-
 Fruit Photosynthesis: More to Know about Where, How and Why
Fruit Photosynthesis: More to Know about Where, How and Why -
 The Growth Oscillator and Plant Stomata: An Open and Shut Case
The Growth Oscillator and Plant Stomata: An Open and Shut Case -
 Tracking Permeation of Dimethyl Sulfoxide (DMSO) in Mentha × piperita Shoot Tips Using Coherent Raman Microscopy
Tracking Permeation of Dimethyl Sulfoxide (DMSO) in Mentha × piperita Shoot Tips Using Coherent Raman Microscopy -
 Genetic Mapping of Seven Kinds of Locus for Resistance to Asian Soybean Rust
Genetic Mapping of Seven Kinds of Locus for Resistance to Asian Soybean Rust -
 Effect of Growth Stages on Anthocyanins and Polyphenols in the Root System of Sweet Potato
Effect of Growth Stages on Anthocyanins and Polyphenols in the Root System of Sweet Potato
Journal Description
Plants
Plants
is an international, scientific, peer-reviewed, open access journal published semimonthly online by MDPI. The Australian Society of Plant Scientists (ASPS), the Spanish Phytopathological Society (SEF), the Spanish Society of Plant Physiology (SEFV), the Spanish Society of Horticultural Sciences (SECH) and the Italian Society of Phytotherapy (S.I.Fit.) are affiliated with Plants and their members receive a discount on the article processing charges.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within Scopus, SCIE (Web of Science), PubMed, PMC, PubAg, AGRIS, CAPlus / SciFinder, and other databases.
- Journal Rank: JCR - Q1 (Plant Sciences) / CiteScore - Q1 (Plant Science)
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 15.3 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 3.1 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the first half of 2023).
- Recognition of Reviewers: reviewers who provide timely, thorough peer-review reports receive vouchers entitling them to a discount on the APC of their next publication in any MDPI journal, in appreciation of the work done.
Impact Factor:
4.5 (2022);
5-Year Impact Factor:
4.8 (2022)
Latest Articles
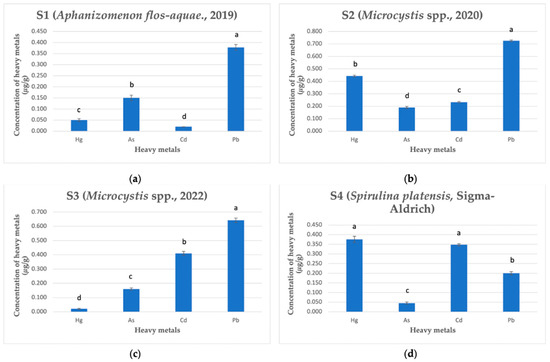
Determination of Heavy Metal Content: Arsenic, Cadmium, Mercury, and Lead in Cyano-Phycocyanin Isolated from the Cyanobacterial Biomass
Plants 2023, 12(17), 3150; https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12173150 (registering DOI) - 01 Sep 2023
Abstract
Cyano-phycocyanin (C-PC) is a light-absorbing biliprotein found in cyanobacteria, commonly known as blue-green algae. Due to its antioxidative, anti-inflammatory, and anticancer properties, this protein is a promising substance in medicine and pharmaceuticals. However, cyanobacteria tend to bind heavy metals from the environment, making
[...] Read more.
Cyano-phycocyanin (C-PC) is a light-absorbing biliprotein found in cyanobacteria, commonly known as blue-green algae. Due to its antioxidative, anti-inflammatory, and anticancer properties, this protein is a promising substance in medicine and pharmaceuticals. However, cyanobacteria tend to bind heavy metals from the environment, making it necessary to ensure the safety of C-PC for the development of pharmaceutical products, with C-PC isolated from naturally collected cyanobacterial biomass. This study aimed to determine the content of the most toxic heavy metals, arsenic (As), cadmium (Cd), mercury (Hg), and lead (Pb) in C-PC isolated from different cyanobacterial biomasses collected in the Kaunas Lagoon during 2019–2022, and compare them with the content of heavy metals in C-PC isolated from cultivated Spirulina platensis (S. platensis). Cyanobacteria of Aphanizomenon flos-aquae (A. flos-aquae) dominated the biomass collected in 2019, while the genus Microcystis dominated the biomasses collected in the years 2020 and 2022. Heavy metals were determined using inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS). ICP-MS analysis revealed higher levels of the most investigated heavy metals (Pb, Cd, and As) in C-PC isolated from the biomass with the dominant Microcystis spp. compared to C-PC isolated from the biomass with the predominant A. flos-aquae. Meanwhile, C-PC isolated from cultivated S. platensis exhibited lower concentrations of As and Pb than C-PC isolated from naturally collected cyanobacterial biomass.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Phytochemical Profiles of Plant Materials: From Extracts to Added Value Ingredients)
►
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Screening for Fungicide Efficacy in Controlling Blackleg Disease in Wasabi (Eutrema japonicum)
by
, , , , , , , and
Plants 2023, 12(17), 3149; https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12173149 (registering DOI) - 01 Sep 2023
Abstract
Blackleg disease is devastating for wasabi (Eutrema japonicum) production, occurring at any time and everywhere within the main production area of the Sichuan Province, China. There have been very few studies on the chemical control of this disease. In this study,
[...] Read more.
Blackleg disease is devastating for wasabi (Eutrema japonicum) production, occurring at any time and everywhere within the main production area of the Sichuan Province, China. There have been very few studies on the chemical control of this disease. In this study, we isolated and identified a local popular strain of the pathogen Plenodomus wasabiae. The isolated fungus strain caused typical disease spots on the leaves and rhizomes upon inoculation back to wasabi seedlings. The symptoms of blackleg disease developed very quickly, becaming visible on the second day after exposure to P. wasabiae and leading to death within one week. We then evaluated the efficacy of ten widely used fungicides to screen out effective fungicides. The efficacy of the tested fungicides was determined through mycelial growth inhibition on medium plates. As a result, tebuconazole and pyraclostrobin were able to inhibit the mycelial growth of P. wasabiae, and the most widely used dimethomorph in local production areas produced the lowest inhibition activity (13.8%). Nevertheless, the highest control efficacy of tebuconazole and pyraclostrobin on wasabi seedlings was only 47.48% and 39.03%, respectively. Generally, the control efficacy of spraying the fungicide before inoculation was better than that after inoculation. An increase in the application concentration of the two fungicides did not proportionately result in improved performance. We cloned the full-length sequence of sterol 14-demethylase (CYP51) and cytochrome B (CYTB) of which the mutations may contribute to the possible antifungalresistance. These two genes of the isolated fungus do not possess any reported mutations that lead to fungicide resistance. Previous studies indicate that there is a significant difference between fungicides in terms of the effectiveness of controlling blackleg disease; however, the control efficacy of fungicides is limited in blackleg control. Therefore, field management to prevent wound infection and unfavorable environmental conditions are more important than pesticide management.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Advances in Plant-Fungal Pathogen Interaction)
►▼
Show Figures
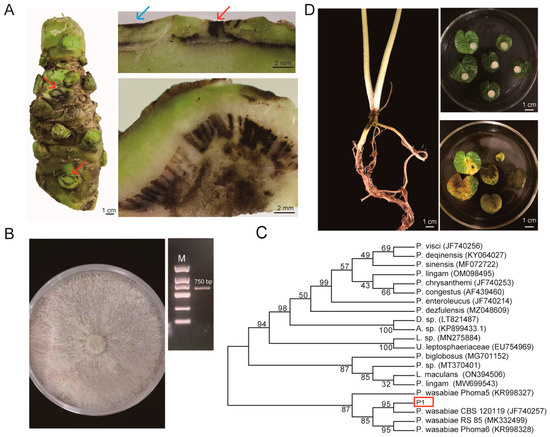
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Humic Substances Isolated from Recycled Biomass Trigger Jasmonic Acid Biosynthesis and Signalling
by
, , , , , , , and
Plants 2023, 12(17), 3148; https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12173148 (registering DOI) - 01 Sep 2023
Abstract
Intensive agriculture maintains high crop yields through chemical inputs, which are well known for their adverse effects on environmental quality and human health. Innovative technologies are required to reduce the risk generated by the extensive and harmful use of pesticides. The plant biostimulants
[...] Read more.
Intensive agriculture maintains high crop yields through chemical inputs, which are well known for their adverse effects on environmental quality and human health. Innovative technologies are required to reduce the risk generated by the extensive and harmful use of pesticides. The plant biostimulants made from humic substances isolated from recyclable biomass offer an alternative approach to address the need for replacing conventional agrochemicals without compromising the crop yield. The stimulatory effects of humic substances are commonly associated with plant hormones, particularly auxins. However, jasmonic acid (JA) is crucial metabolite in mediating the defence responses and governing plant growth and development. This work aimed to evaluate the changes in the biosynthesis and signalling pathway of JA in tomato seedlings treated with humic acids (HA) isolated from vermicompost. We use the tomato model system cultivar Micro-Tom (MT) harbouring a reporter gene fused to a synthetic promoter that responds to jasmonic acid (JERE::GUS). The transcript levels of genes involved in JA generation and activity were also determined using qRT-PCR. The application of HA promoted plant growth and altered the JA status, as revealed by both GUS and qRT-PCR assays. Both JA enzymatic synthesis (LOX, OPR3) and JA signalling genes (JAZ and JAR) were found in higher transcription levels in plants treated with HA. In addition, ethylene (ETR4) and auxin (ARF6) signalling components were positively modulated by HA, revealing a hormonal cross-talk. Our results prove that the plant defence system linked to JA can be emulated by HA application without growth inhibition.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Plant Growth Promoters: The Eliciting Role of Recycled Biomasses)
►▼
Show Figures
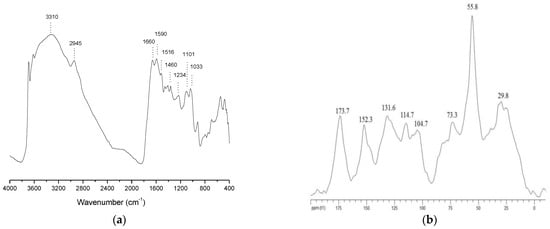
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Recent Advances in Microbial-Assisted Remediation of Cadmium-Contaminated Soil
by
, , , , , , , , and
Plants 2023, 12(17), 3147; https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12173147 (registering DOI) - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
Soil contamination with cadmium (Cd) is a severe concern for the developing world due to its non-biodegradability and significant potential to damage the ecosystem and associated services. Industries such as mining, manufacturing, building, etc., rapidly produce a substantial amount of Cd, posing environmental
[...] Read more.
Soil contamination with cadmium (Cd) is a severe concern for the developing world due to its non-biodegradability and significant potential to damage the ecosystem and associated services. Industries such as mining, manufacturing, building, etc., rapidly produce a substantial amount of Cd, posing environmental risks. Cd toxicity in crop plants decreases nutrient and water uptake and translocation, increases oxidative damage, interferes with plant metabolism and inhibits plant morphology and physiology. However, various conventional physicochemical approaches are available to remove Cd from the soil, including chemical reduction, immobilization, stabilization and electro-remediation. Nevertheless, these processes are costly and unfriendly to the environment because they require much energy, skilled labor and hazardous chemicals. In contrasting, contaminated soils can be restored by using bioremediation techniques, which use plants alone and in association with different beneficial microbes as cutting-edge approaches. This review covers the bioremediation of soils contaminated with Cd in various new ways. The bioremediation capability of bacteria and fungi alone and in combination with plants are studied and analyzed. Microbes, including bacteria, fungi and algae, are reported to have a high tolerance for metals, having a 98% bioremediation capability. The internal structure of microorganisms, their cell surface characteristics and the surrounding environmental circumstances are all discussed concerning how microbes detoxify metals. Moreover, issues affecting the effectiveness of bioremediation are explored, along with potential difficulties, solutions and prospects.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Steps Forward in Phytoremediation Technologies: Overcoming the Challenges)
►▼
Show Figures
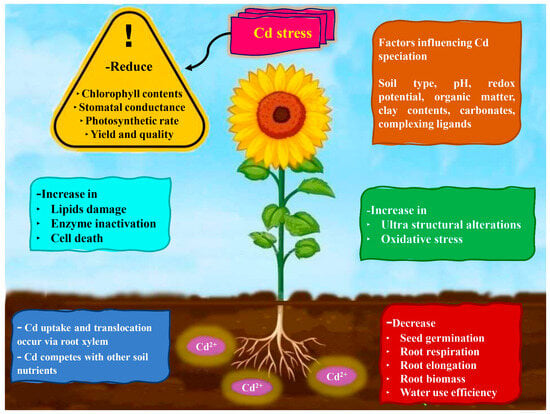
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Environmental Factors Affecting Monoterpene Emissions from Terrestrial Vegetation
by
, , , , , , and
Plants 2023, 12(17), 3146; https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12173146 (registering DOI) - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
Monoterpenes are volatile organic compounds that play important roles in atmospheric chemistry, plant physiology, communication, and defense. This review compiles the monoterpene emission flux data reported for different regions and plant species and highlights the role of abiotic environmental factors in controlling the
[...] Read more.
Monoterpenes are volatile organic compounds that play important roles in atmospheric chemistry, plant physiology, communication, and defense. This review compiles the monoterpene emission flux data reported for different regions and plant species and highlights the role of abiotic environmental factors in controlling the emissions of biogenic monoterpenes and their emission fluxes for terrestrial plant species (including seasonal variations). Previous studies have demonstrated the role and importance of ambient air temperature and light in controlling monoterpene emissions, likely contributing to higher monoterpene emissions during the summer season in temperate regions. In addition to light and temperature dependence, other important environmental variables such as carbon dioxide (CO2), ozone (O3), soil moisture, and nutrient availability are also known to influence monoterpene emissions rates, but the information available is still limited. Throughout the paper, we identify knowledge gaps and provide recommendations for future studies.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic Plants Volatile Compounds)
►▼
Show Figures
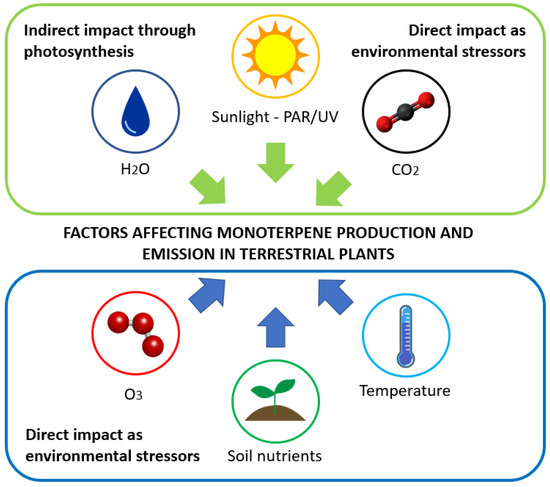
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Effect of the Nonpathogenic Strain Fusarium oxysporum FO12 on Fe Acquisition in Rice (Oryza sativa L.) Plants
by
, , , , , , , and
Plants 2023, 12(17), 3145; https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12173145 - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
Rice (Oryza sativa L.) is a very important cereal worldwide, since it is the staple food for more than half of the world’s population. Iron (Fe) deficiency is among the most important agronomical concerns in calcareous soils where rice plants may suffer
[...] Read more.
Rice (Oryza sativa L.) is a very important cereal worldwide, since it is the staple food for more than half of the world’s population. Iron (Fe) deficiency is among the most important agronomical concerns in calcareous soils where rice plants may suffer from this deficiency. Current production systems are based on the use of high-yielding varieties and the application of large quantities of agrochemicals, which can cause major environmental problems. The use of beneficial rhizosphere microorganisms is considered a relevant sustainable alternative to synthetic fertilizers. The main goal of this study was to determine the ability of the nonpathogenic strain Fusarium oxysporum FO12 to induce Fe-deficiency responses in rice plants and its effects on plant growth and Fe chlorosis. Experiments were carried out under hydroponic system conditions. Our results show that the root inoculation of rice plants with FO12 promotes the production of phytosiderophores and plant growth while reducing Fe chlorosis symptoms after several days of cultivation. Moreover, Fe-related genes are upregulated by FO12 at certain times in inoculated plants regardless of Fe conditions. This microorganism also colonizes root cortical tissues. In conclusion, FO12 enhances Fe-deficiency responses in rice plants, achieves growth promotion, and reduces Fe chlorosis symptoms.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Biochemical Interactions of Iron Nutrition in Plants)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Global Transcriptome and Co-Expression Network Analyses Revealed Hub Genes Controlling Seed Size/Weight and/or Oil Content in Peanut
by
, , , , , , , , , and
Plants 2023, 12(17), 3144; https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12173144 (registering DOI) - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
Cultivated peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.) is an important economic and oilseed crop worldwide, providing high-quality edible oil and high protein content. Seed size/weight and oil content are two important determinants of yield and quality in peanut breeding. To identify key regulators controlling
[...] Read more.
Cultivated peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.) is an important economic and oilseed crop worldwide, providing high-quality edible oil and high protein content. Seed size/weight and oil content are two important determinants of yield and quality in peanut breeding. To identify key regulators controlling these two traits, two peanut cultivars with contrasting phenotypes were compared to each other, one having a larger seed size and higher oil content (Zhonghua16, ZH16 for short), while the second cultivar had smaller-sized seeds and lower oil content (Zhonghua6, ZH6). Whole transcriptome analyses were performed on these two cultivars at four stages of seed development. The results showed that ~40% of the expressed genes were stage-specific in each cultivar during seed development, especially at the early stage of development. In addition, we identified a total of 5356 differentially expressed genes (DEGs) between ZH16 and ZH6 across four development stages. Weighted gene co-expression network analysis (WGCNA) based on DEGs revealed multiple hub genes with potential roles in seed size/weight and/or oil content. These hub genes were mainly involved in transcription factors (TFs), phytohormones, the ubiquitin–proteasome pathway, and fatty acid synthesis. Overall, the candidate genes and co-expression networks detected in this study could be a valuable resource for genetic breeding to improve seed yield and quality traits in peanut.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Plant Genetics, Genomics and Biotechnology)
Open AccessCommunication
Inequality Measure of Leaf Area Distribution for a Drought-Tolerant Landscape Plant
by
, , , , , , , and
Plants 2023, 12(17), 3143; https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12173143 (registering DOI) - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
Measuring the inequality of leaf area distribution per plant (ILAD) can provide a useful tool for quantifying the influences of intra- and interspecific competition, foraging behavior of herbivores, and environmental stress on plants’ above-ground architectural structures and survival strategies. Despite its importance, there
[...] Read more.
Measuring the inequality of leaf area distribution per plant (ILAD) can provide a useful tool for quantifying the influences of intra- and interspecific competition, foraging behavior of herbivores, and environmental stress on plants’ above-ground architectural structures and survival strategies. Despite its importance, there has been limited research on this issue. This paper aims to fill this gap by comparing four inequality indices to measure ILAD, using indices for quantifying household income that are commonly used in economics, including the Gini index (which is based on the Lorenz curve), the coefficient of variation, the Theil index, and the mean log deviation index. We measured the area of all leaves for 240 individual plants of the species Shibataea chinensis Nakai, a drought-tolerant landscape plant found in southern China. A three-parameter performance equation was fitted to observations of the cumulative proportion of leaf area vs. the cumulative proportion of leaves per plant to calculate the Gini index for each individual specimen of S. chinensis. The performance equation was demonstrated to be valid in describing the rotated and right shifted Lorenz curve, given that >96% of root-mean-square error values were smaller than 0.004 for 240 individual plants. By examining the correlation between any of the six possible pairs of indices among the Gini index, the coefficient of variation, the Theil index, and the mean log deviation index, the data show that these indices are closely related and can be used interchangeably to quantify ILAD.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Multiple Response Mechanisms of Plants to Drought Stress)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Tropical Trees Will Need to Acclimate to Rising Temperatures—But Can They?
Plants 2023, 12(17), 3142; https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12173142 - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
For tropical forests to survive anthropogenic global warming, trees will need to avoid rising temperatures through range shifts and “species migrations” or tolerate the newly emerging conditions through adaptation and/or acclimation. In this literature review, we synthesize the available knowledge to show that
[...] Read more.
For tropical forests to survive anthropogenic global warming, trees will need to avoid rising temperatures through range shifts and “species migrations” or tolerate the newly emerging conditions through adaptation and/or acclimation. In this literature review, we synthesize the available knowledge to show that although many tropical tree species are shifting their distributions to higher, cooler elevations, the rates of these migrations are too slow to offset ongoing changes in temperatures, especially in lowland tropical rainforests where thermal gradients are shallow or nonexistent. We also show that the rapidity and severity of global warming make it unlikely that tropical tree species can adapt (with some possible exceptions). We argue that the best hope for tropical tree species to avoid becoming “committed to extinction” is individual-level acclimation. Although several new methods are being used to test for acclimation, we unfortunately still do not know if tropical tree species can acclimate, how acclimation abilities vary between species, or what factors may prevent or facilitate acclimation. Until all of these questions are answered, our ability to predict the fate of tropical species and tropical forests—and the many services that they provide to humanity—remains critically impaired.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue New Perspectives on New World Tropical Forests)
Open AccessArticle
Effect of Co-Application of Azospirillum brasilense and Rhizobium pisi on Wheat Performance and Soil Nutrient Status under Deficit and Partial Root Drying Stress
by
, , , , and
Plants 2023, 12(17), 3141; https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12173141 (registering DOI) - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
Water management techniques are improving at the farm level, but they are not enough to deal with the limited availability of water and increased crop yields. Soil microbes play a vital role in nitrogen fixation, improving soil fertility and enhancing plant growth hormones
[...] Read more.
Water management techniques are improving at the farm level, but they are not enough to deal with the limited availability of water and increased crop yields. Soil microbes play a vital role in nitrogen fixation, improving soil fertility and enhancing plant growth hormones under drought conditions. Therefore, this study was conducted to investigate the impact of water management combined with Azospirillum brasilense and Rhizobium pisi on wheat crop productivity and soil properties in dry regions. Three water management techniques were compared, normal irrigation as a control (C), deficit irrigation (DI), and partial root drying irrigation (PRD), together with the interaction of plant-growth-promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR). Experiments were conducted with six treatments in total: T1 = C + No PGPR, T2 = C + PGPR, T3 = DI + No PGPR, T4 = DI + PGPR, T5 = PRD + No PGPR, and T6 = PRD + PGPR. The highest grain yield was achieved in the control irrigation treatment using seeds inoculated with rhizobacteria, followed by control treatment without any inoculation, and the lowest was recorded with deficit irrigation without rhizobacteria inoculated in the seeds. However, PRD irrigation resulted in significantly higher plant growth and grain yield than the DI treatment. PGPR inoculation combined with PRD resulted in a 22% and 20% higher number of grains per spike, a 19% and 21% higher grain yield, and a 25% and 22% higher crop growth rate compared to rhizobacteria inoculation combined with the DI system in 2021-22 and 2022-23, respectively. This increase was due to the higher production of growth hormones and higher leaf area index under water-limited conditions. A greater leaf area index leads to a higher chlorophyll content and higher food production for plant growth.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Plant Growth Promoting Bacteria)
►▼
Show Figures
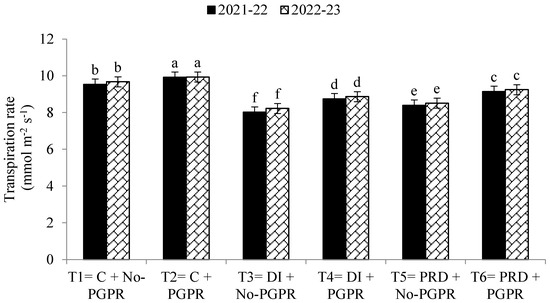
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Seed Germination and Seedling Growth Influenced by Genetic Features and Drought Tolerance in a Critically Endangered Maple
Plants 2023, 12(17), 3140; https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12173140 (registering DOI) - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
Understanding the adaptation of plant species will help us develop effective breeding programs, guide the collection of germplasm, and improve the success of population restoration projects for threatened species. Genetic features correlate with species adaptation. Acer yangbiense is a critically endangered plant species
[...] Read more.
Understanding the adaptation of plant species will help us develop effective breeding programs, guide the collection of germplasm, and improve the success of population restoration projects for threatened species. Genetic features correlate with species adaptation. Acer yangbiense is a critically endangered plant species with extremely small populations (PSESP). However, no information was available on its seed germination and seedling growth in populations with different genetic characteristics. In this study, we investigated seed germination and compared the performance of 566 seedlings in 10 maternal half-sib families cultivated in Kunming Botanical Garden. The results showed that A. yangbiense seeds required an average of 44 days to start germinating, with a 50% germination rate estimated to take about 47–76 days, indicating slow and irregular germination. There is a trade-off between the growth and survival in A. yangbiense seedlings, with fast growth coming at the cost of low survival. Groups that were able to recover from a recent bottleneck consistently had higher relative growth rates. High genetic diversity and low levels of inbreeding are likely to be responsible for their improved survival during drought conditions and rapid growth under optimal environmental conditions. Our results suggest that maternal genetic traits might be used as indicators for conservation and population restoration. These findings provide us with new information that could be applied to support ex situ conservation and reintroduction of threatened species.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Plant Response to Abiotic Stress and Climate Change)
►▼
Show Figures
Figure 1
Open AccessBrief Report
Flavonoid Composition and Antioxidant Activity of Tragia volubilis L. Methanolic Extract
Plants 2023, 12(17), 3139; https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12173139 - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
Several species from the genus Tragia L. in the family Euphorbiaceae are part of the ethnomedicine of traditional cultures, and have a variety of uses. Tragia volubilis L. is a species spread through tropical America and Africa with several ethnomedical uses, particularly for
[...] Read more.
Several species from the genus Tragia L. in the family Euphorbiaceae are part of the ethnomedicine of traditional cultures, and have a variety of uses. Tragia volubilis L. is a species spread through tropical America and Africa with several ethnomedical uses, particularly for wound healing and reproductive issues. In this study, we assess the phytochemical composition and antioxidant activity of the methanolic extract of the aerial parts of T. volubilis collected in southern Ecuador. The phytochemical screening of the extract shows the preliminary presence of carbohydrates, alkaloids, flavonoids, and tannins. The extract shows an Antioxidant Activity Index of 1.14, interpreted as strong antioxidant activity. Four flavonoid compounds were isolated through chromatographic procedures and identified through NMR spectroscopy: avicularin, quercitrin, afzelin, and amentoflavone. The biological activity of these compounds matches the ethnopharmacological uses of the species. This is the first phytochemical study of T. volubilis and supports its traditional medicinal uses.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Biological and Chemical Activity of Metabolites of Medicinal Plants, Volume II)
►▼
Show Figures
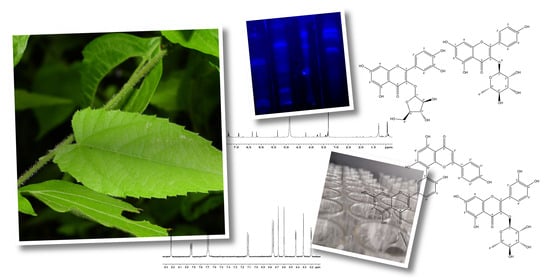
Graphical abstract
Open AccessFeature PaperArticle
Quantifying Chilling Injury on the Photosynthesis System of Strawberries: Insights from Photosynthetic Fluorescence Characteristics and Hyperspectral Inversion
Plants 2023, 12(17), 3138; https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12173138 - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
Chilling injury can adversely affect strawberry bud differentiation, pollen vitality, fruit yield, and quality. Photosynthesis is a fundamental process that sustains plant life. However, different strawberry varieties exhibit varying levels of cold adaptability. Quantitatively evaluating the physiological activity of the photosynthetic system under
[...] Read more.
Chilling injury can adversely affect strawberry bud differentiation, pollen vitality, fruit yield, and quality. Photosynthesis is a fundamental process that sustains plant life. However, different strawberry varieties exhibit varying levels of cold adaptability. Quantitatively evaluating the physiological activity of the photosynthetic system under low-temperature chilling injury remains a challenge. In this study, we investigated the effects of different levels of chilling stress on twenty photosynthetic fluorescence parameters in strawberry plants, using short-day strawberry variety “Toyonoka” and day-neutral variety “Selva” as representatives. Three dynamic chilling treatment levels (20/10 °C, 15/5 °C, and 10/0 °C) and three durations (3 days, 6 days, and 9 days) were applied to each variety. WUE, LCP, Y(II), qN,
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Horticultural Crops Cultivation and Physiology)
►▼
Show Figures
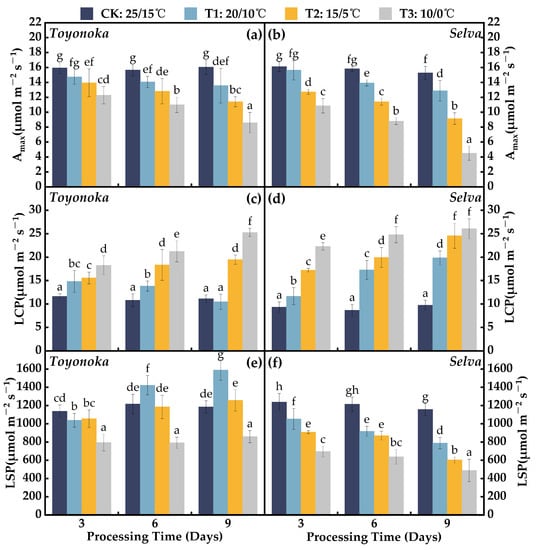
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Realistic Physiological Options to Increase Grain Legume Yield under Drought
Plants 2023, 12(17), 3137; https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12173137 - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
Increasing yield resiliency under water deficits remains a high priority for crop improvement. In considering the yield benefit of a plant trait modification, two facts are often overlooked: (1) the total amount of water available to a crop through a growing season ultimately
[...] Read more.
Increasing yield resiliency under water deficits remains a high priority for crop improvement. In considering the yield benefit of a plant trait modification, two facts are often overlooked: (1) the total amount of water available to a crop through a growing season ultimately constrains growth and yield cannot exceed what is possible with the limited amount of available water, and (2) soil water content always changes over time, so plant response needs to be considered within a temporally dynamic context of day-to-day variation in soil water status. Many previous evaluations of drought traits have implicitly considered water deficit from a “static” perspective, but while the static approach of stable water deficit treatments is experimentally congruous, the results are not realistic representations of real-world drought conditions, where soil water levels are always changing. No trait always results in a positive response under all drought scenarios. In this paper, we suggest two key traits for improving grain legume yield under water deficit conditions: (1) partial stomata closure at elevated atmospheric vapor pressure deficit that results in soil water conservation, and (2) lessening of the high sensitivity of nitrogen fixation activity to soil drying.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Legumes and Stressful Conditions)
►▼
Show Figures
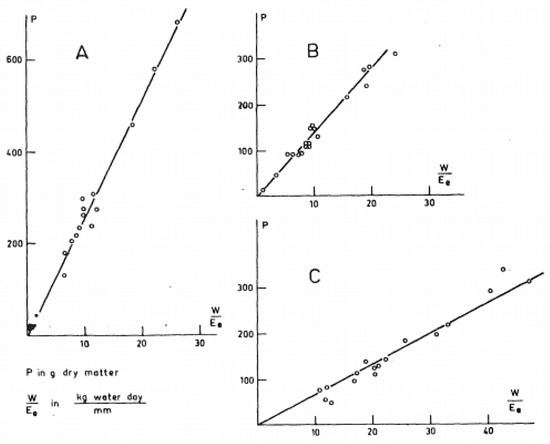
Figure 1
Open AccessFeature PaperArticle
Antimicrobial, Cytotoxic, and Anti-Inflammatory Activities of Tigridia vanhouttei Extracts
by
, , , , , , and
Plants 2023, 12(17), 3136; https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12173136 - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
In this work, bulb extracts of Tigridia vanhouttei were obtained by maceration with solvents of increasing polarity. The extracts were evaluated against a panel of pathogenic bacterial and fungal strains using the minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC) assay. The cytotoxicity of the extracts was
[...] Read more.
In this work, bulb extracts of Tigridia vanhouttei were obtained by maceration with solvents of increasing polarity. The extracts were evaluated against a panel of pathogenic bacterial and fungal strains using the minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC) assay. The cytotoxicity of the extracts was tested against two cell lines (THP-1 and A549) using the MTT assay. The anti-inflammatory activity of the extracts was evaluated in THP-1 cells by measuring the secretion of pro-inflammatory (IL-6 and TNF-α) and anti-inflammatory (IL-10) cytokines by ELISA. The chemical composition of the extracts was recorded by FTIR spectroscopy, and their chemical profiles were evaluated using GC-MS. The results revealed that only hexane extract inhibited the growth of the clinical isolate of Pseudomonas aeruginosa at 200 μg/mL. Against THP-1 cells, hexane and chloroform extracts were moderately cytotoxic, as they exhibited LC50 values of 90.16, and 46.42 μg/mL, respectively. Treatment with methanol extract was weakly cytotoxic at LC50 443.12 μg/mL against the same cell line. Against the A549 cell line, hexane, chloroform, and methanol extracts were weakly cytotoxic because of their LC50 values: 294.77, 1472.37, and 843.12 μg/mL. The FTIR analysis suggested the presence of natural products were confirmed by carboxylic acids, ketones, hydroxyl groups, or esters. The GC-MS profile of extracts revealed the presence of phytosterols, tetracyclic triterpenes, multiple fatty acids, and sugars. This report confirms the antimicrobial, cytotoxic, and anti-inflammatory activities of T. vanhouttei.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Bioactivities of Nature Products)
►▼
Show Figures
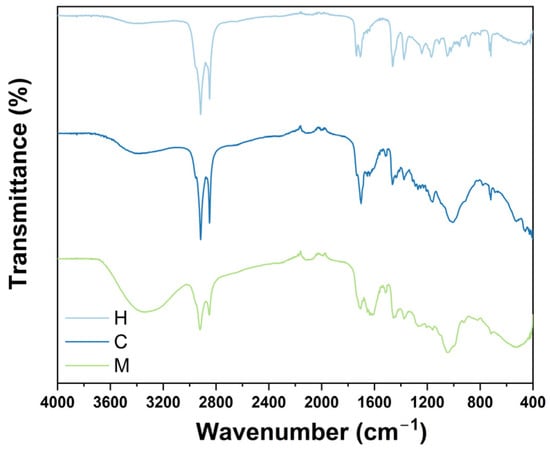
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Quantification of Dry Matter Content in Hass Avocado by Near-Infrared Spectroscopy (NIRS) Scanning Different Fruit Zones
Plants 2023, 12(17), 3135; https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12173135 - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
Accurate dry matter determination (DM) in Hass avocados is vital for optimal harvesting and ensuring fruit quality. Predictive models based on NIRS need to capture fruit DM gradient. This work aimed to determine the DM content in Hass avocado whole by NIRS scanning
[...] Read more.
Accurate dry matter determination (DM) in Hass avocados is vital for optimal harvesting and ensuring fruit quality. Predictive models based on NIRS need to capture fruit DM gradient. This work aimed to determine the DM content in Hass avocado whole by NIRS scanning different fruit zones. Spectra were recorded for each zone of the fruit: peduncle (P), equator (E), and base (B). The calibration and validation included fruit from different orchards in two harvest cycles. The results show a DM gradient within the fruit: 24.47% (E), 24.68% (B), and 24.79% (P). The DM gradient was observed within the spectra using the RMSi (root mean square) criterion and PCA. The results show that at least one spectrum per fruit zone was needed to represent the variability within the fruit. The performances of the calibration using the whole set of data were R2: 0.74 and standard error of cross-validation (SECV) = 1.18%. In the validation stage using independent validation sets, the models showed similar performance (R2: 0.75, SECV 1.15%) with low values of the standard error of prediction (SEP): 1.62%. These results demonstrate the potential of near-infrared spectroscopy for high-throughput sorting of avocados based on their commercial quality.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Spectra Analysis and Plants Research 2.0)
►▼
Show Figures
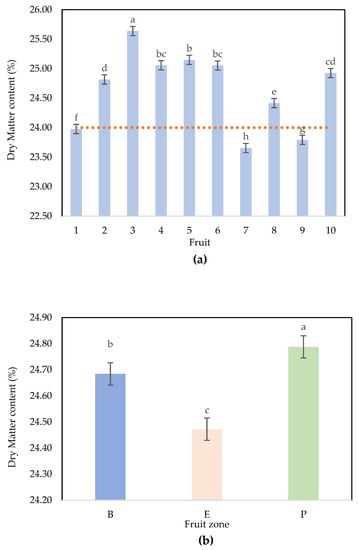
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Selection of Soybean and Cowpea Cultivars with Superior Performance under Drought Using Growth and Biochemical Aspects
by
, , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , and
Plants 2023, 12(17), 3134; https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12173134 - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
Identifying cultivars of leguminous crops exhibiting drought resistance has become crucial in addressing water scarcity issues. This investigative study aimed to select soybean and cowpea cultivars with enhanced potential to grow under water restriction during the vegetative stage. Two parallel trials were conducted
[...] Read more.
Identifying cultivars of leguminous crops exhibiting drought resistance has become crucial in addressing water scarcity issues. This investigative study aimed to select soybean and cowpea cultivars with enhanced potential to grow under water restriction during the vegetative stage. Two parallel trials were conducted using seven soybean (AS3810IPRO, M8644IPRO, TMG1180RR, NS 8338IPRO, BMX81I81IPRO, M8808IPRO, and BÔNUS8579IPRO) and cowpea cultivars (Aracê, Novaera, Pajeú, Pitiúba, Tumucumaque, TVU, and Xique-xique) under four water levels (75, 60, 45, and 30% field capacity—FC) over 21 days. Growth, water content, membrane damage, photosynthetic pigments, organic compounds, and proline levels were analyzed. Drought stress significantly impacted the growth of both crops, particularly at 45 and 30% FC for soybean and 60 and 45% FC for cowpea plants. The BÔNUS8579IPRO and TMG1180RR soybean cultivars demonstrated the highest performance under drought, a response attributed to increased amino acids and proline contents, which likely help to mitigate membrane damage. For cowpea, the superior performance of the drought-stressed Xique-xique cultivar was associated with the maintenance of water content and elevated photosynthetic pigments, which contributed to the preservation of the photosynthetic efficiency and carbohydrate levels. Our findings clearly indicate promising leguminous cultivars that grow under water restriction, serving as viable alternatives for cultivating in water-limited environments.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Molecular Basis of Crops and Fruit Plants in Response to Stress)
►▼
Show Figures
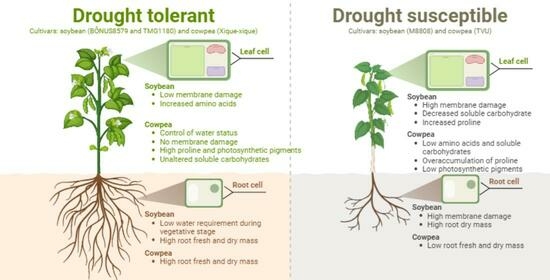
Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Water Deficit at Vegetative Stage Induces Tolerance to High Temperature during Anthesis in Rice
by
, , , , , and
Plants 2023, 12(17), 3133; https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12173133 - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
Background: Crop yields have been affected by many different biotic and abiotic factors. Generally, plants experience more than one stress during their life cycle, and plants can tolerate multiple stresses and develop cross-tolerance. The expected rise in atmospheric CO2 concentration ([CO2
[...] Read more.
Background: Crop yields have been affected by many different biotic and abiotic factors. Generally, plants experience more than one stress during their life cycle, and plants can tolerate multiple stresses and develop cross-tolerance. The expected rise in atmospheric CO2 concentration ([CO2]) can contribute to cross-tolerance. Priming is a strategy to increase yield or to maintain yield under stress conditions. Thus, our objective was to evaluate if priming the rice plants with water deficit during the vegetative stage can induce tolerance to heat stress at anthesis and to evaluate the contribution of e[CO2]. Methods: The experiment was arranged in a completely randomized design in a factorial arrangement. Factor A consisted of the following treatments: water deficit at four-leaf stage (no-stress, and drought stress), heat at anthesis (normal temperature, high temperature), and priming with water deficit at four-leaf stage and heat stress at anthesis; and Factor B was two [CO2] treatments: a[CO2] = 400 ± 40 μmol mol−1 and e[CO2] = 700 ± 40 μmol mol−1. We assessed the effect of the treatments on plant growth, yield, biochemical, and transcriptome alterations. Results: Although e[CO2] affected rice growth parameters, it did not affect the priming effect. Primed plants showed an increase in yield and number of panicles per plant. Primed plants showed upregulation of OsHSP16.9A, OsHSP70.1, and OsHSP70.6. These results showed induced cross-tolerance. Conclusions: Water deficit at the rice vegetative stage reduces the effect of heat stress at the reproductive stage. Water deficit at the vegetative stage can be used, after further testing in field conditions, to reduce the effect of heat stress during flowering in rice.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue New Insights into Plant Resistance to Stress)
►▼
Show Figures
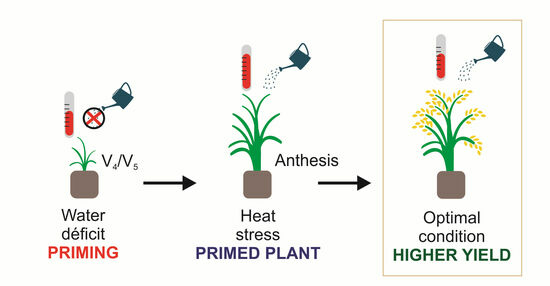
Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Optimizing Nitrogen Application for Jojoba under Intensive Cultivation
by
, , , , , , and
Plants 2023, 12(17), 3132; https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12173132 - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
Although jojoba (Simmondsia chinensis) has been cultivated for years, information on its N requirements is limited. A 6-year study of mature jojoba plants grown under field conditions with an intensive management regime evaluated the effect of N application rate on plant
[...] Read more.
Although jojoba (Simmondsia chinensis) has been cultivated for years, information on its N requirements is limited. A 6-year study of mature jojoba plants grown under field conditions with an intensive management regime evaluated the effect of N application rate on plant nutrient status, growth, and productivity, and nitrate accumulation in the soil. Five levels of N application were tested: 50, 150, 250, 370, and 500 kg N ha−1. Fertilizers were provided throughout the growing season via a subsurface drip irrigation system. Leaf N concentration, in both spring and summer, reflected the level of N applied. A diagnostic leaf (youngest leaf that has reached full size) concentration of 1.3% N was identified as the threshold for N deficiency. Increasing rates of N application resulted in higher P levels in young leaves. Plant K status, as reflected in the leaf analysis, was not affected by N treatment but was strongly affected by fruit load. Vegetative growth was inhibited when only 50 kg N ha−1 was applied. Soil analysis at the end of the fertilization season showed substantial accumulation of nitrate for the two highest application rates. Considering productivity, N costs, and environmental risk, 150 kg N ha−1 is the recommended dosage for intensively grown jojoba. N deficiencies can be identified using leaf analysis, and excess N can be detected via soil sampling toward the end of the growing season. These results and tools will facilitate precise N fertilization in intensive jojoba plantations.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Role of Nitrogen in Plant Growth and Development)
►▼
Show Figures
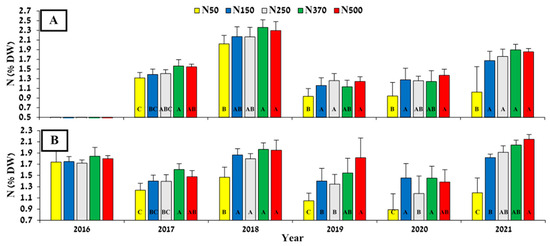
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
The Features of Potassium Dynamics in ‘Soil–Plant’ System of Sour Cherry Orchard
Plants 2023, 12(17), 3131; https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12173131 - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
This research aimed to study interannual and seasonal dynamics of different potassium compounds in orchard soil and the potassium status of sour cherry trees affected by the application of nitrogen and potash fertilizers. Afield experiment was started in 2017 at an orchard located
[...] Read more.
This research aimed to study interannual and seasonal dynamics of different potassium compounds in orchard soil and the potassium status of sour cherry trees affected by the application of nitrogen and potash fertilizers. Afield experiment was started in 2017 at an orchard located in the forest-steppe zone of the Central Russian upland. Urea and potassium sulfate were applied to the soil once a year in early spring with rates from N30K40 to N120K160 kg/ha. The content of exchangeable and water-soluble potassium compounds was determined in soil samples five times throughout the growing season from May to September 2018–2020. The content of non-exchangeable potassium was determined twice, in 2017 and 2020. The interannual and seasonal dynamics of plant-available potash in unfertilized soil depended on the weather patterns and the uptake of potassium by trees. In the unfertilized plots, the first signs of potassium nutrition insufficiency appeared, such as low leaf and fruit potassium status and a decrease in the non-exchangeable potassium reserves in the20–40 cm soil layer. The annual fertilization led to the gradual accumulation of exchangeable potassium in the root zone. The accumulation was accelerated with increasing rates. When the exchangeable potassium level in the topsoil reached 200 mg/kg, the intensification of both the seasonal fluctuations in potash content and the potash leaching into the depths of the soil occurred in all treatments. In the conditions of our experiment, one-time treatments with superfluous potassium rates (over 80 kg/ha) did not provide an enlarged stock of plant-available potash in the soil but caused unreasonable losses of it due to leaching. An increase in fertilizer rates was not essential for normal metabolic processes and did not manifest itself as an increase in potassium content in leaves and fruits or as an increase in yield.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Innovative Technologies & Approaches in Agro-Ecosystems)
►▼
Show Figures
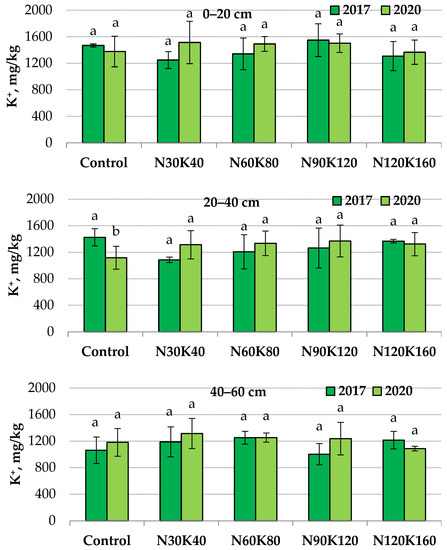
Figure 1

Journal Menu
► ▼ Journal Menu-
- Plants Home
- Aims & Scope
- Editorial Board
- Reviewer Board
- Topical Advisory Panel
- Instructions for Authors
- Special Issues
- Topics
- Sections & Collections
- Article Processing Charge
- Indexing & Archiving
- Editor’s Choice Articles
- Most Cited & Viewed
- Journal Statistics
- Journal History
- Journal Awards
- Society Collaborations
- Conferences
- Editorial Office
Journal Browser
► ▼ Journal BrowserHighly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Agronomy, Diversity, Ecologies, Microorganisms, Plants
Plant-Associated Microbiota: From the Assembly to the Function
Topic Editors: Alessandra Salvioli Di Fossalunga, Vincenza CozzolinoDeadline: 30 September 2023
Topic in
Agriculture, Agronomy, Crops, Plants, Viruses
Plant Virus
Topic Editors: Munir Mawassi, Sergey MorozovDeadline: 31 October 2023
Topic in
Diversity, Forests, IJPB, Land, Plants
Forest Ecosystem Restoration
Topic Editors: Dominick A. DellaSala, Lin Qi, Wangming ZhouDeadline: 15 November 2023
Topic in
Agriculture, Agronomy, Crops, JoF, Plants
Interaction between Plants and Fungi and Oomycetes
Topic Editors: Ana P. G. C. Marques, Nadia Massa, Santa Olga CacciolaDeadline: 30 November 2023

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
Plants
Advances in Seed Longevity
Guest Editors: José Vacas, Sara PérezDeadline: 1 September 2023
Special Issue in
Plants
Flax: A Traditional Culture with Modern Advantages
Guest Editors: Anthony Quéro, Christophe HanoDeadline: 20 September 2023
Special Issue in
Plants
Role of Plants and Cyanobacteria in Environmental Resilience and Ecosystem Sustainability
Guest Editor: Leonardo Martín PérezDeadline: 30 September 2023
Special Issue in
Plants
Microelements in Plant and Soil
Guest Editor: Hongmei CaiDeadline: 15 October 2023
Topical Collections
Topical Collection in
Plants
Advances in Plant Diversification and Biosystematics
Collection Editors: José María Postigo-Mijarra, Yang Liu, Ângela Sartori
Topical Collection in
Plants
New Trends in Plant Science in Italy
Collection Editors: Claudio Moser, Massimo Galbiati
Topical Collection in
Plants
New Trends in Plant Science in China
Collection Editors: Ming Chen, Dijun Chen, Xianwen Meng
Topical Collection in
Plants
Essential Oils of Plants (Chemical Composition, Variation and Properties)
Collection Editors: Jésus Palá-Pául, Joe Brophy