Journal Description
Processes
Processes
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal on processes/systems in chemistry, biology, material, energy, environment, food, pharmaceutical, manufacturing, automation control, catalysis, separation, particle and allied engineering fields published monthly online by MDPI. The Systems and Control Division of the Canadian Society for Chemical Engineering (CSChE S&C Division) and the Brazilian Association of Chemical Engineering (ABEQ) are affiliated with Processes and their members receive a discount on the article processing charges. Please visit Society Collaborations for more details.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within Scopus, SCIE (Web of Science), CAPlus / SciFinder, Inspec, AGRIS, and other databases.
- Journal Rank: JCR - Q2 (Engineering, Chemical) / CiteScore - Q2 (Chemical Engineering (miscellaneous))
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 13.9 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 2.9 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the first half of 2023).
- Recognition of Reviewers: reviewers who provide timely, thorough peer-review reports receive vouchers entitling them to a discount on the APC of their next publication in any MDPI journal, in appreciation of the work done.
Impact Factor:
3.5 (2022);
5-Year Impact Factor:
3.4 (2022)
Latest Articles
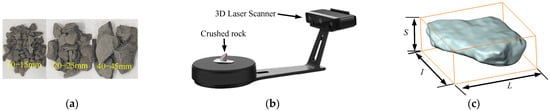
Spatial Structure Characteristics of Underground Reservoir Water Storage Space in Coal Mines Considering Shape Characteristics of Crushed Rock
Processes 2023, 11(9), 2611; https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11092611 (registering DOI) - 01 Sep 2023
Abstract
In order to investigate the impact of a crushed rock shape on the storage coefficient of underground reservoirs in coal mines, statistical analysis of the shape characteristics of crushed rocks was conducted, which was followed by numerical packing tests using the rigid block
[...] Read more.
In order to investigate the impact of a crushed rock shape on the storage coefficient of underground reservoirs in coal mines, statistical analysis of the shape characteristics of crushed rocks was conducted, which was followed by numerical packing tests using the rigid block model. These tests aimed to investigate the spatial structure characteristics of underground reservoir water storage space in coal mines under the influence of different shapes of crushed rock. The results demonstrated the following: (1) Crushed rock exhibits a lognormal distribution in its shape characteristic parameters at different scales with a predominant discoid shape. The shape coefficient M can be utilized as a comprehensive indicator to characterize the shape characteristics of crushed rock. (2) The average storage coefficient of crushed rock increases exponentially as the shape coefficient M increases. There is a 50.1% increase in the storage coefficient from M = 1 to 3.5. (3) The spatial structure of the water storage space exhibits self-similarity, and both the void fractal dimension and the void boundary fractal dimension increase with an increase in the shape coefficient M. (4) When comparing the non-spherical particle system with the spherical particle system, it is observed that the spherical particle system has smaller water storage space, lower connectivity among voids, and more irregular void space. In the non-spherical particle system, the water storage space becomes larger as the shape of crushed rock becomes more irregular, resulting in more irregular void space. However, there is no significant effect on void connectivity.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Numerical Simulation and Application of Process in Deep Mining Engineering and Petroleum Engineering)
►
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Research on the Formulation Design of Nano-Oil Displacement Agents Suitable for Xinjiang Jimusaer Shale Oil
Processes 2023, 11(9), 2610; https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11092610 (registering DOI) - 01 Sep 2023
Abstract
In order to improve the recovery efficiency of the Jimusaer tight reservoir in Xinjiang, the nanometer oil displacement agent system suitable for the Jimusaer reservoir was used. In view of the low permeability, high formation temperature, and high salinity characteristics of the prepared
[...] Read more.
In order to improve the recovery efficiency of the Jimusaer tight reservoir in Xinjiang, the nanometer oil displacement agent system suitable for the Jimusaer reservoir was used. In view of the low permeability, high formation temperature, and high salinity characteristics of the prepared water in the Jimusaer tight conglomerate reservoir in Xinjiang, the performance of the nanometer oil displacement agent affecting oil recovery was studied; the study considered interfacial tension, temperature resistance, wetting performance, static oil washing efficiency, and long-term stability. Nanometer oil displacement agent No. 4 had the lowest interfacial tension and could reach the order of 10−1 mN∙m−1; it had excellent temperature resistance and the best static oil washing efficiency and stability. Nano-oil displacement agent No. 2 had the best emulsification performance and wettability and also had good stability. By studying the performance and final oil displacement effect of the nano-oil displacement agent, it was found that the key factor affecting the oil displacement effect of this reservoir was the interfacial activity of the nano-oil displacement agent. When the interfacial tension was lower, it produced strong dialysis for oil displacement. The emulsification effect has a negative effect on low-permeability reservoirs, mainly because the fluid produces strong emulsification in low-permeability reservoirs; thus, it can easily block the formation and cause high pressure. An excessive or small contact angle is not conducive to oil displacement. An excessive contact angle means strong hydrophilicity, which can cause a strong Jamin effect in oil-friendly formations. If the contact angle is too small, it has strong lipophilicity and can lead to poor solubility in water. Nano-oil displacement agent No. 4 had the best oil displacement effect, with an oil recovery increase of 7.35%, followed by nanometer oil displacement agent No. 1, with an oil recovery increase of 5.70%. Based on all the performance results, nanometer oil displacement agent No. 4 was more suitable as the oil displacement agent and can be used to enhance oil recovery in the Jimusaer reservoir. This study has laid a foundation for the chemical flooding development of shale oil in the Xinjiang oilfield.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic Enhanced Oil Recovery Technologies, 2nd Volume)
►▼
Show Figures
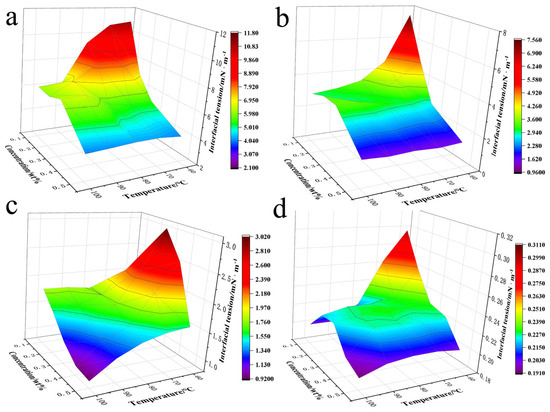
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
The Evaluation of the Fire Safety of the Digestate as An Alternative Bedding Material
Processes 2023, 11(9), 2609; https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11092609 (registering DOI) - 01 Sep 2023
Abstract
Digestate is the material remaining after the anaerobic digestion of a biodegradable feedstock. The use of digestate as a bedding material is analyzed marginally. The aim of the paper is to monitor the change of the solid phase of digestate due to the
[...] Read more.
Digestate is the material remaining after the anaerobic digestion of a biodegradable feedstock. The use of digestate as a bedding material is analyzed marginally. The aim of the paper is to monitor the change of the solid phase of digestate due to the action of radiant heat and, based on the results, determine the options of using the solid phase of the digestate for bedding material. Experimental determination of the digestate ignition temperature was carried out according to EN 50281-2-1 (1998) by a hotplate device. Different amounts of samples (3, 5, and 10 g) on the course of thermal degradation were monitored. The results showed higher temperatures of thermal degradation in samples of additionally dried digestate, where these processes were observed earlier in terms of time. Samples of 3 and 10 g of digestate are not suitable as bedding material due to the fire safety of the material.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Design and Optimization of Fire Protection)
►▼
Show Figures
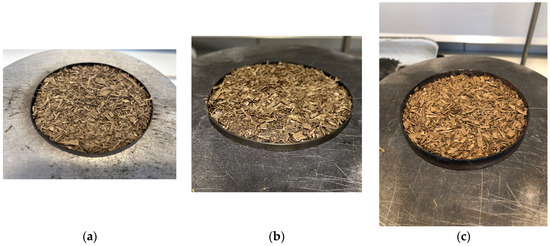
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Prediction of Leakage Pressure during a Drilling Process Based on SSA-LSTM
Processes 2023, 11(9), 2608; https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11092608 (registering DOI) - 01 Sep 2023
Abstract
Drilling-fluid loss has always been one of the challenging issues in the field of drilling engineering. This article addresses the limitations of a single fluid-loss pressure mechanism model and the challenges in predicting positive drilling-fluid-loss pressure. By categorizing fluid losses of various types
[...] Read more.
Drilling-fluid loss has always been one of the challenging issues in the field of drilling engineering. This article addresses the limitations of a single fluid-loss pressure mechanism model and the challenges in predicting positive drilling-fluid-loss pressure. By categorizing fluid losses of various types encountered during drilling, different geological formations associated with distinct mechanisms are considered. The actual drilling-fluid density in the wellbore at the time of fluid-loss occurrence is taken as a reference value for calculating the positive drilling-fluid-loss pressure of the already drilled well. Building upon this foundation, a combined model utilizing the Sparrow Search Algorithm (SSA) and Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) neural network is constructed. This model effectively explores the intricate nonlinear relationship between well logging, logging engineering data, and fluid-loss pressure. By utilizing both data from the already drilled wells and upper formation data from ongoing drilling, precise prediction of positive drilling formation fluid-loss pressure can be achieved. Case studies demonstrate that the approach established in this paper, incorporating upper formation data, reduces the average absolute percentage error of fluid-loss pressure prediction to 2.4% and decreases the root mean square error to 0.0405. Through the synergy of mechanistic models and data-driven techniques, not only has the accuracy of predicting positive drilling formation fluid-loss pressure has been enhanced, but also valuable insights have been provided for preventing and mitigating fluid losses during drilling operations.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Oil and Gas Well Engineering Measurement and Control)
►▼
Show Figures
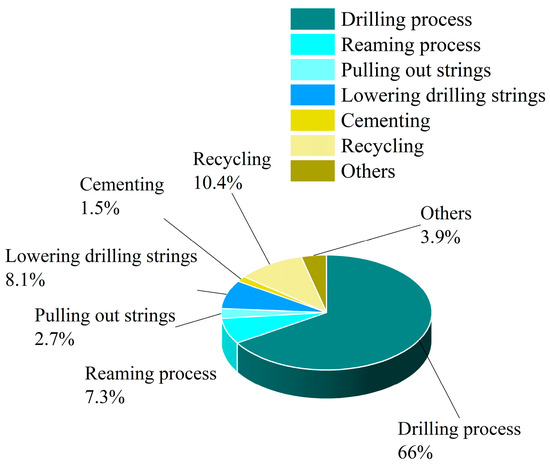
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Experimental Investigation of Stress Sensitivity of Elastic Wave Velocities for Anisotropic Shale in Wufeng–Longmaxi Formation
Processes 2023, 11(9), 2607; https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11092607 (registering DOI) - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
The shale of the Wufeng–Longmaxi formation in the Sichuan Basin is the preferred layer for shale gas exploration in China, and its petrophysical characteristics are the key to geological and engineering sweet spot prediction. However, the characteristics and impact mechanisms of its acoustic
[...] Read more.
The shale of the Wufeng–Longmaxi formation in the Sichuan Basin is the preferred layer for shale gas exploration in China, and its petrophysical characteristics are the key to geological and engineering sweet spot prediction. However, the characteristics and impact mechanisms of its acoustic wave velocity and elastic anisotropy are currently unclear. In this paper, the Wufeng–Longmaxi shale is taken as the research object, and the P-wave and S-wave velocities of the samples are tested under the loading and unloading processes of confining pressure. The stress sensitivity variations in parameters such as wave velocity, wave velocity ratio, and anisotropy are discussed. P-wave and S-wave anisotropy parameters are correlated under different pressure conditions. X-ray diffraction, casting thin sections, scanning electron microscopy, micron CT scanning, and other analytical techniques are used to explore the mechanisms of stress sensitivity of elastic parameters. The research results indicate that: (1) the acoustic velocities of samples from different angles are V90° > V45° > V0°, and there is a positive correlation between the wave velocity and the confining pressure. After unloading the confining pressure, irreversible plastic deformation occurs due to the closure of some microfractures in the rock core, causing the wave velocity to be higher than the initial value. (2) The stress sensitivity coefficient of the P-wave (The mean is 3.00 m·s−1·MPa−1) is higher than that of the S-wave (the mean is 1.23 m·s−1·MPa−1), and the stress sensitivity coefficient of the compacted stage (the mean is 3.02 m·s−1·MPa−1) is higher than that of the elastic stage (the mean is 1.21 m·s−1·MPa−1). (3) The anisotropy of the P-wave and S-wave is negatively correlated with the confining pressure. When the confining pressure is loaded to 65 MPa, the change rate of the P-wave anisotropy coefficient is 23%, and its stress sensitivity is higher than that of S-wave anisotropy coefficient (the change rate is 13.7%). After unloading the confining pressure, the degree of anisotropy is reduced due to the closure of some microfractures. The empirical formula of P-wave and S-wave anisotropy parameters under different pressures is established through linear regression, which can provide a reference for mutual predictions. (4) The variation in wave velocity anisotropy with stress can be divided into stress and material anisotropy, which are related to the directional arrangement of microfractures and clay minerals, respectively. The quantitative characterization of shale anisotropy can be realized by evaluating the development degree of reservoir fractures and mineral components, providing a reference for logging interpretations, sweet spot prediction, and fracturing construction of shale gas reservoirs.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Recent Advances in Shale Gas Exploration, Development and Production)
►▼
Show Figures
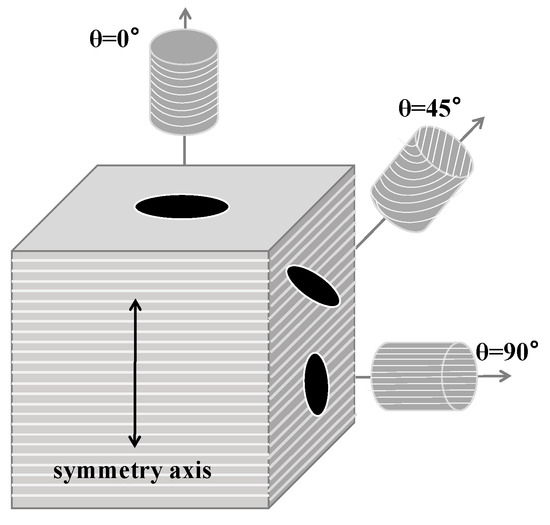
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Research on Optimization Algorithm of AGV Scheduling for Intelligent Manufacturing Company: Taking the Machining Shop as an Example
Processes 2023, 11(9), 2606; https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11092606 - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
Intelligent manufacturing workshop uses automatic guided vehicles as an important logistics and transportation carrier, and most of the existing research adopts the intelligent manufacturing workshop layout and Automated Guided Vehicle (AGV) path step-by-step optimization, which leads to problems such as low AGV operation
[...] Read more.
Intelligent manufacturing workshop uses automatic guided vehicles as an important logistics and transportation carrier, and most of the existing research adopts the intelligent manufacturing workshop layout and Automated Guided Vehicle (AGV) path step-by-step optimization, which leads to problems such as low AGV operation efficiency and inability to achieve the optimal layout. For this reason, a smart manufacturing assembly line layout optimization model considering AGV path planning with the objective of minimizing the amount of material flow and the shortest AGV path is designed for the machining shop of a discrete manufacturing enterprise of a smart manufacturing company. Firstly, the information of the current node, the next node and the target node is added to the heuristic information, and the dynamic adjustment factor is added to make the heuristic information guiding in the early stage and the pheromone guiding in the later stage of iteration; secondly, the Laplace distribution is introduced to regulate the volatilization of the pheromone in the pheromone updating of the ant colony algorithm, which speeds up the speed of convergence; the path obtained by the ant colony algorithm is subjected to the deletion of the bi-directional redundant nodes, which enhances the path smoothing degree; and finally, the improved ant colony algorithm is fused with the improved dynamic window algorithm, so as to enable the robots to arrive at the end point safely. Simulation shows that in the same map environment, the ant colony algorithm compared with the basic ant colony algorithm reduces the path length by 40% to 67% compared to the basic ant colony algorithm and reduces the path inflection points by 34% to 60%, which is more suitable for complex environments. It also verifies the feasibility and superiority of the conflict-free path optimization strategy in solving the production scheduling problem of the flexible machining operation shop.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Process Automation and Smart Manufacturing in Industry 4.0/5.0)
►▼
Show Figures
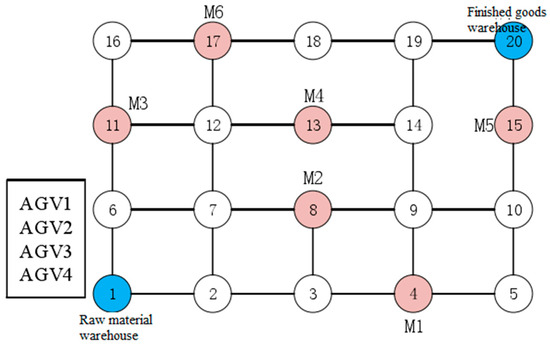
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Stability Study of Selected Coxibs Used in the Treatment of Rheumatoid Diseases in Various Drug Combinations
Processes 2023, 11(9), 2605; https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11092605 (registering DOI) - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
Coxibs are a group of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), selective cyclooxygenase 2 inhibitors, characterized by a much lower gastrotoxicity compared to classic NSAIDs. They are often used in conjunction with other drugs, which greatly increases the likelihood of adverse drug interactions. The presented
[...] Read more.
Coxibs are a group of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), selective cyclooxygenase 2 inhibitors, characterized by a much lower gastrotoxicity compared to classic NSAIDs. They are often used in conjunction with other drugs, which greatly increases the likelihood of adverse drug interactions. The presented study analyzed the degradation rate of celecoxib and cimicoxib in solutions under the influence of other medicinal substances at different temperatures. For this purpose, triple-drug mixtures were prepared, consisting of coxib and eleven different commonly used drugs (paracetamol, ketoprofen, diclofenac, acetylsalicylic acid, ibuprofen, meloxicam, tramadol, doxycycline, bisoprolol, and caffeine). Then, the mixtures were incubated at two temperatures. Within the time specified by the research plan, further aliquots of the mixtures were subjected to a chromatographic analysis. Separation was conducted on HPTLC F254 silica gel chromatographic plates as a stationary phase, using chloroform: acetone: toluene as a mobile phase, and was detected densitometrically at wavelengths of 254 nm. The percentage changes in the tested coxibs content, depending on the time and conditions of incubation, were presented. Based on the obtained data, the basic kinetic parameters of the degradation processes were determined. The celecoxib and cimicoxib showed a relatively high durability in changing environmental conditions. It was observed that the rate of decomposition of cimicoxib and celecoxib in the tested mixtures was different and depended on the temperature and presence of other components, with cimicoxib turning out to be a more stable compound.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Chromatographic Techniques in Drugs and Food Analysis)
►▼
Show Figures
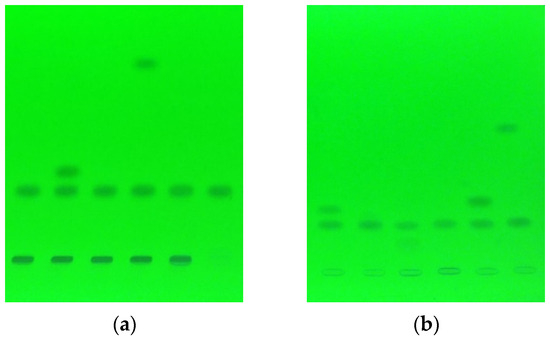
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Removal of Nano-Zinc Oxide (nZnO) from Simulated Waters by C/F/S—Focusing on the Role of Synthetic Coating, Organic Ligand, and Solution Chemistry
Processes 2023, 11(9), 2604; https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11092604 - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
Increased usage of nano-zinc oxide (nZnO) in different commercial fields has raised serious concerns regarding their discharge into the water streams containing natural and synthetic coating agents. Moreover, utilization of ground and surface water for drinking purposes is a common approach in many
[...] Read more.
Increased usage of nano-zinc oxide (nZnO) in different commercial fields has raised serious concerns regarding their discharge into the water streams containing natural and synthetic coating agents. Moreover, utilization of ground and surface water for drinking purposes is a common approach in many countries. Therefore, the removal of nZnO particles from water is essential to minimize the risk to the environment. The present research investigated the removal of nZnO from complex water matrices by conventional coagulation-flocculation-sedimentation (C/F/S) process using polyaluminum chloride (PACl) as coagulants. The result showed that removal of uncoated nZnO through sedimentation was efficient in waters containing divalent cations in the absence of dissolved organic matter (DOM). For the water containing higher salt concentration, PACl coagulant showed better removal performance with increasing coagulant dosage; however, synthetic organic coating agent and DOM significantly decreased the removal up to 75%. The surface potential of studied waters indicated that the addition of PACl affects the charge potential of nZnO particles resulting in charge neutralization. The result of the particle size analyzer revealed the presence of smaller particles with size of 430 nm even after C/F/S process, which may increase the possibility of particles release into aquatic environment. The results of the present study may help in understating the removal behavior of other coated nanoparticles during conventional water treatment.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Wastewater Treatment: Control, Removal and Separation Processes)
►▼
Show Figures
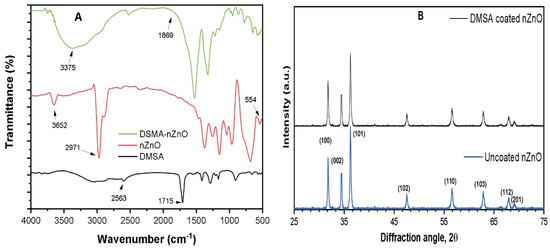
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
A Comprehensive Prediction Method for Pore Pressure in Abnormally High-Pressure Blocks Based on Machine Learning
by
, , , , , , and
Processes 2023, 11(9), 2603; https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11092603 - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
In recent years, there has been significant research and practical application of machine learning methods for predicting reservoir pore pressure. However, these studies frequently concentrate solely on reservoir blocks exhibiting normal-pressure conditions. Currently, there exists a scarcity of research addressing the prediction of
[...] Read more.
In recent years, there has been significant research and practical application of machine learning methods for predicting reservoir pore pressure. However, these studies frequently concentrate solely on reservoir blocks exhibiting normal-pressure conditions. Currently, there exists a scarcity of research addressing the prediction of pore pressure within reservoir blocks characterized by abnormally high pressures. In light of this, the present paper introduces a machine learning-based approach to predict pore pressure within reservoir blocks exhibiting abnormally high pressures. The methodology is demonstrated using the X block as a case study. Initially, the combination of the density–sonic velocity crossplot and the Bowers method is favored for elucidating the overpressure-to-compact mechanism within the X block. The elevated pressure within the lower reservoir is primarily attributed to the pressure generated during hydrocarbon formation. The Bowers method has been chosen to forecast the pore pressure in well X-1. Upon comparison with real pore pressure data, the prediction error is found to be under 5%, thus establishing it as a representative measure of the reservoir’s pore pressure. Intelligent prediction models for pore pressure were developed using the KNN, Extra Trees, Random Forest, and LightGBM algorithms. The models utilized five categories of well logging data, sonic time difference (DT), gamma ray (GR), density (ZDEN), neutron porosity (CNCF), and well diameter (CAL), as input. After training and comparison, the results demonstrate that the LightGBM model exhibits significantly superior performance compared to the other models. Specifically, it achieves R2 values of 0.935 and 0.647 on the training and test sets, respectively. The LightGBM model is employed to predict the pore pressure of two wells neighboring well X-1. Subsequently, the predicted data are juxtaposed with the actual pore pressure measurements to conduct error analysis. The achieved prediction accuracy exceeds 90%. This study delivers a comprehensive analysis of pore pressure prediction within sections exhibiting anomalously high pressure, consequently furnishing scientific insights to facilitate both secure and efficient drilling operations within the X block.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Natural Gas Hydrate Production Technology and Rock Mechanics in Petroleum Engineering (Volume II))
►▼
Show Figures
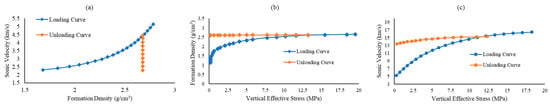
Figure 1
Open AccessCommunication
Microwave-Assisted Reductive Amination under Heterogeneous Catalysis for the Synthesis of β-Adrenergic Agonist and Related Structures
by
, , , , and
Processes 2023, 11(9), 2602; https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11092602 - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
Reductive amination is a powerful tool in sustainable organic synthesis that allows chemists to access a wide range of valuable amine products using renewable feedstocks and mild reaction conditions, with minimal waste generation. Practical applications can be found in various fields, including pharmaceuticals,
[...] Read more.
Reductive amination is a powerful tool in sustainable organic synthesis that allows chemists to access a wide range of valuable amine products using renewable feedstocks and mild reaction conditions, with minimal waste generation. Practical applications can be found in various fields, including pharmaceuticals, contributing to greener and more sustainable chemical processes. In this work, we present a heterogeneous (Rh and Pt) catalyzed protocol for the fast and efficient synthesis of ractopamine hydrochloride (β-adrenergic drug) under microwave-assisted reductive amination protocol starting from raspberry ketone and octopamine. Microwave (MW) successfully accelerated the hydrogenation reaction and reduced the reaction time from 13 h to only 3 h under mild conditions (50 °C at 10 bar). The best catalysts were Pt/C and Rh/C, which led to high conversion and selectivity towards ractopamine:HCl. Different solvents and ketone substrates were also experimented. Acetophenone, cyclohexanone, and 2-butanone reacted at lower H2 pressure (5 bar), and highest selectivity was observed with cyclohexanone (99%). These preliminary experiments may be useful for further process improvements in the synthesis of β-adrenergic agonists and related structures and underline the positive synergy between MW and heterogeneous catalysis.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue 10th Anniversary of Processes: Design of the Chemical Industry of the Future)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Experimental Investigation of the Relationship of Failure Mode and Energy Dissipation in Grouted Rockbolt Systems under Pullout Load
Processes 2023, 11(9), 2601; https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11092601 - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
In underground engineering, the deformation of surrounding rock caused by “three heights and one disturbance” leads to the failure of grouted rockbolt systems, which causes huge economic losses to the mining industry. The research shows that the failure process of grouted rockbolt systems
[...] Read more.
In underground engineering, the deformation of surrounding rock caused by “three heights and one disturbance” leads to the failure of grouted rockbolt systems, which causes huge economic losses to the mining industry. The research shows that the failure process of grouted rockbolt systems is the result of energy accumulation and release, but the relationship between failure mode and energy dissipation is rarely studied. Based on this, the load transfer behavior, energy dissipation, failure mode and failure mechanism of the grouted rockbolt systems are investigated from the perspective of energy in this study using the indoor pullout test. Test results show that the load decreases rapidly, and the absorbed energy decreases due to the whole-body splitting crack. The absorbed energy of the specimen in the splitting crack mode is lower than that in the pullout failure mode. When the pullout load reaches its peak, the pullout load of the specimen with split failure mode decreases sharply. Meanwhile, the load of the specimen with pullout failure mode is relatively slow, and the energy absorption rate decreases gradually due to the occurrence of cracks. However, the reduction in the energy absorption rate under pullout failure is lower than that under split failure. The radial pressure in the grouted rockbolt systems increases due to the wedge action. When the radial pressure exceeds the tensile strength of concrete, the specimen will experience split failure, otherwise pullout failure will occur.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Process Safety and Monitoring of Intelligent and Green Mining Technology)
►▼
Show Figures
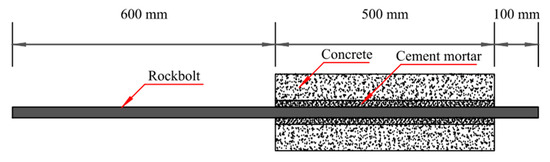
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Assessment of Triglyceride Droplet Crystallization Using Mixtures of β-Lactoglobulin and Phospholipids as Emulsifiers
Processes 2023, 11(9), 2600; https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11092600 - 30 Aug 2023
Abstract
Many applications in the life science and food industries require (semi-)crystalline oil-in-water (O/W) dispersions. Unfortunately, high supercooling and, thus, low temperatures are often needed to induce the crystallization of droplets. As low molecular weight emulsifiers (LMWEs) are able to act as nucleation templates,
[...] Read more.
Many applications in the life science and food industries require (semi-)crystalline oil-in-water (O/W) dispersions. Unfortunately, high supercooling and, thus, low temperatures are often needed to induce the crystallization of droplets. As low molecular weight emulsifiers (LMWEs) are able to act as nucleation templates, they might help to decrease the required level of supercooling. Furthermore, proteins and LMWEs are frequently co-formulated to improve the colloidal stability of emulsions and dispersions. Hence, choosing a suitable protein and LMWE mixture would allow for achieving specific product properties for controlling the solid fat content (SFC) and take advantage of the stabilization mechanisms of both emulsifiers. Therefore, this study focuses on the impact of the co-existence of β-lactoglobulin (β-lg) and phospholipids (PLs) LMWEs on the SFC of triglyceride (TAG) droplets at isothermal conditions using a thermo-optical method. When β-lg alone was used as an emulsifier, a maximum SFC of 80% was obtained at a supercooling of 32 K and 42 K for trilaurin and tripalmitin, respectively. The SFC could be increased to 100% using a PL containing saturated fatty acids (FAs) and a small hydrophilic headgroup. At the same supercooling, a PL containing saturated FAs and a large hydrophilic headgroup led to a maximum SFC of 80%. At lower supercooling, the SFC was reduced with this PL by 10% compared to β-lg alone. In addition, when the PLs had more time to adsorb and rearrange with ß-lg at the interface, even lower SFCs were observed compared to cooling directly after emulsification.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Emulsions and Emulsion Stability Analysis and Application in Chemical, Pharmaceutical and Food Industries)
►▼
Show Figures
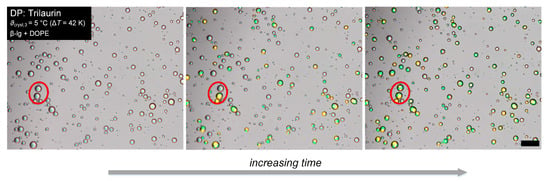
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Evaluating Fractal Damage and Acoustic Emissions of Soft Rock–Coal Combinations in a Deep Mining Area
by
, , , , , , and
Processes 2023, 11(9), 2599; https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11092599 - 30 Aug 2023
Abstract
Weakly cemented soft rock mines in the Ordos Basin are susceptible to mining disasters, including roof collapse and substantial deformation of surrounding rocks, during coal mining operations. Researching the damage characteristics of structures composed of low-strength “soft rock–coal” combinations is crucial for effectively
[...] Read more.
Weakly cemented soft rock mines in the Ordos Basin are susceptible to mining disasters, including roof collapse and substantial deformation of surrounding rocks, during coal mining operations. Researching the damage characteristics of structures composed of low-strength “soft rock–coal” combinations is crucial for effectively preventing and controlling disasters in deep soft rock mining. To investigate the fractal damage characteristics of soft rock–coal combinations with different height ratios, uniaxial compression tests were conducted on specimens containing soft rock percentages of 20%, 40%, 50%, 60%, and 80%. The results show that the uniaxial compressive strength and modulus of elasticity of the soft rock–coal combinations increased with increasing proportions of soft rock. The soft rock–coal combination was clearly segmented, and the 40%, 50%, and 60% soft rock–coal combinations had good self-similarity. The fractal dimensions were 2.374, 2.508 and 2.586, which are all within the interval [2, 3]. When the percentage of soft rock was 20%, the specimen damage yielded flaky coal bodies with smaller grain size, whereas the coal–rock interface was spalled by small conical rock bodies. As the soft rock proportion increased, the percentage mass of fragments with particle size greater than 20 mm increased from 83.34% to 94.15%. The failure mode in soft rock–coal combinations is primarily attributed to the partial tensile splitting of the coal body. As the proportion of soft rock increased, there was a gradual reduction in the extent of coal body damage. Moreover, the acoustic emission absolute energies and counts decreased as the proportion of soft rock increased. The acoustic emission energy was reduced from 2.46 × 109 attoJ to 3.41 × 108 attoJ, and the acoustic emission counts were reduced from 18,276 to 7852.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Advanced Technologies of Deep Mining)
►▼
Show Figures
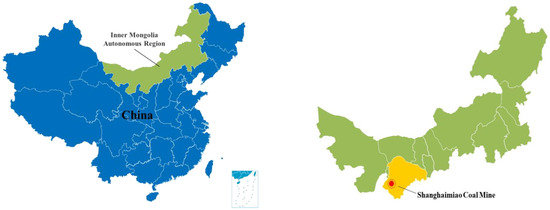
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
A Study on the Oil-Bearing Stability of Salt-Resistant Foam and an Explanation of the Viscoelastic Phenomenon
by
and
Processes 2023, 11(9), 2598; https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11092598 - 30 Aug 2023
Abstract
Foam is a medium-stable system composed of gas and liquid phases, which has the advantages of low density at the gas phase and high viscosity at the liquid phase, and has a wide application in oil and gas field development and mineral flotation,
[...] Read more.
Foam is a medium-stable system composed of gas and liquid phases, which has the advantages of low density at the gas phase and high viscosity at the liquid phase, and has a wide application in oil and gas field development and mineral flotation, but its special medium-stable system also brings many problems in industry applications. Scientists have carried out extensive analyses and research on the foam stability and bubble-bursting mechanism, which initially clarified the rules of bubble breakage caused by environmental factors such as temperature and pressure, but the mechanism of bubble bursting under the action of internal factors such as liquid mineralization and oil concentration of the films is still not clearly defined. In this paper, we propose a compound salt-resistant foaming agent, investigated the influence of the aggregation and adsorption behavior of oil droplets on the liquid films and boundaries, and established a relevant aggregation and adsorption model with the population balance equation. We put forward a liquid film drainage mechanism based on the distribution, aggregation, and transport of oil droplets in the liquid films, so as to explain the changes in foam stability under the action of oil droplets. On the other hand, the viscoelastic analysis of foam fluid is performed with a rheometer, and the results show that in comparison with conventional power-law fluid, foam fluid has a complex rheological behavior for low shear thickening, but high shear thinning.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic Enhanced Oil Recovery Technologies, 2nd Volume)
►▼
Show Figures
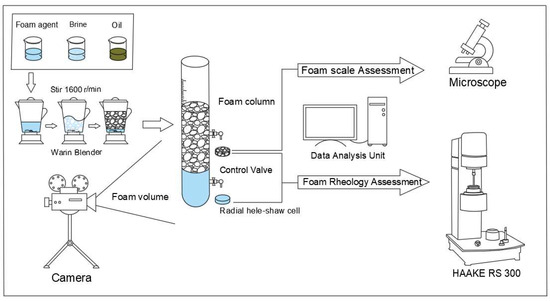
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
A New Integrated Model for Simulating Adaptive Cycle Engine Performance Considering Variations in Tip Clearance
Processes 2023, 11(9), 2597; https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11092597 - 30 Aug 2023
Abstract
The low-fidelity simulation method cannot meet the requirements for predicting the performance of an adaptive cycle engine (ACE), especially when considering tip clearance variations in the compression and expansion systems. The tip clearances of the components of an ACE, such as the adaptive
[...] Read more.
The low-fidelity simulation method cannot meet the requirements for predicting the performance of an adaptive cycle engine (ACE), especially when considering tip clearance variations in the compression and expansion systems. The tip clearances of the components of an ACE, such as the adaptive fan and turbine, vary drastically under different operating conditions. Though the tip clearance significantly impacts the engine’s performance, including its thrust and fuel consumption, variations in tip clearance are not considered in traditional ACE simulation models. This paper developed a new integrated model for predicting ACE performance, including multi-fidelity simulation models of the components and a newly developed, simplified model for predicting tip clearance. Specifically, the integrated model consists of a zero-dimensional (0D) engine performance simulation model, a three-dimensional (3D) adaptive fan numerical simulation model, a one-dimensional (1D) low-pressure-turbine (LPT) mean line model, and a multi-dimensional (MD) tip clearance prediction model. The integrated model solved the problem of considering the impact of tip clearance on an ACE and further improved the accuracy of thrust and fuel consumption predictions. Specifically, considering variations in the tip clearances under the design conditions, the differences in the thrust and specific fuel consumption (SFC) of the ACE are 1% and 0.3%, respectively. In conclusion, the integrated model provides a useful tool for evaluating the performance of an ACE while considering tip clearance variations.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Energy Systems)
►▼
Show Figures
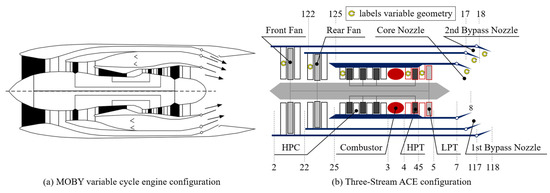
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Numerical Evaluation of the Effect of Buoyancy-Driven Flow on the Migration of Respiratory Droplets
by
and
Processes 2023, 11(9), 2596; https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11092596 - 30 Aug 2023
Abstract
The understanding of the impact of buoyancy-driven flow on the migration of respiratory droplets remains limited. To investigate this phenomenon, the Lagrangian–Eulerian approach (k-ε turbulent model and discrete phase model) was employed to analyze the interaction between buoyancy-driven flow and coughing activity. The
[...] Read more.
The understanding of the impact of buoyancy-driven flow on the migration of respiratory droplets remains limited. To investigate this phenomenon, the Lagrangian–Eulerian approach (k-ε turbulent model and discrete phase model) was employed to analyze the interaction between buoyancy-driven flow and coughing activity. The simulation approach was validated by simulating a jet problem in water. Although this problem describes the jet penetration in water, the governing equations for this problem are the same as those for coughing activity in the air. The results demonstrated that an umbrella-shaped airflow was generated above a person and a temperature stratification existed in the room. The buoyancy-driven flow significantly altered the dispersion pattern of the droplets. Notably, for large droplets with an initial diameter of 100 μm, the flow in the boundary layer led to an increased deposition time by about five times. Conversely, for small droplets with an initial diameter of 20 μm, the umbrella-shaped airflow resulted in a more rapid dispersion of droplets and subsequently facilitated their quicker removal by the room walls. After a duration of 300 s, the suspended droplet number of the case with buoyancy-driven flow was 33.4% smaller than that of the case without buoyancy-driven flow. Two or three persons being in the room resulted in a faster droplet removal.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Environmental and Green Processes)
►▼
Show Figures
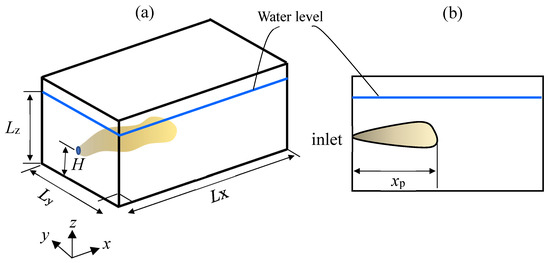
Figure 1
Open AccessEditorial
Special Issue on “Machine-Learning-Assisted Intelligent Processing and Optimization of Complex Systems”
by
and
Processes 2023, 11(9), 2595; https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11092595 - 30 Aug 2023
Abstract
Complex systems and their various characteristics have been widely considered in economic and industrial systems [...]
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Machine-Learning-Assisted Intelligent Processing and Optimization of Complex Systems)
Open AccessArticle
Prediction Model of Fouling Thickness of Heat Exchanger Based on TA-LSTM Structure
Processes 2023, 11(9), 2594; https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11092594 - 30 Aug 2023
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Heat exchangers in operation often experience scaling, which can lead to a decrease in heat exchange efficiency and even safety accidents when fouling accumulates to a certain thickness. To address this issue, manual intervention is currently employed to monitor fouling thickness in advance.
[...] Read more.
Heat exchangers in operation often experience scaling, which can lead to a decrease in heat exchange efficiency and even safety accidents when fouling accumulates to a certain thickness. To address this issue, manual intervention is currently employed to monitor fouling thickness in advance. In this study, we propose a two-layer LSTM neural network model with an attention mechanism to effectively learn fouling thickness data under different working conditions. The model accurately predicts the scaling thickness of the heat exchanger during operation, enabling timely human intervention and ensuring that the scaling remains within a safe range. The experimental results demonstrate that our proposed neural network model (TA-LSTM) outperforms both the traditional BP neural network model and the LSTM neural network model in terms of accuracy and stability. Our findings provide valuable technical support for future research on heat exchanger descaling and fouling growth detection.
Full article
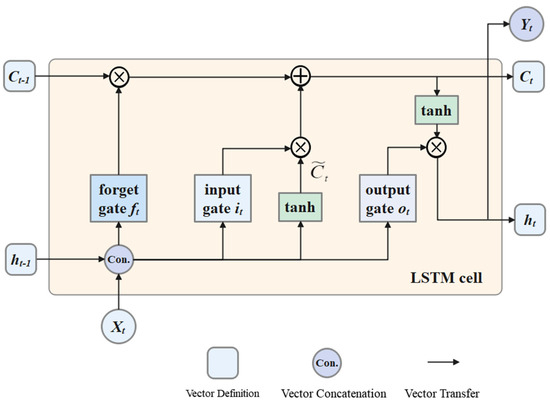
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Unveiling the Latest Breakthroughs in Menaquinone-7 Research through Fermentation-Based Production
by
and
Processes 2023, 11(9), 2593; https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11092593 - 30 Aug 2023
Abstract
MK-7, like other biological molecules, exists in geometric isomers, including cis and trans forms, among which only the all-trans form holds biological significance. Recent studies have drawn attention to the manifold health advantages linked to the consumption of menaquinone-7 (MK-7). Nonetheless, the scarcity
[...] Read more.
MK-7, like other biological molecules, exists in geometric isomers, including cis and trans forms, among which only the all-trans form holds biological significance. Recent studies have drawn attention to the manifold health advantages linked to the consumption of menaquinone-7 (MK-7). Nonetheless, the scarcity of MK-7 in natural dietary sources underscores the necessity for creating dietary supplements to fulfil daily intake requisites. Obtaining MK-7 involves employing production techniques encompassing solid- or liquid-state fermentation. However, upscaling this process becomes intricate in static fermentation due to challenges in heat and mass transfer. Consequently, the bulk of research on MK-7 synthesis via fermentation has concentrated on the liquid-state approach. To this end, endeavors have been dedicated to refining MK-7 biosynthesis by exploring diverse fermentation media compositions, optimal growth conditions, and even integrating nanobiotechnology methodologies. Innovative biofilm reactors, capable of facilitating biofilm attachment on plastic composite substrates, have also emerged as a promising solution, particularly when utilizing B. subtilis cells. The biofilm reactors exhibit robust extracellular MK-7 secretion, effectively surmounting the hurdles posed by high aeration and agitation rates. However, a demonstration of the scalability of this technology to pilot and industrial scales is still pending. This work offers an outline of the latest advancements in MK-7 research, with a specific focus on the strides made in MK-7 production through fermentation techniques. The paramount importance of the all-trans form of MK-7 is underscored, accentuating its role in enhancing human well-being. The ramifications of this work hold the potential to pave the way for novel strategies to amplify MK-7 production and formulate products with an optimized MK-7 profile, thereby promising avenues for enhancing human health and nutrition.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Applications of Nanomaterials in Bioprocess and Biosystem Engineering: Challenges and Trends)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Effect of Cavitating Hydraulic Elements on Pump Characteristics
Processes 2023, 11(9), 2592; https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11092592 - 30 Aug 2023
Abstract
The effective and reliable performance of any pump can be significantly impacted by the piping system design. One of the essential points is the pump suction pipe. Poor design and dimension of the suction piping can lead to cavitation in the pump which
[...] Read more.
The effective and reliable performance of any pump can be significantly impacted by the piping system design. One of the essential points is the pump suction pipe. Poor design and dimension of the suction piping can lead to cavitation in the pump which affects its head and efficiency. The primary objective is to reduce the hydraulic losses of the suction piping in order to maintain a Net Positive Suction Head required by the pump. Suction piping is recommended to be short and straight, and branch connections, valves and elbows should be avoided, which is not always possible. In addition, cavitation can occur in the actual hydraulic elements installed on the pump suction. This work is focused on the investigation of cavitating hydraulic element in the suction pipe on the pump performance. A converging-diverging nozzle with a circular cross-section was used for this purpose. A straight pipe segment of constant diameter and the same length was used for comparison. Both elements were characterized by the loss coefficient and the cavitation number. Their influence on the pump head and the Net Positive Suction Head Available (NPSHA) was investigated.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Design and Optimization Method of Pumps)
►▼
Show Figures
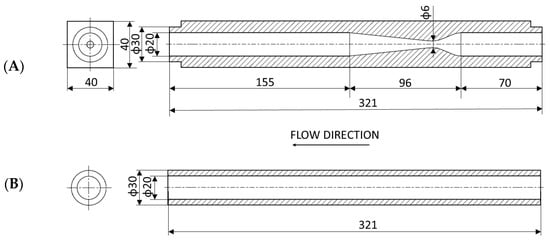
Figure 1

Journal Menu
► ▼ Journal Menu-
- Processes Home
- Aims & Scope
- Editorial Board
- Reviewer Board
- Topical Advisory Panel
- Instructions for Authors
- Special Issues
- Topics
- Sections & Collections
- Article Processing Charge
- Indexing & Archiving
- Editor’s Choice Articles
- Most Cited & Viewed
- Journal Statistics
- Journal History
- Journal Awards
- Society Collaborations
- Conferences
- Editorial Office
- 10th Anniversary of Processes
Journal Browser
► ▼ Journal BrowserHighly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Applied Sciences, Energies, Geosciences, Polymers, Processes
Enhanced Oil Recovery Technologies, 2nd Volume
Topic Editors: Jan Vinogradov, Ali Habibi, Zhengyuan LuoDeadline: 30 September 2023
Topic in
Energies, Processes, Electronics, Applied Sciences, WEVJ
Energy Management and Efficiency in Electric Motors, Drives, Power Converters and Related Systems
Topic Editors: Mario Marchesoni, Alfonso DamianoDeadline: 15 October 2023
Topic in
Energies, Materials, Minerals, Processes, Sustainability
Advanced Materials and Technologies in Deep Rock Engineering
Topic Editors: Jiangyu Wu, Hong Wong, Lang Liu, Wen Zhong, Dan MaDeadline: 26 October 2023
Topic in
Energies, JMSE, Processes, Inventions
Marine Renewable Energy, 2nd Volume
Topic Editors: Eugen Rusu, Kostas Belibassakis, George LavidasDeadline: 30 November 2023

Conferences
27 October–10 November 2023
The 4th International Electronic Conference on Applied Sciences (ASEC2023)

Special Issues
Special Issue in
Processes
Advances in Supported Nanoparticle Catalysts (Volume II)
Guest Editor: Sónia CarabineiroDeadline: 5 September 2023
Special Issue in
Processes
Design and Optimization in Process Engineering
Guest Editors: Bor-Yih Yu, Vincentius Surya Kurnia Adi, Chien-Yuan Su, Felicia Januarlia NovitaDeadline: 10 September 2023
Special Issue in
Processes
Dental Engineering: Materials, Technologies and Devices for Dentistry 4.0
Guest Editors: Leszek Dobrzański, Lech Bolesław Dobrzański, Anna D. Dobrzańska-Danikiewicz, Joanna DobrzańskaDeadline: 30 September 2023
Special Issue in
Processes
Modelling and Optimization of Chemical Reactors
Guest Editors: Maria Cristina Annesini, Maria Anna MurmuraDeadline: 15 October 2023
Topical Collections
Topical Collection in
Processes
Modeling, Simulation and Computation on Dynamics of Complex Fluids
Collection Editors: Gabriella Bognár, Krisztian Hriczo
Topical Collection in
Processes
Multi-Objective Optimization of Processes
Collection Editors: Gade Pandu Rangaiah, Andrew Hoadley
Topical Collection in
Processes
Principles of Modular Design and Control in Complex Systems
Collection Editor: Cong T. Trinh
Topical Collection in
Processes
Sustainable Food Processing Processes
Collection Editors: Dariusz Dziki, Renata Różyło, Urszula Gawlik-Dziki