-
 The Design and Performance Prediction Model of an Integrated Scheme of a Membrane Bioreactor and Anaerobic Digester for the Treatment of Domestic Wastewater and Biowaste
The Design and Performance Prediction Model of an Integrated Scheme of a Membrane Bioreactor and Anaerobic Digester for the Treatment of Domestic Wastewater and Biowaste -
 Structural Equation Modeling of the Marine Ecological System in Nanwan Bay Using SPSS Amos
Structural Equation Modeling of the Marine Ecological System in Nanwan Bay Using SPSS Amos -
 The Evolution of Multifunctional Agriculture in Italy
The Evolution of Multifunctional Agriculture in Italy -
 Assessing the Suitability of Sediment Soil to Be Reused by Different Soil Treatments for Forest Agriculture
Assessing the Suitability of Sediment Soil to Be Reused by Different Soil Treatments for Forest Agriculture
Journal Description
Sustainability
Sustainability
is an international, cross-disciplinary, scholarly, peer-reviewed and open access journal of environmental, cultural, economic, and social sustainability of human beings. It provides an advanced forum for studies related to sustainability and sustainable development, and is published semimonthly online by MDPI. The Canadian Urban Transit Research & Innovation Consortium (CUTRIC) and International Council for Research and Innovation in Building and Construction (CIB) are affiliated with Sustainability and their members receive discounts of the article processing charge.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within Scopus, SCIE and SSCI (Web of Science), GEOBASE, GeoRef, Inspec, AGRIS, RePEc, CAPlus / SciFinder, and other databases.
- Journal Rank: JCR - Q2 (Environmental Studies) / CiteScore - Q1 (Geography, Planning and Development)
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 18.3 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 3.5 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the first half of 2023).
- Recognition of Reviewers: reviewers who provide timely, thorough peer-review reports receive vouchers entitling them to a discount on the APC of their next publication in any MDPI journal, in appreciation of the work done.
- Testimonials: See what our editors and authors say about Sustainability.
- Companion journals for Sustainability include: World, Sustainable Chemistry, Conservation, Future Transportation, Architecture, Standards, Merits and Wind.
Impact Factor:
3.9 (2022);
5-Year Impact Factor:
4.0 (2022)
Latest Articles
Experimental Investigation on the Performance of Compressors for Small-Scale Compressed Air Energy Storage in Parallel Mode
Sustainability 2023, 15(17), 13164; https://doi.org/10.3390/su151713164 (registering DOI) - 01 Sep 2023
Abstract
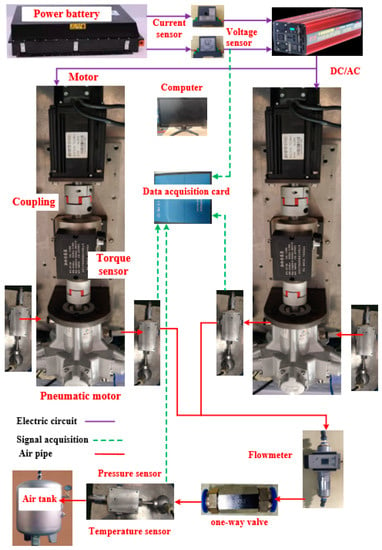
The Compressed Air Energy Storage (CAES) system is a promising energy storage technology that has the advantages of low investment cost, high safety, long life, and is clean and non-polluting. The compressor/expander is the core equipment of the CAES system, and its performance
[...] Read more.
The Compressed Air Energy Storage (CAES) system is a promising energy storage technology that has the advantages of low investment cost, high safety, long life, and is clean and non-polluting. The compressor/expander is the core equipment of the CAES system, and its performance has a decisive impact on the overall system efficiency and economic performance. Based on the pneumatic motor, this study proposes and designs a test bench of the CAES system that integrates compression and expansion functions. The off-design operation condition represented by the pressure change in the air tank has an important influence on the efficiency and economy of the CAES system. The effect of key parameters such as air tank pressure, torque, and mass flow rate on the output and efficiency of the compressor is investigated. When the CAES system is operating in energy storage mode, the compressor must continuously deliver gas to the gas storage. The working pressure of the compressor increases with the pressure in the air tank, so the compressor used for energy storage must operate continuously over a wide range of working conditions. The parallel operation mode of the compressor is proposed to improve the working condition range of the compressor torque and current, and improve the isotropic efficiency. When the air receiver pressure is 2.6 bar and the rotational speed is 2850 r/min, the power consumption of the compressor reaches the maximum value of approximately 1233.1 W. This new parallel mode could provide a CAES unit a systematic solution.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Renewable Energy and Energy Systems: New Concept, Design, and Optimization)
►
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Unveiling Ancestral Sustainability: A Comprehensive Study of Economic, Environmental, and Social Factors in Potato and Quinoa Cultivation in the Highland Aynokas of Puno, Peru
by
, , , , , and
Sustainability 2023, 15(17), 13163; https://doi.org/10.3390/su151713163 (registering DOI) - 01 Sep 2023
Abstract
Centuries of cultivation in the Highland Aynoka of Puno, Peru, have endowed indigenous crops such as potato and quinoa with rich cultural and nutritional value deeply ingrained in local traditions. This study meticulously evaluates their economic viability, environmental implications, and cultural importance by
[...] Read more.
Centuries of cultivation in the Highland Aynoka of Puno, Peru, have endowed indigenous crops such as potato and quinoa with rich cultural and nutritional value deeply ingrained in local traditions. This study meticulously evaluates their economic viability, environmental implications, and cultural importance by employing a mixed-methods research approach involving surveys, interviews, and observations. The outcome reveals that while the Economic Sustainability Index (EKI) moderately supports potato and quinoa production sustainability, with a value of 2.98, it falls short of significant impact. Conversely, the Environmental Sustainability Index (ESI) and the Social Sustainability Index (SSI) exhibit moderate levels of sustainability, recording values of 4.04 and 3.38 for ESI and SSI, respectively. These crops demonstrate acceptable economic feasibility, marked by consistent sales, income generation, and manageable production expenses. The findings underscore the urgency of endorsing sustainable farming methods to safeguard cultural heritage, boost market prospects, and fortify regional ecological robustness. Rooted in ancestral sustainability, potato and quinoa cultivation is a cornerstone in local food systems. Recognizing the cultural, economic, and environmental significance inherent to these crops, efforts can be channeled towards nurturing sustainable agricultural systems that uphold community well-being, conserve biodiversity, and facilitate cultural resilience in Puno’s Highland Aynoka.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Agriculture, Land and Farm Management)
►▼
Show Figures
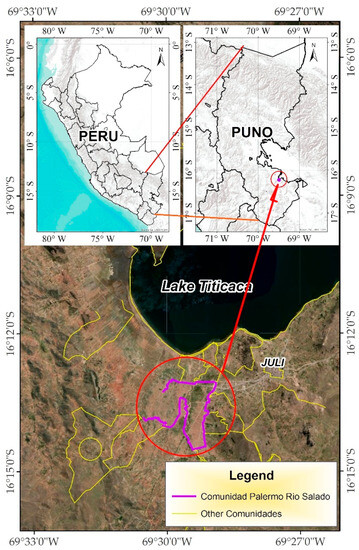
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Widespread Urban Regeneration of Existing Residential Areas in European Medium-Sized Cities—A Framework to Locate Redevelopment Interventions
Sustainability 2023, 15(17), 13162; https://doi.org/10.3390/su151713162 (registering DOI) - 01 Sep 2023
Abstract
Within the scientific debate on urban regeneration, this paper intends to question possible planning techniques to address the implementation of widespread regeneration interventions in obsolete residential areas within medium-sized European cities, with particular attention to constructing a cognitive framework to locate redevelopment interventions.
[...] Read more.
Within the scientific debate on urban regeneration, this paper intends to question possible planning techniques to address the implementation of widespread regeneration interventions in obsolete residential areas within medium-sized European cities, with particular attention to constructing a cognitive framework to locate redevelopment interventions. The widespread urban regeneration approach has yet to be sufficiently explored in the scientific literature, which focuses much more on replacing large derelict areas, though it seems particularly relevant for research and urban practice. This paper aims to illustrate a methodological framework for defining obsolete and degraded areas (at the block scale) suitable for redevelopment. Various criteria are considered, e.g., land use, buildings’ dating, state of preservation, population density, public spaces, and facility provision, and degree of accessibility. The methodological framework is then tested in the medium-sized Italian city of Parma. Data set parameters and threshold values to quantify the previously introduced criteria and perform GIS-based statistical and spatial analysis. The results show 96 areas potentially in need of regeneration, providing an opportunity to reflect on the criteria of suitability and priority for transformation and the framework of past and future planning scenarios.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Urban Planning for Smart and Sustainable Cities)
►▼
Show Figures
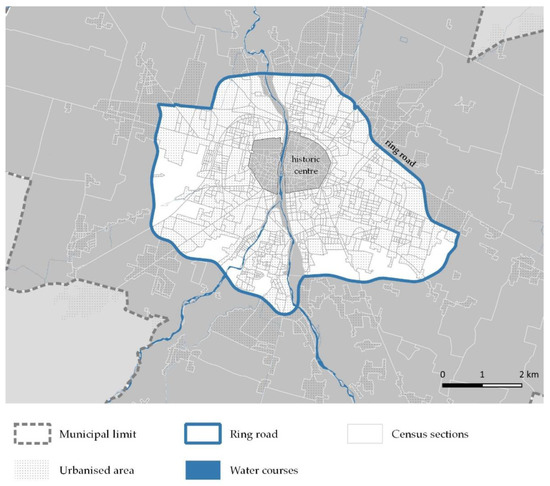
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Soil Contaminants and Their Removal through Surfactant-Enhanced Soil Remediation: A Comprehensive Review
Sustainability 2023, 15(17), 13161; https://doi.org/10.3390/su151713161 (registering DOI) - 01 Sep 2023
Abstract
This review provides a comprehensive analysis of the effectiveness of surfactants in enhancing the remediation of contaminated soils. The study examines recent and older research on the use of effluent treatment techniques combined with synthetic surface-active agents, bio-surfactants, and various categories of surfactants
[...] Read more.
This review provides a comprehensive analysis of the effectiveness of surfactants in enhancing the remediation of contaminated soils. The study examines recent and older research on the use of effluent treatment techniques combined with synthetic surface-active agents, bio-surfactants, and various categories of surfactants for soil reclamation purposes. The main purpose of this review is to evaluate the effectiveness of surfactants in enhancing the remediation of contaminated soils. The research question is to explore the mechanisms through which surfactants enhance soil remediation and to assess the potential benefits and limitations of surfactant-based remediation methods. This review was conducted through an extensive literature search of relevant articles published in scientific databases. The articles were selected based on their relevance to the topic and their methodological rigor. Types of possible soil pollutants and the requirements of specific surfactants were discussed. Structural relationships between pollutant and surfactants were described thoroughly. Extensive study revealed that surfactants have shown great potential in enhancing the remediation of contaminated soils. Surfactants can improve the solubility and mobility of hydrophobic contaminants and facilitate their removal from soil. However, the effectiveness of surfactant-based remediation methods depends on several factors, including the type of contaminant, the soil properties, and the surfactant concentration and type. Surfactant-enhanced soil remediation can be an effective and sustainable method for addressing soil contamination. However, the optimal conditions for using surfactants depend on the specific site characteristics and contaminant properties, and further research is needed to optimize the use of surfactants in soil remediation.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Soil Conservation and Sustainability)
►▼
Show Figures
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Sustainable Exploration of “Plug-In Design” in Public Space of the Old City in Guangzhou: Case Study on Xudi-Gaodijie
Sustainability 2023, 15(17), 13160; https://doi.org/10.3390/su151713160 (registering DOI) - 01 Sep 2023
Abstract
The current regeneration mode of public space in the old city of Guangzhou is ineffective, thus necessitating supplementation with a more systematic methodology. The “plug-in design” targets sustainable regeneration while preserving the overall urban texture and context, i.e., it has little impact on
[...] Read more.
The current regeneration mode of public space in the old city of Guangzhou is ineffective, thus necessitating supplementation with a more systematic methodology. The “plug-in design” targets sustainable regeneration while preserving the overall urban texture and context, i.e., it has little impact on the spatial qualities of the old city. The ultimate goal is to activate the public space of the old city of Guangzhou point to area through the insertion of various plug-ins. In this study, the methodology is applied to Xudi Gaodi Street, the core area of the old city of Guangzhou, to explore its effects on sustainability. The internal public space is isolated and supplied with rigid and flexible plug-ins from multiple dimensions, which not only improves the spatial environment but also injects new urban formats. This work provides a specific solution for regeneration in Guangzhou’s old city while enhancing empirical knowledge of the plug-in design to support urban regeneration theory and further practical development.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Sustainable Urban and Rural Development)
►▼
Show Figures
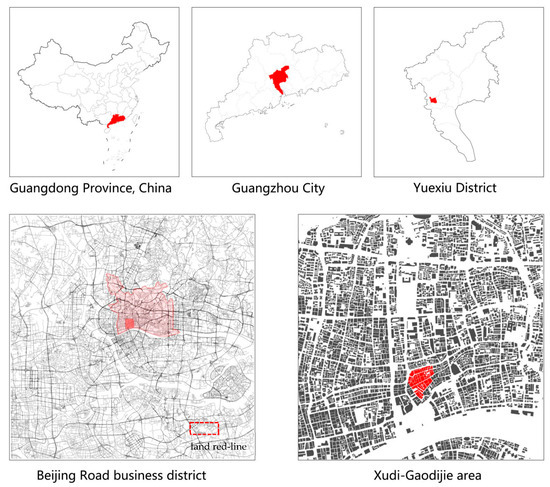
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Eco-Environmental Quality Assessment Using the Remote Sensing Ecological Index in Suzhou City, China
Sustainability 2023, 15(17), 13158; https://doi.org/10.3390/su151713158 (registering DOI) - 01 Sep 2023
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
This study utilizes four environmental indicators derived from six-phase Landsat images (TM, OLI, and TIRS) to construct a remote sensing ecological index (RSEI) and to quantitatively and comprehensively assess the spatiotemporal changes in the eco-environmental quality (EEQ) of Suzhou City, China. The environmental
[...] Read more.
This study utilizes four environmental indicators derived from six-phase Landsat images (TM, OLI, and TIRS) to construct a remote sensing ecological index (RSEI) and to quantitatively and comprehensively assess the spatiotemporal changes in the eco-environmental quality (EEQ) of Suzhou City, China. The environmental indicators consist of the wetness index (WI), greenness index (GI), dryness index (DI), and heat index (HI). The obtained results showed: (1) positive effects of the WI and GI, as well as negative effects of the DI and HI, on the EEQ of Suzhou City in the 2002–2022 period. The GI was observed to have the greatest impact on the RSEI of Suzhou City. (2) The average RSEI values of Suzhou City exhibit a “W” shape pattern in the 2002–2022 period. The lowest and highest average RSEI values were 0.632 and 0.746, respectively, while the average annual RSEI value was 0.702. The EEQ of Suzhou City was observed to be at a relatively good level. (3) The EEQ of Suzhou City exhibits sharp declines in the periods of 2006–2010 and 2014–2018, for which the degraded RSEI area covers 440.60 and 404.16 km2, while the area ratios are 56.13% and 51.48%, respectively. The EEQ of Suzhou City has substantially increased during the periods of 2010–2014, 2018–2022, and 2002–2022, showing improved RSEI areas of 583.7, 390.13, and 347.02 km2 and area ratios of 74.36%, 49.70%, and 44.21%, respectively. The results of this study provide a scientific basis for the protection, utilization, and development of the ecological environment (EE) of Suzhou City. They also provide valuable references and data support for the sustainable development, the high-quality development of the EE, and the construction of the ecological civilization of Suzhou City. The policymakers of environmental protection departments in Suzhou City can use this study’s inferences to devise local environmental protection policies.
Full article
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Livelihoods and Perceptions of Climate Change among Dairy Farmers in the Andes: Implications for Climate Education
by
, , , , , , , , , and
Sustainability 2023, 15(17), 13157; https://doi.org/10.3390/su151713157 (registering DOI) - 01 Sep 2023
Abstract
Climate change mainly affects the production and consumption systems associated with food, livelihoods, production (e.g., reduced milk production), water, and land use. The role of local knowledge is recognized as important for decision-making under changing circumstances. This study was conducted in the northern
[...] Read more.
Climate change mainly affects the production and consumption systems associated with food, livelihoods, production (e.g., reduced milk production), water, and land use. The role of local knowledge is recognized as important for decision-making under changing circumstances. This study was conducted in the northern part of the Ecuadorian Andes using a sample of 170 dairy-cattle-farming households. The objectives were to: (i) characterize the rural livelihoods of dairy cattle farmers; (ii) evaluate access to climate information and perceptions of climate change; and (iii) determine the relationship between livelihoods and perceptions of climate change. Significant differences were identified between the groups evaluated in relation to the dairy farmers’ livelihoods. In addition, 85.29% of the respondents indicated that climate information is important, but 67.83% did not trust the sources of information. It was found that there is a significant relationship between the level of education and age with the variables of climate change perceptions. This combined knowledge will allow people to promote agri-environmental and educational policies to achieve climate literacy at a rural level.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Climate Change Mitigation and Adaptation in Sustainable Agriculture)
►▼
Show Figures
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Knowledge-Based Faultlines and Corporate Social Irresponsibility: Evidence from Chinese High-Polluting Companies
by
and
Sustainability 2023, 15(17), 13156; https://doi.org/10.3390/su151713156 (registering DOI) - 01 Sep 2023
Abstract
Government requests and societal expectations have pressured high-polluting companies to focus on corporate social responsibility strategies. Using the upper echelons theory as a theoretical framework, we investigated how top management team (TMT) faultlines influence corporate social performance (CSP) based on data from 212
[...] Read more.
Government requests and societal expectations have pressured high-polluting companies to focus on corporate social responsibility strategies. Using the upper echelons theory as a theoretical framework, we investigated how top management team (TMT) faultlines influence corporate social performance (CSP) based on data from 212 high-polluting companies. The results showed that CSP can be improved by reducing corporate social irresponsibility (CSiR), knowledge-based faultlines have a U-shaped effect on CSiR, and there is a knowledge-based faultline critical point. This implies that knowledge-based faultlines can improve CSiR before reaching this critical point. Additionally, medium-strength knowledge-based faultlines are more conducive to improving irresponsible behavior. CEO power plays a significant moderating role in the relationship between TMT faultlines and CSiR and slows the U-shaped effect of knowledge-based faultlines on CSiR. These findings could help enterprises optimize team structures, adjust corporate social responsibility strategies, and maintain sustainable development in high-polluting sectors.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Business, Innovation, and Economics Sustainability)
Open AccessArticle
Effect of Moisture Content on the Permanent Strain of Yellow River Alluvial Silt under Long-Term Cyclic Loading
Sustainability 2023, 15(17), 13155; https://doi.org/10.3390/su151713155 (registering DOI) - 01 Sep 2023
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The Yellow River alluvial silt has unique engineering properties and is unstable when encountering moisture. The mechanical properties of silt subgrade can be impaired by the increase in moisture content due to rainwater infiltration, which has a negative effect on traffic safety. To
[...] Read more.
The Yellow River alluvial silt has unique engineering properties and is unstable when encountering moisture. The mechanical properties of silt subgrade can be impaired by the increase in moisture content due to rainwater infiltration, which has a negative effect on traffic safety. To further reveal the influence of moisture content on the deformation characteristics of silt, a series of monotonic and cyclic triaxial tests were conducted on the alluvial silt with different moisture contents. The development law of cyclic accumulative permanent strain and the effects of moisture content, cyclic deviator stress and confining pressure on the axial permanent strain of silt were explored. The study shows that the static strength of silt decreases with the increase in moisture content, and the attenuation of static strength is mainly caused by the decrease in cohesion due to the reduction in matric suction. The permanent strain rises linearly with the increase in moisture content and cyclic deviator stress, and decreases with the increase in confining pressure. An empirical model for predicting the permanent strain of silt under long-term cyclic loading considering the effect of moisture content was established. Compared with the test data and other existing models, the established model has easier obtained parameters, higher prediction accuracy and better applicability.
Full article
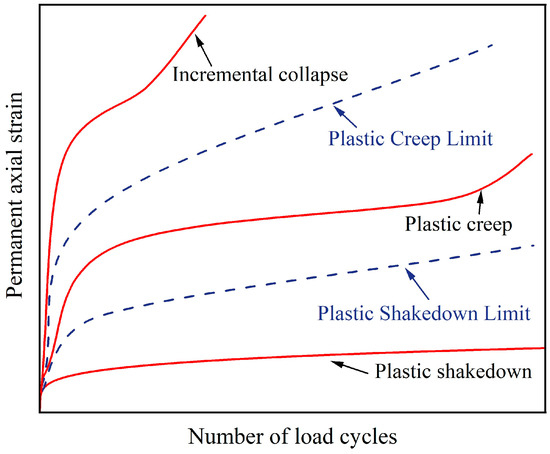
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
The Effects of Non-Uniformly-Aged Photovoltaic Array on Mismatch Power Loss: A Practical Investigation towards Novel Hybrid Array Configurations
by
, , , , , , , and
Sustainability 2023, 15(17), 13153; https://doi.org/10.3390/su151713153 (registering DOI) - 01 Sep 2023
Abstract
One of the most important causes of a reduction in power generation in PV panels is the non-uniform aging of photovoltaic (PV) modules. The increase in the current–voltage (I–V) mismatch among the array modules is the primary cause of this kind of degradation.
[...] Read more.
One of the most important causes of a reduction in power generation in PV panels is the non-uniform aging of photovoltaic (PV) modules. The increase in the current–voltage (I–V) mismatch among the array modules is the primary cause of this kind of degradation. There have been several array configurations investigated over the years to reduce mismatch power loss (MPL) caused by shadowing, but there have not been any experimental studies that have specifically examined the impact of various hybrid array topologies taking PV module aging into consideration. This research examines the influence of the non-uniform aging scenario on the performance of solar PV modules with various interconnection strategies. Experiments have been carried out on a 4 × 10, 400 W array with 12 possible configurations, including three proposed configurations (LD-TCT, SP-LD, and LD-SP), to detect the electrical characteristics of a PV system. Finally, the performances of different module configurations are analyzed where the newly proposed configurations (SP-LD and LD-SP) show 15.80% and 15.94% higher recoverable energy (RE), respectively, than the most-adopted configuration (SP). Moreover, among the twelve configurations, the SP configuration shows the highest percentage of MPL, which is about 17.96%, whereas LD-SP shows the lowest MPL at about 4.88%.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Renewable Energy Sources: A Solution in the Operation of Smart Grids and Sustainable Energy Systems)
►▼
Show Figures
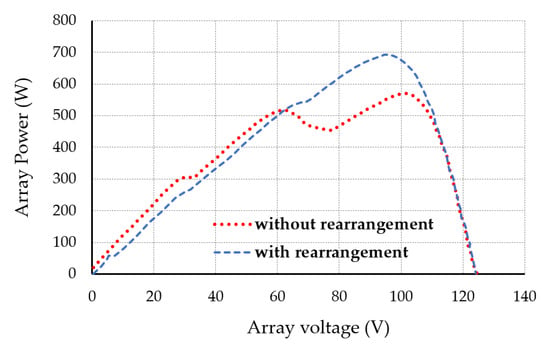
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Reflective and Cooperative Learning for Understanding Sustainability through an Eco-Innovation Strategy in Rural Travel and Hospitality: A STEAM Case Study
Sustainability 2023, 15(17), 13152; https://doi.org/10.3390/su151713152 (registering DOI) - 01 Sep 2023
Abstract
Eco-innovation denotes developing green practices using environmentally friendly innovative approaches or technologies. Although eco-innovation has been broadly applied in different industries, such as low-carbon production and manufacturing, how to implement such innovation in education for sustainable development (ESD) has rarely been studied. Therefore,
[...] Read more.
Eco-innovation denotes developing green practices using environmentally friendly innovative approaches or technologies. Although eco-innovation has been broadly applied in different industries, such as low-carbon production and manufacturing, how to implement such innovation in education for sustainable development (ESD) has rarely been studied. Therefore, this research considered a reflective and cooperative learning approach to science, technology, engineering, arts, and math (STEAM) education. A case study examined Wanluan Township of Pingtung County in southern Taiwan. Four departments’ students and lecturers at Meiho University were involved in situated learning. Hospitality management students played farm owners who engaged in organic agriculture to produce food and beverages. These agricultural products were farm-to-table, cooked, and served to customers in a natural dining setting through the students’ teamwork. Tourism, sports and leisure management, and food science and nutrition students played tourists in a self-guided travel context, who engaged in acts such as visiting buildings to understand heritage while observing that the houses were still in use as dwellings. This encouraged reflection on the importance of cultural preservation. The results showed that eco-innovation can represent a sustainable marketing strategy for improving the local community economy and can be implemented in a practical situation in STEAM. The ESD goal for 2030—societal transformation—is to foster students’ responsible behavior and attitudes in a personally authentic manner, thereby fostering sustainable learning and understanding.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Collection Sustainable Innovation in Tourism and Hospitality)
►▼
Show Figures
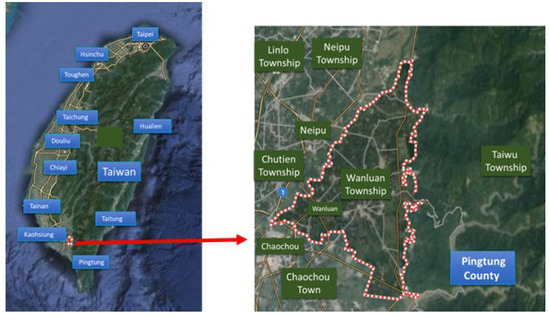
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
A Maturity Model to Become a Smart Organization Based on Lean and Industry 4.0 Synergy
Sustainability 2023, 15(17), 13151; https://doi.org/10.3390/su151713151 (registering DOI) - 01 Sep 2023
Abstract
This paper proposes a maturity model (MM) to become a smart organization considering Lean as a key enabler to drive I4.0 adoption. A systematic literature review on I4.0 and Lean concepts plus I4.0 adoption models was conducted through the PRISMA method based on
[...] Read more.
This paper proposes a maturity model (MM) to become a smart organization considering Lean as a key enabler to drive I4.0 adoption. A systematic literature review on I4.0 and Lean concepts plus I4.0 adoption models was conducted through the PRISMA method based on articles from Scopus and Web of Science databases, and records from official websites (e.g., consulting firms) published between 2011 and 2022. Identifying the Lean and I4.0 relationship and comparing the models’ relevant characteristics allowed the development of the MM proposal. Although previous research refers to Lean and I4.0 collaboration, the opportunity to design a reference model for adopting both approaches was identified since their interaction enhances value creation. The comprehensive model supports structuring the types of Lean principles/methods/tools and I4.0 technologies and their action to link them and define which of them need to be implemented according to the maturity level chronologically. Additionally, the proposed MM provides an adoption roadmap that starts eliminating non-added activities in the initial stages for process improvement to integrate I4.0 enabling technologies later. The model makes it possible for practitioners to generate implementation and development processes oriented toward I4.0 adoption based on maturity levels in which Lean has the starting point at the first ones. Hence, it defines the enabling technologies to be incorporated and linked throughout the value chain, enhancing a Lean culture. This model will help organizations to become “smart” by allowing them to transition toward the best technology investment and continuously add value to their processes, people, and products. Moreover, the results will motivate researchers to study further the application of models for I4.0 adoption in which Lean is integrated to fill the gap with the I4.0 embrace caused by quickly changing industrial environments and the uncertainty and unknowledge of guidelines associated with incorporating new technologies.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Towards Lean Production in Industry 4.0)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Governance and Corporate Management System Supported by Innovation, Technology, and Digital Transformation as a Driver of Change
Sustainability 2023, 15(17), 13150; https://doi.org/10.3390/su151713150 (registering DOI) - 01 Sep 2023
Abstract
Governance and Corporate Management Systems have become key tools for the comprehensive management of organizations, which, when implemented, guarantee corporate success, which can materialize in obtaining corporate goals, strategic objectives, KPIs, and KRP. This paper is the product of research exercises where a
[...] Read more.
Governance and Corporate Management Systems have become key tools for the comprehensive management of organizations, which, when implemented, guarantee corporate success, which can materialize in obtaining corporate goals, strategic objectives, KPIs, and KRP. This paper is the product of research exercises where a Governance and Corporate Management System is exposed, supported by three main pillars: Technology Management, Innovation Management, and Digital Transformation, which we will call GCMS+ from now on. The work developed is based on a quasi-experimental longitudinal research methodology, in which three key phases are addressed; the first phase corresponds to the systematic review of the literature, which allows the identification of the key components of the proposed GCMS+ system. The second phase of the methodology focused on the modelling of the GCMS+ system, which visually and descriptively describes the structural components, flows, and control mechanisms. The third phase of the methodology focuses on the validation of the GCMS+ system proposed from the discussed literature and contrasting the position of the authors, which is identified through a conceptual discussion. In this case, it seeks to validate the structural elements of GCMS+, the constraints, adoption of good practices, integration of standards, adoption of principles, integration of drivers, strategic taxonomy, organizational structures, governance and management approach, as well as methodologies, roles, initiatives, metrics, and indicators.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Digitalization and Innovative Business Strategy)
►▼
Show Figures
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Digital Literacy of Smallholder Farmers in Tanzania
Sustainability 2023, 15(17), 13149; https://doi.org/10.3390/su151713149 (registering DOI) - 01 Sep 2023
Abstract
The objective of this study was to assess the digital literacy of smallholder farmers in their agricultural production activities. Based on six proposed factors, the researchers developed questions to guide studying and measuring digital literacy (DL) of smallholder farmers. On a 5-point Likert
[...] Read more.
The objective of this study was to assess the digital literacy of smallholder farmers in their agricultural production activities. Based on six proposed factors, the researchers developed questions to guide studying and measuring digital literacy (DL) of smallholder farmers. On a 5-point Likert scale, 23 questions measured the ability of smallholders to access, manage, interpret, evaluate, create and communicate agriculture information online. Moreover, 257 smallholder farmers were involved in the study. To measure DL level, descriptive statistics and mean scores for the responses were calculated. A comparison of low and high levels of DL with demographic variables was conducted. The item-wise distribution of responses show that smallholders have high DL in accessing and communicating information, while they had low DL in managing, integrating, evaluating and creating information. The item’s mean score reveals that most of the responses were average. The overall mean score for the questionnaire was 75.17 + 5.79, and based on demographic characteristics, 58.0% of the smallholders reported high DL. Overall, smallholder farmers have an average level of DL. The study findings of this study may help governments and responsible institutions to develop strategies to ensure smallholders are digitally literate and use digital technologies in agricultural activities.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Sustainable Agriculture)
►▼
Show Figures
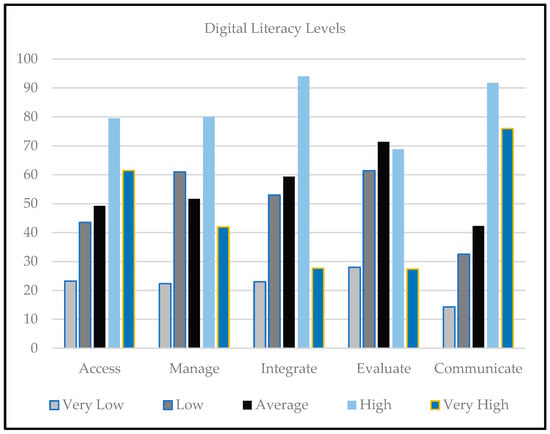
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Accounting and Decomposition of Energy Footprint: Evidence from 28 Sectors in China
Sustainability 2023, 15(17), 13148; https://doi.org/10.3390/su151713148 (registering DOI) - 01 Sep 2023
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
This study aims to clarify the sectoral level of environmental pollution “rights, responsibilities and benefits” and to identify the sectoral pollution “background” to lay the foundation to achieving sustainable economic development. We use input output table data to account for and decompose the
[...] Read more.
This study aims to clarify the sectoral level of environmental pollution “rights, responsibilities and benefits” and to identify the sectoral pollution “background” to lay the foundation to achieving sustainable economic development. We use input output table data to account for and decompose the sectoral energy footprint. Firstly, based on the principles of producer responsibility and consumer responsibility, the consumption-based energy footprint (CBEF) and the responsible-based energy footprint (RBEF) are accounted for. Secondly, the sectoral energy footprint is decomposed based on energy consumption and responsibility and direct and indirect perspectives. The results show that (1) the distribution of the sectoral CBEF is characterized by a high sector concentration and large inter-sector differences. (2) The distribution of the sectoral RBEF is more balanced, and the difference is smaller. (3) There are also asymmetries and heterogeneity in trends between the sectoral CBEF and the sectoral RBEF. (4) The energy footprint generated by the production of intermediate-use products is an important source of the sectoral energy footprint (EF). The Chinese government should develop differentiated energy saving and emission reduction measures and optimize the sectoral structure to enhance sectoral cleanliness. Policy references for energy saving and emission reduction at the sectoral level and early achievement of carbon-peak and carbon-neutral targets are proposed.
Full article
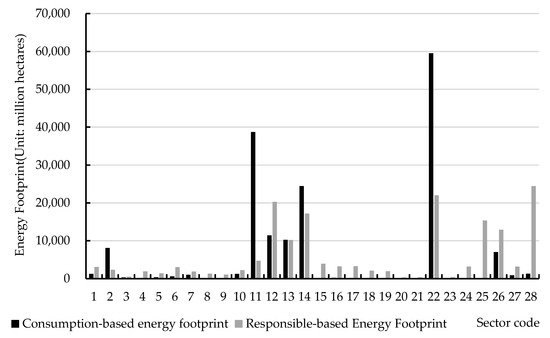
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Boosting Biowaste Valorisation—Do We Need an Accelerated Regional Implementation of the European Law for End-of-Waste?
Sustainability 2023, 15(17), 13147; https://doi.org/10.3390/su151713147 (registering DOI) - 01 Sep 2023
Abstract
The valorisation of municipal and household biowaste as a relevant component of the EU’s Circular Economy Strategy is currently under discussion. However, there are several legal, technical and economic challenges associated with biowaste valorisation. This paper aims to pinpoint factors affecting biowaste supply
[...] Read more.
The valorisation of municipal and household biowaste as a relevant component of the EU’s Circular Economy Strategy is currently under discussion. However, there are several legal, technical and economic challenges associated with biowaste valorisation. This paper aims to pinpoint factors affecting biowaste supply chains using the PESTEL+I method and stakeholder workshops. Our analysis focuses on the macro-environment of an integrated biowaste conversion and valorisation concept in the region of Wallonia, Belgium. One key influencing factor is the EU’s legal framework on waste, which describes the end-of-waste status and defines criteria for biowaste reuse. While the analysis shows that EU regulations support biowaste valorisation, its transposition into national and regional law is lagging behind. The technological development of biowaste concepts might be hampered and many questions related to the marketisation of bio-based products remain unanswered. We therefore suggest that legal procedures for biowaste management have to be facilitated at the regional level. The region of Wallonia should establish a category for biowaste that would include standardized procedures for biowaste valorisation and products. It is essential that such regional barriers be overcome to establish the necessary cooperation with local stakeholders and to transfer biowaste supply chains to the market.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Biowaste Valorization for a Circular Bioeconomy and Sustainable Society)
►▼
Show Figures
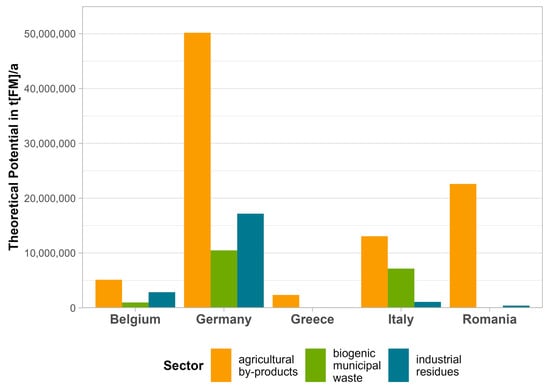
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
XGBoost–SFS and Double Nested Stacking Ensemble Model for Photovoltaic Power Forecasting under Variable Weather Conditions
Sustainability 2023, 15(17), 13146; https://doi.org/10.3390/su151713146 (registering DOI) - 01 Sep 2023
Abstract
Sustainability can achieve a balance among economic prosperity, social equity, and environmental protection to ensure the sustainable development and happiness of current and future generations; photovoltaic (PV) power, as a clean, renewable energy, is closely related to sustainability providing a reliable energy supply
[...] Read more.
Sustainability can achieve a balance among economic prosperity, social equity, and environmental protection to ensure the sustainable development and happiness of current and future generations; photovoltaic (PV) power, as a clean, renewable energy, is closely related to sustainability providing a reliable energy supply for sustainable development. To solve the problem with the difficulty of PV power forecasting due to its strong intermittency and volatility, which is influenced by complex and ever-changing natural environmental factors, this paper proposes a PV power forecasting method based on eXtreme gradient boosting (XGBoost)–sequential forward selection (SFS) and a double nested stacking (DNS) ensemble model to improve the stability and accuracy of forecasts. First, this paper analyzes a variety of relevant features affecting PV power forecasting and the correlation between these features and then constructs two features: global horizontal irradiance (GHI) and similar day power. Next, a total of 16 types of PV feature data, such as temperature, azimuth, ground pressure, and PV power data, are preprocessed and the optimal combination of features is selected by establishing an XGBoost–SFS to build a multidimensional climate feature dataset. Then, this paper proposes a DNS ensemble model to improve the stacking forecasting model. Based on the gradient boosting decision tree (GBDT), XGBoost, and support vector regression (SVR), a base stacking ensemble model is set, and a new stacking ensemble model is constructed again with the metamodel of the already constructed stacking ensemble model in order to make the model more robust and reliable. Finally, PV power station data from 2019 are used as an example for validation, and the results show that the forecasting method proposed in this paper can effectively integrate multiple environmental factors affecting PV power forecasting and better model the nonlinear relationships between PV power forecasting and relevant features. This is more applicable in the case of complex and variable environmental climates that have higher forecasting accuracy requirements.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Regulation and Control of Flexible Resources in Resilient and Sustainable Power Systems)
►▼
Show Figures
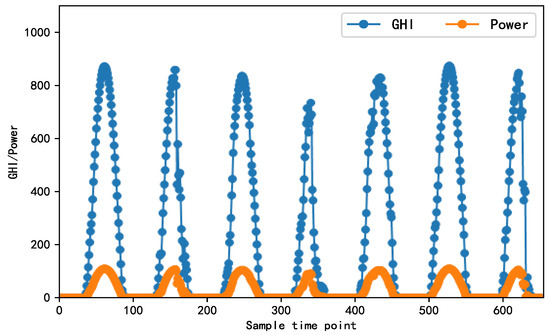
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
How Does Carbon Emissions Efficiency Affect OFDI? Evidence from Chinese Listed Companies
Sustainability 2023, 15(17), 13145; https://doi.org/10.3390/su151713145 (registering DOI) - 01 Sep 2023
Abstract
With the in-depth promotion of the “double carbon” strategy, the effectiveness of the green and low-carbon transition is not only fundamental to breaking the environmental shackles of domestic economic development, but is also an inevitable choice for Chinese enterprises to participate in international
[...] Read more.
With the in-depth promotion of the “double carbon” strategy, the effectiveness of the green and low-carbon transition is not only fundamental to breaking the environmental shackles of domestic economic development, but is also an inevitable choice for Chinese enterprises to participate in international economic cooperation in the context of global climate change. However, the relationship between green low-carbon transition effects and outward foreign direct investment (OFDI) has not been adequately studied, and the transmission mechanism is not yet clear. Based on the above research gaps, this study made an empirical analysis on how carbon emissions efficiency affects companies’ OFDI using the OFDI data of China’s A-share-listed companies and matching carbon emissions efficiency data with the cities where listed companies are located, from 2007 to 2019. This study found that carbon emissions efficiency increases the possibility of OFDI, and carbon emissions efficiency significantly expanded the scale of OFDI through reducing financing costs and improving technological innovation, and the regression results are all significantly positive at the 1% level. We used ventilation coefficients as the instrumental variable, and the 2SLS results showed that this correlation is still robust. The heterogeneity analysis found that the role of carbon efficiency in promoting OFDI is more prominent for SOEs, large companies, clean companies and companies in competitive markets. In addition, financial development can positively moderate the influence of carbon emissions efficiency on OFDI, and carbon emissions efficiency deepens the embeddedness of the investment market compared to the degree of diversification of the corporate OFDI market. This research deepens the theoretical study on the factors of China’s OFDI, and provides insights for the government to coordinate carbon emissions efficiency and OFDI growth to achieve sustainable development. This study proposes continuing to promote clean production enterprises to shape their own sustainable development advantages, continuing to optimise the market environment and talent development environment, grasping the financing policy and technical support of the two important means, and accelerating the internationalisation of self-owned brands. These are the urgent priorities in driving Chinese enterprises to ‘go global’.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Carbon Emission Reduction and Energy Conservation Methods)
Open AccessCase Report
Fuzzy K-Means and Principal Component Analysis for Classifying Soil Properties for Efficient Farm Management and Maintaining Soil Health
by
and
Sustainability 2023, 15(17), 13144; https://doi.org/10.3390/su151713144 (registering DOI) - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
Soil health indicators can guide soil management-related decisions for sustainable agriculture. Principle component (PC) analysis and the fuzzy k-means technique, also known as continuous classification, are useful for designing site-specific management strategies for varying soil properties within a contiguous area. The objective of
[...] Read more.
Soil health indicators can guide soil management-related decisions for sustainable agriculture. Principle component (PC) analysis and the fuzzy k-means technique, also known as continuous classification, are useful for designing site-specific management strategies for varying soil properties within a contiguous area. The objective of this study was to identify appropriate soil health indicators as well as to create contiguous areas for precision management of a large diverse farm from measured soil properties. From the farm, which is sited on Armijo–Harkey soil, 286 loose and intact samples were obtained, representing a depth of 15 cm from the soil surface. Statistical analysis showed that several data were log-normally distributed. PCA analysis showed that the first three PCs explained 73% of the variation with PC1, consisting of factors related to the soil’s physical condition; PC2, containing factors related to chemical properties; and PC3, including factors related to macro- and micro-porosities. Minimizing the fuzziness performance index (FPI) and modified partition entropy (MPE) delineated four management classes. The membership class maps showed that the contrasting management strategies could be developed for the four management zones to achieve yield goals while conserving scarce surface water for irrigation, increasing water use efficiency, and decreasing nitrate leaching in arid and semi-arid irrigated farmlands.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Planning and Sustainable Management of Irrigation in Agricultural Operations)
►▼
Show Figures
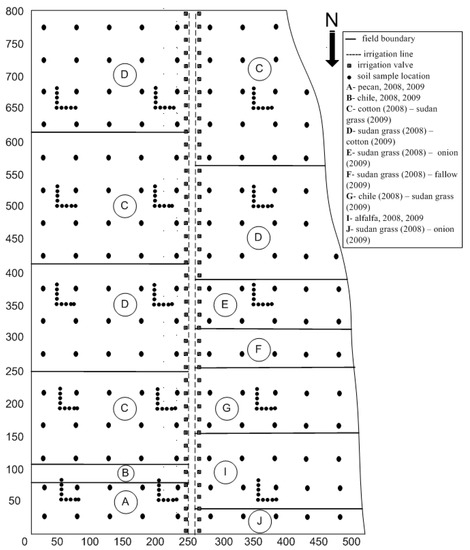
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Exploring the Spatiotemporal Dynamics of CO2 Emissions through a Combination of Nighttime Light and MODIS NDVI Data
Sustainability 2023, 15(17), 13143; https://doi.org/10.3390/su151713143 (registering DOI) - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
Climate change caused by CO2 emissions is posing a huge challenge to human survival, and it is crucial to precisely understand the spatial and temporal patterns and driving forces of CO2 emissions in real time. However, the available CO2 emission
[...] Read more.
Climate change caused by CO2 emissions is posing a huge challenge to human survival, and it is crucial to precisely understand the spatial and temporal patterns and driving forces of CO2 emissions in real time. However, the available CO2 emission data are usually converted from fossil fuel combustion, which cannot capture spatial differences. Nighttime light (NTL) data can reveal human activities in detail and constitute the shortage of statistical data. Although NTL can be used as an indirect representation of CO2 emissions, NTL data have limited utility. Therefore, it is necessary to develop a model that can capture spatiotemporal variations in CO2 emissions at a fine scale. In this paper, we used the nighttime light and the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI), and proposed a normalized urban index based on combination variables (NUI-CV) to improve estimated CO2 emissions. Based on this index, we used the Theil–Sen and Mann–Kendall trend analysis, standard deviational ellipse, and a spatial economics model to explore the spatial and temporal dynamics and influencing factors of CO2 emissions over the period of 2000–2020. The experimental results indicate the following: (1) NUI-CV is more suitable than NTL for estimating the CO2 emissions with a 6% increase in average . (2) The center of China’s CO2 emissions lies in the eastern regions and is gradually moving west. (3) Changes in industrial structure can strongly influence changes in CO2 emissions, the tertiary sector playing an important role in carbon reduction.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Using Multi-Source Data to Assess Urban Carbon Emissions)

Journal Menu
► ▼ Journal Menu-
- Sustainability Home
- Aims & Scope
- Editorial Board
- Reviewer Board
- Topical Advisory Panel
- Instructions for Authors
- Special Issues
- Topics
- Sections & Collections
- Article Processing Charge
- Indexing & Archiving
- Editor’s Choice Articles
- Most Cited & Viewed
- Journal Statistics
- Journal History
- Journal Awards
- Society Collaborations
- Conferences
- Editorial Office
Journal Browser
► ▼ Journal BrowserHighly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Machines, Micromachines, Remote Sensing, Sustainability, Symmetry, Wind
Energy Equipment and Condition Monitoring
Topic Editors: Zhifeng Xiao, Bin Huang, Lida LiaoDeadline: 15 September 2023
Topic in
Batteries, Designs, Energies, Materials, Sustainability
Materials for Energy Harvesting and Storage
Topic Editors: Xia Lu, Xueyi LuDeadline: 30 September 2023
Topic in
Buildings, COVID, Energies, Environments, IJERPH, Sustainability
Advanced Ventilation in and beyond the COVID-19 Pandemic
Topic Editors: John Z Lin, Zhaosong Fang, Sheng Zhang, Jian Liu, Yong Cheng, Chao HuanDeadline: 20 October 2023
Topic in
Forests, Microorganisms, Sustainability
Climate and Substrate Control on Decomposition across Temperate and Tropical Forests
Topic Editors: Xiaoming Zou, Honghua RuanDeadline: 1 November 2023

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
Sustainability
Protecting Vulnerable Water Resources by Integrated Wastewater Management
Guest Editor: Marc BreulmannDeadline: 1 September 2023
Special Issue in
Sustainability
Human–River Interactions in Cities
Guest Editors: G. Mathias Kondolf, Amir Gohar, Yves-François Le LayDeadline: 15 September 2023
Special Issue in
Sustainability
Renewable Energy Technologies for Sustainable Development
Guest Editor: Mohammad JafariDeadline: 30 September 2023
Special Issue in
Sustainability
Supply Chain Management for Sustainable Development
Guest Editor: Dominik ZimonDeadline: 15 October 2023
Topical Collections
Topical Collection in
Sustainability
Eutrophication and Sustainable Management of Water
Collection Editor: Marco Ragazzi
Topical Collection in
Sustainability
Power System and Sustainability
Collection Editors: Gaetano Zizzo, Favuzza Salvatore
Topical Collection in
Sustainability
Marketing and Sustainability
Collection Editor: Colin Michael Hall
Topical Collection in
Sustainability
Teacher Professional Development in ESD
Collection Editor: Michele Biasutti