Journal Description
Pharmaceuticals
Pharmaceuticals
is a peer-reviewed, open access journal of medicinal chemistry and related drug sciences, published monthly online by MDPI. The Academy of Pharmaceutical Sciences (APS) is partners of Pharmaceuticals and their members receive a discount on the article processing charge.
- Open Access free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within Scopus, SCIE (Web of Science), PubMed, PMC, Embase, CAPlus / SciFinder, and other databases.
- Journal Rank: JCR - Q2 (Pharmacology & Pharmacy) / CiteScore - Q2 (Pharmaceutical Science)
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 15.7 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 3.6 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the first half of 2023).
- Recognition of Reviewers: reviewers who provide timely, thorough peer-review reports receive vouchers entitling them to a discount on the APC of their next publication in any MDPI journal, in appreciation of the work done.
- Testimonials: See what our editors and authors say about Pharmaceuticals.
- International Electronic Conference on Medicinal Chemistry (https://sciforum.net/series/ecmc/latest)
- Companion journals for Pharmaceuticals include: Pharmacoepidemiology, Psychoactives and Drugs and Drug Candidates.
Impact Factor:
4.6 (2022);
5-Year Impact Factor:
4.9 (2022)
Latest Articles
Practical Approach to Hypersensitivity to Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs) in Children
Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16(9), 1237; https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16091237 (registering DOI) - 01 Sep 2023
Abstract
Background: We aimed to assess the real-life prevalence, patient profile, and clinical presentation of drug hypersensitivity to NSAIDs in children after an incidence of an adverse event during treatment, verified by a drug challenge test. Methods: We included 56 children, aged 4–18 years,
[...] Read more.
Background: We aimed to assess the real-life prevalence, patient profile, and clinical presentation of drug hypersensitivity to NSAIDs in children after an incidence of an adverse event during treatment, verified by a drug challenge test. Methods: We included 56 children, aged 4–18 years, referred to our allergy clinic due to the incidence of adverse reaction during treatment. Skin prick tests and a drug provocation test were performed in all patients. Diagnostics for persistent urticaria were performed. Results: In 56 patients suspected of drug allergy, we proved NSAID hypersensitivity in 17 patients (30.1%). In 84.9% (n = 47) of patients, the clinical manifestations of hypersensitivity revealed angioedema and urticaria. The most common culprit drug among NSAIDs in children was ibuprofen. Thirty-one (55.4%) reactions were immediate, and 25 (44.6%) were delayed or late. Previous history of allergy was a risk factor for NSAID hypersensitivity (p = 0.001). Vitamin D deficiency in the blood serum was a risk factor for NASID hypersensitivity (OR = 5.76 (95% Cl: 1.42–23.41)). Conclusions: Hypersensitivity to NSAIDs is a difficult diagnostic problem in pediatric allergy. The most common manifestation of hypersensitivity to ibuprofen in children is acute urticaria and angioedema. Two important problems in the differential diagnosis are cofactors such as vitamin D levels and viral infections, which require further research.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Pharmacology)
Open AccessArticle
Regulation of Adipose-Derived Stem Cell Activity by Melatonin Receptors in Terms of Viability and Osteogenic Differentiation
Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16(9), 1236; https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16091236 (registering DOI) - 01 Sep 2023
Abstract
Melatonin is a hormone secreted mainly by the pineal gland and acts through the Mel1A and Mel1B receptors. Among other actions, melatonin significantly increases osteogenesis during bone regeneration. Human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells (ADSCs) are also known to have the potential to differentiate
[...] Read more.
Melatonin is a hormone secreted mainly by the pineal gland and acts through the Mel1A and Mel1B receptors. Among other actions, melatonin significantly increases osteogenesis during bone regeneration. Human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells (ADSCs) are also known to have the potential to differentiate into osteoblast-like cells; however, inefficient culturing due to the loss of properties over time or low cell survival rates on scaffolds is a limitation. Improving the process of ADSC expansion in vitro is crucial for its further successful use in bone regeneration. This study aimed to assess the effect of melatonin on ADSC characteristics, including osteogenicity. We assessed ADSC viability at different melatonin concentrations as well as the effect on its receptor inhibitors (luzindole or 4-P-PDOT). Moreover, we analyzed the ADSC phenotype, apoptosis, cell cycle, and expression of MTNR1A and MTNR1B receptors, and its potential for osteogenic differentiation. We found that ADSCs treated with melatonin at a concentration of 100 µM had a higher viability compared to those treated at higher melatonin concentrations. Melatonin did not change the phenotype of ADSCs or induce apoptosis and it promoted the activity of some osteogenesis-related genes. We concluded that melatonin is safe, non-toxic to normal ADSCs in vitro, and can be used in regenerative medicine at low doses (100 μM) to improve cell viability without negatively affecting the osteogenic potential of these cells.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Osteogenesis Imperfecta—Current and Future Therapies)
►▼
Show Figures
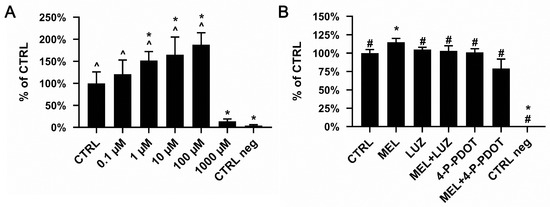
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Rational Design, Synthesis, and Evaluation of Fluorescent CB2 Receptor Ligands for Live-Cell Imaging: A Comprehensive Review
Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16(9), 1235; https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16091235 - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
The cannabinoid receptors CB1 and CB2 are class A G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) that are activated via endogenous lipids called endocannabinoids. The endocannabinoid system (ECS) plays a critical role in the regulation of several physiological states and a wide range of
[...] Read more.
The cannabinoid receptors CB1 and CB2 are class A G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) that are activated via endogenous lipids called endocannabinoids. The endocannabinoid system (ECS) plays a critical role in the regulation of several physiological states and a wide range of diseases. In recent years, drug discovery approaches targeting the cannabinoid type 2 receptor (CB2R) have gained prominence. Particular attention has been given to selective agonists targeting the CB2 receptors to circumvent the neuropsychotropic side effects associated with CB1 receptors. The pharmacological modulation of CB2R holds therapeutic promise for various diseases, such as inflammatory disorders and immunological conditions, as well as pain management and cancer treatment. Recently, the utilization of fluorescent probes has emerged as a valuable technique for investigating the interactions between ligands and proteins at an exceptional level of spatial and temporal precision. In this review, we aim to examine the progress made in the development of fluorescent probes targeting CB2 receptors and highlight their significance in facilitating the successful clinical translation of CB2R-based therapies.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Therapeutic Potential for Cannabinoids and Their Receptors)
►▼
Show Figures
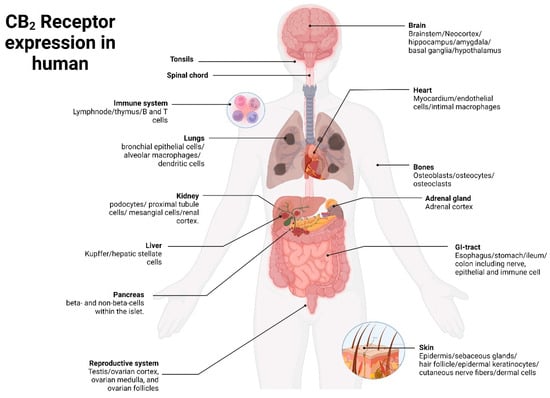
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Neuroprotective Properties of Oleanolic Acid—Computational-Driven Molecular Research Combined with In Vitro and In Vivo Experiments
Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16(9), 1234; https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16091234 - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
Oleanolic acid (OA), as a ubiquitous compound in the plant kingdom, is studied for both its neuroprotective and neurotoxic properties. The mechanism of acetylcholinesterase (AChE) inhibitory potential of OA is investigated using molecular dynamic simulations (MD) and docking as well as biomimetic tests.
[...] Read more.
Oleanolic acid (OA), as a ubiquitous compound in the plant kingdom, is studied for both its neuroprotective and neurotoxic properties. The mechanism of acetylcholinesterase (AChE) inhibitory potential of OA is investigated using molecular dynamic simulations (MD) and docking as well as biomimetic tests. Moreover, the in vitro SH-SY5Y human neuroblastoma cells and the in vivo zebrafish model were used. The inhibitory potential towards the AChE enzyme is examined using the TLC-bioautography assay (the IC50 value is 9.22 μM). The CH-π interactions between the central fragment of the ligand molecule and the aromatic cluster created by the His440, Phe288, Phe290, Phe330, Phe331, Tyr121, Tyr334, Trp84, and Trp279 side chains are observed. The results of the in vitro tests using the SH-SY5Y cells indicate that the viability rate is reduced to 71.5%, 61%, and 43% at the concentrations of 100 µg/mL, 300 µg/mL, and 1000 µg/mL, respectively, after 48 h of incubation, whereas cytotoxicity against the tested cell line with the IC50 value is 714.32 ± 32.40 µg/mL. The in vivo tests on the zebrafish prove that there is no difference between the control and experimental groups regarding the mortality rate and morphology (p > 0.05).
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Structural and Computational-Driven Molecule Design in Drug Discovery)
►▼
Show Figures
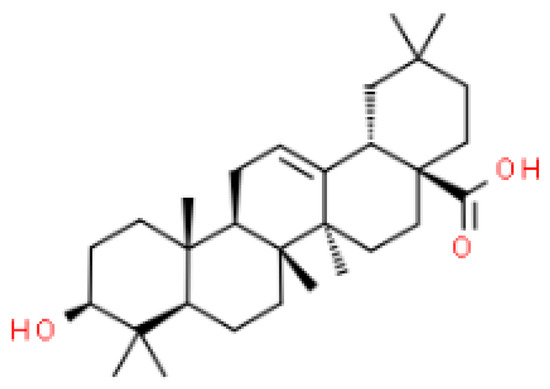
Figure 1
Open AccessEditorial
Special Issue “Osteosarcomas: Treatment Strategies”
Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16(9), 1233; https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16091233 - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
This Special Issue, titled “Osteosarcomas: Treatment Strategies”, aims to overview the recent and future research trends related to the treatment of osteosarcoma [...]
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Osteosarcomas: Treatment Strategies)
Open AccessArticle
In Vitro, Oral Acute, and Repeated 28-Day Oral Dose Toxicity of a Mixed-Valence Polyoxovanadate Cluster
by
, , , , , , , , , , , , , , and
Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16(9), 1232; https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16091232 - 30 Aug 2023
Abstract
Polyoxovanadates (POV) are a subgroup of polyoxometalates (POM), which are nanosized clusters with reported biological activities. This manuscript describes the first toxicity evaluation of a mixed-valence polyoxovanadate, pentadecavanadate, (Me4N)6[V15O36Cl], abbreviated as V15. Cytotoxicity
[...] Read more.
Polyoxovanadates (POV) are a subgroup of polyoxometalates (POM), which are nanosized clusters with reported biological activities. This manuscript describes the first toxicity evaluation of a mixed-valence polyoxovanadate, pentadecavanadate, (Me4N)6[V15O36Cl], abbreviated as V15. Cytotoxicity experiments using peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC), larvae of Artemia salina Leach, and in vivo oral acute and repeated 28-day doses in mice was carried out. The LC50 values in PBMC cells and A. salina were 17.5 ± 5.8 μmol L−1, and 17.9 µg L−1, respectively, which indicates high cytotoxic activity. The toxicity in mice was not observed upon acute exposure in a single dose, however, the V15 repeated 28-day oral administration demonstrated high toxicity using 25 mg/kg, 50 mg/kg and, 300 mg/kg doses. The biochemical and hematological analyses during the 28-day administration of V15 showed significant alteration of the metabolic parameters related to the kidney and liver, suggesting moderate toxicity. The V15 toxicity was attributed to the oxidative stress and lipid peroxidation, once thiobarbituric acid (TBAR) levels significantly increased in both males and females treated with high doses of the POV and also in males treated with a lower dose of the POV. This is the first study reporting a treatment-related mortality in animals acutely administrated with a mixed-valence POV, contrasting with the well-known, less toxic decavanadate. These results document the toxicity of this mixed-valence POV, which may not be suitable for biomedical applications.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Metal Nanoparticles’ Biological Activity and Pharmaceutical Applications)
►▼
Show Figures
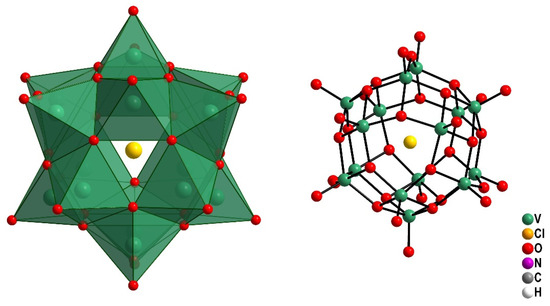
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children Following COVID-19 Vaccination: A Sex-Stratified Analysis of the VAERS Database Using Brighton Collaboration Criteria
by
, , , , , , , , , , and
Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16(9), 1231; https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16091231 - 30 Aug 2023
Abstract
Multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-c) is an uncommon, but serious, inflammatory response that occurs after SARS-CoV-2 infection. As time went by, MIS-c was also reported as a potential adverse event following COVID-19 vaccination. A descriptive analysis was performed of Individual Case Safety
[...] Read more.
Multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-c) is an uncommon, but serious, inflammatory response that occurs after SARS-CoV-2 infection. As time went by, MIS-c was also reported as a potential adverse event following COVID-19 vaccination. A descriptive analysis was performed of Individual Case Safety Reports (ICSRs) associated with anti COVID-19 vaccines and related to the pediatric population from 2020 to 2022. The present pharmacovigilance study aimed to describe cases of MIS-c following COVID-19 vaccination, stratified by sex, reported in the Vaccine Adverse Events Reporting System (VAERS) and meeting the Brighton Collaboration criteria for case definition. We assessed all suspected cases through the case definition and classification of the Brighton Collaboration Group, and only definitive, probable, and possible cases were included in the analysis. The Reporting Odds Ratio (ROR) with 95% Confidence Interval (CI) was computed to assess if males have a lower/higher probability of reporting ICSRs with MIS-c compared with females. Overall, we found 79 cases of potentially reported MIS-c following vaccination. This study demonstrated that MIS-c following vaccination was more commonly reported for male subjects with a median age of 10 years (IQR 10.0–11.4), especially after the first dose of anti COVID-19 vaccines with a median time to onset of 27 days. Even so, the rate of occurrence of MIS-c following anti COVID-19 vaccines is lower (0.12/100,000 vaccinated subjects; 95% CI, 0.12–0.13). Overall, all ICSRs were serious and caused or prolonged hospitalization. Finally, disproportionality analysis showed that males had a higher reporting probability of MIS-c compared with females following immunization with mRNA COVID-19 vaccines. Since only a few years of marketing are available, further data from real-life contexts are needed.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Pharmacology)
►▼
Show Figures
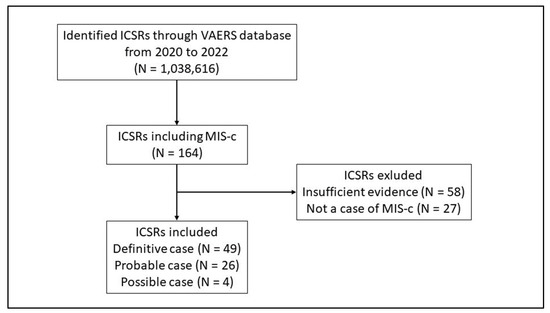
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Age of Antibiotic Resistance in MDR/XDR Clinical Pathogen of Pseudomonas aeruginosa
by
, , , , , , , , and
Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16(9), 1230; https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16091230 - 30 Aug 2023
Abstract
Antibiotic resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa remains one of the most challenging phenomena of everyday medical science. The universal spread of high-risk clones of multidrug-resistant/extensively drug-resistant (MDR/XDR) clinical P. aeruginosa has become a public health threat. The P. aeruginosa bacteria exhibits remarkable genome plasticity
[...] Read more.
Antibiotic resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa remains one of the most challenging phenomena of everyday medical science. The universal spread of high-risk clones of multidrug-resistant/extensively drug-resistant (MDR/XDR) clinical P. aeruginosa has become a public health threat. The P. aeruginosa bacteria exhibits remarkable genome plasticity that utilizes highly acquired and intrinsic resistance mechanisms to counter most antibiotic challenges. In addition, the adaptive antibiotic resistance of P. aeruginosa, including biofilm-mediated resistance and the formation of multidrug-tolerant persisted cells, are accountable for recalcitrance and relapse of infections. We highlighted the AMR mechanism considering the most common pathogen P. aeruginosa, its clinical impact, epidemiology, and save our souls (SOS)-mediated resistance. We further discussed the current therapeutic options against MDR/XDR P. aeruginosa infections, and described those treatment options in clinical practice. Finally, other therapeutic strategies, such as bacteriophage-based therapy and antimicrobial peptides, were described with clinical relevance.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Antimicrobial Peptides and Proteins: A Potential Approach to Treat and Combat Antimicrobial Resistance)
►▼
Show Figures
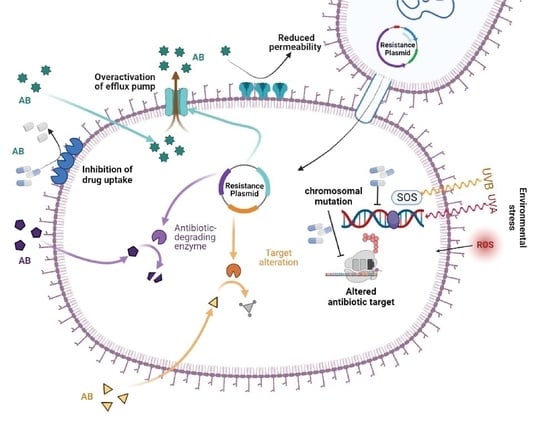
Graphical abstract
Open AccessReview
Anticancer Potential of Flavonoids: An Overview with an Emphasis on Tangeretin
by
, , and
Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16(9), 1229; https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16091229 - 30 Aug 2023
Abstract
Natural compounds with pharmacological activity, flavonoids have been the subject of an exponential increase in studies in the field of scientific research focused on therapeutic purposes due to their bioactive properties, such as antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anti-aging, antibacterial, antiviral, neuroprotective, radioprotective, and antitumor activities.
[...] Read more.
Natural compounds with pharmacological activity, flavonoids have been the subject of an exponential increase in studies in the field of scientific research focused on therapeutic purposes due to their bioactive properties, such as antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anti-aging, antibacterial, antiviral, neuroprotective, radioprotective, and antitumor activities. The biological potential of flavonoids, added to their bioavailability, cost-effectiveness, and minimal side effects, direct them as promising cytotoxic anticancer compounds in the optimization of therapies and the search for new drugs in the treatment of cancer, since some extensively antineoplastic therapeutic approaches have become less effective due to tumor resistance to drugs commonly used in chemotherapy. In this review, we emphasize the antitumor properties of tangeretin, a flavonoid found in citrus fruits that has shown activity against some hallmarks of cancer in several types of cancerous cell lines, such as antiproliferative, apoptotic, anti-inflammatory, anti-metastatic, anti-angiogenic, antioxidant, regulatory expression of tumor-suppressor genes, and epigenetic modulation.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Pharmacological Activities of Flavonoids and Its Analogues)
►▼
Show Figures
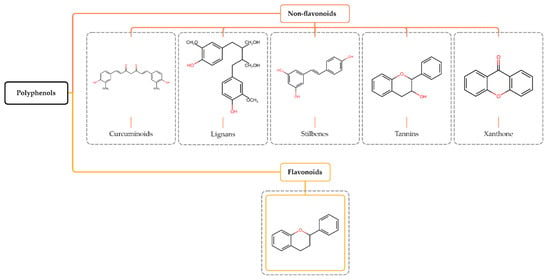
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Hawaiian Plants with Beneficial Effects on Sleep, Anxiety, and Mood, etc.
Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16(9), 1228; https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16091228 - 30 Aug 2023
Abstract
Diverse chemical messengers are responsible for maintaining homeostasis in the human body, for example, hormones and neurotransmitters. Various Hawaiian plant species produce compounds that exert effects on these messengers and the systems of which they are a part. The main purpose of this
[...] Read more.
Diverse chemical messengers are responsible for maintaining homeostasis in the human body, for example, hormones and neurotransmitters. Various Hawaiian plant species produce compounds that exert effects on these messengers and the systems of which they are a part. The main purpose of this review article is to evaluate the potential effects of Hawaiian plants on reducing pain and anxiety and improving sleep and mood. A comprehensive literature search was conducted in SciFinder, PubMed, Science Direct, Scopus, Google Scholar, and Scientific Information Database between 2019 and 2023 to identify related articles. Results indicate that several Hawaiian plant species, such as M. citrifolia and P. methysticum, have medicinal properties associated with these effects. These plants have been used in traditional Hawaiian cultural practices for centuries, suggesting their potential to benefit human health and well-being. This review presents a comprehensive analysis of the available evidence concerning the potential impacts of Hawaiian plants on sleep, anxiety, mood, and pain.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Neuropharmacology of Plant Extracts and Their Active Compounds)
►▼
Show Figures
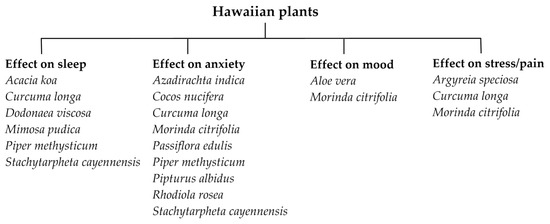
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Evaluation of Pupillometry for CYP2D6 Phenotyping in Children Treated with Tramadol
by
, , , , , , , and
Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16(9), 1227; https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16091227 - 30 Aug 2023
Abstract
Following the contraindication of codeine use in children, increasing use of tramadol has been observed in pain management protocols. However, tramadol’s pharmacokinetics (PK) and pharmacodynamics are influenced by cytochrome P450 (CYP)2D6 activity, similarly to codeine. Previous studies in adults have demonstrated a correlation
[...] Read more.
Following the contraindication of codeine use in children, increasing use of tramadol has been observed in pain management protocols. However, tramadol’s pharmacokinetics (PK) and pharmacodynamics are influenced by cytochrome P450 (CYP)2D6 activity, similarly to codeine. Previous studies in adults have demonstrated a correlation between pupillary response and tramadol PK. Our objective was to evaluate pupillometry as a phenotyping method to assess CYP2D6 activity in children treated with tramadol. We included 41 children (mean age 11 years) receiving a first dose of tramadol (2 mg/kg) in the emergency room (ER) as part of their routine care. CYP2D6 phenotyping and genotyping were performed. The concentrations of tramadol and its active metabolite, M1, were measured, and static and dynamic pupillometry was conducted using a handheld pupillometer at the time of tramadol administration and during the ER stay. Pupillometric measurements were obtained for 37 children. Tramadol affected pupillary parameters, with a decrease in pupil diameter in 83.8% of children (p = 0.002) (mean decrease 14.1 ± 16.7%) and a decrease in reflex amplitude constriction in 78.4% (p = 0.011) (mean decrease 17.7 ± 34.5%) at T150 compared to T0. We were unable to identify a correlation between pupillometry measurements and CYP2D6 activity. Likely confounding factors include light intensity, pain, and stress, making the procedure less feasible in paediatric emergency settings.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Pharmacology of Pediatric Medicines)
►▼
Show Figures
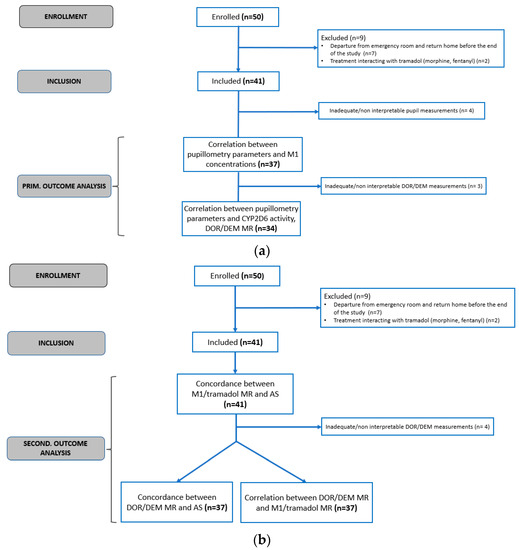
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Hot Melt Extrusion for Improving the Physicochemical Properties of Polydatin Derived from Polygoni cuspidati Extract; A Solution Recommended for Buccal Applications
Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16(9), 1226; https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16091226 - 30 Aug 2023
Abstract
Three different types of solid dispersions based on polyvinyl polymers and related copolymers (Kollidon® VA64, Soluplus® and Kollicoat IR®) comprising polydatin-rich Polygoni cuspidati extract were prepared by hot melt extrusion. The systems were characterized using X-ray powder diffraction, infrared
[...] Read more.
Three different types of solid dispersions based on polyvinyl polymers and related copolymers (Kollidon® VA64, Soluplus® and Kollicoat IR®) comprising polydatin-rich Polygoni cuspidati extract were prepared by hot melt extrusion. The systems were characterized using X-ray powder diffraction, infrared spectroscopy as well as by polydatin release and in vitro permeability. Mucoadhesive tablets were prepared from the extrudates based on Kollidon® VA64 and Soluplus® to obtain a suitable pharmaceutical form, where (hydroxypropyl)methyl cellulose was added as a mucoadhesive agent. The tablets were evaluated in terms of the kinetics of polydatin release as well as their mucoadhesive properties. The best tabletability properties, polydatin release profile and adequate mucoadhesive properties were obtained by the formulation containing the Kollidon® VA64-based extrudate, which makes it an excellent prototype for enhancing the release of poorly water-soluble compounds.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Pharmaceutical Applications of Polymers for Drug Discovery and Delivery)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Effect of Repeated Administration of ɣ-Valerolactone (GVL) and GHB in the Mouse: Neuroadaptive Changes of the GHB and GABAergic System
by
, , , , , , , and
Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16(9), 1225; https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16091225 - 30 Aug 2023
Abstract
Background: Gamma-hydroxybutyric acid (GHB) at low dosages has anxiolytic effects and promotes REM sleep and low-wave deep sleep. In the U.S., the legal form of GHB is prescribed to adults suffering from narcolepsy-associated cataplexy; the sodium salt of GHB is reserved for alcohol-addiction
[...] Read more.
Background: Gamma-hydroxybutyric acid (GHB) at low dosages has anxiolytic effects and promotes REM sleep and low-wave deep sleep. In the U.S., the legal form of GHB is prescribed to adults suffering from narcolepsy-associated cataplexy; the sodium salt of GHB is reserved for alcohol-addiction treatment. GHB is also a molecule of abuse and recreational use, it is a controlled substance in several countries, so gamma-valerolactone (GVL) has frequently been used as a legal substitute for it. GHB’s abuse profile is most likely attributable to its anxiolytic, hypnotic, and euphoric properties, as well as its widespread availability and inexpensive/low cost on the illicit market. Methods: Our study is focused on evaluating the potential effects on the mouse brain after repeated/prolonged administration of GHB and GVL at a pharmacologically active dose (100 mg/kg) through behavioral study and immunohistochemical analysis using the markers tetraspanin 17 (TSPAN17), aldehyde dehydrogenase 5 (ALDH5A1), Gamma-aminobutyric acid type A receptor (GABA-A), and Gamma-aminobutyric acid type B receptor (GABA-B). Results: Our findings revealed that prolonged administration of GHB and GVL at a pharmacologically active dose (100 mg/kg) can have effects on a component of the mouse brain, the intensity of which can be assessed using immunohistochemistry. The findings revealed that long-term GHB administration causes a significant plastic alteration of the GHB signaling system, with downregulation of the putative binding site (TSPAN17) and overexpression of ALDH5A1, especially in hippocampal neurons. Our findings further revealed that GABA-A and GABA-B receptors are downregulated in these brain locations, resulting in a greater decrease in GABA-B expression. Conclusions: The goal of this study, from the point of view of forensic pathology, is to provide a new methodological strategy for better understanding the properties of this controversial substance, which could help us better grasp the unknown mechanism underlying its abuse profile.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Psychoactive Substances: Clinical and Forensic Aspects 2023)
►▼
Show Figures
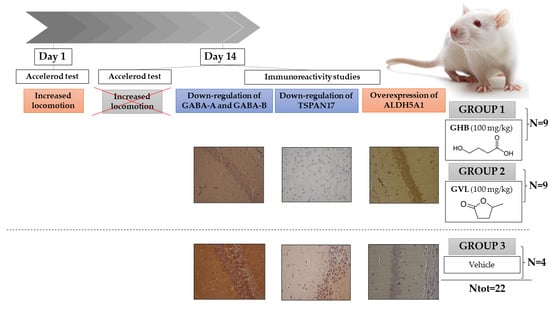
Graphical abstract
Open AccessCommunication
Effect of Betanin, the Major Pigment of Red Beetroot (Beta vulgaris L.), on the Activity of Recombinant Human Cytochrome P450 Enzymes
Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16(9), 1224; https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16091224 - 30 Aug 2023
Abstract
Most of the currently available drugs are derived from natural sources, but they are used only after extensive chemical modifications to improve their safety and efficacy. Natural products are used in health supplements and cosmetic preparations and have been used as auxiliary drugs
[...] Read more.
Most of the currently available drugs are derived from natural sources, but they are used only after extensive chemical modifications to improve their safety and efficacy. Natural products are used in health supplements and cosmetic preparations and have been used as auxiliary drugs or alternative medicines. When used in combination with conventional drugs, these herbal products are known to alter their pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics, reducing their therapeutic effects. Moreover, herb–drug interactions (HDIs) may have serious side effects, which is one of the major concerns in health practice. It is postulated that HDIs affect the pathways regulating cytochrome P450 enzymes (CYPs). Betanin, the chief pigment of red beetroot (Beta vulgaris L.), has various types of pharmacological activity, such as anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and anticancer effects. However, the potential risk of HDIs for betanin has not yet been studied. Thus, we aimed to predict more specific HDIs by evaluating the effects of betanin on CYPs (CYP1A2, CYP2B6, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP2D6, and CYP3A4), the major phase I metabolic enzymes, using fluorescence-/luminescence-based assays. Our results showed that betanin inhibited CYP3A4 activity in a dose-dependent manner (IC50 = 20.97 µΜ). Moreover, betanin acted as a competitive inhibitor of CYP3A4, as confirmed by evaluating Lineweaver–Burk plots (Ki value = 19.48 µΜ). However, no significant inhibitory effects were observed on other CYPs. Furthermore, betanin had no significant effect on CYP1A2, CYP2B6, or CYP2C9 induction in HepG2 cells. In conclusion, betanin acted as a competitive inhibitor of CYP3A4, and thus it should be used cautiously with other drugs that require metabolic enzymes as substrates. Additional in vivo studies and clinical trials are needed to further elucidate the HDIs of betanin.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Natural Products)
►▼
Show Figures
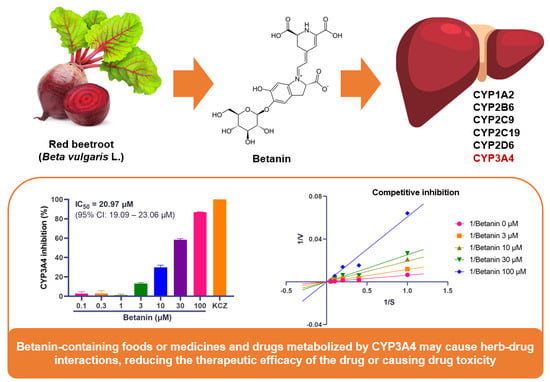
Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Ameliorative Effect of Ethanolic Extract of Moringa oleifera Leaves in Combination with Curcumin against PTZ-Induced Kindled Epilepsy in Rats: In Vivo and In Silico
by
, , , , , , and
Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16(9), 1223; https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16091223 - 30 Aug 2023
Abstract
The ameliorative effect of ethanolic extract of M. oleifera (MOEE) leaves in combination with curcumin against seizures, cognitive impairment, and oxidative stress in the molecular docking of PTZ-induced kindled rats was performed to predict the potential phytochemical effects of MOEE and curcumin against
[...] Read more.
The ameliorative effect of ethanolic extract of M. oleifera (MOEE) leaves in combination with curcumin against seizures, cognitive impairment, and oxidative stress in the molecular docking of PTZ-induced kindled rats was performed to predict the potential phytochemical effects of MOEE and curcumin against epilepsy. The effect of pretreatment with leaves of M. oleifera ethanolic extracts (MOEE) (250 mg/kg and 500 mg/kg, orally), curcumin (200 mg/kg and 300 mg/kg, orally), valproic acid used as a standard (100 mg/kg), and the combined effect of MOEE (250 mg/kg) and curcumin (200 mg/kg) at a low dose on Pentylenetetrazole was used for (PTZ)-induced kindling For the development of kindling, individual Wistar rats (male) were injected with pentyletetrazole (40 mg/kg, i.p.) on every alternate day. Molecular docking was performed by the Auto Dock 4.2 tool to merge the ligand orientations in the binding cavity. From the RCSB website, the crystal structure of human glutathione reductase (PDB ID: 3DK9) was obtained. Curcumin and M. oleifera ethanolic extracts (MOEE) showed dose-dependent effects. The combined effects of MOEE and curcumin leaves significantly improved the seizure score and decreased the number of myoclonic jerks compared with a standard dose of valproic acid. PTZ kindling induced significant oxidative stress and cognitive impairment, which was reversed by pretreatment with MOEE and curcumin. Glutathione reductase (GR) is an enzyme that plays a key role in the cellular control of reactive oxygen species (ROS). Therefore, activating GR can uplift antioxidant properties, which leads to the inhibition of ROS-induced cell death in the brain. The combination of the ethanolic extract of M. oleifera (MOEE) leaves and curcumin has shown better results than any other combination for antiepileptic effects by virtue of antioxidant effects. As per the docking study, chlorogenic acid and quercetin treated with acombination of curcumin have much more potential.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Natural Products)
►▼
Show Figures
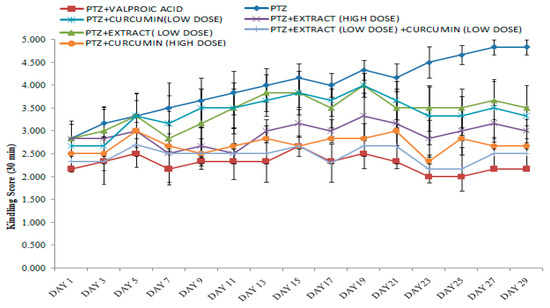
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Quinoline- and Isoindoline-Integrated Polycyclic Compounds as Antioxidant, and Antidiabetic Agents Targeting the Dual Inhibition of α-Glycosidase and α-Amylase Enzymes
Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16(9), 1222; https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16091222 - 30 Aug 2023
Abstract
Novel analogs of quinoline and isoindoline containing various heterocycles, such as tetrazole, triazole, pyrazole, and pyridine, were synthesized and characterized using FT-IR, NMR, and mass spectroscopy, and their antioxidant and antidiabetic activities were investigated. The previously synthesized compound 1 was utilized in conjugation
[...] Read more.
Novel analogs of quinoline and isoindoline containing various heterocycles, such as tetrazole, triazole, pyrazole, and pyridine, were synthesized and characterized using FT-IR, NMR, and mass spectroscopy, and their antioxidant and antidiabetic activities were investigated. The previously synthesized compound 1 was utilized in conjugation with ketone-bearing tetrazole and isoindoline-1,3-dione to synthesize Schiff’s bases 2 and 3. Furthermore, hydrazide 1 was treated with aryledines to provide pyrazoles 4a–c. Compound 5 was obtained by treating 1 with potassium thiocyanate, which was then cyclized in a basic solution to afford triazole 6. On the other hand, pyridine derivatives 7a–d and 8a–d were synthesized using 2-(4-acetylphenyl)isoindoline-1,3-dione via a one-pot condensation reaction with aryl aldehydes and active methylene compounds. From the antioxidant and antidiabetic studies, compound 7d showed significant antioxidant activity with an EC50 = 0.65, 0.52, and 0.93 mM in the free radical scavenging assays (DPPH, ABTS, and superoxide anion radicals). It also displayed noteworthy inhibitory activity against both enzymes α-glycosidase (IC50: 0.07 mM) and α-amylase (0.21 mM) compared to acarbose (0.09 mM α-glycosidase and 0.25 mM for α-amylase), and higher than in the other compounds. During in silico assays, compound 7d exhibited favorable binding affinities towards both α-glycosidase (−10.9 kcal/mol) and α-amylase (−9.0 kcal/mol) compared to acarbose (−8.6 kcal/mol for α-glycosidase and −6.0 kcal/mol for α-amylase). The stability of 7d was demonstrated by molecular dynamics simulations and estimations of the binding free energy throughout the simulation session (100 ns).
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Medicinal Chemistry of Indole and Quinoline Derivatives: Trends, and Future Directions as Therapeutic Drugs)
►▼
Show Figures
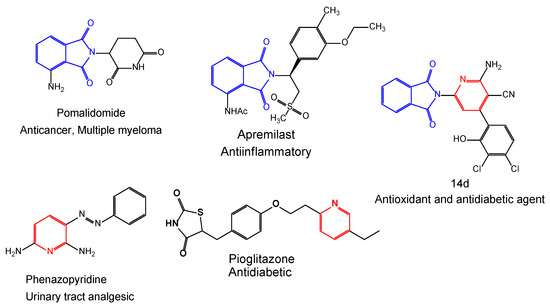
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
OR2H2 Activates CAMKKβ–AMPK–Autophagy Signaling Axis and Suppresses Senescence in VK2/E6E7 Cells
by
, , , , , , , , , , , , , and
Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16(9), 1221; https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16091221 - 29 Aug 2023
Abstract
Olfactory receptors are expressed in multiple extra-nasal tissues and these ectopic olfactory receptors mediate tissue-specific functions and regulate cellular physiology. Ectopic olfactory receptors may play key roles in tissues constantly exposed to odorants, thus the functionality of these receptors in genital tissues is
[...] Read more.
Olfactory receptors are expressed in multiple extra-nasal tissues and these ectopic olfactory receptors mediate tissue-specific functions and regulate cellular physiology. Ectopic olfactory receptors may play key roles in tissues constantly exposed to odorants, thus the functionality of these receptors in genital tissues is of particular interest. The functionality of ectopic olfactory receptors expressed in VK2/E6E7 human vaginal epithelial cells was investigated. OR2H2 was the most highly expressed olfactory receptor expressed in VK2/E6E7 cells, and activation of OR2H2 by aldehyde 13-13, a ligand of OR2H2, increased the intracellular calcium and cAMP concentrations. Immunoblotting demonstrated that activation of OR2H2 by aldehyde 13-13 stimulated the CAMKKβ–AMPK–mTORC1–autophagy signaling axis, and that these effects were negated by OR2H2 knockdown. AMPK is known to regulate senescence; consequently, we investigated further the effect of aldehyde 13-13 on senescence. In H2O2-induced senescent cells, activation of OR2H2 by aldehyde 13-13 restored proliferation, and reduced the expression of senescence markers, P16 and P19. Additionally, aldehyde 13-13 induced apoptosis of H2O2-induced senescent cells, compared with non-senescent normal cells. In vivo, aldehyde 13-13 increased the lifespan of Caenorhabditis elegans and budding yeast. These findings demonstrate that OR2H2 is a functional receptor in VK2/E6E7 cells, and that activation of OR2H2 activates the AMPK–autophagy axis, and suppresses cellular aging and senescence, which may increase cellular health.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Potential Therapeutic Methods in Reproductive Aging)
►▼
Show Figures
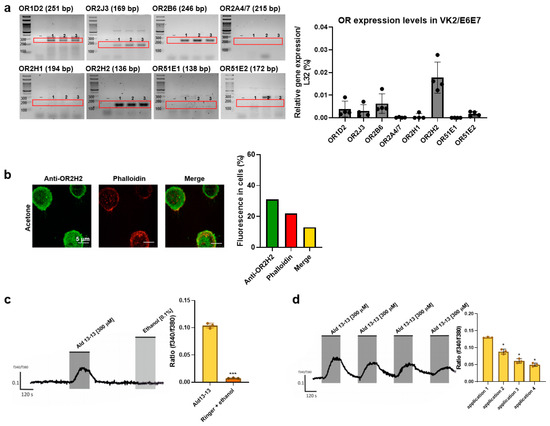
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Enhanced Antidepressant Activity of Nanostructured Lipid Carriers Containing Levosulpiride in Behavioral Despair Tests in Mice
by
, , , , , , , and
Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16(9), 1220; https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16091220 - 29 Aug 2023
Abstract
The potential of levosulpiride-loaded nanostructured lipid carriers (LSP-NLCs) for enhanced antidepressant and anxiolytic effects was evaluated in the current study. A forced swim test (FST) and tail suspension test (TST) were carried out to determine the antidepressant effect whereas anxiolytic activity was investigated
[...] Read more.
The potential of levosulpiride-loaded nanostructured lipid carriers (LSP-NLCs) for enhanced antidepressant and anxiolytic effects was evaluated in the current study. A forced swim test (FST) and tail suspension test (TST) were carried out to determine the antidepressant effect whereas anxiolytic activity was investigated using light–dark box and open field tests. Behavioral changes were evaluated in lipopolysaccharide-induced depressed animals. The access of LSP to the brain to produce therapeutic effects was estimated qualitatively by using fluorescently labeled LSP-NLCs. The distribution of LSP-NLCs was analyzed using ex vivo imaging of major organs after oral and intraperitoneal administration. Acute toxicity studies were carried out to assess the safety of LSP-NLCs in vivo. An improved antidepressant effect of LSP-NLCs on LPS-induced depression showed an increase in swimming time (237 ± 51 s) and struggling time (226 ± 15 s) with a reduction in floating (123 ± 51 s) and immobility time (134 ± 15 s) in FST and TST. The anxiolytic activity in the light–dark box and open field tests exhibited superiority over LSP dispersion. Near-infrared images of fluorescently labeled LSP-NLCs demonstrated the presence of coumarin dye in the brain after 1 h of administration. An acute toxicity study revealed no significant changes in organ-to-body weight ratio, serum biochemistry or tissue histology of major organs. It can be concluded that nanostructured lipid carriers can efficiently deliver LSP to the brain for improved therapeutic efficacy.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Current Insights on Lipid-Based Nanosystems 2023)
►▼
Show Figures
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Investigation of the Interaction between Mechanosynthesized ZnS Nanoparticles and Albumin Using Fluorescence Spectroscopy
by
, , , , , and
Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16(9), 1219; https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16091219 - 29 Aug 2023
Abstract
In this paper, ZnS nanoparticles were bioconjugated with bovine serum albumin and prepared in a form of nanosuspension using a wet circulation grinding. The stable nanosuspension with monomodal particle size distribution (d50 = 137 nm) and negative zeta potential (−18.3 mV) was
[...] Read more.
In this paper, ZnS nanoparticles were bioconjugated with bovine serum albumin and prepared in a form of nanosuspension using a wet circulation grinding. The stable nanosuspension with monomodal particle size distribution (d50 = 137 nm) and negative zeta potential (−18.3 mV) was obtained. The sorption kinetics and isotherm were determined. Interactions between ZnS and albumin were studied using the fluorescence techniques. The quenching mechanism, describing both static and dynamic interactions, was investigated. Various parameters were calculated, including the quenching rate constant, binding constant, stoichiometry of the binding process, and accessibility of fluorophore to the quencher. It has been found that tryptophan, in comparison to tyrosine, can be closer to the binding site established by analyzing the synchronous fluorescence spectra. The cellular mechanism in multiple myeloma cells treated with nanosuspension was evaluated by fluorescence assays for quantification of apoptosis, assessment of mitochondrial membrane potential and evaluation of cell cycle changes. The preliminary results confirm that the nontoxic nature of ZnS nanoparticles is potentially applicable in drug delivery systems. Additionally, slight changes in the secondary structure of albumin, accompanied by a decrease in α-helix content, were investigated using the FTIR method after analyzing the deconvoluted Amide I band spectra of ZnS nanoparticles conjugated with albumin. Thermogravimetric analysis and long-term stability studies were also performed to obtain a complete picture about the studied system.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Fluorescence Approaches in Drug Delivery)
►▼
Show Figures
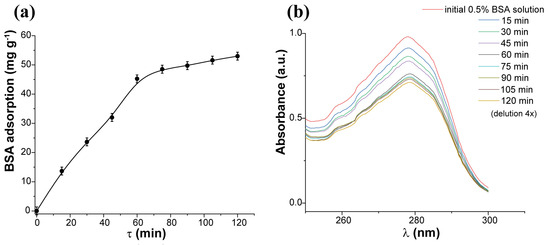
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Tryptophan Substitution in CJ-15,208 (cyclo[Phe-D-Pro-Phe-Trp]) Introduces δ-Opioid Receptor Antagonism, Preventing Antinociceptive Tolerance and Stress-Induced Reinstatement of Extinguished Cocaine-Conditioned Place Preference
by
, , , , , , and
Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16(9), 1218; https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16091218 - 29 Aug 2023
Abstract
The macrocyclic tetrapeptide CJ-15,208 (cyclo[Phe-D-Pro-Phe-Trp]) and its D-Trp isomer exhibit kappa opioid receptor (KOR) antagonism which prevents stress-induced reinstatement of extinguished cocaine-conditioned place preference. Here, we evaluated the effects of substitution of Trp and D-Trp on the peptides’ opioid activity, antinociceptive
[...] Read more.
The macrocyclic tetrapeptide CJ-15,208 (cyclo[Phe-D-Pro-Phe-Trp]) and its D-Trp isomer exhibit kappa opioid receptor (KOR) antagonism which prevents stress-induced reinstatement of extinguished cocaine-conditioned place preference. Here, we evaluated the effects of substitution of Trp and D-Trp on the peptides’ opioid activity, antinociceptive tolerance, and the ability to prevent relapse to extinguished drug-CPP. Six analogs were synthesized using a combination of solid-phase peptide synthesis and cyclization in solution. The analogs were evaluated in vitro for opioid receptor affinity in radioligand competition binding assays, efficacy in the [35S]GTPγS assay, metabolic stability in mouse liver microsomes, and for opioid activity and selectivity in vivo in the mouse 55 °C warm-water tail-withdrawal assay. Potential liabilities of locomotor impairment, respiratory depression, acute tolerance, and conditioned place preference (CPP) were also assessed in vivo, and the ameliorating effect of analogs on the reinstatement of extinguished cocaine-place preference was assessed. Substitutions of other D-amino acids for D-Trp did not affect (or in one case increased) KOR affinity, while two of the three substitutions of an L-amino acid for Trp decreased KOR affinity. In contrast, all but one substitution increased mu opioid receptor (MOR) affinity in vitro. The metabolic stabilities of the analogs were similar to those of their respective parent peptides, with analogs containing a D-amino acid being much more rapidly metabolized than those containing an L-amino acid in this position. In vivo, CJ-15,208 analogs demonstrated antinociception, although potencies varied over an 80-fold range and the mediating opioid receptors differed by substitution. KOR antagonism was lost for all but the D-benzothienylalanine analog, and the 2′-naphthylalanine analog instead demonstrated significant delta opioid receptor (DOR) antagonism. Introduction of DOR antagonism coincided with reduced acute opioid antinociceptive tolerance and prevented stress-induced reinstatement of extinguished cocaine-CPP.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Recent Trends in Cyclic Peptides as Therapeutic Agents)
►▼
Show Figures
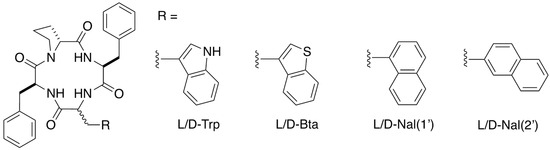
Figure 1

Journal Menu
► ▼ Journal Menu-
- Pharmaceuticals Home
- Aims & Scope
- Editorial Board
- Reviewer Board
- Topical Advisory Panel
- Instructions for Authors
- Special Issues
- Topics
- Sections & Collections
- Article Processing Charge
- Indexing & Archiving
- Editor’s Choice Articles
- Most Cited & Viewed
- Journal Statistics
- Journal History
- Journal Awards
- Society Collaborations
- Conferences
- Editorial Office
Journal Browser
► ▼ Journal BrowserHighly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Antibiotics, Biomolecules, IJMS, Marine Drugs, Pharmaceuticals
Compounds with Medicinal Value (2nd Volume)
Topic Editor: Maria Stefania SinicropiDeadline: 30 September 2023
Topic in
Biomedicines, Clinics and Practice, Diagnostics, JCM, Pharmaceuticals
C-reactive Protein in Inflammatory Diseases: Clinical Aspects
Topic Editors: Ahmed Sheriff, Jan TorzewskiDeadline: 31 October 2023
Topic in
JCM, Pharmaceuticals, Pharmacoepidemiology, Pharmacy, Vaccines, Healthcare
Mass Vaccination Campaigns: From Post-authorization Benefit-Risk Assessment to Public Health Impact
Topic Editors: Giampiero Mazzaglia, Lorenzo Giovanni Mantovani, Ippazio Cosimo AntonazzoDeadline: 30 November 2023
Topic in
Healthcare, JPM, Medicines, Pharmacy, Pharmaceutics, Pharmaceuticals
Drug Utilization and Medication Adherence: Strategies, Technologies and Practices
Topic Editors: Tamás Ágh, Enrica MendittoDeadline: 31 December 2023

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
Pharmaceuticals
Feature Reviews in Natural Products
Guest Editors: Daniela De Vita, Sabina Lachowicz-WiśniewskaDeadline: 5 September 2023
Special Issue in
Pharmaceuticals
NMDA Receptor-Based Therapeutics
Guest Editor: Antonius M. J. VanDongenDeadline: 15 September 2023
Special Issue in
Pharmaceuticals
Molecular and Cellular Studies of Natural Antioxidants as Potential Therapeutics for Cancer
Guest Editors: Hsueh-Wei Chang, Chien-Chih ChiuDeadline: 30 September 2023
Special Issue in
Pharmaceuticals
Chitosan Based Novel Pharmaceutical Dosage Forms and Drug Delivery Systems
Guest Editors: Ljiljana Djekic, Anđelija M. MalenovićDeadline: 15 October 2023
Topical Collections
Topical Collection in
Pharmaceuticals
Old Pharmaceuticals with New Applications
Collection Editor: Massimiliano Tognolini
Topical Collection in
Pharmaceuticals
Drug Discovery and Development for Tropical Diseases (TDs)
Collection Editor: Christophe DardonvilleConference Reports
Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16(3), 432; https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16030432
Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15(4), 388; https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15040388












.jpg)







