-
 Introduction of an Ultraviolet C-Irradiated 4T1 Murine Breast Cancer Whole-Cell Vaccine Model
Introduction of an Ultraviolet C-Irradiated 4T1 Murine Breast Cancer Whole-Cell Vaccine Model -
 Impact of Influenza Vaccination on the Burden of Severe Influenza in the Elderly: Spain, 2017–2020
Impact of Influenza Vaccination on the Burden of Severe Influenza in the Elderly: Spain, 2017–2020 -
 Developing Vaccines to Improve Preparedness for Filovirus Outbreaks: The Perspective of the USA Biomedical Advanced Research and Development Authority (BARDA)
Developing Vaccines to Improve Preparedness for Filovirus Outbreaks: The Perspective of the USA Biomedical Advanced Research and Development Authority (BARDA) -
 Influenza Vaccination Coverage Rates and Determinants in Greek Children until the Age of Ten (2008–2019), the Rhea Mother–Child Cohort
Influenza Vaccination Coverage Rates and Determinants in Greek Children until the Age of Ten (2008–2019), the Rhea Mother–Child Cohort -
 A Mother’s Dilemma: The 5-P Model for Vaccine Decision-Making in Pregnancy
A Mother’s Dilemma: The 5-P Model for Vaccine Decision-Making in Pregnancy
Journal Description
Vaccines
Vaccines
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal published monthly online by MDPI. The American Society for Virology (ASV) is affiliated with Vaccines and their members receive a discount on the article processing charges.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within Scopus, SCIE (Web of Science), PubMed, PMC, Embase, CAPlus / SciFinder, and other databases.
- Journal Rank: JCR - Q1 (Immunology) / CiteScore - Q1 (Pharmacology (medical))
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 17.6 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 2.9 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the first half of 2023).
- Recognition of Reviewers: reviewers who provide timely, thorough peer-review reports receive vouchers entitling them to a discount on the APC of their next publication in any MDPI journal, in appreciation of the work done.
Impact Factor:
7.8 (2022);
5-Year Impact Factor:
7.4 (2022)
Latest Articles
Emergency Departments: An Underutilized Resource for Expanding COVID-19 Vaccine Coverage in Children
Vaccines 2023, 11(9), 1445; https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11091445 (registering DOI) - 01 Sep 2023
Abstract
COVID-19 vaccine (CV) acceptance rates remain suboptimal in children. Emergency departments (EDs) represent a unique opportunity to improve vaccination rates, particularly in underserved children. Little is known about the presence or reach of CV programs in US EDs. We assessed, via a cross-sectional
[...] Read more.
COVID-19 vaccine (CV) acceptance rates remain suboptimal in children. Emergency departments (EDs) represent a unique opportunity to improve vaccination rates, particularly in underserved children. Little is known about the presence or reach of CV programs in US EDs. We assessed, via a cross-sectional survey of pediatric ED physicians, the number of EDs offering CVs to children, the approximate numbers of vaccines administered annually, and the perceived facilitators/barriers to vaccination. The proportion of EDs offering CVs is reported. Chi-square tests compared facilitators and barriers among frequent vaccinators (≥50 CVs/year), infrequent vaccinators (<50 CVs/year), and non-vaccinators. Among 492 physicians from 166 EDs, 142 responded (representing 61 (37.3%) EDs). Most EDs were in large, urban, academic, freestanding children’s hospitals. Only 11 EDs (18.0%) offer ≥1 CV/year, and only two (18.2%) of these gave ≥50 CVs. Common facilitators of vaccination included the electronic health record facilitation of vaccination, a strong provider/staff buy-in, storage/accessibility, and having a leadership team or champion. Barriers included patient/caregiver refusal, forgetting to offer vaccines, and, less commonly, a lack of buy-in/support and the inaccessibility of vaccines. Many (28/47, 59.6%) EDs expressed interest in establishing a CV program.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Vaccination Strategies for COVID-19 II)
►
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Does IPV Boost Intestinal Immunity among Children under Five Years of Age? An Experience from Pakistan
by
, , , , , , , and
Vaccines 2023, 11(9), 1444; https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11091444 (registering DOI) - 01 Sep 2023
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The oral poliovirus vaccine (OPV) has been the mainstay of polio eradication, especially in low-income countries, and its use has eliminated wild poliovirus type 2. However, the inactivated poliovirus vaccine (IPV) is safer than OPV, as IPV protects against paralytic poliomyelitis without producing
[...] Read more.
The oral poliovirus vaccine (OPV) has been the mainstay of polio eradication, especially in low-income countries, and its use has eliminated wild poliovirus type 2. However, the inactivated poliovirus vaccine (IPV) is safer than OPV, as IPV protects against paralytic poliomyelitis without producing adverse reactions. The present study compared mucosal and humoral responses to poliovirus vaccines administered to previously OPV-immunized children to assess the immunity gap in children in areas of high poliovirus transmission. A cluster-randomized trial was implemented in three high-risk districts of Pakistan—Karachi, Kashmore, and Bajaur—from June 2013 to May 2014. This trial was community-oriented and included three arms, focusing on healthy children below five years of age. The study involved the randomization of 387 clusters, of which 360 were included in the final analysis. The control arm (A) received the routine polio program bivalent poliovirus vaccine (bOPV). The second arm (B) received additional interventions, including health camps providing routine vaccinations and preventive maternal and child health services. In addition to the interventions in arm B, the third arm (C) was also provided with IPV. Blood and stool samples were gathered from children to evaluate humoral and intestinal immunity. The highest levels of poliovirus type 1 serum antibodies were observed in Group C (IPV + OPV). The titers for poliovirus type 2 (P2) and poliovirus type 3 (P3) were noticeably higher in those who had received a routine OPV dose than in those who had not across all study groups and visits. Providing an IPV booster after at least two OPV doses could potentially fill immunity gaps in regions where OPV does not show high efficacy. However, IPV only marginally enhances humoral immunity and fails to offer intestinal immunity, which is critical to stop the infection and spread of live poliovirus in populations that have not been exposed before.
Full article
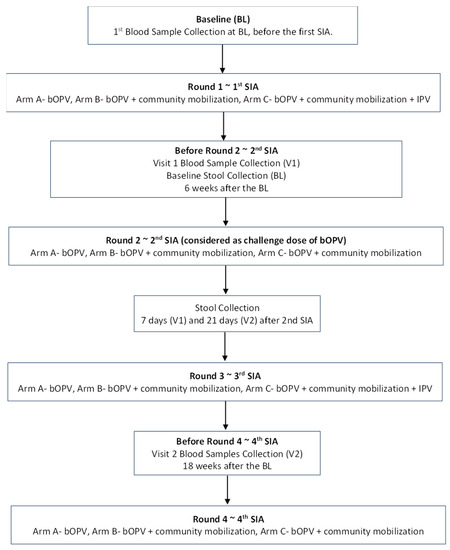
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Whole Genomic Characterization of Streptococcus iniae Isolates from Barramundi (Lates calcarifer) and Preliminary Evidence of Cross-Protective Immunization
Vaccines 2023, 11(9), 1443; https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11091443 (registering DOI) - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
Lates calcarifer, also known as Barramundi or Asian seabass, is a highly productive and fast-growing species that is well suited to large-scale aquaculture due to its attractive harvestable yields (premium fish). This fish has been envisioned as having the potential to be
[...] Read more.
Lates calcarifer, also known as Barramundi or Asian seabass, is a highly productive and fast-growing species that is well suited to large-scale aquaculture due to its attractive harvestable yields (premium fish). This fish has been envisioned as having the potential to be the “Salmon of Tropics”. Cultivating Lates calcarifer in aquaculture poses challenges, as the dense populations that make such aquaculture commercially viable facilitate the rapid spread of infectious diseases, which in turn significantly impact yield. Hence, the immunization of juveniles is necessary, and the development of new immunization agents enhances the efficiency of aquaculture and improves food security. In our study, we characterize seven novel strains of the bacterial pathogen Streptococcus iniae that were collected from commercial fish farms in Singapore and Australia. We find that the capsular operon in our strains is highly conserved and identify a number of major surface antigens previously described in Streptococcus. A genome analysis indicates that the present strains are closely related but form distinct strains within the S. iniae species. We then proceed to demonstrate that inoculation with the inactivated strain P3SAB cross-protects Lates calcarifer against S. iniae infections in vivo from a variety of strains found in both Singapore and Australia.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Fish Immunology, Vaccines and Novel Treatments)
►▼
Show Figures
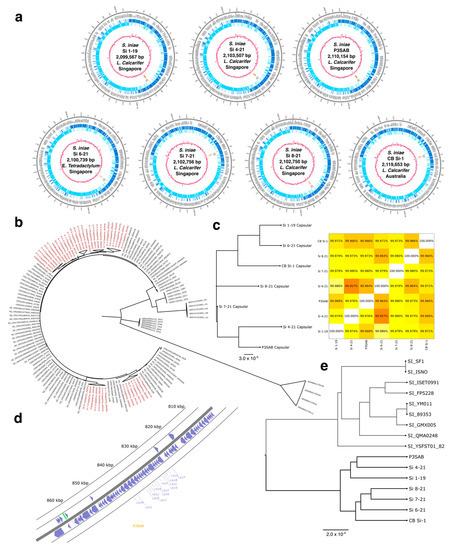
Figure 1
Open AccessBrief Report
Safety of Interchanging the Live Attenuated MAV/06 Strain and OKA Strain Varicella Vaccines in Children
Vaccines 2023, 11(9), 1442; https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11091442 (registering DOI) - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
Two live attenuated varicella vaccine (VZV) strains have been mainly used across the globe: MAV/06 and OKA strains. We aimed to explore the safety of interchanging the two VZV strains for primary and booster immunizations. South Korea’s vaccine adverse event reporting system (VAERS)
[...] Read more.
Two live attenuated varicella vaccine (VZV) strains have been mainly used across the globe: MAV/06 and OKA strains. We aimed to explore the safety of interchanging the two VZV strains for primary and booster immunizations. South Korea’s vaccine adverse event reporting system (VAERS) was accessed and searched to find filed reports of all adverse events (AEs) following immunization with the second dose of the varicella vaccine. The electronic medical records were reviewed for all visits to the hospital following the second dose of the varicella vaccine. Of the total 406 study participants, 27.5% (n = 112) were in the MAV/06–MAV/06 group, 30.3% (n = 123) in the MAV/06–OKA, 17.5% (n = 71) in the OKA–MAV/06 group, and 24.6% (n = 100) in the OKA–OKA group. Mean age at immunization with the first dose was 1.10 (standard deviation [SD] ±0.34) years old, and second dose was 4.77 (SD ± 1.13) (p = 0.772 and 0.933, respectively). There were no filed reports of AEs following the second dose in the national VAERS. Hospital visit records showed a total of 10.3% (95% confidence interval [CI], 7.6–13.7) (n = 42) had recorded AEs following the 2nd administered dose; however, only 0.7% (95% CI, 0.2–2.4) (n = 3) were regarded as possibly vaccine related. Two patients in the MAV/06–OKA group were diagnosed with Henoch-Schonlein purpura after the second dose; however, both had also received the MMR vaccine on the same day. No safety signals associated with interchanging the MAV/06 and OKA strain live attenuated varicella vaccines were observed in this patient cohort of healthy children.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Research in Vaccine Epidemiology: Immunogenicity, Effectiveness, and Safety)
Open AccessArticle
Effectiveness of Mix-and-Match Vaccination in Preventing SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Variant Infection in Taiwan: A Test-Negative Control Study
Vaccines 2023, 11(9), 1441; https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11091441 (registering DOI) - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
This study aimed to evaluate the effectiveness (VE) of mix-and-match vaccination against SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant infection and severe outcomes. An SARS-CoV-2 PCR-confirmed retrospective cohort from Chang Gung Medical System in Taiwan was constructed. Vaccination records were tracked from the National Immunization Information System
[...] Read more.
This study aimed to evaluate the effectiveness (VE) of mix-and-match vaccination against SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant infection and severe outcomes. An SARS-CoV-2 PCR-confirmed retrospective cohort from Chang Gung Medical System in Taiwan was constructed. Vaccination records were tracked from the National Immunization Information System and categorized by different regimens or unvaccinated status. The main outcomes are VE against PCR-confirmed infection and COVID-19-associated moderate to severe disease. Participants were observed during the Omicron wave from March to August 2022. Of 298,737 PCR testing results available, 162,219 were eligible for analysis. VE against infection was modest, ranging from 38.3% to 49.0%, while mRNA-based vaccine regimens revealed better protection against moderate to severe disease, ranging from 80.8% to 90.3%. Subgroup analysis revealed lower VE among persons with major illness in preventing moderate to severe disease. For young adults, the VE of protein-based vaccine regimens showed a comparable protection with other mixed vaccine regimens. The mix-and-match vaccination strategy provided modest clinical effectiveness in preventing Omicron variant infection. mRNA vaccine-based regimens were superior to other regimens against moderate to severe disease especially in older adults. The mix-and-match vaccination strategy could be an alternative to prevent COVID-19 in unstable vaccine supply regions.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Immune Effectiveness of COVID-19 Vaccines)
►▼
Show Figures
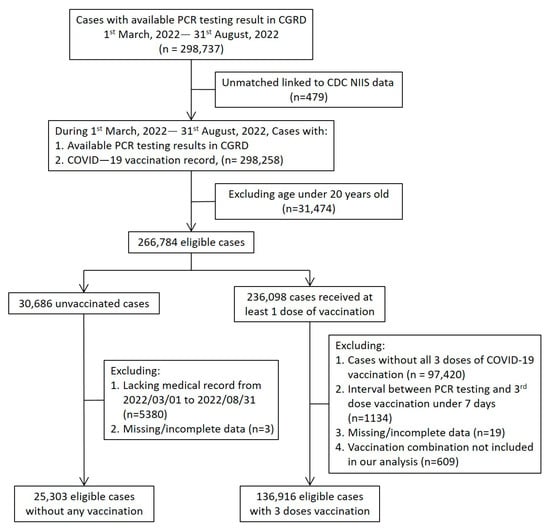
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Nanotechnology-Assisted Immunogenic Cell Death for Effective Cancer Immunotherapy
Vaccines 2023, 11(9), 1440; https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11091440 (registering DOI) - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
Tumor vaccines have been used to treat cancer. How to efficiently induce tumor-associated antigens (TAAs) secretion with host immune system activation is a key issue in achieving high antitumor immunity. Immunogenic cell death (ICD) is a process in which tumor cells upon an
[...] Read more.
Tumor vaccines have been used to treat cancer. How to efficiently induce tumor-associated antigens (TAAs) secretion with host immune system activation is a key issue in achieving high antitumor immunity. Immunogenic cell death (ICD) is a process in which tumor cells upon an external stimulus change from non-immunogenic to immunogenic, leading to enhanced antitumor immune responses. The immune properties of ICD are damage-associated molecular patterns and TAA secretion, which can further promote dendritic cell maturation and antigen presentation to T cells for adaptive immune response provocation. In this review, we mainly summarize the latest studies focusing on nanotechnology-mediated ICD for effective cancer immunotherapy as well as point out the challenges.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Advances in Cancer Immunotherapy and Vaccination)
Open AccessArticle
Effect of Influenza Vaccination on Rate of Influenza Virus Infection in Chinese Military Personnel, 2015–2016: A Cluster Randomized Trial
by
, , , , , , , , , , , , and
Vaccines 2023, 11(9), 1439; https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11091439 - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Influenza is a major cause of morbidity and mortality. The protective effect of a trivalent influenza vaccine (TIV) is undetermined in military personnel. We conducted an open-label, cluster randomized trial on active-duty servicemen of Beijing, Tianjin, and Shijiazhuang, who were randomly assigned to
[...] Read more.
Influenza is a major cause of morbidity and mortality. The protective effect of a trivalent influenza vaccine (TIV) is undetermined in military personnel. We conducted an open-label, cluster randomized trial on active-duty servicemen of Beijing, Tianjin, and Shijiazhuang, who were randomly assigned to receive either a single dose of TIV or no treatment, according to cluster randomized sampling. The subjects were then followed for a maximum of six months to assess the incidence of laboratory-confirmed influenza. A total of 5445 subjects in 114 clusters received one dose of TIV before the 2015/2016 influenza season. Laboratory-confirmed influenza was identified in 18 in the vaccine group compared with 87 in the control group (6031 subjects in 114 clusters), resulting in a vaccine effectiveness (VE) of 76.4% (95%CI: 60.7 to 85.8) against laboratory-confirmed influenza. Influenza-like illness was diagnosed in 132 in the vaccine group compared with 420 in the control group, resulting in a VE of 64.1% (95%CI: 56.2 to 70.6). The estimated VE against influenza B viruses was 80.5% (95%CI: 65.6 to 88.9) and 8.6% (95%CI: −241 to 75.5) against influenza A viruses. In conclusion, the trivalent influenza vaccine is moderately effective, highly immunogenic, and generally safe to use in healthy male military servicemen.
Full article
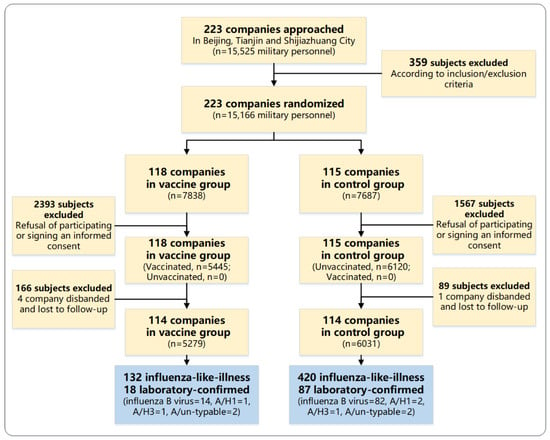
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Enhancing Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Neutralizing Immunity by Genetic Delivery of Enveloped Virus-like Particles Displaying SARS-CoV-2 Spikes
by
, , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , and add
Show full author list
remove
Hide full author list
Vaccines 2023, 11(9), 1438; https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11091438 (registering DOI) - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
New vaccine delivery technologies, such as mRNA, have played a critical role in the rapid and efficient control of SARS-CoV-2, helping to end the COVID-19 pandemic. Enveloped virus-like particles (eVLPs) are often more immunogenic than protein subunit immunogens and could be an effective
[...] Read more.
New vaccine delivery technologies, such as mRNA, have played a critical role in the rapid and efficient control of SARS-CoV-2, helping to end the COVID-19 pandemic. Enveloped virus-like particles (eVLPs) are often more immunogenic than protein subunit immunogens and could be an effective vaccine platform. Here, we investigated whether the genetic delivery of eVLPs could achieve strong immune responses in mice as previously reported with the immunization of in vitro purified eVLPs. We utilized Newcastle disease virus-like particles (NDVLPs) to display SARS-CoV-2 prefusion-stabilized spikes from the WA-1 or Beta variant (S-2P or S-2Pᵦ, respectively) and evaluated neutralizing murine immune responses achieved by a single-gene-transcript DNA construct for the WA-1 or Beta variant (which we named S-2P-NDVLP-1T and S-2Pᵦ-NDVLP-1T, respectively) by multiple-gene-transcript DNA constructs for the Beta variant (S-2Pᵦ-NDVLP-3T), and by a protein subunit–DNA construct for the WA-1 or Beta variant (S-2P-TM or S-2Pᵦ-TM, respectively). The genetic delivery of S-2P-NDVLP-1T or S-2Pᵦ-NDVLP-1T yielded modest neutralizing responses after a single immunization and high neutralizing responses after a second immunization, comparable to previously reported results in mice immunized with in vitro purified S-2P-NDVLPs. Notably, genetic delivery of S-2Pᵦ-NDVLP-3T yielded significantly higher neutralizing responses in mice after a second immunization than S-2Pᵦ-NDVLP-1T or S-2Pᵦ-TM. Genetic delivery also elicited high spike-specific T-cell responses. Collectively, these results indicate that genetic delivery can provide an effective means to immunize eVLPs and that a multiple-gene transcript eVLP platform may be especially efficacious and inform the design of improved vaccines.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section COVID-19 Vaccines and Vaccination)
►▼
Show Figures
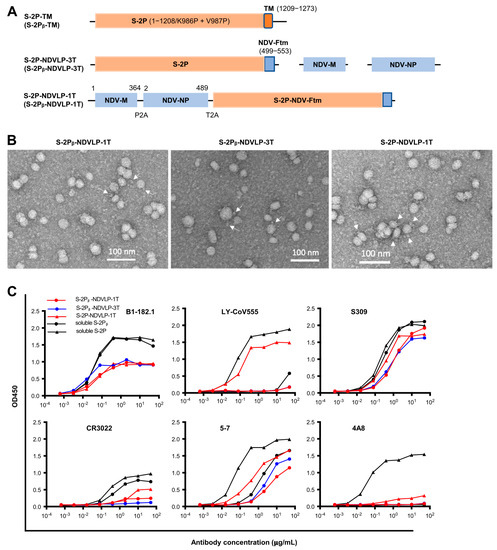
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Inhibition of Trichinella spiralis Membrane-Associated Progesterone Receptor (MAPR) Results in a Reduction in Worm Burden
by
, , , , , , , and
Vaccines 2023, 11(9), 1437; https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11091437 (registering DOI) - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
Trichinella spiralis (T. spiralis), a nematode parasite, is the major cause of Trichinellosis, a zoonotic disease. A key role of MAPR in the reproductive system is to maintain pregnancy. Previous studies found that antihormone drug design and vaccine therapy of recombinant
[...] Read more.
Trichinella spiralis (T. spiralis), a nematode parasite, is the major cause of Trichinellosis, a zoonotic disease. A key role of MAPR in the reproductive system is to maintain pregnancy. Previous studies found that antihormone drug design and vaccine therapy of recombinant protein (rTs-MAPRC2) control T. spiralis infection. The current study investigates the inhibitory effects of different ratios of antibodies against Ts-MAPRC2 on the development of muscle larvae (ML) and newborn larvae (NBL). First, we performed indirect immunofluorescence assays and examined the effects of rTs-MAPRC2-Ab on ML and NBL in vitro as well as in vivo. Afterward, siRNA-Ts-MAPRC2 was transfected into T. spiralis muscle larvae. Following that, Ts-MAPRC2 protein was detected by Western Blotting, and mRNA levels were determined by qPCR. We also assessed whether siRNA-treated NBLs were infective by analyzing muscle larvae burden (MLs). Our results showed that rTs-MAPRC2-Ab greatly inhibited the activity of the Ts-MAPRC2 in ML and NBL of T. spiralis and rTs-MAPRC2-Ab reduced larval infectivity and survival in the host in a dose-dependent manner (1:50, 1:200, 1:800 dilutions). Furthermore, siRNA-Ts-MAPRC2 effectively silenced the Ts-MAPRC2 gene in muscle larvae (ML) in vitro, as well as in newborn larvae (NBL) of T. spiralis in vivo. In addition, siRNA-Ts-MAPRC2 (siRNA180, siRNA419, siRNA559) reduced host larval survival and infectivity significantly. This study, therefore, suggests that Ts-MAPRC2 might be a novel molecular target useful in the development of vaccines against T. spiralis infection.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Vaccine for Parasitic Diseases)
►▼
Show Figures
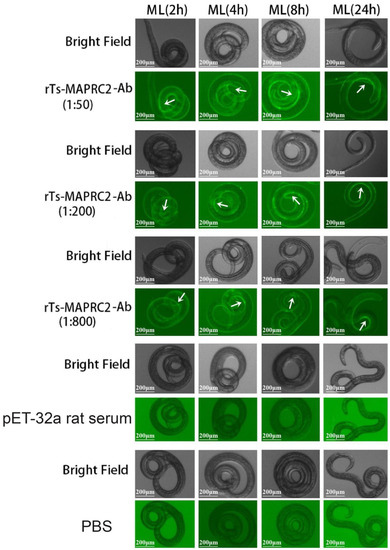
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Determinants of Vaccine Hesitancy among Home Health Care Service Recipients in Saudi Arabia
by
, , , , , and
Vaccines 2023, 11(9), 1436; https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11091436 - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
Background: Vaccine hesitancy has been identified by the World Health Organization (WHO) as a major worldwide health threat. Home Health Care (HHC) service recipients represent a vulnerable group and were prioritized to receive coronavirus disease (COVID-19) vaccination during the national vaccine campaigns in
[...] Read more.
Background: Vaccine hesitancy has been identified by the World Health Organization (WHO) as a major worldwide health threat. Home Health Care (HHC) service recipients represent a vulnerable group and were prioritized to receive coronavirus disease (COVID-19) vaccination during the national vaccine campaigns in Saudi Arabia. We aimed to investigate the most frequent reasons for vaccine hesitancy among home health care recipients in Saudi Arabia. Methods: This cross-sectional survey was conducted among home health care (HHC) service recipients in Saudi Arabia from February 2022 to September 2022. The behavioral and social drivers (BeSD) model developed by the WHO was used to understand the factors affecting vaccination decision making in our cohort. Results: Of the 426 HHC service recipients enrolled in the study, a third were hesitant to complete the COVID-19 vaccination series. The most prevalent reported reason for COVID-19 vaccine refusal was concerns about the vaccine side effects (41.6%). Factors independently associated with COVID-19 vaccination hesitancy were: having chronic conditions (odds ratio [OR] = 2.59; 95% confidence interval [CI] = 1.33–5.05, p = 0.005), previous COVID-19 diagnosis (OR = 0.48; 95% CI: 0.28–0.82, p = 0.008), ease of getting the COVID-19 vaccine by themselves (OR = 0.49; 95% CI: 0.28–0.89, p = 0.018), belief in the importance of COVID-19 vaccine in protecting their health (OR = 0.60; 95% CI: 0.38–0.96, p = 0.032), and confidence in the safety of COVID-19 vaccination (OR = 0.38; 95% CI: 0.21–0.69, p = 0.001). Conclusion: Only one-third of the study participants were hesitant to complete the series of COVID-19 vaccination. Understanding the factors underpinning vaccine hesitancy among this group would help healthcare workers and policymakers in developing personalized health awareness campaigns aimed at improving vaccine acceptance levels.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Infectious Diseases: The Role of Vaccines and Complementary Measures)
►▼
Show Figures
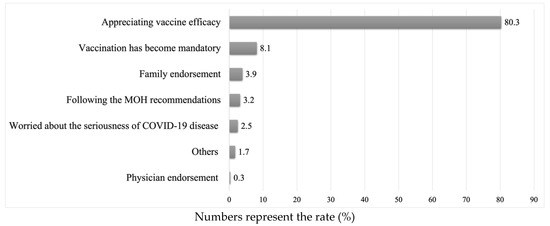
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
HPV Opportunistic Vaccination: A Literature Review and a Single-Center Experience in Northern Italy through the COVID-19 Pandemic
Vaccines 2023, 11(9), 1435; https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11091435 - 31 Aug 2023
Abstract
The World Health Organization (WHO) set the goal of 90% HPV vaccination coverage in the population to eliminate cervical cancer. Opportunistic vaccination is performed outside the free vaccination or catch-up programs. Both free and opportunistic HPV vaccination programs experienced slowdowns during the COVID-19
[...] Read more.
The World Health Organization (WHO) set the goal of 90% HPV vaccination coverage in the population to eliminate cervical cancer. Opportunistic vaccination is performed outside the free vaccination or catch-up programs. Both free and opportunistic HPV vaccination programs experienced slowdowns during the COVID-19 pandemic. In this retrospective study, we aimed to identify the benefits and the obstacles of opportunistic vaccination among male and female individuals who took advantage of the “on-demand” service offered by San Raffaele Hospital in Milan from April 2018 to May 2023. The impact that the COVID-19 pandemic had on vaccination adherence was also analyzed. Data on a total of 527 subjects were collected from an in-house database and through personal interviews. Women in the cohort of older patients (over 25) adhered to the vaccination schedule more than younger women. Opportunistic vaccination request is influenced by the need of a gynecologist, a general practitioner, or public health clinic availability. Women also showed good adherence to screening, demonstrating awareness of the importance of cervical cancer secondary prevention despite vaccination. Opportunistic vaccination offers the possibility of including individuals excluded from the free vaccination campaigns, often already affected by lesions caused by HPV, providing increased viral clearance and faster lesion regression. The main limit remains the economic burden.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue HPV Vaccination: Basic and Clinical Research)
Open AccessArticle
Adherence to SARS-CoV-2 Vaccination Recommendations among Patients with Substance Use Disorders: A Cross-Sectional Study in Rome, Italy
by
, , , , , , , , , , , , , , and
Vaccines 2023, 11(9), 1434; https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11091434 - 30 Aug 2023
Abstract
Adherence to vaccination recommendations is a challenge for national immunization programs. We quantified adherence to COVID-19 vaccination recommendations in people with substance use disorders (SUDs) attending an outpatient addiction center in Rome, Italy; we investigated the determinants of adherence, and also analyzed patient
[...] Read more.
Adherence to vaccination recommendations is a challenge for national immunization programs. We quantified adherence to COVID-19 vaccination recommendations in people with substance use disorders (SUDs) attending an outpatient addiction center in Rome, Italy; we investigated the determinants of adherence, and also analyzed patient risk perception and compliance with preventive measures. A multivariable logistic regression model identified predictors of adherence to vaccination recommendations, with statistical validity tested by estimating adjusted odds ratios (aORs) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs). From December 2021 to January 2022, 200 SUD patients completed a questionnaire, 80% of whom reported being vaccinated against SARS-CoV-2 (minimum one dose). Negative predictors of vaccine uptake included being non-Italian (aOR: 0.36, 95% CI: 0.13–0.97), having coexisting comorbidities (aOR: 0.35, 95% CI: 0.13–0.95), and previous use of heroin (aOR: 0.24, 95% CI: 0.08–0.71). No difference was found for cocaine use, demographic characteristics, previous COVID-19 infection, methadone therapy, or compliance with preventive measures. Major reasons for non-adherence to vaccination recommendations were fear of side effects, insufficient recognition of the importance of vaccination, bureaucratic issues, and lack of trust in the authorities. Given their vulnerability, additional efforts are needed to facilitate access to vaccination for people with SUDs, and to limit disinformation around vaccines..
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Vaccines and Vaccinations in the Pandemic Period)
Open AccessArticle
SARS-CoV-2-Specific CD8+ T-Cells in Blood but Not in the Lungs of Vaccinated K18-hACE2 Mice after Infection
by
, , , , , , , , , , , and
Vaccines 2023, 11(9), 1433; https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11091433 - 30 Aug 2023
Abstract
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV)-2 enters the host by infecting nasal ciliated cells. Then, the virus can spread towards the oropharyngeal cavity and the pulmonary tissues. The antiviral adaptive immunity is promptly induced in response to the virus’s detection, with virus-specific T-lymphocytes
[...] Read more.
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV)-2 enters the host by infecting nasal ciliated cells. Then, the virus can spread towards the oropharyngeal cavity and the pulmonary tissues. The antiviral adaptive immunity is promptly induced in response to the virus’s detection, with virus-specific T-lymphocytes appearing before antiviral antibodies. Both the breadth and potency of antiviral CD8+ T-cell immunity have a key role in containing viral spread and disease severity. Current anti-SARS-CoV-2 vaccines do not impede the virus’s replication in the upper respiratory tract, and there is consensus on the fact that the best potency of the antiviral immune response in both blood and the upper respiratory tract can be reached upon infection in vaccinees (i.e., breakthrough infection). However, whether the antiviral CD8+ T-cells developing in response to the breakthrough infection in the upper respiratory tract diffuse to the lungs is also still largely unknown. To fill the gap, we checked the CD8+ T-cell immunity elicited after infection of K18-hACE2 transgenic mice both at 3 weeks and 3 months after anti-spike vaccination. Virus-specific CD8+ T-cell immunity was monitored in both blood and the lungs before and after infection. By investigating the de novo generation of the CD8+ T-cells specific for SARS-CoV-2 viral proteins, we found that both membrane (M) and/or nucleocapsid (N)-specific CD8+ T-cells were induced at comparable levels in the blood of both unvaccinated and vaccinated mice. Conversely, N-specific CD8+ T-cells were readily found in the lungs of the control mice but were either rare or absent in those of vaccinated mice. These results support the idea that the hybrid cell immunity developing after asymptomatic/mild breakthrough infection strengthens the antiviral cell immunity in the lungs only marginally, implying that the direct exposition of viral antigens is required for the induction of an efficient antiviral cell immunity in the lungs.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Humoral and Cellular Response after COVID-19 Vaccination)
►▼
Show Figures
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Mpox Vaccination Hesitancy and Its Associated Factors among Men Who Have Sex with Men in China: A National Observational Study
by
, , , , , , , , , , , , and
Vaccines 2023, 11(9), 1432; https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11091432 - 30 Aug 2023
Abstract
More than 400 confirmed mpox cases have been reported in China. The mpox vaccination is crucial to mitigate mpox transmission, especially for at-risk populations. This study aimed to determine mpox vaccination hesitancy and its associated factors in Chinese men who have sex with
[...] Read more.
More than 400 confirmed mpox cases have been reported in China. The mpox vaccination is crucial to mitigate mpox transmission, especially for at-risk populations. This study aimed to determine mpox vaccination hesitancy and its associated factors in Chinese men who have sex with men (MSM). This nationwide cross-sectional study was conducted among 7538 Chinese MSM in 27 MSM social organizations from 21 provinces, municipalities, and autonomous regions of China from 31 July to 4 August 2023. Of them, the rate of mpox vaccination hesitancy was 5.59% (421/7538). The most common reason for mpox vaccination hesitation was concerns of safety and side effects (62.71%, 264/421), followed by concerns of privacy (38.24%, 161/421), thoughts of impossible infection (37.53%, 158/421), no effectiveness in preventing reinfection (30.88%, 130/421), and no worry about infection (12.35%, 52/421). Regarding the concerning characteristics of the vaccines, concerns of vaccine safety ranked first (71.74%, 5408/7538), followed by vaccine effectiveness (14.05%, 1059/7538), vaccine costs (7.35%, 554/7538), and the continuity of vaccine effectiveness (3.91%, 295/7538). The highest odds ratio of mpox vaccination hesitation was seen in MSM who were infected with mpox virus (aOR = 2.38; 95%CI = 1.08, 5.23), followed by those aged ≥60 years (aOR = 2.25; 95%CI = 1.31, 3.88), those who were unemployed (aOR = 1.66; 95%CI = 1.25, 2.19), and those who had an education level of postgraduate and above (aOR = 1.55; 95%CI = 1.01, 2.37). However, MSM who had a higher level of mpox-related knowledge (moderate: aOR = 0.53; 95%CI = 0.36, 0.77; high: aOR = 0.30; 95%CI = 0.23, 0.40) had a lower odds ratio of mpox vaccination hesitation. MSM in China had low hesitancy toward mpox vaccination. The safety and effectiveness of the vaccine and privacy were important aspects of hesitancy. Health education on mpox-related knowledge should be encouraged to promote future vaccination plans.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Acceptance and Hesitancy in Vaccine Uptake)
►▼
Show Figures
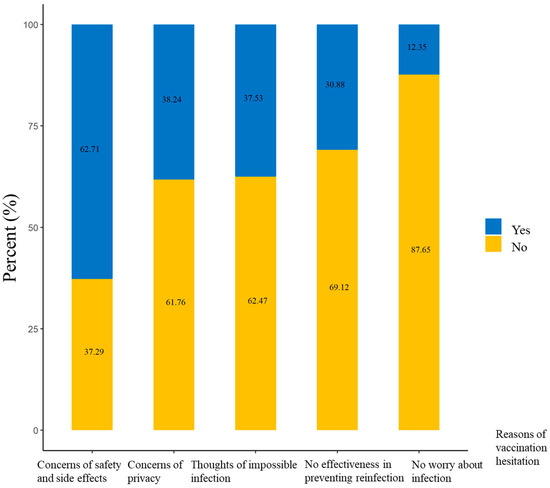
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Exploring the Impact of COVID-19 on Physical Activity One Month after Infection and Its Potential Determinants: Re-Infections, Pre-Illness Vaccination Profiles/Types, and Beyond
by
, , , and
Vaccines 2023, 11(9), 1431; https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11091431 - 29 Aug 2023
Abstract
This study investigated changes in physical activity (PA) after severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection while considering age, PA level, underlying medical conditions (UMCs), vaccination profiles/types, re-infections, disease severity, and treatment. Data were collected from 5829 respondents by using a validated
[...] Read more.
This study investigated changes in physical activity (PA) after severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection while considering age, PA level, underlying medical conditions (UMCs), vaccination profiles/types, re-infections, disease severity, and treatment. Data were collected from 5829 respondents by using a validated web-based questionnaire. The findings showed that there was a significant overall decrease in PA (−16.2%), including in daily occupation (−11.9%), transportation (−13.5%), leisure-time (−16.4%), and sporting (−27.6%) activities. Age, PA level, UMCs, vaccination profiles/types, disease severity, and treatment played a role in determining PA in individuals’ post-acute SARS-CoV-2 infections. Re-infections did not impact the decline in PA. Unvaccinated individuals experienced a significant decline in PA (−13.7%). Younger (−22.4%) and older adults (−22.5%), those with higher PA levels (−20.6%), those with 2–5 UMCs (−23.1%), those who were vaccinated (−16.9%) or partially vaccinated (−19.1%), those with mRNA-type vaccines only (−17.1%), those with recurrent (−19.4%)-to-persistent (−54.2%) symptoms, and those that required hospital (−51.8%) or intensive care unit (−67.0%) admission during their infections had more pronounced declines in PA. These findings emphasize the complex relationship between post-acute SARS-CoV-2 infection and PA and highlight the need for targeted interventions, further research, and multidisciplinary care to promote PA resumption and mitigate long-term effects on global public health.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section COVID-19 Vaccines and Vaccination)
►▼
Show Figures
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Predicting the Influences of Depression and Sexual Stigma on Motivation to Get Vaccinated against COVID-19 in Lesbian, Gay, and Bisexual Young Adults: A 4-Year Follow-Up Study
Vaccines 2023, 11(9), 1430; https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11091430 - 28 Aug 2023
Abstract
Vaccination is a crucial preventive measure against COVID-19. However, limited research has focused on identifying the factors predicting motivation to get vaccinated against COVID-19 (MoVAC-19) among lesbian, gay, and bisexual (LGB) individuals. This study examined the predictive effects of depression and sexual stigma
[...] Read more.
Vaccination is a crucial preventive measure against COVID-19. However, limited research has focused on identifying the factors predicting motivation to get vaccinated against COVID-19 (MoVAC-19) among lesbian, gay, and bisexual (LGB) individuals. This study examined the predictive effects of depression and sexual stigma (i.e., perceived sexual stigma from family members, perceived sexual orientation microaggression, and internalized sexual stigma) before the COVID-19 pandemic on MoVAC-19 among LGB individuals 4 years later during the COVID-19 pandemic in Taiwan. Baseline data related to depression and sexual stigma were collected in 2018 and 2019. Depression was assessed using the 20-item Mandarin Chinese version of the Center for Epidemiologic Studies Depression Scale. Perceived sexual stigma from family members was assessed using the Homosexuality-Related Stigma Scale. Internalized sexual stigma was assessed using the Measure of Internalized Sexual Stigma for Lesbians and Gay Men. Perceived sexual orientation microaggression was assessed using the Sexual Orientation Microaggression Inventory. Participant MoVAC-19 during the pandemic was assessed using the nine-item Motors of COVID-19 Vaccination Acceptance Scale. The associations of depression and sexual stigma at baseline with MoVAC-19 at follow-up were examined through multivariate linear regression analysis. Internalized sexual stigma was negatively associated with MoVAC-19, whereas perceived sexual orientation microaggression was positively associated with MoVAC-19. Depression and perceived sexual stigma from family members were not significantly associated with MoVAC-19. Although male sex and older age were positively associated with increased MoVAC-19, sex and age did not moderate the relationship between sexual stigma and motivation to get vaccinated. Among LGB individuals, sexual stigma experiences should be considered when developing intervention strategies aimed at enhancing MoVAC-19.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Vaccination Against COVID-19 in Individuals with Mental Illness)
Open AccessArticle
The Potential Risk Compensation after Receiving HPV Vaccination among Men Who Have Sex with Men in Southwest China: A HAPA-Based Analysis
Vaccines 2023, 11(9), 1429; https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11091429 - 28 Aug 2023
Abstract
Background: men who have sex with men (MSM) are a high-risk group for human papillomavirus (HPV) infection, and the HPV vaccine is effective in preventing it. However, according to risk compensation theory, people may increase sexual risk behaviors after receiving HPV vaccination.
[...] Read more.
Background: men who have sex with men (MSM) are a high-risk group for human papillomavirus (HPV) infection, and the HPV vaccine is effective in preventing it. However, according to risk compensation theory, people may increase sexual risk behaviors after receiving HPV vaccination. Based on the Health Action Process Approach (HAPA), this study investigated the influencing factors to predict intention to reduce condom use (risk compensation intention) among MSM after taking HPV vaccination in southwest China. Methods: we conducted a cross-sectional study among 948 MSM in southwest China using a non-probability sampling method and an electronic questionnaire including sociodemographic characteristics, sexual risk behavior characteristics, HPV-related prevention behavior, and the HAPA scale. Confirmatory factor analysis was performed using a structural equation model. Results: among 948 MSM, the incidence rate of reducing the frequency of condom use was 14.1%. The structural equation model showed that self-efficacy (β = −0.378, p = 0.020) and positive outcome expectancy (β = 0.366, p < 0.05) had greater effects on behavioral intention, followed by negative outcome expectancy (β = −0.296, p < 0.05) and risk perception (β = −0.232, p < 0.05). Conclusions: risk compensation may not be a major barrier to receiving HPV vaccination among MSM. Nevertheless, the recognition of possible risk compensation is necessary to implement appropriate interventions to reduce the occurrence of risk compensation.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Collection HPV-Vaccines)
►▼
Show Figures
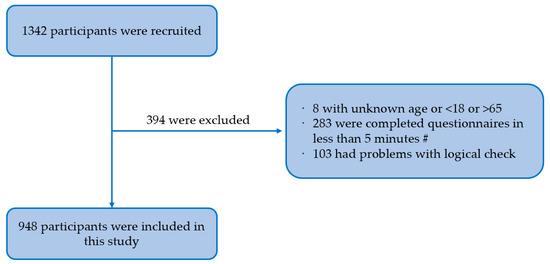
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Riding the Omicron BA.5 Wave: Improved Humoral Response after Vaccination with Bivalent Omicron BA.4-5-Adapted mRNA SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine in Chronic Hemodialysis Patients
by
, , , , , , and
Vaccines 2023, 11(9), 1428; https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11091428 - 28 Aug 2023
Abstract
Hemodialysis patients faced an excess morbidity and mortality during the COVID-19 pandemic. We evaluated the effect of second-generation mRNA vaccines against Omicron BA.4 and BA.5 variants of SARS-CoV-2 on humoral immunity. The study population comprised 66 adult hemodialysis patients who have encountered four
[...] Read more.
Hemodialysis patients faced an excess morbidity and mortality during the COVID-19 pandemic. We evaluated the effect of second-generation mRNA vaccines against Omicron BA.4 and BA.5 variants of SARS-CoV-2 on humoral immunity. The study population comprised 66 adult hemodialysis patients who have encountered four SARS-CoV-2 antigen contacts through vaccination or infection. We assessed their humoral response using an anti-SARS-CoV-2 spike receptor binding domain IgG antibody assay (S-RBD-ab), measuring neutralizing antibodies against ancestral strain of SARS-CoV-2, Delta, and Omicron in a surrogate virus neutralization test (SVNT), and specifically against BA.5 in a plaque reduction neutralization test (PRNT) before and four weeks after vaccination with Comirnaty Original/Omicron BA.4-5. During the following six months, SARS-CoV-2 infections and symptom severity were documented. The bivalent mRNA vaccine led to a 7.6-fold increase in S-RBD-ab levels and an augmented inhibition of the Omicron variant in SVNT by 35% (median). Seroconversion in the Omicron BA.5-specific PRNT was attained by in 78.4% of previously negative patients (29/37). Levels of S-RBD-ab correlated with inhibition in the Omicron-specific SVNT and neutralization titers in the BA.5-PRNT. Eleven SARS-CoV-2 infections occurred in the six-month follow-up, none of which took a life-threatening course. The bivalent mRNA vaccine improved the SARS-CoV-2 virus variant-specific humoral immunity in chronic hemodialysis patients. Measurement of S-RBD-ab can be used in hemodialysis patients to estimate their humoral immunity status against Omicron BA.5.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Vaccines against SARS-CoV-2 Variants)
►▼
Show Figures
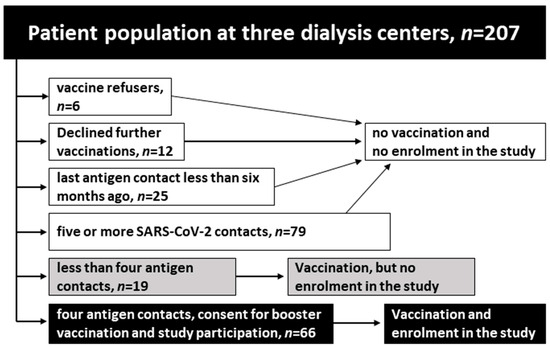
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Aerosol Inhalation of Chimpanzee Adenovirus Vectors (ChAd68) Expressing Ancestral or Omicron BA.1 Stabilized Pre–Fusion Spike Glycoproteins Protects Non–Human Primates against SARS-CoV-2 Infection
by
, , , , , , , , , , , , , , , and
Vaccines 2023, 11(9), 1427; https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11091427 - 28 Aug 2023
Abstract
Current COVID-19 vaccines are effective countermeasures to control the SARS-CoV-2 virus pandemic by inducing systemic immune responses through intramuscular injection. However, respiratory mucosal immunization will be needed to elicit local sterilizing immunity to prevent virus replication in the nasopharynx, shedding, and transmission. In
[...] Read more.
Current COVID-19 vaccines are effective countermeasures to control the SARS-CoV-2 virus pandemic by inducing systemic immune responses through intramuscular injection. However, respiratory mucosal immunization will be needed to elicit local sterilizing immunity to prevent virus replication in the nasopharynx, shedding, and transmission. In this study, we first compared the immunoprotective ability of a chimpanzee replication–deficient adenovirus–vectored COVID-19 vaccine expressing a stabilized pre–fusion spike glycoprotein from the ancestral SARS-CoV-2 strain Wuhan–Hu–1 (BV-AdCoV-1) administered through either aerosol inhalation, intranasal spray, or intramuscular injection in cynomolgus monkeys and rhesus macaques. Compared with intranasal administration, aerosol inhalation of BV-AdCoV-1 elicited stronger humoral and mucosal immunity that conferred excellent protection against SARS-CoV-2 infection in rhesus macaques. Importantly, aerosol inhalation induced immunity comparable to that obtained by intramuscular injection, although at a significantly lower dose. Furthermore, to address the problem of immune escape variants, we evaluated the merits of heterologous boosting with an adenovirus–based Omicron BA.1 vaccine (C68–COA04). Boosting rhesus macaques vaccinated with two doses of BV-AdCoV-1 with either the homologous or the heterologous C68–COA04 vector resulted in cross–neutralizing immunity against WT, Delta, and Omicron subvariants, including BA.4/5 stronger than that obtained by administering a bivalent BV-AdCoV-1/C68–COA04 vaccine. These results demonstrate that the administration of BV-AdCoV-1 or C68–COA04 via aerosol inhalation is a promising approach to prevent SARS-CoV-2 infection and transmission and curtail the pandemic spread.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue COVID-19 Vaccines and Immune Response)
►▼
Show Figures
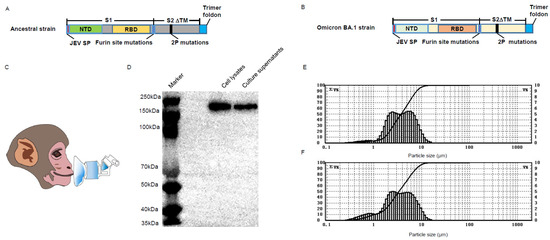
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
COVID-19 Vaccine Booster Hesitancy among Hispanic Adults: A Cross-Sectional Study from the Puerto Rico Community Engagement Alliance against COVID-19 Disparities (PR-CEAL)
by
, , , , and
Vaccines 2023, 11(9), 1426; https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11091426 - 28 Aug 2023
Abstract
Hispanic/Latino communities have suffered a disproportionate burden of the COVID-19 pandemic. Although Puerto Rico has one of the highest COVID-19 primary series vaccination rates nationwide, this estimate contrasts with the reported booster doses’ low uptake. This study aimed to assess health belief correlates
[...] Read more.
Hispanic/Latino communities have suffered a disproportionate burden of the COVID-19 pandemic. Although Puerto Rico has one of the highest COVID-19 primary series vaccination rates nationwide, this estimate contrasts with the reported booster doses’ low uptake. This study aimed to assess health belief correlates of COVID-19 vaccine booster uptake. Using a convenience sampling approach, the Puerto Rico-Community Engagement Alliance (PR-CEAL) conducted a cross-sectional study where 787 participants were recruited using online and in-person strategies between December 2021 and February 2022. Participants were adults 18 years or older, Spanish-speaking, and residents of Puerto Rico. The Health Belief Model was used to evaluate attitudes and beliefs. A total of 784 participants were used in this analysis. Adjusted Poisson regression models were used to estimate prevalence ratios (PR) and 95% confidence intervals (CI) of booster refusal. Overall, 22% of participants refused the vaccine booster or had not gotten it yet. Adjusted models showed that (i) participants who disagreed that getting the booster dose either made them feel less worried about COVID-19 or (ii) felt that the vaccine decreased their chances of getting COVID-19 presented higher booster-refusal prevalence ratios (PR = 4.20, 95% CI: 3.00, 5.90; PR = 3.70, 95% CI: 2.64, 5.18). Moreover, participants that (iii) reported having concerns for booster side effects [PR = 2.47; 95% CI = 1.73, 3.51], (iv) booster efficacy [PR = 2.50; 95% CI = 1.75, 3.58], and (v) booster safety [PR = 2.80; 95% CI = 1.96, 3.99] were significantly more likely to refuse the booster. In conclusion, booster vaccination refusal was associated with lower perceived vaccine benefits and greater barriers among adults in Puerto Rico. These results informed the development of PR-CEAL’s targeted community outreach strategies and public health campaigns to increase booster vaccine uptake.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Knowledge, Attitudes, Beliefs and Hesitancy towards COVID-19 Vaccination and Booster Doses)

Journal Menu
► ▼ Journal Menu-
- Vaccines Home
- Aims & Scope
- Editorial Board
- Reviewer Board
- Topical Advisory Panel
- Instructions for Authors
- Special Issues
- Topics
- Sections & Collections
- Article Processing Charge
- Indexing & Archiving
- Editor’s Choice Articles
- Most Cited & Viewed
- Journal Statistics
- Journal History
- Journal Awards
- Society Collaborations
- Conferences
- Editorial Office
Journal Browser
► ▼ Journal BrowserHighly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Brain Sciences, Clinics and Practice, COVID, Life, Vaccines, Viruses
Multifaceted Efforts from Basic Research to Clinical Practice in Controlling COVID-19 Disease
Topic Editors: Yih-Horng Shiao, Rashi OjhaDeadline: 30 September 2023
Topic in
JCM, Pharmaceuticals, Pharmacoepidemiology, Pharmacy, Vaccines, Healthcare
Mass Vaccination Campaigns: From Post-authorization Benefit-Risk Assessment to Public Health Impact
Topic Editors: Giampiero Mazzaglia, Lorenzo Giovanni Mantovani, Ippazio Cosimo AntonazzoDeadline: 30 November 2023
Topic in
Antibiotics, Biomedicines, Microorganisms, Parasitologia, Pathogens, Vaccines
Advances in Vaccines and Antimicrobial Therapy
Topic Editors: Roberto Paganelli, Raffaele D’AmelioDeadline: 30 December 2023
Topic in
Biologics, Biology, MPs, Pathogens, Vaccines
Global Analysis of SARS-CoV-2 Serology, Part 2
Topic Editors: Ger Rijkers, Jean-Luc MurkDeadline: 31 December 2023

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
Vaccines
SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) Vaccination and Compliance/Hesitancy
Guest Editors: Tiziana Ramaci, Massimiliano BarattucciDeadline: 2 September 2023
Special Issue in
Vaccines
Immune Response of SARS-CoV-2 Infection
Guest Editor: Velmurugan BalaramanDeadline: 10 September 2023
Special Issue in
Vaccines
Infectious Diseases: The Role of Vaccines and Complementary Measures
Guest Editors: Harunor Rashid, Catherine KingDeadline: 30 September 2023
Special Issue in
Vaccines
The Willingness toward Vaccination: A Focus on Non-mandatory Vaccinations
Guest Editors: Elisa Maietti, Angelo Capodici, Francesco Sanmarchi, Claudio Costantino, Nicole BonaccorsoDeadline: 16 October 2023
Topical Collections
Topical Collection in
Vaccines
COVID-19 Vaccine Hesitancy: Correlates and Interventions
Collection Editors: Manoj Sharma, Kavita Batra
Topical Collection in
Vaccines
Topic Advisory Panel Members’ Collection Series: Immunization and Vaccines for Infectious Diseases
Collection Editors: Shumaila Hanif, Ravinder Kumar
Topical Collection in
Vaccines
Vaccines against Chronic and Persistent Bacterial Infections














