awards
- Society Collaborations
- Conferences
- Editorial Office
Journal Browser
► ▼ Journal BrowserHighly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Agriculture, Energies, Foods, Sustainability
New Insights in Agriculture: Sustainability, Digitalization and Food Safety
Topic Editors: Kristina Kljak, Klaudija Carović-Stanko, Darija Lemić, Jernej Jakše, Kurt A. Rosentrater, Arup Kumar Goswami, Craig SturrockDeadline: 15 September 2023
Topic in
Applied Sciences, AppliedChem, Foods, MPs, Molecules
Future Food Analysis and Detection - 2nd Volume
Topic Editors: Alessandra Biancolillo, Federico MariniDeadline: 30 September 2023
Topic in
Agriculture, Beverages, Foods, Microorganisms, Toxins
Emerging Food Safety Issues Associated with Mycotoxins
Topic Editors: Wayne L. Bryden, Naresh MaganDeadline: 1 December 2023
Topic in
Foods, Forests, IJERPH, Sustainability, Urban Science
Nature Therapy: The Physiological Effects of Nature on Humans
Topic Editors: Harumi Ikei, Hyunju Jo, Yoshifumi MiyazakiDeadline: 25 December 2023

Conferences
27 October–10 November 2023
The 4th International Electronic Conference on Applied Sciences (ASEC2023)

Special Issues
Special Issue in
Foods
Traditional and Ethnic Foods in the Context of Food Nutritional Security
Guest Editors: Sampat Ghosh, Chuleui Jung, Victor Benno Meyer-RochowDeadline: 1 September 2023
Special Issue in
Foods
Rethinking Agri-Food and Marine Waste and Byproducts for Circular and Sustainable Bio-Based Food Packaging
Guest Editors: Sílvia Petronilho, Mario M. MartinezDeadline: 20 September 2023
Special Issue in
Foods
Safety and Quality of Postharvest Fresh Fruits and Vegetables: 2nd Volume
Guest Editor: Rinaldo BotondiDeadline: 30 September 2023
Special Issue in
Foods
Health Benefits of Dietary Polysaccharides on Metabolic Disorders via Regulating Gut Microbiota
Guest Editors: Dingtao Wu, Ren-You Gan, Yichen HuDeadline: 15 October 2023
Topical Collections
Topical Collection in
Foods
Reviews on Food Microbiology, Foodborne Pathogens, and Probiotics
Collection Editor: Arun K. Bhunia
Topical Collection in
Foods
Food Modelling
Collection Editors: Ursula Gonzales-Barron, Vasco Cadavez
Topical Collection in
Foods
Analytical Chemical Methods Combined with Multivariate Analysis for Food Authenticity Assessment and Quality Evaluation
Collection Editors: Francesco Longobardi, Ana María Jiménez Carvelo
Topical Collection in
Foods
Bioactive Molecules and Health-Promoting Properties in Traditional and Innovative Food and Beverage
Collection Editor: Dario Donno