Journal Description
Life
Life
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal of scientific studies related to fundamental themes in life sciences, from basic to applied research, published monthly online by MDPI. The Astrobiology Society of Britain (ASB) and Spanish Association for Cancer Research (ASEICA) are affiliated with Life and their members receive a discount on the article processing charges.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within Scopus, SCIE (Web of Science), PubMed, PMC, CAPlus / SciFinder, AGRIS, and other databases.
- Journal Rank: JCR - Q2 (Biology) / CiteScore - Q2 (Paleontology)
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 16.9 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 2.6 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the first half of 2023).
- Recognition of Reviewers: reviewers who provide timely, thorough peer-review reports receive vouchers entitling them to a discount on the APC of their next publication in any MDPI journal, in appreciation of the work done.
- Testimonials: See what our editors and authors say about Life.
- Companion journals for Life include: Gastroenterology Insights, Physiologia, Hydrobiology, and Anatomia.
Impact Factor:
3.2 (2022);
5-Year Impact Factor:
3.2 (2022)
Latest Articles
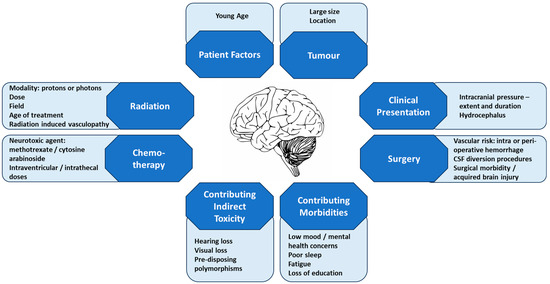
Approaches to Minimise the Neurodevelopmental Impact of Choroid Plexus Carcinoma and Its Treatment
Life 2023, 13(9), 1855; https://doi.org/10.3390/life13091855 (registering DOI) - 01 Sep 2023
Abstract
Choroid plexus carcinomas (CPC) are rare aggressive tumours that primarily affect very young children. Treatment for CPC typically involves a combination of surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy. Whilst considered necessary for a cure, these therapies have significant neurocognitive consequences for patients, negatively impacting
[...] Read more.
Choroid plexus carcinomas (CPC) are rare aggressive tumours that primarily affect very young children. Treatment for CPC typically involves a combination of surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy. Whilst considered necessary for a cure, these therapies have significant neurocognitive consequences for patients, negatively impacting cognitive function including memory, attention, executive functioning, and full-scale intelligence quotients (FSIQ). These challenges significantly impact the quality of life and ultimately socioeconomic parameters such as the level of educational attainment, marital status, and socioeconomic status. This review looks at the tumour- and treatment-related causes of neurocognitive damage in CPC patients and the progress made in finding strategies to reduce these. Opportunities to mitigate the neurodevelopmental consequences of surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy are explored in the context of CPC treatment. Evaluation of the pathological and biological mechanisms of injury has identified innovative approaches to neurocognitive protection and neurorehabilitation, which aim to limit the neurocognitive damage. This review aims to highlight multiple approaches physicians can use when treating young children with CPC, to focus on neurocognitive outcomes as a measure of success.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue The Brain Barriers: Functions and Implications)
►
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
Acquired Male Hypogonadism in the Post-Genomic Era—A Narrative Review
by
, , , , and
Life 2023, 13(9), 1854; https://doi.org/10.3390/life13091854 (registering DOI) - 01 Sep 2023
Abstract
Although precision medicine took its first steps from genomic medicine, it has gone far beyond genomics, considering the full complexity of cellular physiology. Therefore, the present time can be considered as the “post-genomic era”. In detail, proteomics captures the overall protein profile of
[...] Read more.
Although precision medicine took its first steps from genomic medicine, it has gone far beyond genomics, considering the full complexity of cellular physiology. Therefore, the present time can be considered as the “post-genomic era”. In detail, proteomics captures the overall protein profile of an analyzed sample, whilst metabolomics has the purpose of studying the molecular aspects of a known medical condition through the measurement of metabolites with low molecular weight in biological specimens. In this review, the role of post-genomic platforms, namely proteomics and metabolomics, is evaluated with a specific interest in their application for the identification of novel biomarkers in male hypogonadism and in the identification of new perspectives of knowledge on the pathophysiological function of testosterone. Post-genomic platforms, including MS-based proteomics and metabolomics based on ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography-HRMS, have been applied to find solutions to clinical questions related to the diagnosis and treatment of male hypogonadism. In detail, seminal proteomics helped us in identifying novel non-invasive markers of androgen activity to be translated into clinical practice, sperm proteomics revealed the role of testosterone in spermatogenesis, while serum metabolomics helped identify the different metabolic pathways associated with testosterone deficiency and replacement treatment, both in patients with insulin sensitivity and patients with insulin resistance.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Human Infertility and Reproductive Endocrinology)
►▼
Show Figures
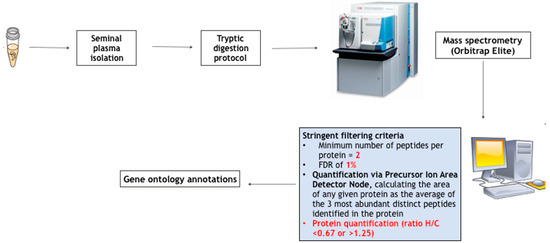
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
A Retrospective Observational Study Using Administrative Databases to Assess the Risk of Spontaneous Abortions Related to Environmental and Socioeconomic Conditions
Life 2023, 13(9), 1853; https://doi.org/10.3390/life13091853 (registering DOI) - 01 Sep 2023
Abstract
Miscarriage is one of the most frequent adverse events that occurs during pregnancy. This retrospective study aimed to verify if the environmental and socioeconomic conditions related to geographical areas where women live, and the socio-demographic and clinical factors play a role in the
[...] Read more.
Miscarriage is one of the most frequent adverse events that occurs during pregnancy. This retrospective study aimed to verify if the environmental and socioeconomic conditions related to geographical areas where women live, and the socio-demographic and clinical factors play a role in the risk of spontaneous abortion (SA). The analyses were conducted by hospital discharge records (HDRs) from public and private hospitals in Apulia from 1 January 2021 to 31 December 2021. Women with an age over 40 years old had a major risk of SA compared with women under 18 years (OR 2.30, IC95%1.16–4.54). A reduction in the risk of SA was found for women with an endocrinological or metabolic disease (OR 0.28, 95% CI 0.19–0.41), while genetic disease greatly increases the risk (OR 9.63, IC95% 1.98–46.86). The greatest risk of spontaneous abortion was found in the province of Taranto compared to the province of Foggia (OR 2.01, 95% CI 1.52–2.64). The provinces with a higher risk of SA in the multiple comparisons were Taranto, Brindisi, and BAT. Municipalities with socioeconomic disadvantages classified as very low, low, and medium had a higher risk of SA compared to the municipalities with a high disadvantage. In conclusion, our study indicates the possible association between SA rate and environmental conditions. Additionally, the socioeconomic, clinical, and demographic factors were related to the risk of SAs.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue The Implications of General Conditions during Pregnancy on Possible Complications for Mother and Fetus)
►▼
Show Figures
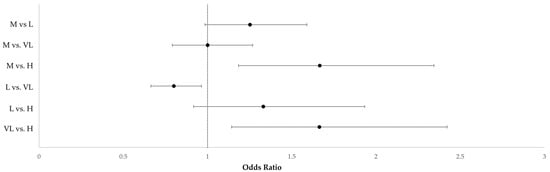
Figure 1
Open AccessPerspective
Circuits and Biomarkers of the Central Nervous System Relating to Astronaut Performance: Summary Report for a NASA-Sponsored Technical Interchange Meeting
by
, , , , , , , , , , and
Life 2023, 13(9), 1852; https://doi.org/10.3390/life13091852 (registering DOI) - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
Biomarkers, ranging from molecules to behavior, can be used to identify thresholds beyond which performance of mission tasks may be compromised and could potentially trigger the activation of countermeasures. Identification of homologous brain regions and/or neural circuits related to operational performance may allow
[...] Read more.
Biomarkers, ranging from molecules to behavior, can be used to identify thresholds beyond which performance of mission tasks may be compromised and could potentially trigger the activation of countermeasures. Identification of homologous brain regions and/or neural circuits related to operational performance may allow for translational studies between species. Three discussion groups were directed to use operationally relevant performance tasks as a driver when identifying biomarkers and brain regions or circuits for selected constructs. Here we summarize small-group discussions in tables of circuits and biomarkers categorized by (a) sensorimotor, (b) behavioral medicine and (c) integrated approaches (e.g., physiological responses). In total, hundreds of biomarkers have been identified and are summarized herein by the respective group leads. We hope the meeting proceedings become a rich resource for NASA’s Human Research Program (HRP) and the community of researchers.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Current Challenges in Space Neuroscience)
Open AccessCase Report
Outcomes of Third-Line Trastuzumab Deruxtecan in a Patient with De Novo Stage 4 HER2-Positive Gastric Adenocarcinoma with Enteroblastic Differentiation: A Case Report
Life 2023, 13(9), 1851; https://doi.org/10.3390/life13091851 (registering DOI) - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
This case report describes the treatment of a patient diagnosed with de novo stage 4 human epidermal growth factor 2 (HER2)-positive gastric adenocarcinoma with enteroblastic differentiation (GAED), a rare and aggressive form of gastric cancer characterized by a tubulopapillary growth pattern and enteroblastic
[...] Read more.
This case report describes the treatment of a patient diagnosed with de novo stage 4 human epidermal growth factor 2 (HER2)-positive gastric adenocarcinoma with enteroblastic differentiation (GAED), a rare and aggressive form of gastric cancer characterized by a tubulopapillary growth pattern and enteroblastic cell lineage markers such as GPC3, SALL4, and alpha fetoprotein. Given the patient’s symptomatic, advanced-stage cancer, treatment objectives were focused on effectively deterring disease progression and ameliorating symptoms throughout the anticipated multiple lines of therapy. Subsequent to standard first- and second-line therapies for HER2-positive metastatic GC, third-line treatment using the antibody-drug conjugate trastuzumab deruxtecan (T-DXd) for seven cycles resulted in satisfactory tumor control and well-preserved physical performance and quality of life, with minimal hematologic and pulmonary toxicities. The patient retained acceptable physical performance to receive subsequent lines of therapies, and still showed a tumor marker response to 5L trastuzumab-based chemotherapy. As the tumor was positive for both HER2 and programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) expressions, the selection and sequencing of anti-HER2 and anti-PD-L1 therapies were discussed in relation to the latest U.S. Food and Drug Administration approvals and trial results.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Current Status and Novel Strategies for Treatment of Therapy-Resistant Cancers)
►▼
Show Figures
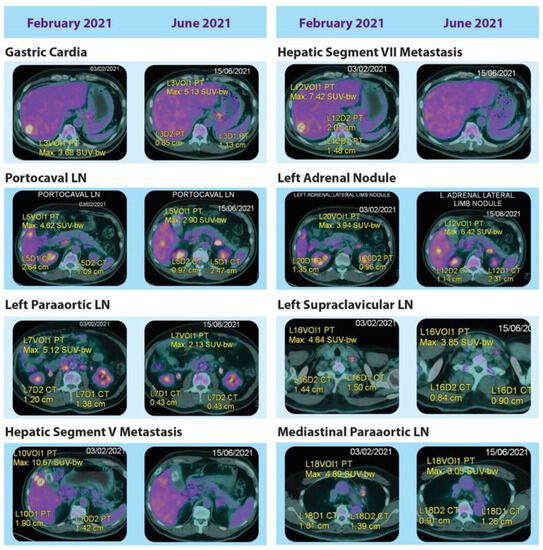
Figure 1
Open AccessOpinion
Planetary Scale Information Transmission in the Biosphere and Technosphere: Limits and Evolution
Life 2023, 13(9), 1850; https://doi.org/10.3390/life13091850 - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
Information transmission via communication between agents is ubiquitous on Earth, and is a vital facet of living systems. In this paper, we aim to quantify this rate of information transmission associated with Earth’s biosphere and technosphere (i.e., a measure of global information flow)
[...] Read more.
Information transmission via communication between agents is ubiquitous on Earth, and is a vital facet of living systems. In this paper, we aim to quantify this rate of information transmission associated with Earth’s biosphere and technosphere (i.e., a measure of global information flow) by means of a heuristic order-of-magnitude model. By adopting ostensibly conservative values for the salient parameters, we estimate that the global information transmission rate for the biosphere might be ∼
(This article belongs to the Section Astrobiology)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Selenium-Containing Organic Fertilizer Application Affects Yield, Quality, and Distribution of Selenium in Wheat
by
, , , , , , , , and
Life 2023, 13(9), 1849; https://doi.org/10.3390/life13091849 - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
This study was designed to investigate the effect on wheat yield of applying organic fertilizers (OF) with five different selenium (Se) concentrations. The mineral nutrients, cadmium (Cd) content, and the distribution of Se in wheat plants were also measured. The results showed that
[...] Read more.
This study was designed to investigate the effect on wheat yield of applying organic fertilizers (OF) with five different selenium (Se) concentrations. The mineral nutrients, cadmium (Cd) content, and the distribution of Se in wheat plants were also measured. The results showed that wheat yields reached a maximum of 9979.78 kg ha−1 in Mengcheng (MC) County and 8868.97 kg ha−1 in Dingyuan (DY) County, Anhui Province, China when the application amount of selenium-containing organic fertilizer (SOF) was up to 600 kg ha−1. Among the six mineral nutrients measured, only the calcium (Ca) content of the grains significantly increased with an increase in the application amount of SOF in the two regions under study. Cd content showed antagonistic effects with the Se content of wheat grains, and when the SOF was applied at 1200 kg ha−1, the Cd content of the grains was significantly reduced by 30.1% in MC and 67.3% in DY, compared with under the Se0 treatment. After application of SOF, the Se content of different parts of the wheat plant ranked root > grain > spike-stalk > glume > leaf > stem. In summary, SOF application at a suitable concentration could increase wheat yields and significantly promote the Ca content of the grains. Meanwhile, the addition of Se effectively inhibited the level of toxic Cd in the wheat grains.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Advances in Novel Biomaterials-Based Fertilizing Products and Bio-Fertilizers for Sustainable Agricultural Production)
►▼
Show Figures
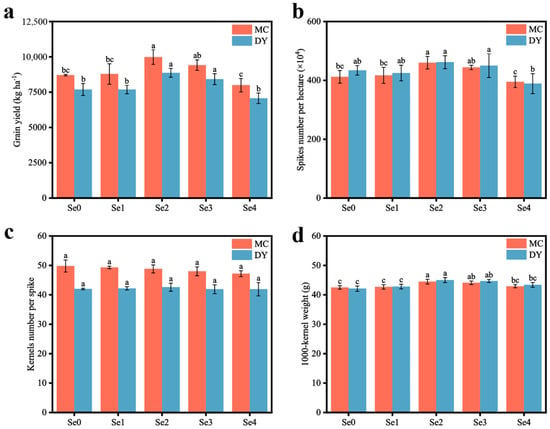
Figure 1
Open AccessCommunication
The Impact of Number of Medications on Falls in Aging Persons with Human Immunodeficiency Virus
Life 2023, 13(9), 1848; https://doi.org/10.3390/life13091848 - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
We aimed to evaluate the impact of polypharmacy on the risk of having a fall in older persons with HIV (PWH). PWH at least 50 years of age who were seen at our institution from September 2012 to August 2017 were included. Unique
[...] Read more.
We aimed to evaluate the impact of polypharmacy on the risk of having a fall in older persons with HIV (PWH). PWH at least 50 years of age who were seen at our institution from September 2012 to August 2017 were included. Unique participants were selected for either a case or control cohort depending on the presence of a documented fall during the study time period. Demographics, HIV-related measures, VACS score, number of medications, as well as the impact of taking benzodiazepines and opioids were compared between the two cohorts. Fall was documented for 637 patients compared to 1534 without a fall during the same time period. Multivariable logistic regression revealed that the total number of medications, having a higher VACS score, taking an opioid, being female sex assigned at birth, and having a lower nadir CD4 count were significantly associated with higher odds of having a fall. In this cohort of older PWH, taking a higher number of non-ARV medications significantly increased the odds of having a fall. In addition, taking an opioid resulted in the highest odds of having a fall. These results suggest the importance of deprescribing and addressing opioid use in reducing the risk of having a fall in older PWH.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Exploration of the Unmet Needs of Aging People Living with HIV)
Open AccessSystematic Review
The Role of Bifidobacterium in COVID-19: A Systematic Review
Life 2023, 13(9), 1847; https://doi.org/10.3390/life13091847 - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
The COVID-19 pandemic, caused by the SARS-CoV-2 virus, mainly causes respiratory and intestinal symptoms and changes in the microbiota of patients. We performed a systematic search in major databases using “Bifidobacterium” and “COVID-19” or “SARS-CoV-2” as key terms to assess the
[...] Read more.
The COVID-19 pandemic, caused by the SARS-CoV-2 virus, mainly causes respiratory and intestinal symptoms and changes in the microbiota of patients. We performed a systematic search in major databases using “Bifidobacterium” and “COVID-19” or “SARS-CoV-2” as key terms to assess the relationship of the genus to COVID-19. After the selection steps, 25 articles were analyzed. Of these, eighteen were observational, and seven were interventional articles that evaluated the use of Bifidobacterium alone or in mix as probiotics for additional treatment of patients with COVID-19. All stages and severities were contemplated, including post-COVID-19 patients. Overall, Bifidobacterium was associated with both protective effects and reduced abundance in relation to the disease. The genus has been found to be abundant in some cases and linked to disease severity. The studies evaluating the use of Bifidobacterium as probiotics have demonstrated the potential of this genus in reducing symptoms, improving pulmonary function, reducing inflammatory markers, alleviating gastrointestinal symptoms, and even contributing to better control of mortality. In summary, Bifidobacterium may offer protection against COVID-19 through its ability to modulate the immune response, reduce inflammation, compete with pathogenic microbes, and maintain gut barrier function. The findings provide valuable insights into the relationship between the disease and the genus Bifidobacterium, highlighting the potential of microbiota modulation in the treatment of COVID-19.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Collection Feature Papers in Microbiology)
►▼
Show Figures
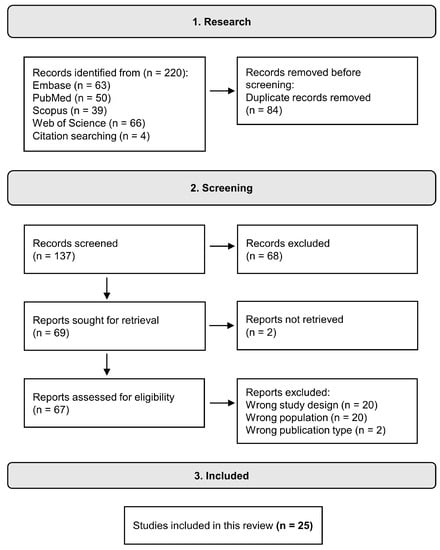
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Effects of Acute Long- versus Short-Interval High-Intensity Interval Training on Attention and Psychological States in a Sample of Male and Female Adolescents: A Pilot Study
Life 2023, 13(9), 1846; https://doi.org/10.3390/life13091846 - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
The aim of this study was to assess the effect of acute short- versus long-interval high-intensity interval training (HIIT) on cognitive performance and psychological states in secondary school students. Fifteen secondary school students (nine males and six females: mean age = 16.2 ±
[...] Read more.
The aim of this study was to assess the effect of acute short- versus long-interval high-intensity interval training (HIIT) on cognitive performance and psychological states in secondary school students. Fifteen secondary school students (nine males and six females: mean age = 16.2 ± 0.4 years, mean Body Mass Index = 21.2 ± 1.5 kg/m2, and maximum oxygen uptake = 42.2 ± 5.9 mL/kg/min) participated in the current study. They performed one of the following three sessions in a randomized order: (i) a long-interval HIIT (LIHIIT), (ii) a short-interval HIIT (SIHIIT), and (iii) a control condition (CC). Cognitive performance and perceived exertion were assessed pre and immediately post each condition using the d2 test and the Rating of Perceived Exertion (RPE) tool, respectively. Mood state was quantified using the Brunel Mood Scale (BRUMS) questionnaire immediately post each condition. The findings reported higher concentration performance in the SIHIIT compared to the LIHIIT condition (p = 0.043) and the CC (p < 0.001) and in the LIHIIT compared to the CC (p = 0.023). Moreover, the total count of errors was higher in the CC than in the LIHIIT (p = 0.01) and in the SIHIIT conditions (p < 0.001) and in the LIHIIT than in the SIHIIT condition (p = 0.03). RPE value was higher in the LIHIIT and SIHIIT conditions than in the CC (both p < 0.001), whereas no statistically significant difference between LIHIIT and SIHIIT conditions (p = 0.24) was found. Regarding the BRUMS, a significant difference between conditions in the fatigue subscale was found, being higher in LIHIIT with respect to SIHIIT (p = 0.03) and CC (p < 0.05). Vigor differed between conditions, with a higher value than in the LIHIIT (p = 0.04) and CC (p < 0.001). All the remaining subscales did not significantly differ between conditions (p > 0.05). Practitioners may implement short-interval HIIT prior to any tasks that require high levels of visual attention.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Effects of Single or Multiple Lifestyle Behaviors on Human Health and Disease-Related Outcomes)
Open AccessReview
Topiramate (Topamax): Evolving Role in Weight Reduction Management: A Narrative Review
by
, , , , , , , and
Life 2023, 13(9), 1845; https://doi.org/10.3390/life13091845 - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
Obesity has emerged as a widespread disease with epidemic proportions, necessitating effective management to enhance the overall health outcomes of patients. Medical intervention for weight loss becomes necessary when diet and exercise prove ineffective, and topiramate emerges as a potential treatment option for
[...] Read more.
Obesity has emerged as a widespread disease with epidemic proportions, necessitating effective management to enhance the overall health outcomes of patients. Medical intervention for weight loss becomes necessary when diet and exercise prove ineffective, and topiramate emerges as a potential treatment option for this global problem. Currently approved as an anti-epileptic and migraine prophylaxis medication, topiramate is frequently utilized as adjunctive therapy for patients with mood and eating disorders, as well as for alcohol use disorders. Its multifaceted mechanisms of action contribute to reducing neuronal excitation and enhancing neuronal inhibition. Given its variety of mechanisms, topiramate shows several off-label outcomes, including weight loss, for patients prescribed this medication. Although the specific mechanism of action concerning weight loss remains uncertain, various hypotheses have been reported. Notably, topiramate may contribute to weight loss by reducing calorie intake, decreasing fat gain, and lowering triglyceride and cholesterol levels. Additionally, its impact on reward pathways associated with food could play a role. Multiple clinical studies have supported the use of topiramate as a weight-loss medication. Notably, the medication demonstrates effectiveness in reducing body weight across different dosages and sustaining weight loss over time, outperforming alternative weight loss methods. Moreover, it was generally well-tolerated in clinical studies, with few side effects observed. In conclusion, topiramate offers promising potential as a weight loss solution and can be a valuable addition to the range of treatment options for combating obesity.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Physiology and Pathology)
►▼
Show Figures
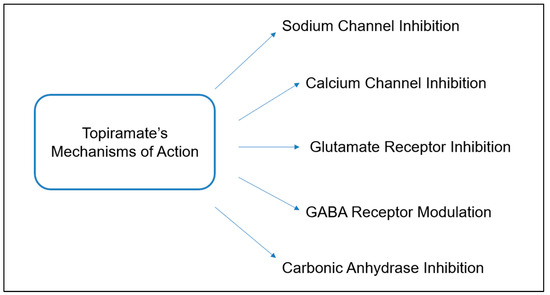
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Relaxing Retinotomy in Recurrent and Refractory Full-Thickness Macular Holes: The State of the Art
by
, , , , , , and
Life 2023, 13(9), 1844; https://doi.org/10.3390/life13091844 - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
The prevailing standard of care for primary repair of full-thickness macular holes (FTMHs) is pars plana vitrectomy with internal limiting membrane (ILM) peeling and gas tamponade, as it gives a high closure rate of roughly 90%. On the other hand, the surgical management
[...] Read more.
The prevailing standard of care for primary repair of full-thickness macular holes (FTMHs) is pars plana vitrectomy with internal limiting membrane (ILM) peeling and gas tamponade, as it gives a high closure rate of roughly 90%. On the other hand, the surgical management of recurrent and refractory FTMHs represents, so far, a demanding and debated subject in vitreoretinal surgery since various approaches have been proposed, with no consensus concerning both adequate selection criteria and the best surgical approach. In addition, the existence of multiple case series/interventional studies showing comparable results and the lack of studies with a direct comparison of multiple surgical techniques may lead to uncertainty. We present an organized overview of relaxing retinotomy technique, a surgical approach available nowadays for the secondary repair of recurrent and refractory FTMHs. Besides the history and the description of the various techniques to perform relaxing retinotomies, we underline the results and the evidence available to promote the use of this surgical approach.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Novel Diagnosis and Therapeutics Approaches in Retina Diseases)
►▼
Show Figures
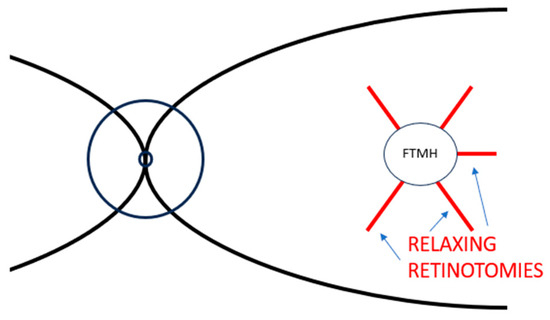
Figure 1
Open AccessCommunication
Biochar Enhances Soil Resource Availability and Suppresses Microbial Metabolism Genes in the Rhizosphere of Wheat
by
, , , , , , , and
Life 2023, 13(9), 1843; https://doi.org/10.3390/life13091843 (registering DOI) - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
Despite the well-documented role of biochar in promoting soil quality and crop productivity, the underlying biological mechanisms remain poorly understood. Here, we explored the effects of straw biochar on soil microbiome in the rhizosphere from wheat using metagenomic sequencing. Our results showed that
[...] Read more.
Despite the well-documented role of biochar in promoting soil quality and crop productivity, the underlying biological mechanisms remain poorly understood. Here, we explored the effects of straw biochar on soil microbiome in the rhizosphere from wheat using metagenomic sequencing. Our results showed that straw return decreased the yields of wheat, while the straw biochar return increased the wheat yields. Further, both the richness and community composition confirmed different effects of the straw return and straw biochar return. The straw biochar return also resulted in greater rhizosphere effects from wheat, represented by resource availability, including soil organic carbon, soil total nitrogen, available phosphorus, and available potassium. The rhizosphere effects from wheat, represented by microbial metabolism genes involved in carbon, nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium cycling, however, were decreased by straw biochar returning. In addition, the rhizosphere effects from nitrogen content and the nitrogen cycling genes showed negative relationships with wheat yields. Together, these results revealed that straw biochar enhanced soil resource availability but suppressed microbial metabolism genes in the rhizosphere from wheat, supporting the idea that straw biochar serves as a nutrient pool for crops.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Advances in Novel Biomaterials-Based Fertilizing Products and Bio-Fertilizers for Sustainable Agricultural Production)
►▼
Show Figures
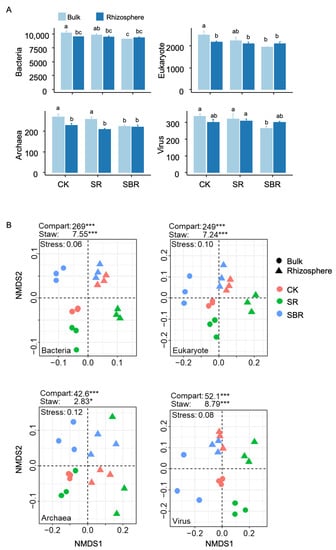
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
A Review Study of the Participation of Late Domains in Sorting and Transport of Viral Factors to Exosomes
by
, , , , , , , , , and
Life 2023, 13(9), 1842; https://doi.org/10.3390/life13091842 - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
Cellular communication depends heavily on the participation of vesicular systems generated by most cells of an organism. Exosomes play central roles in this process. Today, these vesicles have been characterized, and it has been determined that the cargo they transport is not within
[...] Read more.
Cellular communication depends heavily on the participation of vesicular systems generated by most cells of an organism. Exosomes play central roles in this process. Today, these vesicles have been characterized, and it has been determined that the cargo they transport is not within a random system. In fact, it depends on various molecular signals and the recruitment of proteins that participate in the biogenesis of exosomes. It has also been shown that multiple viruses can recruit these vesicles to transport viral factors such as genomes or proteins. It has been shown that the late domains present in viral proteins are critical for the exosomal selection and biogenesis systems to recognize these viral proteins and introduce them into the exosomes. In this review, the researchers discuss the evidence related to the characterization of these late domains and their role in exosome recruitment during viral infection.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue New Insights into Extracellular Vesicles in Health and Disease)
►▼
Show Figures
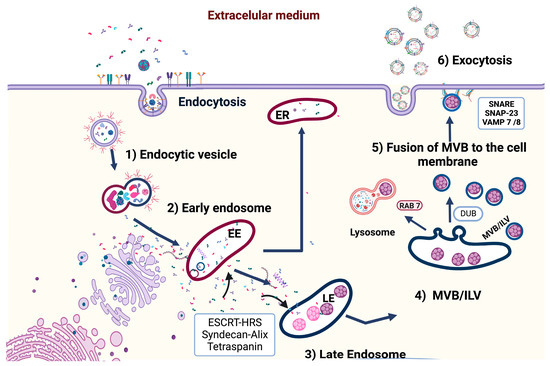
Figure 1
Open AccessCommunication
Clinical Outcomes of Patients with Multiple Myeloma after Daratumumab Failure
by
, , , , , , , , and
Life 2023, 13(9), 1841; https://doi.org/10.3390/life13091841 - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
Anti-CD38 monoclonal antibody (MoAB) therapy has significantly improved the prognosis of patients with multiple myeloma. However, not all patients sustain durable responses. We aimed to describe the natural history of patients relapsed or refractory (R/R) to CD38 MoAB therapy. We performed a single-center,
[...] Read more.
Anti-CD38 monoclonal antibody (MoAB) therapy has significantly improved the prognosis of patients with multiple myeloma. However, not all patients sustain durable responses. We aimed to describe the natural history of patients relapsed or refractory (R/R) to CD38 MoAB therapy. We performed a single-center, retrospective analysis of the clinical characteristics and outcomes of 81 patients with multiple myeloma who progressed after treatment with daratumumab. Our cohort was heavily pretreated, with a median of two lines prior to daratumumab and only 17 patients received daratumumab as a first line. A total of 38.2% had received a previous autologous stem cell transplantation (ASCT), and 61.7% had received both an immunomodulatory drug (IMID) and a proteasome inhibitor (PI). The median overall survival (OS) was 21 months for the global cohort but it decreased to 14 months for triple-class refractory patients and 5 months for penta-refractory patients. Most of the patients (83.9%) received treatment after daratumumab progression, in many cases with second generation IMID or PI, but seven patients were treated with anti-BCMA therapy and three patients received CART therapy within a clinical trial. In conclusion, patients R/R to daratumumab represent an unmet clinical need with poor prognosis and in need of incorporation of new treatments.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Multiple Myeloma: Focus on Clinical Practice in the Era of Molecular Analysis)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Pre-Pandemic Distribution of Bacterial Species in Nasopharyngeal Swab Specimens from Pediatric and Adult Patients Detected via RT-PCR Using the Allplex Respiratory Panel
Life 2023, 13(9), 1840; https://doi.org/10.3390/life13091840 - 30 Aug 2023
Abstract
Background: Recently, panel-based molecular diagnostics for the simultaneous detection of respiratory viruses and bacteria in nasopharyngeal swab (NPS) specimens have been highlighted. We identified the distribution of bacterial species in NPS specimens collected from pediatric and adult patients by employing RT-PCR (Allplex respiratory
[...] Read more.
Background: Recently, panel-based molecular diagnostics for the simultaneous detection of respiratory viruses and bacteria in nasopharyngeal swab (NPS) specimens have been highlighted. We identified the distribution of bacterial species in NPS specimens collected from pediatric and adult patients by employing RT-PCR (Allplex respiratory panel 4, RP4, Seegene) to estimate its applicability in a panel-based assay for detecting respiratory viruses. Methods: We used 271 and 173 NPS specimens from pediatric and adult patients, respectively. The results of the Allplex RP4 panel using NPS (NPS-RP4) from adult patients were compared with those of the Seeplex PneumoBacter ACE Detection assay (Seegene), which used sputum for testing (sputum-Seeplex). Results: A total of 147 specimens (54.2%) were positive for the NPS-RP4 panel in pediatric patients. There were 94, 77, 10, 3, 3, and 2 specimens that were positive for Haemophilus influenzae (HI), Streptococcus pneumoniae (SP), Mycoplasma pneumoniae (MP), Chlamydia pneumoniae (CP), Bordetella pertussis (BP), and B. parapertussis (BPP), respectively. Among 173 adult patients, 39 specimens (22.5%) were positive in the NPS-RP4. Thirty specimens were positive for HI, and 13 were positive for SP. One specimen tested positive for both MP and Legionella pneumophila (LP). CP, BP, and BPP results were all negative. However, 126 specimens (72.8%) had positive results with sputum-Seeplex (99 SP, 59 HI, three LP, and two MP), and the overall percentage of agreement between the two assays was 39.3% in the adult patients. Conclusions: Bacterial species in NPS from more than half of pediatric patients were detected. Performing the Allplex RP4 assay with NPS revealed additional respiratory bacteria that are not detected in current clinical practices, which do not include bacterial testing, demanding the use of sputum specimens. However, the use of NPS showed low agreement with standard assays using sputum in adult patients. Thus, more research is needed to develop a reliable RT-PCR method using NPS specimens in adult patients.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Microbiology)
►▼
Show Figures
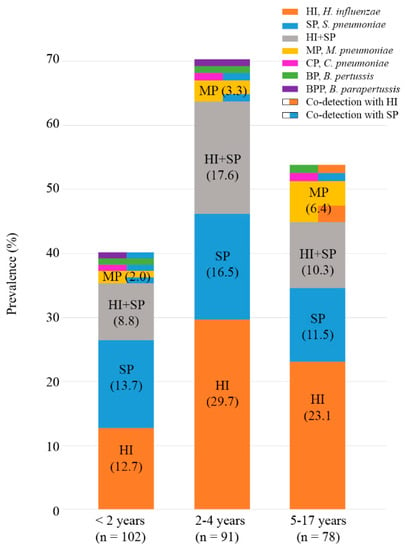
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Anti-Yeasts, Antioxidant and Healing Properties of Henna Pre-Treated by Moist Heat and Molecular Docking of Its Major Constituents, Chlorogenic and Ellagic Acids, with Candida albicans and Geotrichum candidum Proteins
Life 2023, 13(9), 1839; https://doi.org/10.3390/life13091839 - 30 Aug 2023
Abstract
Lawsonia inermis, known as henna, has traditionally been utilized in cosmetics and folk medicine because of their valuable health effects. A lack of information about the processes that increase or decrease release, as well as the biological activities of constituents of natural
[...] Read more.
Lawsonia inermis, known as henna, has traditionally been utilized in cosmetics and folk medicine because of their valuable health effects. A lack of information about the processes that increase or decrease release, as well as the biological activities of constituents of natural origin, is an important pharmacological problem. This investigation evaluates the influence of moist heat on the flavonoid and phenolic contents of henna powder and their biological activities. HPLC analysis reflected the existence of 20 and 19 compounds of flavonoids and phenolics in the extract of unpre-treated henna by moist heat (UPMH) and pre-treated henna by moist heat (PMH). Several compounds such as chlorogenic acid, ellagic acid, rutin, rosmarinic acid, kaempferol, and pyrocatechol occurred with high concentrations of 57,017.33, 25,821.09, 15,059.88, 6345.08, 1248.42, and 819.19 µg/mL UPMH while occurred with low concentrations of 44,286.51, 17,914.26, 3809.85, 5760.05, 49.01, and 0.0 µg/mL, respectively in PMH. C. albicans, C. tropicalis, and G. candidum were more affected by UPMH with inhibition zones of 30.17 ± 0.29, 27 ± 0.5, and 29 ± 1.5 mm than PMH with inhibition zones of 29 ± 0.5, 25.33 ± 0.58, and 24.17 ± 0.29 mm, respectively. UPMH henna exhibited less MIC and MFC against the tested yeasts than PMH. Moreover, UPMH henna showed good wound healing, where the rat of migration, wound closure %, and area difference % were 14.806 um, 74.938 um2, and 710.667% compared with PMH henna 11.360 um, 59.083 um2, 545.333%, respectively. Antioxidant activity of UPMH and PMH henna. Promising antioxidant activity was recorded for both UPMH or PMH henna with IC50 5.46 µg/mL and 7.46 µg/mL, respectively. The docking interaction of chlorogenic acid and ellagic acid with the crystal structures of G. candidum (4ZZT) and C. albicans (4YDE) was examined. The biological screening demonstrated that the compounds had favorable docking results with particular proteins. Chlorogenic acid had robust behavior in the G. candidum (4ZZT) active pocket and displayed a docking score of −7.84379 Kcal/mol, higher than ellagic acid’s −6.18615 Kcal/mol.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Therapeutic Effects of Natural Products on Human Diseases)
►▼
Show Figures
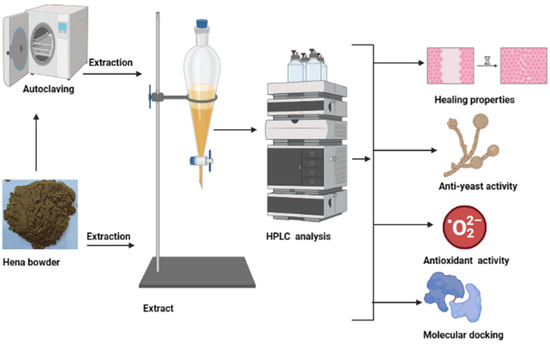
Figure 1
Open AccessCommunication
Evaluation of the Effects of Radiation Therapy on Muscle Contractibility and Skin Healing: An Experimental Study of the Cancer Treatment Implications
by
, , , , , , , , and
Life 2023, 13(9), 1838; https://doi.org/10.3390/life13091838 - 30 Aug 2023
Abstract
Background: Radiotherapy can affect healthy cells, resulting in side effects. This study aimed to assess the impact of radiotherapy on soft tissue in surgical wounds in rats. Methods: The animals were divided into four groups: control (S) group without irradiation, immediate irradiation (S-IIr)
[...] Read more.
Background: Radiotherapy can affect healthy cells, resulting in side effects. This study aimed to assess the impact of radiotherapy on soft tissue in surgical wounds in rats. Methods: The animals were divided into four groups: control (S) group without irradiation, immediate irradiation (S-IIr) group receiving irradiation right after surgery, late irradiation (S-LIr) group receiving irradiation four weeks after surgery, and early irradiation (Ir-S) group receiving irradiation before surgery. The irradiated groups underwent two fractional stages of 15 Gy. Muscle contractibility (EMG) was evaluated at two different time points, and after 2 and 7 weeks, the animals were euthanized for histological analysis of the muscles and skin. Results: There was no significant difference between the EMG1 and EMG2 values of the S and S-LIr groups, but both S-IIr and Ir-S groups exhibited a statistically significant difference. The S group demonstrated a larger diameter of muscle fiber compared to other groups, showing a significant difference. In terms of skin analysis, the S-IIr group had the least inflammatory infiltrate and the highest amount of red fibers, differing significantly from the other groups. Conclusions: Regardless of the duration, radiotherapy was found to have effects on the surrounding soft tissues, as concluded by this study.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Radiobiology and Nuclear Medicine)
►▼
Show Figures
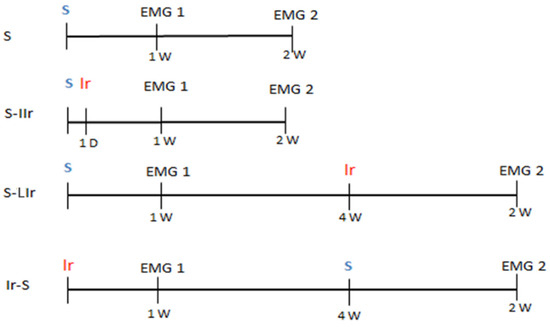
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
COVID-19 and Laboratory Markers from Romanian Patients—A Narrative Review
by
, , , , , , , , , , , and
Life 2023, 13(9), 1837; https://doi.org/10.3390/life13091837 - 30 Aug 2023
Abstract
COVID-19 has significantly impacted the whole world, and Romania was no exception. Biomarkers play a crucial role in understanding and managing the disease. However, research regarding laboratory analyses for patients with COVID-19 is fairly limited. For detection, PCR testing is still considered the
[...] Read more.
COVID-19 has significantly impacted the whole world, and Romania was no exception. Biomarkers play a crucial role in understanding and managing the disease. However, research regarding laboratory analyses for patients with COVID-19 is fairly limited. For detection, PCR testing is still considered the golden standard, while antibodies are still useful for monitoring both patients and their vaccination status. In our country, biomarkers such as CRP, LDH, transaminases, cardiac, and iron markers have been used to assess the status of patients and even predict illness outcome. CRP, IL-6, LDH, FER, fibrinogen, creatinine, and vitamin D levels have been associated with increased severity, risk of ICU admission, and death. Cardiac markers and D-dimers are also good predictors, but their role seems more important in patients with complications. HDL cholesterol and BUN levels were also suggested as potential biomarkers. Hematological issues in SARS-CoV-2 infections include neutrophilia, lymphopenia and their ratio, while PCT, which is a marker of bacterial infections, is better to be used in patients with co- or supra-infections. The current research is a narrative review that focuses on the laboratory results of Romanian COVID-19 patients. The goal of this article is to provide an update on the research on biomarkers and other laboratory tests conducted inside the borders of Romania and identify gaps in this regard. Secondly, options for further research are discussed and encouraged.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Current Research on SARS-CoV-2)
►▼
Show Figures
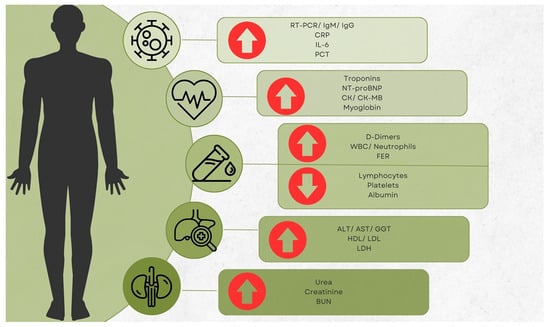
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Small Bowel Imaging from Stepchild of Roentgenology to MR Enterography, Part II: The Reliable Disclosure of Crohn’s Disease and Non-Inflammatory Small Bowel Disorder Plot through MRI Findings
by
, , , , , , , , , and
Life 2023, 13(9), 1836; https://doi.org/10.3390/life13091836 - 30 Aug 2023
Abstract
MRE has become a standard imaging test for evaluating patients with small bowel pathology, but a rigorous methodology for describing and interpreting the pathological findings is mandatory. Strictures, abscess, inflammatory activity, sinus tract, wall edema, fistula, mucosal lesions, strictures, and mesentery fat hypertrophy
[...] Read more.
MRE has become a standard imaging test for evaluating patients with small bowel pathology, but a rigorous methodology for describing and interpreting the pathological findings is mandatory. Strictures, abscess, inflammatory activity, sinus tract, wall edema, fistula, mucosal lesions, strictures, and mesentery fat hypertrophy are all indicators of small bowel damage in inflammatory and non-inflammatory small bowel disease, and they are all commonly and accurately explained by MRE. MRE is a non-invasive modality that accurately assesses the intra-luminal, parietal, and extra-luminal small bowel. Differential MRE appearance allows us to distinguish between Crohn’s disease and non-inflammatory small bowel disorder. The purpose of this paper is to present the MRE pathological findings of small bowel disorder.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Imaging of Gastrointestinal Diseases: Issues and Challenges)
►▼
Show Figures
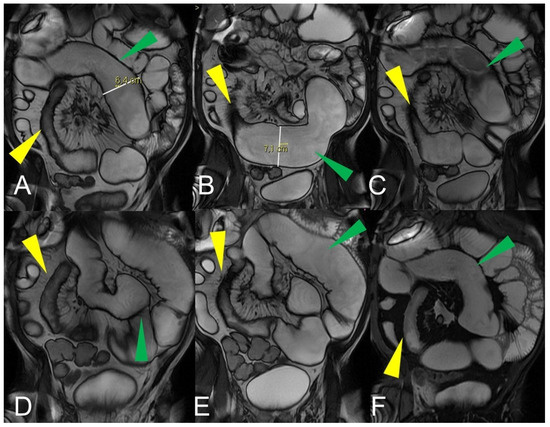
Figure 1

Journal Menu
► ▼ Journal Menu-
- Life Home
- Aims & Scope
- Editorial Board
- Reviewer Board
- Topical Advisory Panel
- Instructions for Authors
- Special Issues
- Topics
- Sections & Collections
- Article Processing Charge
- Indexing & Archiving
- Editor’s Choice Articles
- Most Cited & Viewed
- Journal Statistics
- Journal History
- Journal Awards
- Society Collaborations
- Conferences
- Editorial Office
Journal Browser
► ▼ Journal BrowserHighly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Animals, Behavioral Sciences, Diversity, Insects, Life
Arthropod Biodiversity: Ecological and Functional Aspects
Topic Editors: Paolo Solari, Giorgia Sollai, Roberto Massimo Crnjar, Anita Giglio, Piero G. GiulianiniDeadline: 30 September 2023
Topic in
Gastroenterology Insights, Infectious Disease Reports, Life, Microbiology Research, Microorganisms
High-Throughput Analyses as a Multi-Faceted Approach for Characterizing the Human Microbiota
Topic Editors: Simone Filardo, Rosa Sessa, Andrea Carolina EntrocassiDeadline: 30 October 2023
Topic in
Diversity, Geosciences, Life, Quaternary, Animals, Fishes, Minerals, Heritage
Unanswered Questions in Palaeontology
Topic Editors: Eric Buffetaut, Julien ClaudeDeadline: 15 November 2023
Topic in
Agronomy, Biophysica, IJMS, Life, Plants
Biophysics of Photosynthesis: From Molecules to the Field
Topic Editors: Vasily Ptushenko, Alexei SolovchenkoDeadline: 1 December 2023

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
Life
Upper Respiratory Tract Disorders: From Pathophysiology to Innovative Approaches
Guest Editors: Geng-He Chang, Pei-Rung YangDeadline: 1 September 2023
Special Issue in
Life
Motor Neuron Disease
Guest Editor: Jessica MandrioliDeadline: 22 September 2023
Special Issue in
Life
ILASOL Annual Meetings: Astrobiology and Origin of Life
Guest Editors: Tal Mor, Amri WandelDeadline: 30 September 2023
Special Issue in
Life
Exploiting the Biochemical Properties of Essential Oils for Healthy Products
Guest Editors: Omar Méridas, Azucena González Coloma, Marie-Laure FauconnierDeadline: 18 October 2023
Topical Collections
Topical Collection in
Life
Function, Regulation, and Dysfunction of Intrinsically Disordered Proteins
Collection Editors: Giuliana Fusco, Stefano Gianni, Sonia Longhi
Topical Collection in
Life
Research Updates in Chronic Kidney Disease
Collection Editors: Emilio Nardi, Giuseppe Mule
Topical Collection in
Life
Antimicrobial Resistance
Collection Editors: Caterina Aurilio, Antonella Paladini, Pasquale Sansone, Vincenzo Pota








_9.50.52.png)







