Journal Description
Nutrients
Nutrients
is a peer-reviewed, open access journal of human nutrition published semimonthly online by MDPI. The Asia Pacific Nutrigenomics Nutrigenetics Organisation (APNNO), Italian Society for Pediatric Nutrition and Gastroenterology (SIGENP), Nutrition Society of New Zealand (NSNZ), Ocular Wellness & Nutrition Society (OWNS) and others are affiliated with Nutrients and their members receive a discount on article processing charges.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within Scopus, SCIE (Web of Science), PubMed, MEDLINE, PMC, Embase, PubAg, AGRIS, and other databases.
- Journal Rank: JCR - Q1 (Nutrition & Dietetics) / CiteScore - Q1 (Nutrition and Dietetics)
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 14.7 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 2.6 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the first half of 2023).
- Recognition of Reviewers: reviewers who provide timely, thorough peer-review reports receive vouchers entitling them to a discount on the APC of their next publication in any MDPI journal, in appreciation of the work done.
- Companion journal: Dietetics
Impact Factor:
5.9 (2022);
5-Year Impact Factor:
6.6 (2022)
Latest Articles
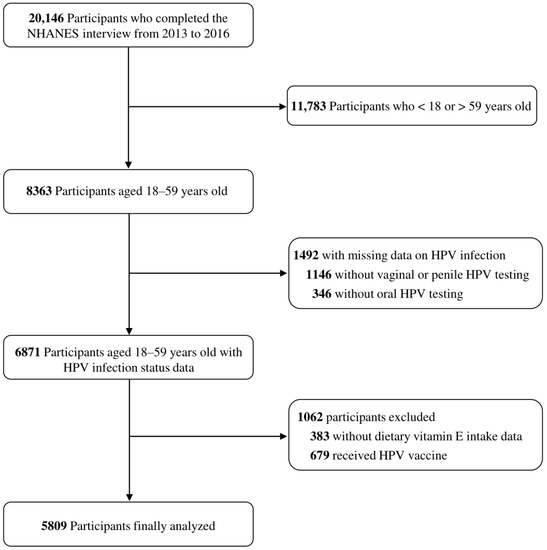
Association between Dietary Vitamin E Intake and Human Papillomavirus Infection among US Adults: A Cross-Sectional Study from National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Nutrients 2023, 15(17), 3825; https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15173825 (registering DOI) - 01 Sep 2023
Abstract
Persistent high-risk human papillomavirus (HPV) infection is responsible for most genital, anal, and oropharyngeal cancers, in which men contribute significantly to infection and subsequent tumorigenesis in women. Vitamin E has been shown to be associated with vaginal HPV infection and cervical cancer. However,
[...] Read more.
Persistent high-risk human papillomavirus (HPV) infection is responsible for most genital, anal, and oropharyngeal cancers, in which men contribute significantly to infection and subsequent tumorigenesis in women. Vitamin E has been shown to be associated with vaginal HPV infection and cervical cancer. However, the association of vitamin E consumption with HPV infection among the overall population remains unclear. We investigate the association between vitamin E consumption and genital and oral HPV infection in both men and women. We used cross-sectional data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey between 2013 and 2016 to collect details on their dietary vitamin E intake, genital and oral HPV infection status, and other essential variables. In total, 5809 participants aged 18–59 years were identified, with overall prevalence of high-risk and low-risk HPV infection of 23.7% and 21.1%, respectively. Compared with the lowest vitamin E group Q1 (<5.18 mg/day), the adjusted OR for vitamin E consumption and overall high-risk HPV infection in Q2 (5.18–7.54 mg/day), Q3 (7.55–10.82 mg/day), and Q4 (>10.82 mg/day) were 0.91 (95% CI: 0.81–1.03, p = 0.134), 0.77 (95% CI: 0.69–0.87, p < 0.001), and 0.72 (95% CI: 0.65–0.80, p < 0.001), respectively. Restricted cubic spline regression showed a linear relationship between vitamin E consumption and overall high-risk HPV infection. This linear relationship also existed for vitamin E consumption and overall low-risk HPV infection. After being stratified by gender and site, vitamin E consumption was inversely related to vaginal low- and high-risk HPV infection, penile high-risk HPV infection, and male oral low-risk HPV infection. In conclusion, we identified inverse linear relationships between dietary vitamin E intake and overall high- and low-risk HPV infection. Future well-designed longitudinal studies are still required to validate the impact of vitamin E on HPV carcinogenesis.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Nutritional Epidemiology)
►
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
Nutrition, Nutritional Status, Micronutrients Deficiency, and Disease Course of Inflammatory Bowel Disease
by
, , , , , , , , and
Nutrients 2023, 15(17), 3824; https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15173824 (registering DOI) - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
During the disease course, most Inflammatory Bowel Disease patients present a condition of malnutrition, undernutrition, or even overnutrition. These conditions are mainly due to suboptimal nutritional intake, alterations in nutrient requirements and metabolism, malabsorption, and excessive gastrointestinal losses. A suboptimal nutritional status and
[...] Read more.
During the disease course, most Inflammatory Bowel Disease patients present a condition of malnutrition, undernutrition, or even overnutrition. These conditions are mainly due to suboptimal nutritional intake, alterations in nutrient requirements and metabolism, malabsorption, and excessive gastrointestinal losses. A suboptimal nutritional status and low micronutrient serum levels can have a negative impact on both induction and maintenance of remission and on the quality of life of Inflammatory Bowel Disease patients. We performed a systematic review including all the studies evaluating the connection between nutrition, nutrition status (including undernutrition and overnutrition), micronutrient deficiency, and both disease course and therapeutic response in Inflammatory Bowel Disease patients. This systematic review was performed using PubMed/MEDLINE and Scopus. Four main clinical settings concerning the effect of nutrition on disease course in adult Inflammatory Bowel Disease patients were analyzed (induction of remission, maintenance of remission, risk of surgery, post-operative recurrence, and surgery-related complications). Four authors independently reviewed abstracts and manuscripts for eligibility. 6077 articles were found; 762 duplicated studies were removed. Out of 412 full texts analyzed, 227 were included in the review. The evidence summarized in this review showed that many nutritional aspects could be potential targets to induce a better control of symptoms, a deeper remission, and overall improve the quality of life of Inflammatory Bowel Disease patients.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Dietary Guidelines for Inflammatory Bowel Disease Patients)
►▼
Show Figures
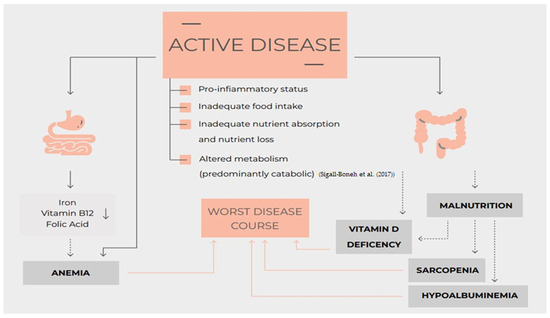
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Maternal Obesity and Kawasaki Disease-like Vasculitis: A New Perspective on Cardiovascular Injury and Inflammatory Response in Offspring Male Mice
Nutrients 2023, 15(17), 3823; https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15173823 (registering DOI) - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
Maternal obesity affects the risk of cardiovascular disease and inflammatory response in offspring. However, the impact of maternal obesity on offspring with Kawasaki disease (KD), the leading cause of childhood acquired heart disease, is still an understudied area. This study aimed to elucidate
[...] Read more.
Maternal obesity affects the risk of cardiovascular disease and inflammatory response in offspring. However, the impact of maternal obesity on offspring with Kawasaki disease (KD), the leading cause of childhood acquired heart disease, is still an understudied area. This study aimed to elucidate the impact of maternal obesity on offspring in KD-like vasculitis and the underlying mechanisms. Offspring of obese female mice and normal diet dams were randomly divided into two subgroups. The pups were injected intraperitoneally with either Candida albicans water-soluble fraction (CAWS) or phosphate buffered saline (PBS) to establish the obesity (OB)-CAWS group, OB group, wild type (WT)-CAWS group, and WT group. Their weight was monitored during the study. After four weeks, echocardiography was applied to obtain the alternation of cardiac structures. Mouse cytokine panel, Hematoxylin-Eosin (HE) staining, western blot, and real-time qPCR were used to study the pathological changes and protein and RNA expression alternations. Based on the study of pathology, serology and molecular biology, maternal obesity lead to more severe vasculitis and induced altered cardiac structure in the offspring mice and promoted the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines through activating the NF-κB signaling pathway. Maternal obesity aggravated the inflammatory response of offspring mice in KD-like vasculitis.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue The Role of Nutrition and Physical Activity in Autoimmune Diseases)
►▼
Show Figures
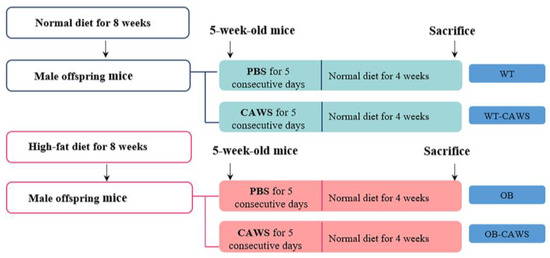
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Parenteral Nutrition in the Pediatric Oncologic Population: Are There Any Sex Differences?
by
, , , , , , and
Nutrients 2023, 15(17), 3822; https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15173822 (registering DOI) - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
Gender-based medicine is attracting increasing interest every day, but studies on pediatric populations are still limited. In this setting, sex differences among patients undergoing total parenteral nutrition (TPN) have not been previously reported. This study investigated the presence of sex differences in parenteral
[...] Read more.
Gender-based medicine is attracting increasing interest every day, but studies on pediatric populations are still limited. In this setting, sex differences among patients undergoing total parenteral nutrition (TPN) have not been previously reported. This study investigated the presence of sex differences in parenteral nutrition composition and outcomes among a cohort of pediatric patients admitted at the Oncohematology and Bone Marrow Transplant Unit of the Institute for Maternal and Child Health “Burlo Garofolo” of Trieste, Italy. For all 145 recruited patients (87 males, 58 females), the following data were collected: age, sex, volume and duration of TPN, macro- and micronutrient composition of TPN bags, electrolytic or blood gases imbalance, glycolipid alterations, liver damage during TPN, and the incidence of sepsis and thrombosis. The analysis showed that females required higher daily phosphate intake (p = 0.054) and essential amino acid supplementation (p = 0.07), while males had a higher incidence of hypertriglyceridemia (p < 0.05) and cholestasis. A higher incidence of sepsis was found in the non-transplanted male population (p < 0.05). No significant differences were appreciable in other analyzed variables. This study aims to create a basis for future gender-based nutritional recommendations in the pediatric field.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Nutrition and Physical Activity for Childhood Cancer Prevention and Treatment)
Open AccessReview
The Importance of Antioxidant Activity for the Health-Promoting Effect of Lycopene
Nutrients 2023, 15(17), 3821; https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15173821 - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
Lycopene is a compound of colored origin that shows strong antioxidant activity. The positive effect of lycopene is the result of its pleiotropic effect. The ability to neutralize free radicals via lycopene is one of the foundations of its pro-health effect, including the
[...] Read more.
Lycopene is a compound of colored origin that shows strong antioxidant activity. The positive effect of lycopene is the result of its pleiotropic effect. The ability to neutralize free radicals via lycopene is one of the foundations of its pro-health effect, including the ability to inhibit the development of many civilization diseases. Therefore, this study focuses on the importance of the antioxidant effect of lycopene in inhibiting the development of diseases such as cardiovascular diseases, diseases within the nervous system, diabetes, liver diseases, and ulcerative colitis. According to the research mentioned, lycopene supplementation has significant promise for the treatment of illnesses marked by chronic inflammation and oxidative stress. However, the majority of the supporting data for lycopene′s health benefits comes from experimental research, whereas the evidence from clinical studies is both scarcer and less certain of any health benefits. Research on humans is still required to establish its effectiveness.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Impact of Plant Extracts and Natural Substances in Oxidation, Inflammation and Diabetes)
►▼
Show Figures
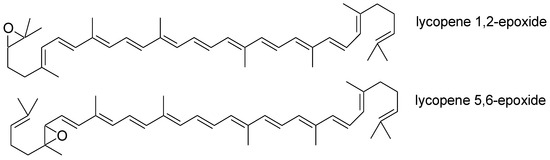
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Effect of Moderate-Intense Training and Detraining on Glucose Metabolism, Lipid Profile, and Liver Enzymes in Male Wistar Rats: A Preclinical Randomized Study
Nutrients 2023, 15(17), 3820; https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15173820 - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
Exercise training positively regulates glucose metabolism. This study investigated the impact of training and detraining on glucose metabolism, lipid profiles, and liver enzymes. Twenty-six rats completed an initial 4-week moderate-intense training (T0–T4). Then, the animals were randomly assigned to two groups at the
[...] Read more.
Exercise training positively regulates glucose metabolism. This study investigated the impact of training and detraining on glucose metabolism, lipid profiles, and liver enzymes. Twenty-six rats completed an initial 4-week moderate-intense training (T0–T4). Then, the animals were randomly assigned to two groups at the end of week 4: AT4: detraining for 8 weeks; AT8: training for 8 weeks and 4-week detraining. Six animals were sacrificed at T0 and T4, four animals/group at T8, and three/group at T12. The study continued for 12 weeks, and all parameters were assessed at T0, T4, T8, and T12. IPGTT significantly improved after 4 weeks of training (p < 0.01) and was further reduced in AT8 at T8. In AT8, 8-week training significantly reduced total cholesterol at T4 and T12 vs. T0 (p < 0.05), LDL at T4, T8, and T12 vs. T0 (p < 0.01), ALP at T8, T12 vs. T0 (p < 0.01), and increased HDL at T8 and ALT at T8 and T12 vs. T0 (p < 0.05). Triglycerides and hexokinase activity increased significantly at T4 and T8 (p < 0.05) and then decreased at T12 in AT8. Pyruvate and glycogen increased at T12 in AT8 vs. AT4. Eight-week training improved LPL and ATGL expressions. Training positively modulated insulin, glucose metabolism, and lipid profiles, but detraining reduced the benefits associated with the initial training.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Eating Behaviors, Body Composition and Neuro Vulnerability in Energy Metabolism Regulation)
►▼
Show Figures
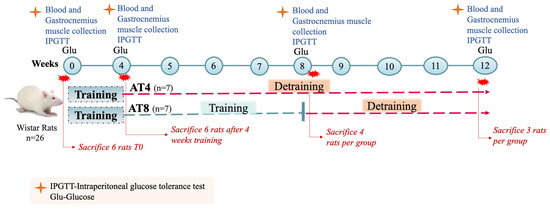
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
The Immunomodulatory Effects of a 6-Month Extra Virgin Olive Oil Intervention on Monocyte Cytokine Secretion and Plasma Cytokine Levels in Dyslipidemic and Post-Infarct Patients: A Clinical Pilot Study
Nutrients 2023, 15(17), 3819; https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15173819 - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
Atherosclerosis is an immuno-inflammatory process underlying cardiovascular diseases. One of the main actors of this inflammation is monocytes, with the switch in their phenotypes and irregularities in their cytokine production. Objective: This study was aimed to investigate the nutraceutical potential of extra virgin
[...] Read more.
Atherosclerosis is an immuno-inflammatory process underlying cardiovascular diseases. One of the main actors of this inflammation is monocytes, with the switch in their phenotypes and irregularities in their cytokine production. Objective: This study was aimed to investigate the nutraceutical potential of extra virgin olive oil (EVOO) on the inflammatory status of monocytes in participants showing different levels of cardiovascular risk. Methods: 43 participants 65–85 years old were recruited including 14 healthy, 12 dyslipidemic patients with hypercholesterolemia recently diagnosed, and 17 post-infarct patients. Participants from all groups were supplemented with EVOO (25 mL/day) for 6 months. IL-1β, IL-6, IL-10, TNF-α cytokine production, and monocyte phenotypes were investigated both at quiescent and at stimulated state by flow cytometry. Results: At the baseline (pre-intervention), dyslipidemic patients, compared to healthy and post-infarct participants, showed monocytes in an inflammatory state characterized by a significantly weaker IL-10 production. Our results do not show a significant modulation of the phenotype or IL-10, IL-6, and TNF-α production following a 6-month EVOO intake whether at quiescence or under stimulation. However, IL-1β is significantly increased by the intervention of EVOO in post-infarct patients. Paradoxically after the 6-month intervention, monocytes from dyslipidemic patients showed a significantly decreased secretion of IL-1β under LPS stimulation despite the increase observed at basal state. Conclusion: Our results show that 6-month EVOO intervention did not induce a monocyte phenotypic change or that this intervention significantly modifies cytokine production.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Nutrition, Lipoproteins and Cardiovascular Diseases)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Emotional Overeating during the COVID-19 Pandemic: Polish Adolescents’ COVID-19 Experience (PLACE-19) Study
Nutrients 2023, 15(17), 3818; https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15173818 - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
Emotional overeating is the most frequently noted type of emotional eating, being commonly associated with increased consumption of energy-dense products, as well as excessive body mass, and weight gain. Even though a number of studies assessed emotional overeating during the COVID-19 pandemic in
[...] Read more.
Emotional overeating is the most frequently noted type of emotional eating, being commonly associated with increased consumption of energy-dense products, as well as excessive body mass, and weight gain. Even though a number of studies assessed emotional overeating during the COVID-19 pandemic in adult populations, studies of children and adolescents are scarce. The aim of the present study was to assess emotional overeating background, including consumption in response to six emotions (anxiety, sadness, loneliness, tiredness, anger, and happiness), in the population of Polish adolescents within the PLACE-19 Study during the COVID-19 pandemic. The PLACE-19 Study is a national Polish population-based study of adolescents gathered upon recruitment based on a random quota sampling of secondary schools, conducted in a population of 1126 students (818 females and 308 males, a median of age 17.0 and 16.5 years, respectively). Emotional overeating was assessed while using the Emotional Overeating Questionnaire (EOQ), and as additional factors, the following were assessed: gender, body mass, body mass change during the COVID-19 pandemic, and declared tempting food products. Female participants declared a higher frequency of overeating in response to feelings of anxiety, sadness, loneliness, and happiness, and were characterized by a higher total score than male participants, while p ≤ 0.05 was interpreted as a statistical significance. Obese participants declared a higher frequency of overeating in response to feelings of sadness, and loneliness than normal weight participants. Participants gaining weight declared a higher frequency of overeating in response to feelings of anxiety, sadness, loneliness, tiredness, and anger, and were characterized by a higher total score than participants losing weight or maintaining a stable weight, while participants gaining weight declared a higher frequency of overeating in response to feelings of happiness than participants losing weight. Participants declaring both sweet and salty products as tempting declared a higher frequency of overeating in response to feelings of anxiety, and sadness than participants declaring no tempting products; participants declaring both sweet and salty products declared a higher frequency of overeating in response to feelings of tiredness than participants declaring only salty products and those declaring no tempting products, as well as declared a higher frequency of overeating in response to feelings of happiness than participants declaring only sweet products, and those declaring no tempting products; participants declaring sweet products declared a higher frequency of overeating in response to feelings of anger than participants declaring no tempting products, while participants declaring both sweet and salty products declared a higher frequency of overeating in response to feelings of loneliness, and were characterized by a higher total score than all other respondents. The sub-groups with the highest frequency of emotional overeating were the female respondents, obese participants, those gaining weight, and those declaring both sweet and salty products as tempting, while among the emotions most often causing emotional overeating, there were sadness and loneliness.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Lifestyle and Health Changes during and after the COVID-19 Pandemic)
Open AccessArticle
Barriers and Facilitators to Cardiovascular Disease Prevention Following Hypertensive Disorders of Pregnancy in Primary Care: Cross-Sectional Surveys
by
, , , , and
Nutrients 2023, 15(17), 3817; https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15173817 - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
Women with a history of hypertensive disorders of pregnancy (HDP) have an increased risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD). Guidelines recommend that women diagnosed with HDP should be advised of their increased CVD risk, have regular blood pressure monitoring by their general practitioner (GP),
[...] Read more.
Women with a history of hypertensive disorders of pregnancy (HDP) have an increased risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD). Guidelines recommend that women diagnosed with HDP should be advised of their increased CVD risk, have regular blood pressure monitoring by their general practitioner (GP), and adopt healthy lifestyle behaviours. However, within Australia, the current practice in primary health care is unknown. The aim of this study was to describe current practices, barriers, and facilitators to the provision of CVD preventative services for women after HDP in the primary care setting and to identify potential strategies to support GPs in providing recommended care. Separate cross-sectional online surveys were undertaken with 35 GPs and 105 women with a history of HDP. Surveys included both closed- and open-ended questions. Closed-ended questions were analysed using basic descriptive statistics, and open-ended questions were themed and tallied. The survey of GPs revealed that GPs are more likely to assess traditional CVD risk markers than lifestyle risk factors or HDP history. GPs identified a lack of resources and skills as barriers to providing CVD preventative care post-HDP. The survey with women after HDP revealed that women with a history of HDP are more likely to be assessed for blood pressure than lifestyle CVD risk factors, and that the women’s barriers to obtaining care included difficulty obtaining an appointment and time required for attending appointments. Strategies to improve CVD preventative care were consistent between surveys, where 70% of GPs and 59% of women chose ‘increasing women’s awareness of increased CVD risk’ and 67% of GPs and 55% of women chose ‘improving communication between hospitals and primary care’ as their preferred strategies. While the findings suggest that women with a history of HDP are receiving advice consistent with guidelines for traditional CVD risk markers, such as blood pressure, they are less likely to receive CVD preventative care for lifestyle or female-specific CVD risk factors.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Improving Nutrition and Physical Activity Behaviours for the Prevention and Treatment of Obesity during Preconception, Pregnancy and Postpartum through Health System Settings)
Open AccessArticle
Methodological Principles of Nasal Food Challenge
by
, , , , , , , and
Nutrients 2023, 15(17), 3816; https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15173816 - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
Thanks to their valuable assessment possibilities (subjective complaints and changes in nasal patency during the examination), nasal provocation tests may serve as an alternative tool for oral food challenges in the future. However, this test requires successive attempts to regulate its methodology in
[...] Read more.
Thanks to their valuable assessment possibilities (subjective complaints and changes in nasal patency during the examination), nasal provocation tests may serve as an alternative tool for oral food challenges in the future. However, this test requires successive attempts to regulate its methodology in order to develop a standardized lyophilisate form and determine the threshold dose for a positive result. The study objective was to present the methodological foundation for nasal food allergen provocation tests induced by freeze-dried powdered chicken egg whites. A control group of 25 individuals with no history of allergy to chicken eggs or any other allergy was included in the study. Optical rhinometry and visual analog scales were used to assess the response of nasal mucosa to local allergen challenges. Minor variations in nasal flows, as measured by optical rhinometry, were observed in the provocation tests. The mean optical density measurements (as measured regardless of the allergen dose used) varied from positive to negative values and vice versa, e.g., amounting to 0.018 OD (standard deviation 0.095) at 15 min and −0.011 OD (standard deviation 0.090) at 30 min. No significant differences were observed concerning the perceived nasal discomfort using the visual analog scale. Due to the absence of nasal mucosal reactivity, nasal challenge is an excellent methodological tool for implementing food allergen tests.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Nutrition in Allergies and Respiratory Diseases)
►▼
Show Figures
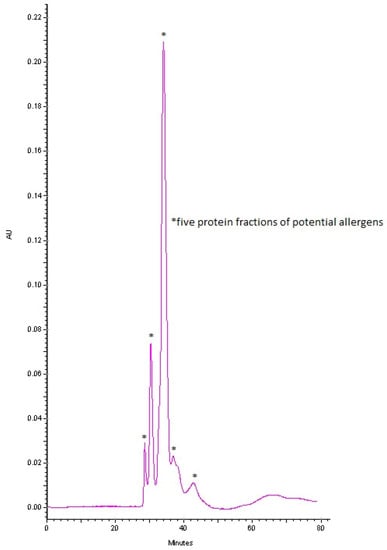
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Novel Psychopharmacological Herbs Relieve Behavioral Abnormalities and Hippocampal Dysfunctions in an Animal Model of Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder
Nutrients 2023, 15(17), 3815; https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15173815 - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) is an anxiety disorder caused by traumatic or frightening events, with intensified anxiety, fear memories, and cognitive impairment caused by a dysfunctional hippocampus. Owing to its complex phenotype, currently prescribed treatments for PTSD are limited. This study investigated the
[...] Read more.
Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) is an anxiety disorder caused by traumatic or frightening events, with intensified anxiety, fear memories, and cognitive impairment caused by a dysfunctional hippocampus. Owing to its complex phenotype, currently prescribed treatments for PTSD are limited. This study investigated the psychopharmacological effects of novel COMBINATION herbal medicines on the hippocampus of a PTSD murine model induced by combining single prolonged stress (SPS) and foot shock (FS). We designed a novel herbal formula extract (HFE) from Chaenomeles sinensis, Glycyrrhiza uralensis, and Atractylodes macrocephala. SPS+FS mice were administered HFE (500 and 1000 mg/kg) once daily for 14 days. The effects of HFE of HFE on the hippocampus were analyzed using behavioral tests, immunostaining, Golgi staining, and Western blotting. HFE alleviated anxiety-like behavior and fear response, improved short-term memory, and restored hippocampal dysfunction, including hippocampal neurogenesis alteration and aberrant migration and hyperactivation of dentate granule cells in SPS+FS mice. HFE increased phosphorylation of the Kv4.2 potassium channel, extracellular signal-regulated kinase, and cAMP response element-binding protein, which were reduced in the hippocampus of SPS+FS mice. Therefore, our study suggests HFE as a potential therapeutic drug for PTSD by improving behavioral impairment and hippocampal dysfunction and regulating Kv4.2 potassium channel-related pathways in the hippocampus.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Nutritional Intervention in Mental Health)
►▼
Show Figures
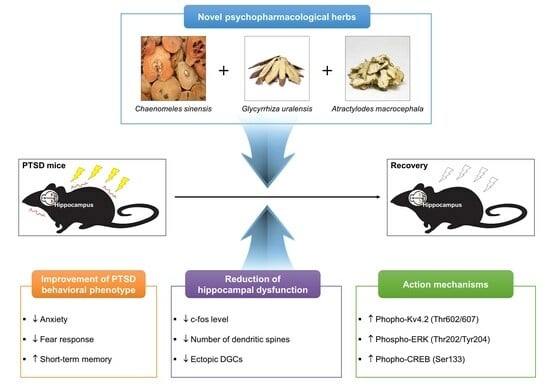
Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Using Body Composition Analysis for Improved Nutritional Intervention in Septic Patients: A Prospective Interventional Study
Nutrients 2023, 15(17), 3814; https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15173814 - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
The study aimed to determine whether using body composition data acquired through bio-electrical impedance analysis (BIA) to adjust diet formulas could improve outcomes in septic patients. There were 132 septic patients in medical intensive care units enrolled in the prospective, randomized, double-blind, interventional
[...] Read more.
The study aimed to determine whether using body composition data acquired through bio-electrical impedance analysis (BIA) to adjust diet formulas could improve outcomes in septic patients. There were 132 septic patients in medical intensive care units enrolled in the prospective, randomized, double-blind, interventional study. For the intervention group, dietitians had access to BIA data for adjusting diet formulas according to body composition variables on days 1, 3, and 8. The patients were also stratified based on nutritional risk using the modified Nutrition Risk in Critically ill (mNUTRIC) score. Patients with intervention were more likely to achieve caloric and protein intake goals compared to the control group, especially in the low-risk group. The intervention did not significantly affect mortality, but the survival curves suggested potential benefits. The high-risk group had longer ICU stays and mechanical ventilation duration, which were mitigated by the intervention. Certain body composition variables (e.g., extracellular water to total body water ratio and phase angle) showed differences between high-risk and low-risk groups and may be related to patient outcomes. Non-invasive body composition assessment using BIA can help dietitians adjust diet formulas for critically ill septic patients. Body composition variables may be associated with sepsis outcomes, but further research with larger patient numbers is needed to confirm these findings.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Enteral/Parenteral Nutrition and Infections)
►▼
Show Figures
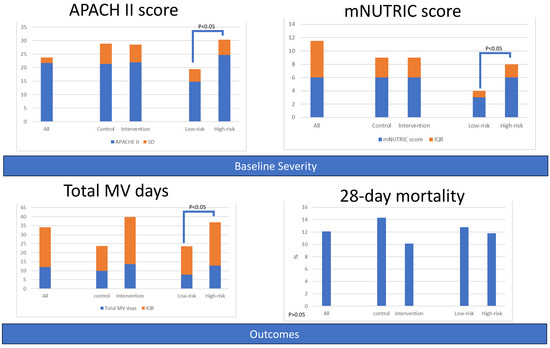
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Obesity and Selected Allergic and Immunological Diseases—Etiopathogenesis, Course and Management
Nutrients 2023, 15(17), 3813; https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15173813 - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
Obesity is a global problem. It affects every age group and is associated with many negative health effects. As an example, there is a relationship between obesity and allergic and immunological diseases, such as asthma, psoriasis, food allergies, allergic rhinitis and atopic dermatitis.
[...] Read more.
Obesity is a global problem. It affects every age group and is associated with many negative health effects. As an example, there is a relationship between obesity and allergic and immunological diseases, such as asthma, psoriasis, food allergies, allergic rhinitis and atopic dermatitis. Obesity undeniably affects their development. In addition, it causes adverse changes in the course and response to therapy in relation to patients without excessive body weight. The treatment of diseases associated with obesity is difficult; drugs are less effective and must be used in higher doses, and their use in patients with obesity is often associated with higher risks. The main form of treatment of all obesity-related diseases is a change in eating habits and increased physical activity, which leads to a decrease in body fat mass. The positive effect of reducing BMI has been confirmed in many independent studies. This paper reviews various types of research documents published since 2019. It aims to systematize the latest knowledge and highlight the need for further research for effective and sustainable treatment options for obesity, its complications and obesity-related diseases.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Recent Developments in Nutrition and Obesity-Associated Health Disorders)
►▼
Show Figures
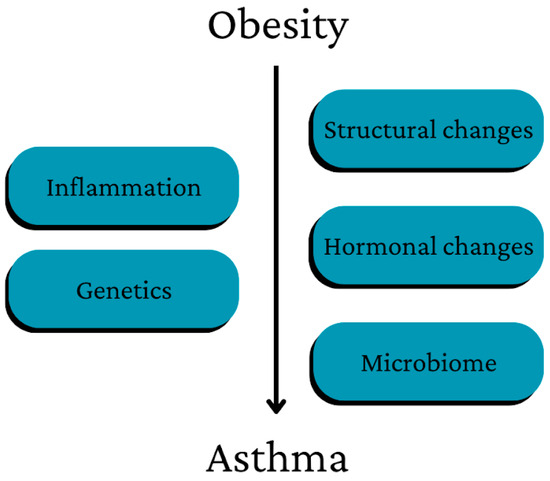
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Relationship between Bladder Cancer, Nutritional Supply, and Treatment Strategies: A Comprehensive Review
Nutrients 2023, 15(17), 3812; https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15173812 - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
Bladder cancer (BC) is the predominant neoplasm affecting the urinary system and ranks among the most widespread malignancies globally. The causes of bladder cancer include genetic factors; age; sex; and lifestyle factors, such as imbalanced nutrition, obesity, and metabolic disorders. The lack of
[...] Read more.
Bladder cancer (BC) is the predominant neoplasm affecting the urinary system and ranks among the most widespread malignancies globally. The causes of bladder cancer include genetic factors; age; sex; and lifestyle factors, such as imbalanced nutrition, obesity, and metabolic disorders. The lack of proper nutrient intake leads to the development of bladder cancer because insufficient nutrients are consumed to prevent this disease. The purpose of this review was to analyze the nutrients closely linked to the onset and advancement of bladder cancer and to explore the relationship between dietary nutrients and bladder cancer. Particular emphasis was placed on nutrients that are frequently ingested in daily life, including sugar, fat, protein, and others. The focus of this research was to analyze how nutritional intake before and after surgery affects the recovery process of patients who have been diagnosed with bladder cancer. This article seeks to increase awareness among both society and the medical community about the significance of implementing appropriate dietary nutrition to reduce the chances of developing bladder cancer, enhance perioperative care for patients with bladder cancer, and aid in their recuperation.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic Nutrition in Cancer and Neurodegenerative Diseases)
►▼
Show Figures
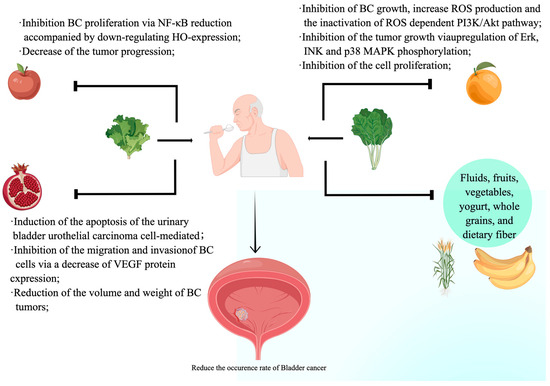
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Analysis of the Diet Quality and Nutritional State of Children, Youth, and Young Adults with Prader–Willi Syndrome: A Polish Multiple Case Study
by
, , , , , , and
Nutrients 2023, 15(17), 3811; https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15173811 - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
Given the lack of data on dietary quality in young individuals with Prader–Willi syndrome (PWS) in Poland, a multiple case study was conducted in which anthropometric measurements and 7-day dietary records were collected from 20 subjects with PWS. The study group consisted of
[...] Read more.
Given the lack of data on dietary quality in young individuals with Prader–Willi syndrome (PWS) in Poland, a multiple case study was conducted in which anthropometric measurements and 7-day dietary records were collected from 20 subjects with PWS. The study group consisted of 8 females and 12 males with a mean age of 14.8 years and a mean BMI of 21.6. Based on BMI analysis, five subjects were overweight, including two subjects who were obese. The study showed that 35% of the subjects had energy intakes above the recommended levels. Protein deficiency was found in one subject in the analyzed diets. However, fat intake was excessive in four subjects, and the majority exceeded the recommended intake of saturated fatty acids. Vitamin E and B12 deficiencies were found in 40% and 85% of the subjects, respectively. All subjects had inadequate intakes of vitamin D and iodine, while the majority had deficiencies in sodium and copper intakes. Calcium intake was deficient in 35% of the subjects. However, most subjects met recommendations for the intakes of other minerals, vitamins, and fiber. These findings confirm the suboptimal dietary patterns of Polish individuals with PWS, with deficits observed in the intake of certain vitamins and minerals.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Dietary Patterns and Clinical Health Outcomes)
Open AccessReview
Dietary Approach of Patients with Hormone-Related Cancer Based on the Glycemic Index and Glycemic Load Estimates
by
, , , , , and
Nutrients 2023, 15(17), 3810; https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15173810 - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
Hormone-related cancers, namely breast, endometrial, cervical, prostate, testicular, and thyroid, constitute a specific group of cancers dependent on hormone levels that play an essential role in cancer growth. In addition to the traditional risk factors, diet seems to be an important environmental factor
[...] Read more.
Hormone-related cancers, namely breast, endometrial, cervical, prostate, testicular, and thyroid, constitute a specific group of cancers dependent on hormone levels that play an essential role in cancer growth. In addition to the traditional risk factors, diet seems to be an important environmental factor that partially explains the steadily increased prevalence of this group of cancer. The composition of food, the dietary patterns, the endocrine-disrupting chemicals, and the way of food processing and preparation related to dietary advanced glycation end-product formation are all related to cancer. However, it remains unclear which specific dietary components mediate this relationship. Carbohydrates seem to be a risk factor for cancer in general and hormone-related cancers, in particular, with a difference between simple and complex carbohydrates. Glycemic index and glycemic load estimates reflect the effect of dietary carbohydrates on postprandial glucose concentrations. Several studies have investigated the relationship between the dietary glycemic index and glycemic load estimates with the natural course of cancer and, more specifically, hormone-related cancers. High glycemic index and glycemic load diets are associated with cancer development and worse prognosis, partially explained by the adverse effects on insulin metabolism, causing hyperinsulinemia and insulin resistance, and also by inflammation and oxidative stress induction. Herein, we review the existing data on the effect of diets focusing on the glycemic index and glycemic load estimates on hormone-related cancers.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Carbohydrates)
►▼
Show Figures
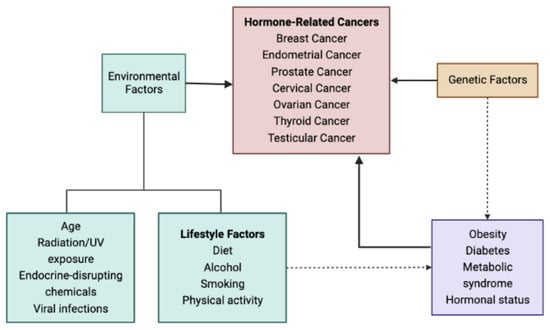
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Pregnancy Cholesterol Metabolism Markers and the Risk of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus: A Nested Case-Control Study
by
, , , , , , , , , , , and
Nutrients 2023, 15(17), 3809; https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15173809 - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
This study aims to determine the association of pregnancy cholesterol metabolism markers with gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) risk. We performed a nested case–control study in the Tongji Birth Cohort. GDM was diagnosed according to the 75 g 2 h oral glucose tolerance test
[...] Read more.
This study aims to determine the association of pregnancy cholesterol metabolism markers with gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) risk. We performed a nested case–control study in the Tongji Birth Cohort. GDM was diagnosed according to the 75 g 2 h oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) at 24–28 gestational weeks. Nine cholesterol metabolism markers were detected using gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Conditional logistic regression models were conducted. A total of 444 pregnant women were matched in a 1:2 ratio. The cholestanolTC and β-sitosterolTC in cholesterol absorption markers presented negative associations with the risks of GDM (adjusted OR: 0.77, 95% CI: 0.61–0.96; adjusted OR: 0.80, 95% CI: 0.64–1.00). The desmosterolTC in cholesterol synthesis markers were positively associated with the risks of GDM (adjusted OR: 1.25, 95% CI: 1.00–1.56), similar in the ratios of cholesterol synthesis to absorption markers. After adjustment for insulin or HOMA-IR, these effects were reduced. In conclusion, higher cholesterol synthesis and lower cholesterol absorption marker levels in the first pregnancy are associated with a higher risk of GDM, and insulin resistance may play a vital role in this association.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Lipid Metabolism and Nutrition Status in Gestational Diabetes Mellitus)
►▼
Show Figures
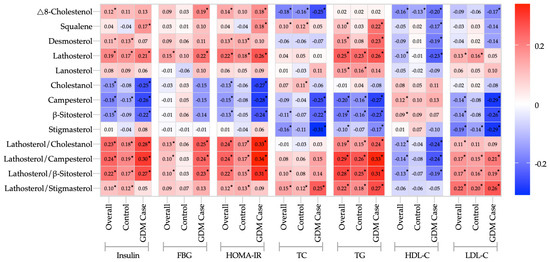
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Binge Eating (BE) and Obesity: Brain Activity and Psychological Measures before and after Roux-En-Y Gastric Bypass (RYGB)
by
, , , , , and
Nutrients 2023, 15(17), 3808; https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15173808 - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
Brain activity in response to food cues following Roux-En-Y Gastric Bypass (RYGB) in binge eating (BE) or non-binge eating (NB) individuals is understudied. Here, 15 RYGB (8 BE; 7 NB) and 13 no treatment (NT) (7 BE; 6 NB) women with obesity underwent
[...] Read more.
Brain activity in response to food cues following Roux-En-Y Gastric Bypass (RYGB) in binge eating (BE) or non-binge eating (NB) individuals is understudied. Here, 15 RYGB (8 BE; 7 NB) and 13 no treatment (NT) (7 BE; 6 NB) women with obesity underwent fMRI imaging while viewing high and low energy density food (HEF and LEF, respectively) and non-food (NF) visual cues. A region of interest (ROI) analysis compared BE participants to NB participants in those undergoing RYGB surgery pre-surgery and 4 months post. Results were corrected for multiple comparisons using liberal (p < 0.006 uncorrected) and stringent (p < 0.05 FDR corrected) thresholds. Four months following RYGB (vs. no treatment (NT) control), both BE and NB participants showed greater reductions in blood oxygen level-dependent (BOLD) signals (a proxy of local brain activity) in the dorsomedial prefrontal cortex in response to HEF (vs. LEF) cues (p < 0.006). BE (vs. NB) participants showed greater increases in the precuneus (p < 0.006) and thalamic regions (p < 0.05 corrected) to food (vs. NF). For RYGB (vs. NT) participants, BE participants, but not NB participants, showed lower BOLD signal in the middle occipital gyrus (p < 0.006), whilst NB participants, but not BE participants, showed lower signal in inferior frontal gyrus (p < 0.006) in response to HEF (vs. LEF). Results suggest distinct neural mechanisms of RGYB in BE and may help lead to improved clinical treatments.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Nutrition, Taste, Reward and Bariatric Surgery)
►▼
Show Figures
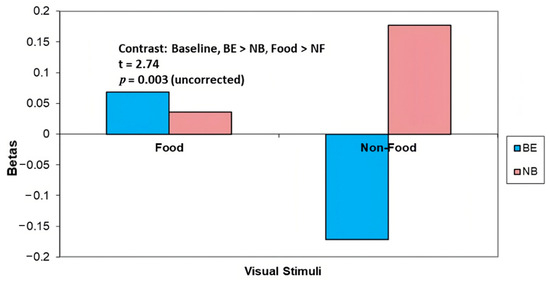
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
A Program of Life-Style Modification Improved the Body Weight and Micronutrient Status in Obese Patients after Bariatric Surgery
by
, , , , and
Nutrients 2023, 15(17), 3807; https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15173807 - 30 Aug 2023
Abstract
Introduction: Bariatric surgery is an efficient approach to rapidly reduce morbid obesity and associated comorbidities. However, approximately one-fourth of patients experience weight and comorbidity recurrence, and both obesity and bariatric surgery can lead to micronutrient deficiencies. Implementing a structured program of lifestyle modification
[...] Read more.
Introduction: Bariatric surgery is an efficient approach to rapidly reduce morbid obesity and associated comorbidities. However, approximately one-fourth of patients experience weight and comorbidity recurrence, and both obesity and bariatric surgery can lead to micronutrient deficiencies. Implementing a structured program of lifestyle modification (PLM) might enhance weight loss and improve micronutrient status. Methodology: A total of 121 severely obese patients underwent Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (RYGB). Among them, 71 adhered to a PLM involving dietary changes (low- and very-low-calorie Mediterranean diets) and physical exercises (aerobic and resistance training) both before and after surgery, while 50 patients followed a conventional protocol. Anthropometric measurements and serological parameter quantifications were conducted throughout the procedures. Results: The obese study population, primarily female (76.9%), with an average age of 47.11 ± 9.68, and a body mass index (BMI) of 44.68 ± 5.08 kg/m2, underwent either RYGB with a PLM or a conventional procedure. Before surgery, the PLM group exhibited significant reductions in body weight (6.3%) and phosphoremia compared to the conventional protocol (0.78%). Post-RYGB, the PLM group demonstrated shortened in-hospital stays and further BMI reductions (−16.12 kg/m2) that persisted for up to 2 years. Furthermore, the PLM group experienced increased plasma vitamin D levels (14.79 ng/mL vs. 1.2 ng/mL) for up to 2 years, as well as elevated folic acid (1.52 vs. −0.29 ng/mL) and phosphorus (0.48 vs. 0.06 mg/dL) levels at 1 month and 1 year after intervention, respectively. Notably, these effects were independent of weight loss. Conclusions: Initiating a structured PLM from the early stages of patients’ preparation for RYGB could enhance and extend the benefits of weight loss and positively impact micronutrient (vitamin D, phosphorus, and folic acid) status in obese patients.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Nutritional Management and Metabolic Complications of Bariatric Surgery)
►▼
Show Figures
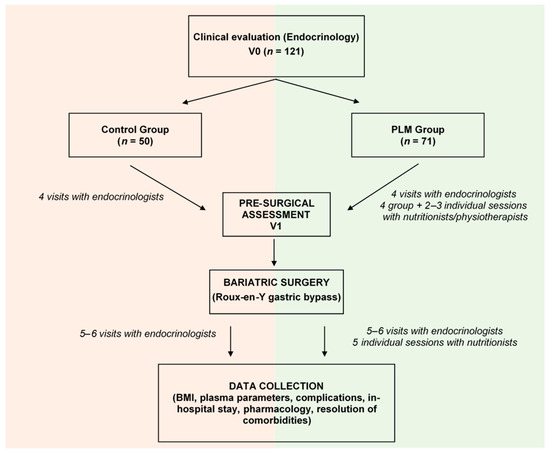
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Exploring the Network between Adipocytokines and Inflammatory Response in SARS-CoV-2 Infection: A Scoping Review
by
, , , , , and
Nutrients 2023, 15(17), 3806; https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15173806 - 30 Aug 2023
Abstract
Adipose tissue is actually regarded as an endocrine organ, rather than as an organ that merely stores energy. During the COVID-19 pandemic, obesity has undoubtedly emerged as one of the most important risk factors for disease severity and poor outcomes related to SARS-CoV-2
[...] Read more.
Adipose tissue is actually regarded as an endocrine organ, rather than as an organ that merely stores energy. During the COVID-19 pandemic, obesity has undoubtedly emerged as one of the most important risk factors for disease severity and poor outcomes related to SARS-CoV-2 infection. The aberrant production of cytokine-like hormones, called adipokines, may contribute to alterations in metabolism, dysfunction in vascular endothelium and the creation of a state of general chronic inflammation. Moreover, chronic, low-grade inflammation linked to obesity predisposes the host to immunosuppression and excessive cytokine activation. In this respect, understanding the mechanisms that link obesity with the severity of SARS-CoV-2 infection could represent a real game changer in the development of new therapeutic strategies. Our review therefore examines the pathogenic mechanisms of SARS-CoV-2, the implications with visceral adipose tissue and the influences of the adipose tissue and its adipokines on the clinical behavior of COVID-19.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Nutrition for the Prevention and Control of Chronic Degenerative Diseases and COVID-19)
►▼
Show Figures
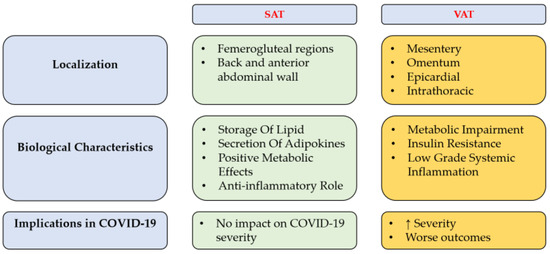
Figure 1

Journal Menu
► ▼ Journal Menu-
- Nutrients Home
- Aims & Scope
- Editorial Board
- Reviewer Board
- Topical Advisory Panel
- Instructions for Authors
- Special Issues
- Topics
- Sections & Collections
- Article Processing Charge
- Indexing & Archiving
- Editor’s Choice Articles
- Most Cited & Viewed
- Journal Statistics
- Journal History
- Journal Awards
- Society Collaborations
- Conferences
- Editorial Office
Journal Browser
► ▼ Journal BrowserHighly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Antioxidants, BioChem, Biomolecules, Cells, IJMS, Nutrients, Pharmaceutics, Foods
Bioactive Compounds with Application Potentials in Nutraceuticals and Nutricosmetics: Focus on Mechanism of Action and Application Science
Topic Editors: Pujie Shi, Tiantian Lin, Lin Chen, Xin Yang, Caili Fu, Hyun-Gyun Yuk, Rong FanDeadline: 30 September 2023
Topic in
Gastroenterology Insights, JCM, Livers, Nutrients, Reports
Multiple Organ Cross-Talk and Nutrition Metabolism in the Development and Progression of NAFLD / MAFLD
Topic Editors: Atsushi Nakajima, Masato YonedaDeadline: 20 October 2023
Topic in
Dietetics, Foods, Horticulturae, Nutrients, Plants
Edible Plants as Sources of Polyphenols: Cultivation Techniques, Extraction, and Nutraceutical Applications
Topic Editors: Luana Beatriz dos Santos Nascimento, Cecilia Brunetti, Antonella GoriDeadline: 20 December 2023
Topic in
Children, Dietetics, Foods, IJERPH, Nutrients
Nutrition Education, Food Literacy and Healthy Diets in Childhood and Adolescence
Topic Editors: Maha Hoteit, Reema Tayyem, Hassan YounesDeadline: 31 December 2023

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
Nutrients
The Role of Nutrition and Body Composition on Metabolism
Guest Editor: Defu MaDeadline: 7 September 2023
Special Issue in
Nutrients
Mediterranean Nutrients and Oils
Guest Editors: Adil El Midaoui, Gérard LizardDeadline: 15 September 2023
Special Issue in
Nutrients
Nutritional Intervention for Competitive Athletes
Guest Editor: Jay R. HoffmanDeadline: 25 September 2023
Special Issue in
Nutrients
Insulin 100th Anniversary: Century of Innovation for Diabetes
Guest Editor: George DimitriadisDeadline: 20 October 2023
Topical Collections
Topical Collection in
Nutrients
Diet and Multi-Omics
Collection Editors: Mohsen Mazidi, Richard Webb
Topical Collection in
Nutrients
Bioactive Peptides: Challenges and Opportunities
Collection Editor: Carmen Lammi
Topical Collection in
Nutrients
The Role of Nutrition in Exercise and Sports
Collection Editors: Roberta Ceci, Guglielmo Duranti
Topical Collection in
Nutrients
Connection between Microbiome, Lifestyle and Diet
Collection Editors: Eva Untersmayr, Peter M. AbujaConference Reports
Nutrients 2023, 15(11), 2451; https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15112451
Nutrients 2018, 10(1), 8; https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10010008