Journal Description
Mathematics
Mathematics
is a peer-reviewed, open access journal which provides an advanced forum for studies related to mathematics, and is published semimonthly online by MDPI. The European Society for Fuzzy Logic and Technology (EUSFLAT) and International Society for the Study of Information (IS4SI) are affiliated with Mathematics and their members receive a discount on article processing charges.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within Scopus, SCIE (Web of Science), RePEc, and other databases.
- Journal Rank: JCR - Q1 (Mathematics) / CiteScore - Q1 (General Mathematics)
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 17.7 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 2.7 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the first half of 2023).
- Recognition of Reviewers: reviewers who provide timely, thorough peer-review reports receive vouchers entitling them to a discount on the APC of their next publication in any MDPI journal, in appreciation of the work done.
- Sections: published in 13 topical sections.
- Companion journals for Mathematics include: Foundations, AppliedMath and Analytics.
Impact Factor:
2.4 (2022);
5-Year Impact Factor:
2.3 (2022)
Latest Articles
An Optimal Control Problem Related to the RSS Model
Mathematics 2023, 11(17), 3762; https://doi.org/10.3390/math11173762 (registering DOI) - 01 Sep 2023
Abstract
In this paper, we consider a discrete-time optimal control problem related to the model of Robinson, Solow and Srinivasan. We analyze this optimal control problem without concavity assumptions on a non-concave utility function which represents the preferences of the planner and establish the
[...] Read more.
In this paper, we consider a discrete-time optimal control problem related to the model of Robinson, Solow and Srinivasan. We analyze this optimal control problem without concavity assumptions on a non-concave utility function which represents the preferences of the planner and establish the existence of good programs and optimal programs which are Stiglitz production programs.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Optimal Control Theory and Its Applications in Medical and Biological Sciences)
Open AccessArticle
Portrait Sketch Generative Model for Misaligned Photo-to-Sketch Dataset
Mathematics 2023, 11(17), 3761; https://doi.org/10.3390/math11173761 (registering DOI) - 01 Sep 2023
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
A deep-learning-based model for generating line-based portrait sketches from portrait photos is proposed in this paper. The misalignment problem is addressed by the introduction of a novel loss term, designed to tolerate misalignments between Ground Truth sketches and generated sketches. Artists’ sketching strategies
[...] Read more.
A deep-learning-based model for generating line-based portrait sketches from portrait photos is proposed in this paper. The misalignment problem is addressed by the introduction of a novel loss term, designed to tolerate misalignments between Ground Truth sketches and generated sketches. Artists’ sketching strategies are mimicked by dividing the portrait into face and hair regions, with separate models trained for each region, and the outcomes subsequently combined. Our contributions include the resolution of misalignment between photos and artist-created sketches, and high-quality sketch results via region-based model training. The experimental results show the effectiveness of our approach in generating convincing portrait sketches, with both quantitative and visual comparisons to State-of-the-Art techniques. The quantitative comparisons demonstrate that our method preserves the identity of the input portrait photos, while applying the style of Ground Truth sketch.
Full article
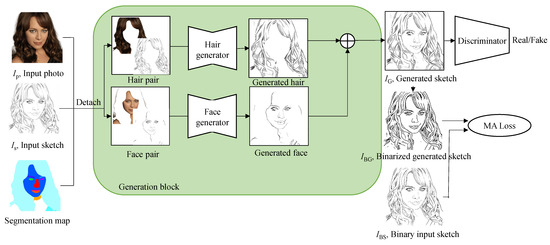
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Bivariate Unit-Weibull Distribution: Properties and Inference
Mathematics 2023, 11(17), 3760; https://doi.org/10.3390/math11173760 (registering DOI) - 01 Sep 2023
Abstract
In this article, we introduce a novel bivariate probability distribution that is absolutely continuous. Considering the Farlie–Gumbel–Morgenstern (FGM) copula and the unit-Weibull distribution, we can obtain a bivariate unit-Weibull distribution. We evaluate the main properties of the new proposal and use two estimation
[...] Read more.
In this article, we introduce a novel bivariate probability distribution that is absolutely continuous. Considering the Farlie–Gumbel–Morgenstern (FGM) copula and the unit-Weibull distribution, we can obtain a bivariate unit-Weibull distribution. We evaluate the main properties of the new proposal and use two estimation methods to estimate the parameter for the bivariate probability distribution. A brief Monte Carlo simulation study is conducted to assess the behavior of the employed estimation method and the characteristics of the estimators. Ultimately, as an illustration, a real-life application is presented, demonstrating the utility of the proposal.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Probability, Statistics & Symmetry)
►▼
Show Figures
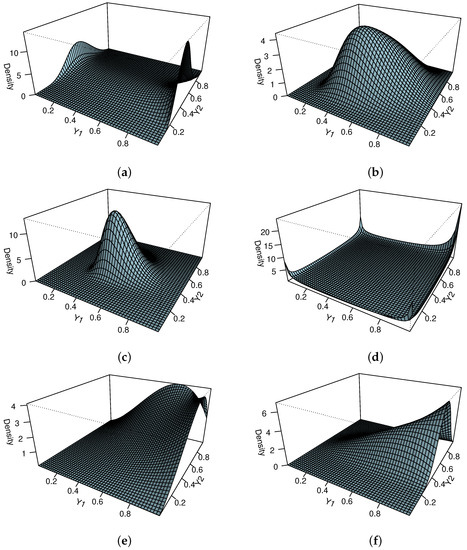
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Enhancing the Security and Privacy in the IoT Supply Chain Using Blockchain and Federated Learning with Trusted Execution Environment
Mathematics 2023, 11(17), 3759; https://doi.org/10.3390/math11173759 (registering DOI) - 01 Sep 2023
Abstract
Federated learning has emerged as a promising technique for the Internet of Things (IoT) in various domains, including supply chain management. It enables IoT devices to collaboratively learn without exposing their raw data, ensuring data privacy. However, federated learning faces the threats of
[...] Read more.
Federated learning has emerged as a promising technique for the Internet of Things (IoT) in various domains, including supply chain management. It enables IoT devices to collaboratively learn without exposing their raw data, ensuring data privacy. However, federated learning faces the threats of local data tampering and upload process attacks. This paper proposes an innovative framework that leverages Trusted Execution Environment (TEE) and blockchain technology to address the data security and privacy challenges in federated learning for IoT supply chain management. Our framework achieves the security of local data computation and the tampering resistance of data update uploads using TEE and the blockchain. We adopt Intel Software Guard Extensions (SGXs) as the specific implementation of TEE, which can guarantee the secure execution of local models on SGX-enabled processors. We also use consortium blockchain technology to build a verification network and consensus mechanism, ensuring the security and tamper resistance of the data upload and aggregation process. Finally, each cluster can obtain the aggregated parameters from the blockchain. To evaluate the performance of our proposed framework, we conducted several experiments with different numbers of participants and different datasets and validated the effectiveness of our scheme. We tested the final global model obtained from federated training on a test dataset and found that increasing both the number of iterations and the number of participants improves its accuracy. For instance, it reaches 94% accuracy with one participant and five iterations and 98.5% accuracy with ten participants and thirty iterations.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Hybrid Data Processing by Combining Machine Learning, Expert, Safety and Security)
►▼
Show Figures
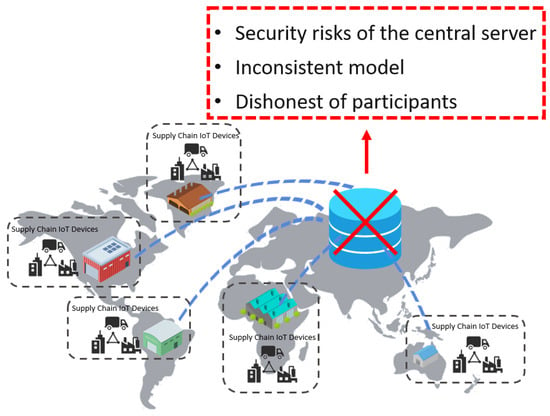
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Automatic Creation of 3D Documentation in CAD/BIM Based on Topology
Mathematics 2023, 11(17), 3758; https://doi.org/10.3390/math11173758 (registering DOI) - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
This paper deals with reverse engineering, namely the as-built documentation of actual construction. The input is data measured in the field using geodetic methods. In addition to modern methods of surveying 3D objects, such as laser scanning, it is still necessary to use
[...] Read more.
This paper deals with reverse engineering, namely the as-built documentation of actual construction. The input is data measured in the field using geodetic methods. In addition to modern methods of surveying 3D objects, such as laser scanning, it is still necessary to use classic surveying using a total station. The bottleneck of the process is the creation of documentation of the construction, which is still created manually in the appropriate CAD/BIM software. The goal of this research was to find a method that would reduce the amount of manual work when drawing documentation in CAD/BIM to a minimum. The core of the solution is the use of a topology that interconnects the points measured in-field. The entire procedure has two parts: (1) creating a topological drawing template in a suitable CAD/GIS software (digital sketch) and (2) adding geometry to this sketch and creating a drawing using topological codes. This method was verified in practice by applying it to several specific buildings in the Czech Republic. The practical application of the method demonstrated 30% time savings and a reduction in work and error rate in the entire process.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Applications of Cloud Computing, Big Data, and Data Dissemination in Information Engineering)
►▼
Show Figures
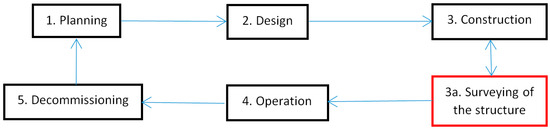
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
The Economic Value of Dual-Token Blockchains
Mathematics 2023, 11(17), 3757; https://doi.org/10.3390/math11173757 - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
It is standard for blockchain platforms to issue native tokens, or crytpocurrencies, that users must own to operate within the platform. Some blockchains, however, decided to issue two tokens, establishing a dual system, with one token typically for governance and the other for
[...] Read more.
It is standard for blockchain platforms to issue native tokens, or crytpocurrencies, that users must own to operate within the platform. Some blockchains, however, decided to issue two tokens, establishing a dual system, with one token typically for governance and the other for implementing functions on the blockchain, such as executing transactions or smart contracts. Therefore, the two tokens are used for different activities. Typically, owning the governance tokens gives the right to receive the other token for free, as a reward for participating in the blockchain decision-making and voting processes. However, both tokens can also be traded on some exchange nodes, which means that platform functions could be implemented even without owning governance tokens. In this paper, we discuss some economic fundamentals of dual-token blockchain platforms—in particular, how to establish their economic value and the market relative attractiveness of the two tokens. We do so by introducing some simple numerical indicators, based on prices, and traded circulating monetary quantities. Such indicators, which are meant to reflect the platform’s view on the tokens’ market desirability, could be computed in real time and used to support the platform’s policy making.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Modeling and Simulation Analysis of Blockchain System)
Open AccessArticle
Transfer-Matrix Method for Calculus of Long Cylinder Tube with Industrial Applications
Mathematics 2023, 11(17), 3756; https://doi.org/10.3390/math11173756 - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
The Transfer-Matrix Method (TMM) is an original and relatively simple mathematical approach for the calculus of thin-walled cylindrical tubes presented in this work. Calculation with TMM is much less used than calculation with the Finite Elements Method (FEM), even though it is much
[...] Read more.
The Transfer-Matrix Method (TMM) is an original and relatively simple mathematical approach for the calculus of thin-walled cylindrical tubes presented in this work. Calculation with TMM is much less used than calculation with the Finite Elements Method (FEM), even though it is much easier to apply in different fields. That is why it was considered imperative to present this original study. The calculus is based on Dirac’s and Heaviside’s functions and operators and on matrix calculation. The state vectors, the transfer-matrix, and the vector corresponding to the external efforts were defined, which were then used in the calculations. A matrix relation can be written, which gives the state vector of the last section depending on the state vector of the first section, a relation in which the conditions of the two end supports can be set. As an application, a heat exchanger was studied, with a large cylinder subjected to a uniformly distributed internal load, and from the inner cylinder bundle, a cylinder subjected to both uniform internal and external loads was considered. For the second cylinder, two possibilities of action for the external forces were considered, a successive action and a simultaneous action, achieving the same results in both situations. The TMM is intended to be used for iterative calculus in optimization problems where rapid successive results are required. In the future, we want to expand this method to other applications, and we want to develop related programs. This is an original theoretical study and is a complement to the research in the field on thin-walled cylinder tubes and their applications in heat exchangers.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Control Theory and Applications)
Open AccessArticle
Numerical Solutions of Stochastic Differential Equations with Jumps and Measurable Drifts
Mathematics 2023, 11(17), 3755; https://doi.org/10.3390/math11173755 (registering DOI) - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
This paper deals with numerical analysis of solutions to stochastic differential equations with jumps (SDEJs) with measurable drifts that may have quadratic growth. The main tool used is the Zvonkin space transformation to eliminate the singular part of the drift. More precisely, the
[...] Read more.
This paper deals with numerical analysis of solutions to stochastic differential equations with jumps (SDEJs) with measurable drifts that may have quadratic growth. The main tool used is the Zvonkin space transformation to eliminate the singular part of the drift. More precisely, the idea is to transform the original SDEJs to standard SDEJs without singularity by using a deterministic real-valued function that satisfies a second-order differential equation. The Euler–Maruyama scheme is used to approximate the solution to the equations. It is shown that the rate of convergence is
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Advanced Numerical Analysis and Scientific Computing)
►▼
Show Figures
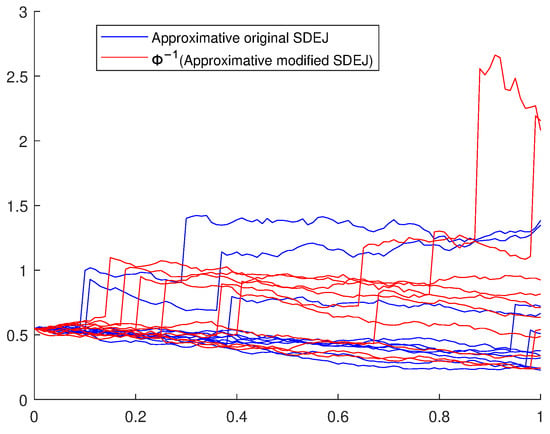
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Existence of Solutions for Planar Kirchhoff–Choquard Problems
by
and
Mathematics 2023, 11(17), 3754; https://doi.org/10.3390/math11173754 - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
In this article, we are interested in the study of the following Kirchhoff–Choquard equations:
[...] Read more.
In this article, we are interested in the study of the following Kirchhoff–Choquard equations:
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Nonlinear Equations: Theory, Methods, and Applications III)
Open AccessArticle
The Existence of Entropy Solutions for a Class of Parabolic Equations
by
and
Mathematics 2023, 11(17), 3753; https://doi.org/10.3390/math11173753 - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
The existence and uniqueness of entropy solutions for a class of parabolic equations involving a
The existence and uniqueness of entropy solutions for a class of parabolic equations involving a
Open AccessArticle
A Novel Prediction Model for Seawall Deformation Based on CPSO-WNN-LSTM
Mathematics 2023, 11(17), 3752; https://doi.org/10.3390/math11173752 - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
Admittedly, deformation prediction plays a vital role in ensuring the safety of seawall during its operation period. However, there still is a lack of systematic study of the seawall deformation prediction model currently. Moreover, the absence of the major influencing factor selection is
[...] Read more.
Admittedly, deformation prediction plays a vital role in ensuring the safety of seawall during its operation period. However, there still is a lack of systematic study of the seawall deformation prediction model currently. Moreover, the absence of the major influencing factor selection is generally widespread in the existing model. To overcome this problem, the Chaotic Particle Swarm Optimization (CPSO) algorithm is introduced to optimize the wavelet neural network (WNN) model, and the CPSO-WNN model is utilized to determine the major influencing factors of seawall deformation. Afterward, on the basis of major influencing factor determination results, the CPSO algorithm is applied to optimize the parameters of Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM). Subsequently, the monitoring datasets are divided into training samples and test samples to construct the prediction model and validate the effectiveness, respectively. Ultimately, the CPSO-WNN-LSTM model is employed to fit and predict the long-term settlement monitoring data series of an actual seawall located in China. The prediction performances of LSTM and BPNN prediction models were introduced to be comparisons to verify the merits of the proposed model. The analysis results indicate that the proposed model takes advantage of practicality, high efficiency, stable capability, and high precision in seawall deformation prediction.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Mathematical Modeling and Numerical Simulation in Engineering, 2nd Edition)
►▼
Show Figures
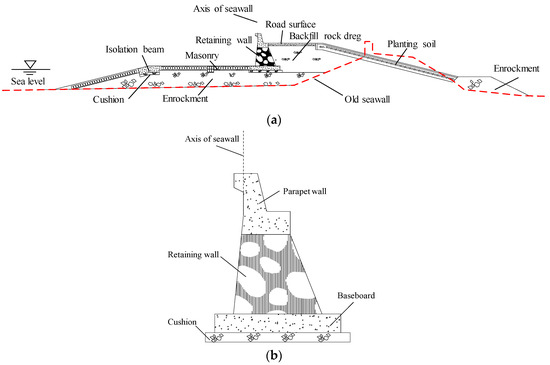
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
A Simple Framework for Scene Graph Reasoning with Semantic Understanding of Complex Sentence Structure
by
and
Mathematics 2023, 11(17), 3751; https://doi.org/10.3390/math11173751 - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
A rapidly expanding multimedia environment in recent years has led to an explosive increase in demand for multimodality that can communicate with humans in various ways. Even though the convergence of vision and language intelligence has shed light on the remarkable success over
[...] Read more.
A rapidly expanding multimedia environment in recent years has led to an explosive increase in demand for multimodality that can communicate with humans in various ways. Even though the convergence of vision and language intelligence has shed light on the remarkable success over the last few years, there is still a caveat: it is unknown whether they truly understand the semantics of the image. More specifically, how they correctly capture relationships between objects represented within the image is still regarded as a black box. In order to testify whether such relationships are well understood, this work mainly focuses on the Graph-structured visual Question Answering (GQA) task which evaluates the understanding of an image by reasoning a scene graph describing the structural characteristics of an image in the form of natural language together with the image. Unlike the existing approaches that have been accompanied by an additional encoder for scene graphs, we propose a simple yet effective framework using pre-trained multimodal transformers for scene graph reasoning. Inspired by the fact that a scene graph can be regarded as a set of sentences describing two related objects with a relationship, we fuse them into the framework separately from the question. In addition, we propose a multi-task learning method that utilizes evaluating the grammatical validity of questions as an auxiliary task to better understand a question with complex structures. This utilizes the semantic role labels of the question to randomly shuffle the sentence structure of the question. We have conducted extensive experiments to evaluate the effectiveness in terms of task capabilities, ablation studies, and generalization.
Full article
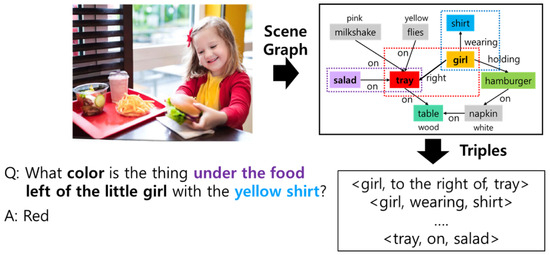
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Z-Number-Based Maximum Expected Linear Programming Model with Applications
Mathematics 2023, 11(17), 3750; https://doi.org/10.3390/math11173750 - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
In research of a better description for information uncertainty, Z-numbers, which are related to both the objective information and the subjective criticism, were first conceptualized by Zadeh. Because of its neologism, there have been multitudinous attempts toward continuation and expansion of the prototype.
[...] Read more.
In research of a better description for information uncertainty, Z-numbers, which are related to both the objective information and the subjective criticism, were first conceptualized by Zadeh. Because of its neologism, there have been multitudinous attempts toward continuation and expansion of the prototype. In this paper, we mainly study varieties of theoretical preparations for classical Z-numbers and derive the maximum expected linear programming model of Z-numbers, which are constructed on the basis of reliability conversion factors and proliferation on applications due to their simplicity. Firstly, by means of transforming Z-numbers into LR fuzzy intervals through their reliability variable, the credibility distribution and inverse distribution of converted Z-numbers are stated precisely. Then, the operational law of independent variables and its expected value can be derived via credibility distribution. The maximum expected Z-number linear programming model is determined on the basis of previous theoretical preparations, and it transforms from a classical Z-number chance-constrained model into a crisp one. Finally, with the aim of improving the programming method, its application in pragmatic practice with the realistic examples of a supplier section and optimal portfolio problems are enumerated to interpret the effectiveness of our model.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Advanced Methods in Fuzzy Control and Their Applications)
►▼
Show Figures
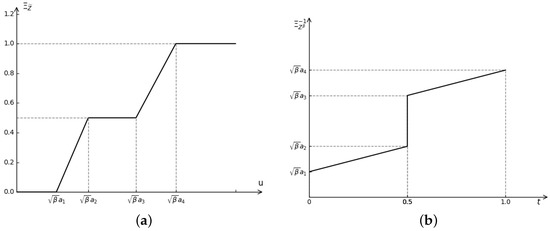
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
One-Parameter Hyperbolic Spatial Locomotions and Invariants of the Axode
Mathematics 2023, 11(17), 3749; https://doi.org/10.3390/math11173749 - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
In this paper, based on the E. Study map, direct appearances were sophisticated for one-parameter hyperbolic dual spherical locomotions and invariants of the axodes. With the suggested technique, the Disteli formulae for the axodes were acquired and the correlations through kinematic geometry of
[...] Read more.
In this paper, based on the E. Study map, direct appearances were sophisticated for one-parameter hyperbolic dual spherical locomotions and invariants of the axodes. With the suggested technique, the Disteli formulae for the axodes were acquired and the correlations through kinematic geometry of a timelike line trajectory were provided. Then, a ruled analogy of the curvature circle of a curve in planar locomotions was expanded into generic spatial locomotions. Lastly, we present new hyperbolic proofs for the Euler–Savary and Disteli formulae.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Advances in Differential Geometry and Its Applications)
►▼
Show Figures
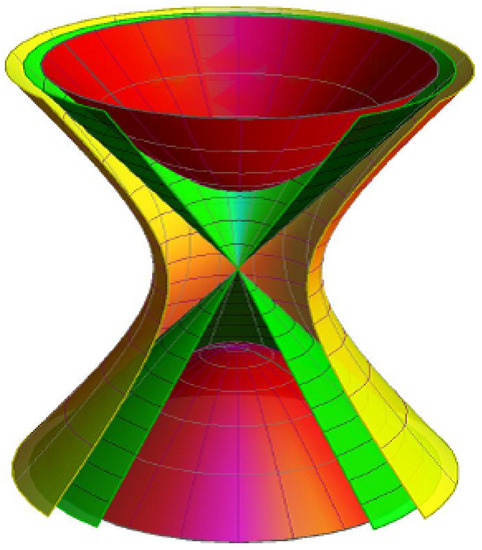
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Knowledge Graph Construction Based on a Joint Model for Equipment Maintenance
Mathematics 2023, 11(17), 3748; https://doi.org/10.3390/math11173748 - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
Under the background of intelligent manufacturing, industrial systems are developing in a more complex and intelligent direction. Equipment maintenance management is facing significant challenges in terms of maintenance workload, system reliability and stability requirements and the overall skill requirements of maintenance personnel. Equipment
[...] Read more.
Under the background of intelligent manufacturing, industrial systems are developing in a more complex and intelligent direction. Equipment maintenance management is facing significant challenges in terms of maintenance workload, system reliability and stability requirements and the overall skill requirements of maintenance personnel. Equipment maintenance management is also developing in the direction of intellectualization. It is important to have a method to construct a domain knowledge graph and to organize and utilize it. As is well known, traditional equipment maintenance is mainly dependent on technicians, and they are required to be very familiar with the maintenance manuals. But it is very difficult to manage and exploit a large quantity of knowledge for technicians in a short time. Hence a method to construct a knowledge graph (KG) for equipment maintenance is proposed to extract knowledge from manuals, and an effective maintenance scheme is obtained with this knowledge graph. Firstly, a joint model based on an enhanced BERT-Bi-LSTM-CRF is put forward to extract knowledge automatically, and a Cosine and Inverse Document Frequency (IDF) based on semantic similarity a presented to eliminate redundancy in the process of the knowledge fusion. Finally, a Decision Support System (DSS) for equipment maintenance is developed and implemented, in which knowledge can be extracted automatically and provide an equipment maintenance scheme according to the requirements. The experimental results show that the joint model used in this paper performs well on Chinese text related to equipment maintenance, with an F1 score of 0.847. The quality of the knowledge graph constructed after eliminating redundancy is also significantly improved.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Advances in Artificial Intelligence: Data, Methods and Interdisciplinary Applications)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Medical Diagnosis under Effective Bipolar-Valued Multi-Fuzzy Soft Settings
Mathematics 2023, 11(17), 3747; https://doi.org/10.3390/math11173747 - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
The Molodtsov-initiated soft set theory plays an important role as a powerful mathematical tool for handling uncertainty. As an extension of the soft set, the fuzzy soft set can be seen to be more generic and flexible than utilizing the soft set only
[...] Read more.
The Molodtsov-initiated soft set theory plays an important role as a powerful mathematical tool for handling uncertainty. As an extension of the soft set, the fuzzy soft set can be seen to be more generic and flexible than utilizing the soft set only that fails to represent problem parameters fuzziness. Through this progress, the fuzzy soft set theory cannot deal with decision-making problems involving multi-attribute sets, bipolarity, or some effective considered parameters. Therefore, the goal of this article is to adapt effectiveness and bipolarity concepts with the multi-fuzzy soft set of order n. One can see that this approach generates a novel, extended, effective decision-making environment that is more applicable than any previously introduced one. In addition, types, concepts, and operations of effective bipolar-valued multi-fuzzy soft sets of dimension n are provided, each with an example. Furthermore, properties like absorption, associative, distributive, commutative, and De Morgan’s laws of those new sets are investigated. Moreover, a decision-making methodology under effective bipolar-valued multi-fuzzy soft settings is established. This technique facilitates reaching the final decision that this student is qualified to take a certain education level, or this patient is suffering from a certain disease, etc. In addition, a case study represented in a medical diagnosis example is discussed in detail to make the proposed algorithm clearer. Applying matrix techniques in this example as well as using MATLAB®, not only makes it easier and faster in doing calculations, but also gives more accurate, optimal, and effective decisions. Finally, the sensitivity analysis, as well as a comparison with the existing methods, are conducted in detail and are summarized in a chart to show the difference between them and the current one.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Fuzzy Logic and Computational Intelligence)
►▼
Show Figures
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Analytical Solution for Bearing Capacity of Reinforced Strip Footings on Unsaturated Soils under Steady Flow
by
and
Mathematics 2023, 11(17), 3746; https://doi.org/10.3390/math11173746 - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
The study of analytical solutions for the bearing capacity of reinforced soil foundations is a very important topic in engineering mathematics. Existing evaluations of the foundation-bearing capacity on reinforced soils are based on dry conditions, while many foundations are located on unsaturated soils
[...] Read more.
The study of analytical solutions for the bearing capacity of reinforced soil foundations is a very important topic in engineering mathematics. Existing evaluations of the foundation-bearing capacity on reinforced soils are based on dry conditions, while many foundations are located on unsaturated soils in real engineering. In this paper, a new formula for the bearing capacity of reinforced strip footings on unsaturated soils is presented. Two sliding failure mechanisms are constructed based on the position of the reinforcement layer relative to the sliding surface. The distribution of apparent cohesion in the depth direction is calculated by considering the effect of matrix suction. By additionally considering the work conducted by the reinforcement and the contribution of the apparent cohesion, the bearing capacity formula is obtained using the upper bound theorem of limit analysis. The bearing capacity solution is obtained by adopting the sequential quadratic programming (SQP) algorithm. Comparing the results under two failure mechanisms, the optimal bearing capacity and the optimal embedment depth of reinforcement are obtained. The results of this paper are consistent with those of the existing literature. Finally, the effects of reinforcement embedment depth, effective internal friction angle, uniform load, and unsaturated soil parameters on the optimal bearing capacity are investigated through parametric analysis. This paper provides useful recommendations for the engineering application of reinforced strip footings on unsaturated soils.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Mathematical Model and Numerical Method in Advanced Geotechnical Engineering and Geomechanics)
►▼
Show Figures
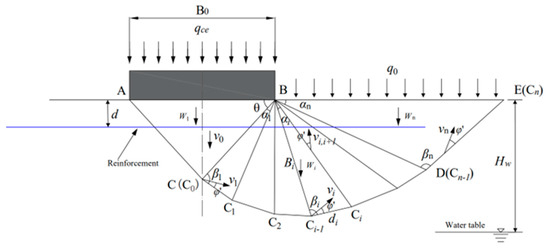
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
The Effects of the Susceptible and Infected Cross-Diffusion Terms on Pattern Formations in an SI Model
Mathematics 2023, 11(17), 3745; https://doi.org/10.3390/math11173745 - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
In this paper, we discuss the pattern dynamics of an SI epidemic model caused by spatial dependency, which is represented by self- and cross-diffusion terms. Cross-diffusion of the susceptible represents a tendency of the susceptible to stay away from the infected. Meanwhile, cross-diffusion
[...] Read more.
In this paper, we discuss the pattern dynamics of an SI epidemic model caused by spatial dependency, which is represented by self- and cross-diffusion terms. Cross-diffusion of the susceptible represents a tendency of the susceptible to stay away from the infected. Meanwhile, cross-diffusion of the infected represents their movement to the location with a high density of the susceptible. This study focuses on the presence of the effects of cross-diffusion terms on the Turing instability. This study applies Turing analysis to yield the Turing space and Turing patterns corresponding to the model by involving the infection rate as the bifurcation parameter. The results show that the presence of cross-diffusion terms narrows the Turing space depending on the magnitude of the cross-diffusion coefficients itself. Dynamical behaviors of the model are then investigated through a series of numerical simulations that successfully perform five types of patterns, i.e., spots, spots–stripes, stripes, stripes–holes, and holes. Those patterns give a description of the spread of an infectious disease. The holes denote an outbreak situation in a region, whereas the non-outbreak situation is emphasized by the spots pattern. Further, the decreasing of the ratio of recruitment and death rates indicates that the increasing of the infection rate triggers an outbreak. The present study confirms that cross-diffusion terms have a significant role in infectious disease transmission, spatially.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Mathematical Biology)
►▼
Show Figures
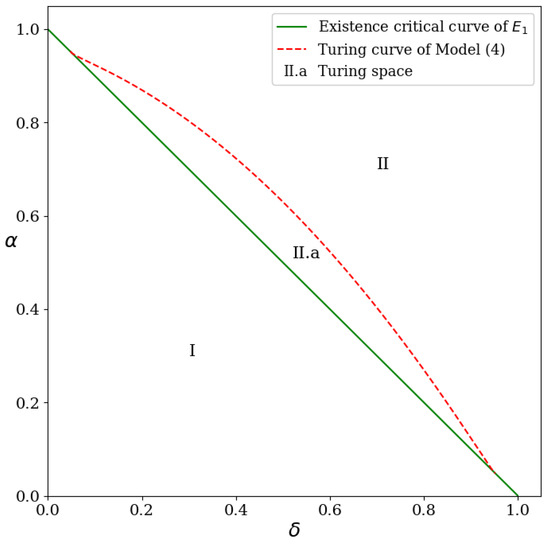
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
The Impact of Code Bloat on Genetic Program Comprehension: Replication of a Controlled Experiment on Semantic Inference
Mathematics 2023, 11(17), 3744; https://doi.org/10.3390/math11173744 - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
Our previous study showed that automatically generated attribute grammars were harder to comprehend than manually written attribute grammars, mostly due to unexpected solutions. This study is an internally differentiated replication of the previous experiment, but, unlike the previous one, it focused on testing
[...] Read more.
Our previous study showed that automatically generated attribute grammars were harder to comprehend than manually written attribute grammars, mostly due to unexpected solutions. This study is an internally differentiated replication of the previous experiment, but, unlike the previous one, it focused on testing the influence of code bloat on comprehension correctness and efficiency. While the experiment’s context, design, and measurements were kept mostly the same as in the original experiment, more realistic code bloat examples were introduced. The replicated experiment was conducted with undergraduate students from two universities, showing statistically significant differences in comprehension correctness and efficiency between attribute grammars without code bloat and attribute grammars with code bloat, although the participants perceived attribute grammars with code bloat as simple as attribute grammars without code bloat. On the other hand, there was no statistically significant difference in comprehension correctness and efficiency between automatically generated attribute grammars with possible unexpected solutions and attribute grammars with code bloat, although there was a statistically significant difference in participants’ perspective of simplicity between automatically generated attribute grammars with possible unexpected solutions and attribute grammars with code bloat. The participants perceived attribute grammars with code bloat as significantly simpler than automatically generated attribute grammars.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Mathematics and Computer Science)
Open AccessArticle
Global Properties of HIV-1 Dynamics Models with CTL Immune Impairment and Latent Cell-to-Cell Spread
Mathematics 2023, 11(17), 3743; https://doi.org/10.3390/math11173743 - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
This paper presents and analyzes two mathematical models for the human immunodeficiency virus type-1 (HIV-1) infection with Cytotoxic T Lymphocyte cell (CTL) immune impairment. These models describe the interactions between healthy CD
This paper presents and analyzes two mathematical models for the human immunodeficiency virus type-1 (HIV-1) infection with Cytotoxic T Lymphocyte cell (CTL) immune impairment. These models describe the interactions between healthy CD
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Mathematical Biology: Modeling, Analysis, and Simulations, 2nd Edition)
►▼
Show Figures
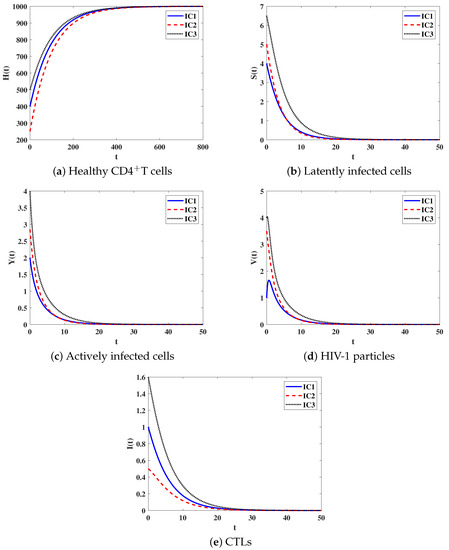
Figure 1

Journal Menu
► ▼ Journal Menu-
- Mathematics Home
- Aims & Scope
- Editorial Board
- Reviewer Board
- Topical Advisory Panel
- Instructions for Authors
- Special Issues
- Topics
- Sections & Collections
- Article Processing Charge
- Indexing & Archiving
- Editor’s Choice Articles
- Most Cited & Viewed
- Journal Statistics
- Journal History
- Journal Awards
- Society Collaborations
- Conferences
- Editorial Office
Journal Browser
► ▼ Journal BrowserHighly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Algorithms, Axioms, Fractal Fract, Mathematics, Symmetry
Approximation Theory in Computer and Computational Sciences
Topic Editors: Faruk Özger, Asif Khan, Syed Abdul Mohiuddine, Zeynep Ödemiş ÖzgerDeadline: 20 September 2023
Topic in
Applied Sciences, Energies, Fluids, Materials, Mathematics
Fluid Mechanics
Topic Editors: Vasily Novozhilov, Cunlu ZhaoDeadline: 30 September 2023
Topic in
Computers, Entropy, Information, Mathematics
Selected Papers from ICCAI 2023 and IMIP 2023
Topic Editors: Zhitao Xiao, Guangxu LiDeadline: 31 October 2023
Topic in
Buildings, JMSE, Materials, Remote Sensing, Sensors, Sustainability, Infrastructures, Mathematics
Development of Monitoring, Analysis and Maintenance Technics of Infrastructures
Topic Editors: Chunxu Qu, Jinhe Gao, Rui Zhang, Ziguang Jia, Jiaxiang LiDeadline: 20 November 2023

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
Mathematics
New Advances in Distribution Theory and Its Applications
Guest Editors: Domma Filippo, Francesca CondinoDeadline: 1 September 2023
Special Issue in
Mathematics
Stochastic Processes Applied to Modelling in Finance: Latest Advances and Prospects
Guest Editors: Peter Lakner, Christoph FreiDeadline: 15 September 2023
Special Issue in
Mathematics
Integral Transforms and Integral Representations with Applications
Guest Editor: Tibor K. PogányDeadline: 30 September 2023
Special Issue in
Mathematics
Advances in Linear Recurrence System
Guest Editors: Lorentz Jäntschi, Virginia NiculescuDeadline: 15 October 2023
Topical Collections
Topical Collection in
Mathematics
Multiscale Computation and Machine Learning
Collection Editors: Yalchin Efendiev, Eric Chung
Topical Collection in
Mathematics
Theoretical and Mathematical Ecology
Collection Editor: Yuri V. Tyutyunov






.jpg)







